VSA Definitions
This chapter lists the VSAs supported by Cisco voice products.
Contents
- Cisco Voice VSAs
- Feature VSA for Supplementary Services
- Store-and-Forward Fax VSAs
- T.38 Fax Statistics VSAs
- Internal Error Codes
- VSA Release History

Note ●![]() VSAs are platform-independent and comply with voice gateways supported by Cisco.
VSAs are platform-independent and comply with voice gateways supported by Cisco.
- Cisco voice-specific VSAs have been developed for VoIP features during the span of numerous Cisco IOS releases. See the “VSA Release History” section to find the Cisco IOS release in which specific VSAs were introduced.
Cisco Voice VSAs
Table 4-1 lists (in alphabetical order) the VSAs used by Cisco voice calls.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Account code entered using the Acct soft key during call setup or when connected to an active call. |
||||
Average ACOM level, in dB, for the call (ACOM is the combined loss achieved by the echo canceler). The value -1 indicates that the level cannot be determined or level detection is disabled. |
||||
Services that are authorized for the user by the RPMS server. There can be multiple instances of this VSA in an access-accept packet. |
||||
cha:t1,sta:t2,cpc:t3,e2ei:t4,e2em:t5,inter:t6,iupu:t7,h:t8,acc:t9,eco:t10,sccpm:t11 where: |
cha:y,sta:f,cpc:o,e2ei:n,e2em:n,inter:y,iupi:n,h:n,acc:n,eco:n,sccpm:u |
The BCI VSA is generated by the gateway’s RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in stop accounting messages for call legs 1 and 4. The BCI VSA is also included in interim-update packets. |
||
calling-party-category= text1 |
The CPC VSA is generated by the gateway’s RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in start and stop accounting messages for call legs 1 and 4. text1 contains the best-fit calling party category value extracted from the Generic Transparency Descriptor (GTD) CPC and stored in a TDUserContainer. If Field Compatibility Information (FDC) is populated and the FDC parameter value is CPC and the FDC field value is cpc, then the optional fields enclosed in [ ] are added to the CPC VSA. country contains the 3-character country code representing the country variant extracted from the GTD Protocol Name (PRN) country field and stored in a TDUserContainer. text2 contains the national value extracted from the GTD FDC data field and stored in a TDUserContainer. |
|||
Originating gateway or gatekeeper of a leg 3 VoIP call. Contains either the IP address of the originating gateway or the interzone ClearToken (IZCT) of the originating gatekeeper zone. |
||||
The CHN VSA is generated by the gateway’s RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in start and stop accounting messages for call legs 1 and 4. |
||||
Number of charged units for this connection. For incoming calls or if charging information is not supplied by the switch, the value of this object is zero. |
||||
Incoming port identification on NAS or gateway. The syntax is as follows: signalling type controller: timeslot group/control channel: bearer channel This VSA has the same function as RADIUS attribute 5, and uses strings assigned by Cisco IOS software to its hardware ports. |
||||
Negotiated coder rate. Specifies the transmit rate of voice/fax compression to its associated call leg for the call. |
||||
Number of received voice packets that arrived too early to store in jitter buffer during the call. |
||||
"feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:10/28/2005 01:30:27.775,cgn:1011011006,cdn:1011011007,frs:0,fid=36,fcid:411CC18B468911DA801DE37EC374A8C6, |
Captures feature-specific information. There can be multiple instances of this VSA in a start or stop record. For information, see the “Feature VSA for Supplementary Services” section. |
|||
Duration, in ms, of voice signal played out with signal synthesized from parameters or samples of data preceding and following in time because of voice data not received on time (or lost) from the voice gateway for this call. |
||||
Duration, in ms, of voice signal played out with signal synthesized from parameters or samples of data preceding in time because of voice data not received on time (or lost) from the voice gateway for this call. An example of such playout is frame-erasure or frame-concealment strategies in G.729 and G.723.1 compression algorithms. This counter object locks at the maximum value, which is approximately two days. |
||||
Duration, in ms, of voice signal played out with signal synthesized from redundancy parameters available because of voice data not received on time (or lost) from the voice gateway for this call. |
||||
Duration, in ms, of voice signal replaced with signal played out during silence because of voice data not received on time (or lost) from voice gateway for this call. |
||||
The gatekeeper presented called number in the ACF RAS message. The GK/GKTMP could modify the called number by appending a prefix or it could be left unchanged. |
||||
The gatekeeper presented calling number in the ACF RAS message. The GK/GKTMP could modify the calling number which is carried in the ACF nonstandard parameter. |
||||
| where: |
||||
The gateway (application) collected destination number that will eventually be used for routing the call. Only applicable for 2-stage calls. |
||||
| where: |
||||
Called number as received by the gateway in the incoming signaling message before any translation rules are applied. |
||||
| where: |
Calling number as received by the gateway in the incoming signaling message before any translation rules are applied. |
|||
|
||||
|
Gateway’s behavior in relation to the connection that is active for this leg. For example, answer on leg 1; originate on leg 2; callback on leg 1. |
|||
16-byte number in hexadecimal notation with one space between each 4-byte integer |
Unique call identifier generated by the gateway. Used to identify the separate billable events (calls) within a single calling session. In Cisco IOS call-control application programming interface (Cisco IOS CCAPI), this value is called the globally unique identifier (GUID). The h323-conf-id is different from the h323-incoming-conf-id. For example, in long pound calls (calls in which you press the # key to make a new call) with a prepaid application, a new h323-conf-id value is generated for each new call. The new value is generated in the leg following authorization (either leg 2 or leg 4) and is subsequently passed to each downstream leg. Gateway-retries because of a connection request failure do not result in a new value; each retry uses the same h323-conf-id value. |
|||
h323-connect-time= value1 |
Connect time in Network Time Protocol (NTP) format: hour, minutes, seconds, microseconds, time_zone, day, month, day_of_month, and year. |
|||
2-character, ASCII-encoded hexadecimal number representing a Q.931 code. Range: 01 to A0 (which is 1to 160 decimal) |
Q.931 disconnect cause code retrieved from CCAPI. The source of the code is the disconnect location such as a PSTN, terminating gateway, or SIP. |
|||
Disconnect time in NTP format: hour, minutes, seconds, microseconds, time_zone, day, month, day_of_month, year. |
||||
Domain name server (DNS) name or local name of the voice gateway that is sending the VSA. |
||||
16-byte number in hexadecimal notation with one space between each 4-byte integer |
Unique number for identifying a calling session on a gateway, where a session is closed when the calling party hangs up. Is used to do the following:
The value used for legs 1 and 2 on the originating gateway can differ from that for legs 3 and 4 on a terminating gateway. The h323-incoming-conf-id is different from h323-conf-id. For example, the h323-incoming-conf-id value remains the same in the start/stop records for long pound calls. |
|||
User-definable AV pairs sent from the RADIUS server to the voice gateway. You can read and use the value at the gateway with a customized Tcl IVR script. |
||||
User-definable AV pairs sent from the voice gateway to the RADIUS server. You can set (write) the value with a customized Tcl IVR script. |
||||
Language to use when playing the audio prompt specified by the h323-prompt-id. |
||||
Index into an array that selects prompt files used at the gateway. |
||||
Phone number to which the call is redirected; for example, to a toll-free number or a customer service number. |
||||
Return codes are instructions from the RADIUS server to the voice gateway. |
||||
Setup time in NTP format: hour, minutes, seconds, microseconds, time_zone, day, month, day_of_month, year. |
||||
Time of day at the dialed number or at the remote gateway in the format: hour, minutes, seconds. |
||||
Value representing impairment/calculated planning impairment factor (ICPIF) of the voice quality on the connection provided by lower-layer drivers (such as the digital signal processor). Low numbers represent better quality. |
||||
High-water mark Voice Playout FIFO Delay during the voice call. |
||||
Carrier ID of the trunk group through which the call arrived or the partnering voice service provider identifier of the incoming VoIP call. |
||||
Gatekeeper identifier, or the source zone or area, of the incoming VoIP call. |
||||
Request-URI as given in the incoming request-line, including any url-parameters. |
||||
| 1=other (not described) |
||||
Description assigned to the voice port of the incoming call. |
||||
ASCII string associated with the port on the gateway used by this call. |
Description associated with the incoming hardware telephony port that is used with this leg of the call. Note This VSA was replaced by in-intrfc-desc in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T. |
|||
Cause of failed calls. For more information, see the “Internal Error Codes” section. |
||||
Contains the trunk group label associated with the group of voice ports from which the incoming time-division multiplexing (TDM) call arrived on the gateway. |
||||
Identifies whether call record is generated by a Cisco Unified SRST or Cisco Unified CME router. |
||||
SCCP phone involved in a call on a shared line. For information, see the “IP Phone Information Attribute for Shared Lines” section. |
||||
The CID VSA is generated by the gateway’s RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in start and stop accounting messages for call legs 1 and 4. |
||||
Number of received voice packets that arrived too late to play out with codec during the call. |
||||
ifIndex value of the logical interface through which this call was made. For ISDN media, this is the ifIndex of the B channel that was used for this call. |
||||
Low-water mark Voice Playout FIFO Delay during the voice call. |
||||
MOSQe (conversational quality MOS). Conversational quality indicates the impact of the quality of the transmission on the dynamics of conversational exchanges between two parties; such metrics take into account delay, echo, and recency. |
||||
| where FQDN is a host, domain name, or dotted IP address (for other field descriptions, see prev-hop-ip) |
Domain name (DN) or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) where the request is forwarded. When DNS SRV is used to resolve the address, then this contains the DN name. (Note that this means that the FQDN is not included.) If only a DNS A query is used to resolve the next hop IP address, then this is the FQDN name. If no resolution is needed, meaning that a dotted IP address was found in a static route entry or the request-uri, then this attribute is not included in the accounting message. |
|||
Duration, in ms, of voice playout from data received on time for this call, in ms. This plus the durations for the GapFills entries provides the Total Voice Playout Duration for Active Voice. |
||||
The OLI VSA is generated by the gateway’s RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in start and stop accounting messages for call legs 1 and 4. |
||||
Gatekeeper identifier, or the destination zone or area, of the outgoing VoIP call. |
||||
Request-URI used in the outgoing request-line, including any url-parameters. |
||||
Carrier ID field of the trunk group through which the call leaves the gateway or the partnering voice services provider identifier of the outgoing VoIP call. |
||||
Description assigned to the voice port of the outgoing call. |
||||
ASCII string associated with the port on the gateway used by this call. |
Description associated with the outgoing hardware telephony port that is used with this leg of the call. Note Replaced by out-intrfc-desc in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T. |
|||
Trunk-group label associated with the group of voice ports from which the outgoing TDM call leaves on the gateway. |
||||
Number that this call was connected to. If the number is not available, then it has a length of zero. |
||||
ID value of the peer table entry to which this call was made. If a peer table entry for this call does not exist, the value of this object is zero. |
||||
ifIndex value of the peer table entry to which this call was made. If a peer table entry for this call does not exist, the value is zero. |
||||
| where “port” is an optional parameter giving the transport layer port number and the default is 5060. where “protocol” is an optional parameter giving the transport layer protocol and the default is UDP. Valid values: TCP and UDP ; because the proxy does not support TCP, this parameter is never included. |
Previous hop IP address, as seen by the proxy. What would normally be placed in the “received” parameter when the proxy detected that the sender does not agree with the top-most via. |
|||
“Sent-by” portion of topmost via when the request arrived at the proxy. |
||||
Average Playout FIFO Delay plus the decoder delay during the voice call. |
||||
The RGN VSA is generated by the gateway RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in start accounting messages for all call legs. The text contains the redirecting number extracted from the redirect number parameter. The redirecting number is encoded in the text value. |
||||
1 : Calling party located in PSTN 2 : Calling party located in VoIP network 3 : Called party located in PSTN 4 : Called party located in VoIP network 5 : Internal release in POTS leg 6 : Internal release in VOIP leg 7 : Internal call-control application (Tcl or VoiceXML script) 8 : Internal release in VoIP AAA 9 : Console command line (CLI or MML) |
If a call was released by the calling party, called party, or an internal or external source. |
|||
Remote system UDP listener port to which voice packets are transmitted. |
||||
Voice-packet round-trip delay, in ms, between the local and remote device on the IP backbone during the call. |
||||
Session protocol used for calls between the local and remote router through the IP backbone. Always equal to “sip” for SIP or “Cisco” for H.323. |
||||
String from T1/CAS (Channel Associated Signaling) or E1/R2 line/signal. |
T1/Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) or E1/R2 signal information about a subscriber. |
|||
TMR VSA is generated by the gateway’s RADIUS client and, where available, is sent to the RADIUS server in start and stop accounting records for call legs 1 and 4. |
||||
Duration, in ms, of transmit path open from this peer to the voice gateway for the call. |
||||
Whether or not voice-activity detection (VAD) is enabled for the voice call. |
||||
The total number of packets lost by the jitter buffer in the RTP stream. |
||||
Duration, in ms, for this call. This value divided by tx-duration equals the Voice Utilization Rate. |
IP PBX Mode Attribute for SRST Mode
The IP PBX Mode attribute (ip-pbx-mode) identifies whether the router generating a call record is either a Cisco Unified SRST or Cisco Unified CME router.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager generates call records for all phones under its control. If the WAN link fails, phones fall back to Cisco Unified SRST or Cisco Unified CME in SRST fallback mode. When the phones register to the Cisco Unified SRST router, the router generates call records with the ip-pbx-mode value reported as either “cme” or “srst” in the stop records for all calls using SCCP.
For Cisco Unified CME in SRST fallback mode, IP phones that automatically learn their configuration from Cisco Unified Communications Manager during fallback are reported as “srst.” If an IP phone is manually configured in Cisco Unified CME, the ip-pbx-mode is reported as “cme.” Typically, you do not configure IP phones manually on the Cisco Unified SRST router.
The mode is determined at call setup for incoming calls, and at connect for outgoing call legs. You can filter call records on this attribute to identify the CDRs generated by the Cisco Unified SRST router for IP phones that rehomed after the WAN link went down. You can combine the filtered records from the Cisco Unified SRST router with the call records from Cisco Unified Communications Manager to generate a complete report.
If the connection to Cisco Unified Communications Manager is lost after a call is established to an external phone on a PSTN trunk, the ip-pbx-mode attribute is not reported in the call record. The ip-pbx-mode attribute is reported only after the phone registers to the Cisco Unified SRST router.
The router generates the ip-pbx-mode in call records only when there is a SCCP leg involved in the call. For non-SCCP-controlled ports connected to the Cisco Unified SRST router, CDRs are generated regardless of the state of the WAN link to Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The ip-pbx-mode is blank in file-based accounting records and omitted in RADIUS accounting records when the WAN link is up or when the call does not involve SCCP.
IP Phone Information Attribute for Shared Lines
The Shared-Line feature in Cisco Unified CME allows multiple phones to share the same directory number. The IP phone information attribute (ip-phone-info) identifies the phone involved in a call on a shared line. It reports the username associated with the phone as defined by the name command and indicates whether the call is going to or from the shared line. Because the username field can be blank, the ephone tag associated with the directory number is also reported.
This information is generated for all calls, whether or not a shared line is involved. It is reported for each call leg as a composite VSA in RADIUS start and stop records and as an attribute in file-based accounting stop records.
Table 4-2 lists (in sequential order) the attribute-value (AV) pairs that are included in ip-phone-info.

Note![]() For file-based accounting, the ip-phone-info attribute is appended to the feature-vsa record and repeated for every feature-vsa instance.
For file-based accounting, the ip-phone-info attribute is appended to the feature-vsa record and repeated for every feature-vsa instance.
Feature VSA for Supplementary Services
The feature VSA (feature-vsa) is a composite VSA in CDRs that captures accounting information about the supplementary services used for all the call legs involved in a call. It includes a feature correlation ID that enables you to track each of the supplementary features invoked on the different call legs of a call within a single gateway.
The feature VSA is written as a simple string containing AV pairs separated by commas; each AV pair uses a colon (:) delimiter. The specific AV pairs included in the feature VSA depend on the type of supplementary feature. There can be multiple instances of this VSA in RADIUS start and stop records. File-based accounting generates only stop records.
Cisco IOS Release 12.4(9)T and later releases support the following supplementary features:
- Two-Way Call (TWC)—A basic two-party call within a single gateway.
- Call Forward All (CFA)—A two-party call where the call is forwarded to the configured destination when the call detects call forward all.
- Call Forward Busy (CFBY)—A two-party call where the original called party is configured to forward calls to another destination when it is busy.
- Call Forward No Answer (CFNA)—A two-party call where the original called party is configured to forward calls to another destination when it does not answer for a specific amount of time.
- Blind Transfer (BXFER)—Call transfer that is basically redirecting a connected call. In a blind transfer, the call gets forwarded by the called party in the original call. Blind call transfer does not involve any interaction between the called party (transferee) and the transferred-to party.
- Consultative Transfer (CXFER)—Call transfer that is similar to blind transfer except that it involves consultation between the transferor and transferred-to party. If the transferred-to party responds positively to the consultation request, the call is transferred to the new destination.
Cisco IOS Release 12.4(20)T and later releases support hairpin call transfers using the trunk optimization feature, for the following types of calls:
- Transfer at Alert (HP_XFER_ALERT)—PSTN call to the trunk DN is transfered (consultative transfer) to a local phone that does not share the trunk DN. The call is hairpin transferred through the DN.
- Transfer at Connect (HP_XFER_CONNECT)—PSTN call to the trunk DN is transfered (consultative transfer at alert) to a local phone that does not share the trunk DN. The call is hairpin transferred through the DN.
- Transfer Recall (HP_XFER_RECALL_ALERT)—PSTN call to the trunk DN is transfered (consultative transfer at alert) to a local phone sharing the trunk DN if the transfer-to party does not answer the call. The call is hairpin transferred through the DN. Transferred-to phone does not answer and the call is recalled to the phone that initiated the transfer.
Cisco IOS Release 12.4(22)T and later releases support the Hold and Resume features.
- Hold (HOLD)—Phone user puts a call on hold by pressing the Hold soft key, or it occurs indirectly through features such as Call Transfer, Call Park, or Conferencing.
- Resume (RESUME)—Phone user connects to a call on hold by pressing the Resume soft key.
The feature VSA captures the hold and resume event including the time stamp, the reason for the event based on the user's supplementary service request, and which user put the caller on hold.
The hold duration is determined by the difference between the Hold time stamp and the Resume time stamp. For Call Transfers, the duration is the difference between the hold time stamp and the disconnect time stamp. You can use this information to identify how long a caller is put on hold and help determine the efficiency of your support personnel.
For an example of a CDR for Hold and Resume, see the “Hold and Resume CDR: Example” section.

Note![]() Hold and Resume information is not supported for VoIP to VoIP hairpin calls.
Hold and Resume information is not supported for VoIP to VoIP hairpin calls.
Feature VSA Examples
The following examples show the format of the feature VSA for different types of calls. Display this output by using the debug radius accounting command or the gw-accounting syslog command.
Oct 28 01:30:27.779: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 127 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:10/28/2005 01:30:27.775,cgn:1011011006,cdn:1011011007,frs:0,fid=36,fcid:411CC18B468911DA801DE37EC374A8C6,legID:13"
Oct 28 01:31:10.271: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 179 "feature-vsa=fn:CXFER,ft:10/28/2005 01:31:10.247,frs:0,fid:40,xconsID:1,fcid:411CC18B468911DA801DE37EC374A8C6,legID:14,
xrson:0,xsts:5,Xor:1011011007,Xee:1011011006,Xto:1011011008"
Oct 28 02:42:03.479: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 191 "feature-vsa=fn:CFNA,ft:10/28/2005 02:42:03.467,frs:0,fid:332,fcid:3E775493469311DA812EE37EC374A8C6,legID:9D,frson:3,fdcnt:1,fwder:1011011009,fwdee:1011011006,fwdto:1011011008,frm:1011011009"
“feature-vsa=fn:HOLD,ft:11/05/2007
12:01:47.747,frs:0,fid:17,fcid:C655249C8B1011DC800AF5E95DD6F9BF,legID:4,hrson:1,holding:5000,held:3000,sl:1,usr:mbrown,tag:5"
"feature-vsa=fn:RESUME,ft:11/05/2007
12:01:52.415,frs:0,fid:20,fcid:C91D6D008B1011DC800BF5E95DD6F9BF,legID:4,hrson:0,holding:5000,held:3000,sl:1,usr:jsmith,tag:7"
May 28 22:26:38.706: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 167 "feature-vsa=fn:HP_XFER_ALERT,ft:05/28/2008 14:26:31.106,frs:0,fid:42,xconsID:,fcid:E802FCF32C3B11DD8021A71BF42E2491,legID:14,xrsn:0,
xsts:5,Xor:1001,Xee:C803,Xto:5003
May 28 22:26:38.706: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 167 "feature-vsa=fn:HP_XFER_CONNECT,ft:05/28/2008 14:26:31.106,frs:0,fid:42,xconsID:,fcid:E802FCF32C3B11DD8021A71BF42E2491,legID:14,xrsn:0,
xsts:5,Xor:1001,Xee:C803,Xto:5003
May 28 22:26:38.706: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 167 "feature-vsa=fn:HP_XFER_RECALL_ALERT,ft:05/28/2008 14:26:31.106,frs:0,fid:42,xconsID:,fcid:E802FCF32C3B11DD8021A71BF42E2491,legID:14,xrsn:0,
xsts:5,Xor:1001,Xee:C803,Xto:5003
Feature VSA Attributes
Table 4-3 lists (in alphabetical order) the attributes that can be included in the feature VSA. The particular attributes that are included in each instance of the VSA are feature-specific.

Note ●![]() Conferencing call-legs are not supported by the feature VSA.
Conferencing call-legs are not supported by the feature VSA.
- For file-based accounting, the ip-phone-info and ip-pbx-mode attributes are appended to the feature-vsa record and are repeated for every feature-vsa instance.
- You can also send Feature-VSA information to a syslog server by using the gw-accounting syslog command. Limitations on the length of syslog messages, however, can restrict the amount of feature-vsa information included in the output. If the feature-vsa information exceeds the size limit for a syslog message, some of the information is not collected.
Feature Correlation ID
The feature correlation ID (fcid) identifies a given feature across all call legs in a call. It is similar to the GUID defined by the h323-conf-id attribute and it allows the call legs to be correlated based on the specific features invoked for the call. For any given feature, the feature VSA carries a unique feature correlation ID, which a postprocessing system can use to correlate the records.
For example, a simple two-way call generates two start records and two stop records. Each record carries a feature VSA of type TWC and all call legs for the two-way call carry the same feature correlation ID. When another feature is invoked during the two-way call, that feature gets a new feature correlation ID, which is common across the participating legs.
Figure 4-1 shows an example of how the feature correlation ID is used in a Call Forward No Answer scenario. In this figure, A and B are in a two-way call, and B invokes Call Forward No Answer to C. The CFNA VSA is captured on legs A and C stop records. A, B and C would have the same feature correlation ID (fcid:1) for their TWC VSA. The CFNA VSA would have a different feature correlation ID (fcid:2). This is present in A and C stop records.
When the records for A are processed by the accounting system, it would detect that there is a basic two-way call between A and B. It would also detect that there is a CFNA to C in A’s stop record. The new forwarded-to leg has the same feature correlation ID for CFNA (fcid:2). It is also carries the same feature correlation ID (fcid:1) for the TWC VSA on the forwarded-to leg.
Figure 4-1 Feature Correlation ID in Call Forward No Answer Scenario
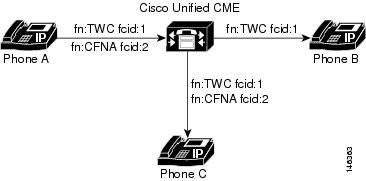
Cisco Unified CME B-ACD and Hunt Groups
Cisco IOS Release 12.4(20)T and later releases allow the correlation of multiple call records for calls routed to Cisco Unified CME Basic Automatic Call Distribution (B-ACD) and hunt groups. The feature correlation ID is the same across all call legs for a given feature.
Figure 4-2 shows an example of a hunt group used with the B-ACD service.
Figure 4-2 B-ACD Hunt Group Example
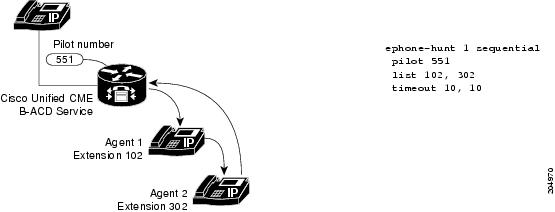
In this example, a call comes into the B-ACD service and proceeds as follows, generating the call records shown:
1.![]() Call goes to the hunt group (CFA from pilot number 551 to agent 1 at extension 102). The call records capture the TWC on incoming leg ID:1, the TWC on legID:2, which is the setup leg, and the CFA to extension 102 on legID:2.
Call goes to the hunt group (CFA from pilot number 551 to agent 1 at extension 102). The call records capture the TWC on incoming leg ID:1, the TWC on legID:2, which is the setup leg, and the CFA to extension 102 on legID:2.
000210: May 31 01:24:01.831: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 121 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:01.743,cgn:771,cdn:551,frs:0,fid:1,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:1"
000311: May 31 01:24:11.855: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 156 "feature-vsa=fn:CFA,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:01.843,frs:0,fid:2,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:2,frson:1,fdcnt:1,fwder:,
fwdee:771,fwdto:102,frm:551"
000313: May 31 01:24:11.855: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 127 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:01.843,cgn:771,cdn:551,frs:0,fid:4,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:2"
2.![]() Agent 1 (102) does not answer so the call is forwarded (CFNA) to agent 2 at extension 302. The call records capture the TWC setup on legID:3, and the CFNA on legID:3 and legID:2.
Agent 1 (102) does not answer so the call is forwarded (CFNA) to agent 2 at extension 302. The call records capture the TWC setup on legID:3, and the CFNA on legID:3 and legID:2.
000334: May 31 01:24:11.855: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 157 "feature-vsa=fn:CFNA,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:11.851,frs:0,fid:6,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:2,frson:3,fdcnt:2,fwder:,
fwdee:771,fwdto:302,frm:551"
000441: May 31 01:24:21.867: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 157 "feature-vsa=fn:CFNA,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:11.851,frs:0,fid:6,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:3,frson:3,fdcnt:2,fwder:,
fwdee:771,fwdto:302,frm:551"
000443: May 31 01:24:21.867: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 127 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:11.855,cgn:771,cdn:102,frs:0,fid:9,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:3"
3.![]() Agent 2 (302) also does not answer so the call is returned to the call queue and directed back to pilot number 551. The call records capture the new TWC for legID:7 and the CFA to agent 1 (102) on legID:8 from the BACD application. This is the second instance of CFA captured on legID:1.
Agent 2 (302) also does not answer so the call is returned to the call queue and directed back to pilot number 551. The call records capture the new TWC for legID:7 and the CFA to agent 1 (102) on legID:8 from the BACD application. This is the second instance of CFA captured on legID:1.
000606: May 31 01:24:50.899: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 154 "feature-vsa=fn:CFA,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:42.087,frs:0,fid:14,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:7,frson:1,fdcnt:1,
fwder:,fwdee:771,fwdto:102,frm:"
000608: May 31 01:24:50.899: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 128 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:42.087,cgn:771,cdn:551,frs:0,fid:13,fcid:2DD915072DE711DD800E931556F18823,legID:7"
4.![]() Agent 1 (102) answers the call. The call is connected to LegID:8. Agent 1 (102) does a consult transfer to extension 202 resulting in legID:9. The CXFER instance is captured on the original incoming legID:1, legID:7, and legID:9.
Agent 1 (102) answers the call. The call is connected to LegID:8. Agent 1 (102) does a consult transfer to extension 202 resulting in legID:9. The CXFER instance is captured on the original incoming legID:1, legID:7, and legID:9.
000657: May 31 01:24:57.611: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 119 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:57.611,cgn:102,cdn:,frs:0,fid:16,fcid:37193E252DE711DD8011931556F18823,legID:8"
000693: May 31 01:24:58.023: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 122 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:58.015,cgn:102,cdn:202,frs:0,fid:17,fcid:37193E252DE711DD8011931556F18823,legID:9"
000753: May 31 01:24:59.127: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 128 "feature-vsa=fn:CXFER,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:59.119,frs:0,fid:18,xconsID:1,fcid:0000,legID:7,xrsn:0,xsts:5,Xor:102,Xee:771,Xto:202"
000791: May 31 01:24:59.143: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 119 "feature-vsa=fn:TWC,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:57.611,cgn:102,cdn:,frs:0,fid:16,fcid:37193E252DE711DD8011931556F18823,legID:8"
000916: May 31 01:25:02.595: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 156 "feature-vsa=fn:CXFER,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:59.127,frs:0,fid:23,xconsID:1,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:9,xrsn:0,
xsts:2,Xor:102,Xee:771,Xto:202"
000978: May 31 01:25:02.599: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 156 "feature-vsa=fn:CXFER,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:59.119,frs:0,fid:21,xconsID:1,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:1,xrsn:0,
xsts:5,Xor:102,Xee:771,Xto:202"
000980: May 31 01:25:02.599: RADIUS: Cisco AVpair [1] 154 "feature-vsa=fn:CFA,ft:05/30/2008 18:24:42.087,frs:0,fid:14,fcid:15CD126F2DE711DD8002931556F18823,legID:1,frson:1,fdcnt:1,
fwder:,fwdee:771,fwdto:102,frm:"
Store-and-Forward Fax VSAs
Table 4-4 lists (in alphabetical order) the fax VSAs used by Cisco voice products.
T.38 Fax Statistics VSAs
The T.38 Fax Statistics feature provides the ability to gather detailed statistics about fax success indicator for T.38 fax relay calls for voice gateways with NextPort Digital Signal Processors (DSPs). The fax statistics and success indicator are available to CDRs through VSAs and added to the call log. These changes provide detailed CDRs that are useful for diagnostic purposes and give service providers more flexibility in their billing methods for fax relay calls.
RADIUS accounting functions allow statistics to be sent as VSAs at the start and end of sessions, indicating the amount of resources (such as time, packets, bytes, and so on) used during the session. These accounting records are recorded in CDRs. This feature adds several VSAs specifically for T.38 fax relay calls with SIP and H.323 signaling.
This feature interoperates with third-party gateways and therefore the Cisco gateway is able to report T.38 fax success and failure based on the following:
The accounting template is expanded to include the new statistics so that the end user can choose the statistics they wish to use.
Table 4-5 lists (in alphabetical order) the T.38 fax-statistics VSAs used by Cisco voice products.
Internal Error Codes
Internal error codes (IEC) identify errors that cause a gateway to release or refuse to accept a call. The following example shows a partial RADIUS stop accounting record for an IEC:
The IEC value takes the form of a dotted string of decimal numbers:
Table 4-6 describes the six fields that identify the components of the IEC.
VSA Release History
Table 4-7 lists each voice VSA (in alphabetical order) and the Cisco IOS release in which the VSA was introduced. Use this table when you configure the RADIUS server to understand which VSAs are supported, or if you want to upgrade to a later Cisco IOS release when new VSAs are introduced.
|
|
|
|---|---|
 Feedback
Feedback