Upgrading the System
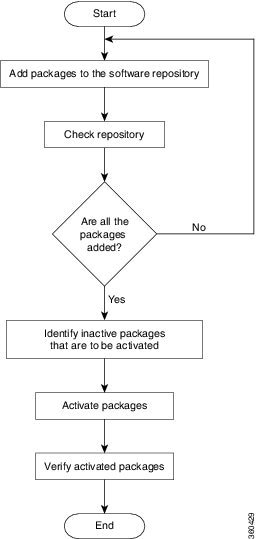
Upgrading the system is the process of installing a new version of the Cisco IOS XR operating system on the router. The router comes preinstalled with the Cisco IOS XR image. However, you can install the new version in order to keep router features up to date. The system upgrade operation is performed from the XR VM. However, during system upgrade, the software that runs on both the XR VM and the System Admin VM get upgraded.
 Note |
The 1G interface flaps twice instead of once in the Modular Port Adapter (MPA) NC55-MPA-12T-S after you reload any of these NCS 55A2 Fixed Chassis - NCS-55A2-MOD-SL, NCS-55A2-MOD-HD-S, NCS-55A2-MOD-HX-S, or NCS-55A2-MOD-SE-S. |
 Note |
If you insert a line card on a router that is running a lower version than the one the line card supports, the line card fails to boot. You must first upgrade the router to a software version that supports the line card, insert the line card and iPXE boot the line card. |
 Note |
If an interface on a router doesn’t have a configuration and is brought up by performing no-shut operation, then upon router reload, the interface state changes to admin-shutdown automatically. |
 Note |
|
Perform a system upgrade by installing a base package–Cisco IOS XR Unicast Routing Core Bundle. To install this bundle, run the install command. The filename for the Cisco IOS XR Unicast Routing Core Bundle bundle is ncs5500-mini-x.iso.
 Caution |
Do not perform any install operations when the router is reloading. Do not reload the router during an upgrade operation. |
 Note |
To enable hardware programming after upgrading the chassis from an older software version to IOS XR Release 7.6.x or later through ISSU, initiate a chassis reload. The chassis reload is mandatory, if you must enable a maximum transmission unit (MTU) value of 9646 on applicable interfaces. |
 Note |
Ensure that the system is on Cisco IOS XR Software Release 7.3.x, for a successful upgrade to Cisco IOS XR Software Release 7.6.x. |
Cisco IOS XR supports RPM signing and signature verification for Cisco IOS XR RPM packages in the ISO and upgrade images. All RPM packages in the Cisco IOS XR ISO and upgrade images are signed to ensure cryptographic integrity and authenticity. This guarantees that the RPM packages haven’t been tampered with and the RPM packages are from Cisco IOS XR. The private key, which is used for signing the RPM packages, is created and securely maintained by Cisco.

 Feedback
Feedback