- Signalling Overview
- Configuring RSVP
- Control Plane DSCP Support for RSVP
- Configuring RSVP Support for Frame Relay
- RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- RSVP Message Authentication
- RSVP-Previous Hop Overwrite
- RSVP Application ID Support
- RSVP Fast Local Repair
- RSVP Interface-Based Receiver Proxy
- RSVP Aggregation
- MPLS TE-Tunnel-Based Admission Control
- Configuring Subnetwork Bandwidth Manager
- RSVP-VRF Lite Admission Control
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Restrictions for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Information About RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- How to Configure RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Configuration Examples for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Additional References
RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
The RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging feature includes refresh reduction, which improves the scalability, latency, and reliability of Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) signaling to enhance network performance and message delivery.
History for the RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging Feature
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.2(13)T |
This feature was introduced. |
| 12.0(24)S |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(24)S. |
| 12.2(14)S |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S. |
| 12.0(26)S |
Two commands, ip rsvp signalling refresh missesand ip rsvp signalling refresh interval, were added into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(26)S. |
| 12.0(29)S |
The burst and max-size argument defaults for the ip rsvp signalling rate-limit command were increased to 8 messages and 2000 bytes, respectively. |
| 12.2(28)SB |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB. |
| 12.2(18)SXF5 |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SXF5. |
| 12.2(33)SRB |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB. |
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn . An account on Cisco.com is not required.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Restrictions for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Information About RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- How to Configure RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Configuration Examples for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Additional References
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
RSVP must be configured on two or more devices within the network before you can use the RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging feature.
Restrictions for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
Multicast flows are not supported for the reliable messages and summary refresh features.
Information About RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Feature Design of RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Types of Messages in RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Benefits of RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
Feature Design of RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
RSVP is a network-control, soft-state protocol that enables Internet applications to obtain special qualities of service (QoS) for their data flows. As a soft-state protocol, RSVP requires that state be periodically refreshed. If refresh messages are not transmitted during a specified interval, RSVP state automatically times out and is deleted.
In a network that uses RSVP signaling, reliability and latency problems occur when an RSVP message is lost in transmission. A lost RSVP setup message can cause a delayed or failed reservation; a lost RSVP refresh message can cause a delay in the modification of a reservation or in a reservation timeout. Intolerant applications can fail as a result.
Reliability problems can also occur when there is excessive RSVP refresh message traffic caused by a large number of reservations in the network. Using summary refresh messages can improve reliability by significantly reducing the amount of RSVP refresh traffic.
 Note |
RSVP packets consist of headers that identify the types of messages, and object fields that contain attributes and properties describing how to interpret and act on the content. |
Types of Messages in RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
The RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging feature (see the figure below) includes refresh reduction, which improves the scalability, latency, and reliability of RSVP signaling by introducing the following extensions:
- Reliable messages (MESSAGE_ID, MESSAGE_ID_ACK objects, and ACK messages)
- Bundle messages (reception and processing only)
- Summary refresh messages (MESSAGE_ID_LIST and MESSAGE_ID_NACK objects)
| Figure 1 | RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging |
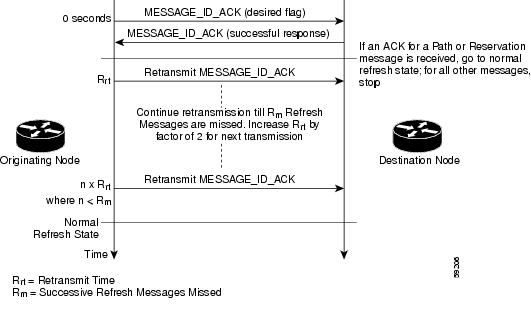
Reliable Messages
The reliable messages extension supports dependable message delivery among neighboring devices by implementing an acknowledgment mechanism that consists of a MESSAGE_ID object and a MESSAGE_ID_ACK object. The acknowledgments can be transmitted in an ACK message or piggybacked in other RSVP messages.
Each RSVP message contains one MESSAGE_ID object. If the ACK_Desired flag field is set within the MESSAGE_ID object, the receiver transmits a MESSAGE_ID_ACK object to the sender to confirm delivery.
Bundle Messages
A bundle message consists of several standard RSVP messages that are grouped into a single RSVP message.
A bundle message must contain at least one submessage. A submessage can be any RSVP message type other than another bundle message. Submessage types include Path, PathErr, Resv, ResvTear, ResvErr, ResvConf, and ACK.
Bundle messages are addressed directly to the RSVP neighbor. The bundle header immediately follows the IP header, and there is no intermediate transport header.
When a device receives a bundle message that is not addressed to one of its local IP addresses, it forwards the message.
 Note |
Bundle messages can be received, but not sent. |
Summary Refresh Messages
A summary refresh message supports the refreshing of RSVP state without the transmission of conventional Path and Resv messages. Therefore, the amount of information that must be transmitted and processed to maintain RSVP state synchronization is greatly reduced.
A summary refresh message carries a set of MESSAGE_ID objects that identify the Path and Resv states that should be refreshed. When an RSVP node receives a summary refresh message, the node matches each received MESSAGE_ID object with the locally installed Path or Resv state. If the MESSAGE_ID objects match the local state, the state is updated as if a standard RSVP refresh message were received. However, if a MESSAGE_ID object does not match the receiver's local state, the receiver notifies the sender of the summary refresh message by transmitting a MESSAGE_ID_NACK object.
When a summary refresh message is used to refresh the state of an RSVP session, the transmission of conventional refresh messages is suppressed. The summary refresh extension cannot be used for a Path or Resv message that contains changes to a previously advertised state. Also, only a state that was previously advertised in Path or Resv messages containing MESSAGE_ID objects can be refreshed by using a summary refresh message.
Benefits of RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
Enhanced Network Performance
Refresh reduction reduces the volume of steady-state network traffic generated, the amount of CPU resources used, and the response time, thereby enhancing network performance.
Improved Message Delivery
The MESSAGE_ID and the MESSAGE_ID_ACK objects ensure the reliable delivery of messages and support rapid state refresh when a network problem occurs. For example, MESSAGE_ID_ACK objects are used to detect link transmission losses.
How to Configure RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- Enabling RSVP on an Interface
- Enabling RSVP Refresh Reduction
- Verifying RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
Enabling RSVP on an Interface
Perform the following task to enable RSVP on an interface.
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling RSVP Refresh Reduction
Perform the following task to enable RSVP refresh reduction.
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
Perform the following task to verify that the RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging feature is functioning.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
Example RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
In the following example, RSVP refresh reduction is enabled:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# interface Ethernet1 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp bandwidth 7500 7500 Device(config-if)# exit Device(config)# ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction Device(config)# end
The following example verifies that RSVP refresh reduction is enabled:
Device# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 1503 bytes
!
version 12.2
no service single-slot-reload-enable
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service internal
!
hostname Device
!
no logging buffered
logging rate-limit console 10 except errors
!
ip subnet-zero
ip cef
!
ip multicast-routing
no ip dhcp-client network-discovery
lcp max-session-starts 0
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip rsvp bandwidth 1705033 1705033
!
interface Tunnel777
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 192.168.0.195 255.0.0.0
no ip mroute-cache
media-type 10BaseT
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 192.168.5.2 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
ip pim dense-mode
no ip mroute-cache
media-type 10BaseT
ip rsvp bandwidth 7500 7500
!
interface Ethernet2
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
ip pim dense-mode
no ip mroute-cache
media-type 10BaseT
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
ip rsvp bandwidth 7500 7500
!
interface Ethernet3
ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0
ip pim dense-mode
media-type 10BaseT
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
!
router eigrp 17
network 192.168.0.0
network 192.168.5.0
network 192.168.12.0
network 192.168.30.0
auto-summary
no eigrp log-neighbor-changes
!
ip classless
no ip http server
ip rsvp signalling refresh reduction
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
transport input pad v120 telnet rlogin udptn
!
end
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging feature.
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| RSVP commands: complete command syntax, command mode, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples |
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference |
| QoS features including signaling, classification, and congestion management |
"Quality of Service Overview" module |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| None |
-- |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| RFC 2205 |
Resource Reservation Protocol |
| RFC 2206 |
RSVP Management Information Base Using SMIv2 |
| RFC 2209 |
RSVP--Version 1 Message Processing Rules |
| RFC 2210 |
The Use of RSVP with IETF Integrated Services |
| RFC 2211/2212 |
Specification of the Controlled-Load Network Element Service |
| RFC 2702 |
Requirements for Traffic Engineering over MPLS |
| RFC 2749 |
Common Open Policy Service (COPS) Usage for RSVP |
| RFC 2750 |
RSVP Extensions for Policy Control |
| RFC 2814 |
SBM Subnet Bandwidth Manager: A Protocol for RSVP-based Admission Control over IEEE 802-style Networks |
| RFC 2961 |
RSVP Refresh Overhead Reduction Extensions |
| RFC 2996 |
Format of the RSVP DCLASS Object |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback