- About this Guide
- Chapter 1, Install the Bay and Backplane Connections
- Chapter 2, Install Cards and Fiber-Optic Cable
- Chapter 3, Connect the PC and Log Into the GUI
- Chapter 4, Turn Up Node
- Chapter 5, Turn Up Network
- Chapter 6, Create Circuits and VT Tunnels
- Chapter 7, Manage Circuits
- Chapter 8, Manage Alarms
- Chapter 9, Monitor Performance
- Chapter 10, Change Card Settings
- Chapter 11, Change Node Settings
- Chapter 12, Convert Network Configurations
- Chapter 13, Add and Remove Nodes
- Chapter 14, Maintain the Node
- Chapter 15, Power Down the Node
- Chapter 16, DLPs E1 to E99
- Chapter 17, DLPs E100 to E199
- Chapter 18, DLPs E200 to E299
- Appendix A, CTC Information and Shortcuts
- Before You Begin
- NTP-E179 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Automatically
- NTP-E99 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Manually
- NTP-E100 Convert a Point-to-Point or Linear ADM to a Two-Fiber BLSR Manually
- NTP-E166 Convert a Two-Fiber BLSR to a Four-Fiber BLSR Automatically
- NTP-E103 Modify a BLSR
Convert Network Configurations
This chapter explains how to convert from one SONET topology to another in a Cisco ONS 15600 network. For initial network turn-up, see Chapter 5, "Turn Up Network."
Before You Begin
This section lists the chapter procedures (NTPs). Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
1. ![]() E179 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Automatically—Complete as needed.
E179 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Automatically—Complete as needed.
2. ![]() E99 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Manually—Complete as needed if the in-service topology upgrade wizard is not available or you need to back out of the wizard.
E99 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Manually—Complete as needed if the in-service topology upgrade wizard is not available or you need to back out of the wizard.
3. ![]() E100 Convert a Point-to-Point or Linear ADM to a Two-Fiber BLSR Manually—Complete as needed if the in-service topology upgrade wizard is not available or you need to back out of the wizard.
E100 Convert a Point-to-Point or Linear ADM to a Two-Fiber BLSR Manually—Complete as needed if the in-service topology upgrade wizard is not available or you need to back out of the wizard.
4. ![]() E166 Convert a Two-Fiber BLSR to a Four-Fiber BLSR Automatically—Complete as needed.
E166 Convert a Two-Fiber BLSR to a Four-Fiber BLSR Automatically—Complete as needed.
5. ![]() E103 Modify a BLSR—Complete as needed.
E103 Modify a BLSR—Complete as needed.
NTP-E179 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Automatically

Note ![]() OC-N transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in the specifications for each card in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.
OC-N transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in the specifications for each card in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.

Note ![]() If overhead circuits exist on the network, an in-service topology upgrade is service-affecting. The overhead circuits will drop traffic and have a status of PARTIAL after the upgrade is complete.
If overhead circuits exist on the network, an in-service topology upgrade is service-affecting. The overhead circuits will drop traffic and have a status of PARTIAL after the upgrade is complete.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at either of the point-to-point nodes. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at either of the point-to-point nodes. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() In network view, right-click the span between the two nodes where you want to add the new node. A dialog box appears.
In network view, right-click the span between the two nodes where you want to add the new node. A dialog box appears.
Step 3 ![]() Choose Upgrade Protection. A drop-down list appears.
Choose Upgrade Protection. A drop-down list appears.
Step 4 ![]() Choose Terminal to Linear and the first page of the wizard, Upgrade Protection: Terminal to Linear, appears. The dialog box lists the following conditions for adding a new node:
Choose Terminal to Linear and the first page of the wizard, Upgrade Protection: Terminal to Linear, appears. The dialog box lists the following conditions for adding a new node:
•![]() The terminal network has no critical or major alarms.
The terminal network has no critical or major alarms.
•![]() The node that you will add has no critical or major alarms.
The node that you will add has no critical or major alarms.
•![]() The node has a compatible software version with that of the terminal nodes.
The node has a compatible software version with that of the terminal nodes.
•![]() The node has four unused optical ports matching the speed of the 1+1 protection and no communications channel has been provisioned on these four ports.
The node has four unused optical ports matching the speed of the 1+1 protection and no communications channel has been provisioned on these four ports.
•![]() Fiber is available to connect the added node to the terminal nodes.
Fiber is available to connect the added node to the terminal nodes.
Step 5 ![]() If all conditions listed in Step 4 are met, click Next.
If all conditions listed in Step 4 are met, click Next.

Note ![]() If you are attempting to add an unreachable node, you must first log into the unreachable node using a separate CTC session and configure that node. Delete any existing protection groups as described in the "DLP-E87 Delete a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 16-91. Delete any existing data communications channel (DCC) terminations as described in the "DLP-E198 Delete a Section DCC Termination" task on page 17-76 or the "DLP-E199 Delete a Line DCC Termination" task on page 17-76.
If you are attempting to add an unreachable node, you must first log into the unreachable node using a separate CTC session and configure that node. Delete any existing protection groups as described in the "DLP-E87 Delete a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 16-91. Delete any existing data communications channel (DCC) terminations as described in the "DLP-E198 Delete a Section DCC Termination" task on page 17-76 or the "DLP-E199 Delete a Line DCC Termination" task on page 17-76.
Step 6 ![]() Enter the node host name or IP address or choose the name of the new node from the drop-down list. If you type in the name, make sure it is identical to the actual node name. The node name is case sensitive.
Enter the node host name or IP address or choose the name of the new node from the drop-down list. If you type in the name, make sure it is identical to the actual node name. The node name is case sensitive.
Step 7 ![]() Click Next. The Select Protection Group Ports page appears (Figure 12-1).
Click Next. The Select Protection Group Ports page appears (Figure 12-1).
Figure 12-1 Selecting Protection Group Ports

Step 8 ![]() From the drop-down lists, select the working and protect ports on the new node that you want to connect to each terminal node.
From the drop-down lists, select the working and protect ports on the new node that you want to connect to each terminal node.
Step 9 ![]() Click Next. The Re-fiber the Protected Path dialog box appears (Figure 12-2). Follow the instructions in the dialog box for connecting the fibers between the nodes.
Click Next. The Re-fiber the Protected Path dialog box appears (Figure 12-2). Follow the instructions in the dialog box for connecting the fibers between the nodes.
Figure 12-2 Refibering the Protect Path

Step 10 ![]() When the fibers are connected properly, click Next. The Update Circuit(s) on Node-Name dialog box appears.
When the fibers are connected properly, click Next. The Update Circuit(s) on Node-Name dialog box appears.

Note ![]() The Back button is not enabled in the wizard. You can click the Cancel button at this point and click Yes if you want to cancel the Upgrade Protection procedure. If the procedure fails after you have physically moved the fiber-optic cables, you must restore the fiber-optic cables to their original positions and verify (through CTC) that traffic is on the working path of the nodes before restarting the process. To check the traffic status, go to node view and click the Maintenance > Protection tabs. In the Protection Groups area, click the 1+1 protection group. You can see the status of the traffic in the Selected Group area.
The Back button is not enabled in the wizard. You can click the Cancel button at this point and click Yes if you want to cancel the Upgrade Protection procedure. If the procedure fails after you have physically moved the fiber-optic cables, you must restore the fiber-optic cables to their original positions and verify (through CTC) that traffic is on the working path of the nodes before restarting the process. To check the traffic status, go to node view and click the Maintenance > Protection tabs. In the Protection Groups area, click the 1+1 protection group. You can see the status of the traffic in the Selected Group area.
Step 11 ![]() Click Next. The Force Traffic to Protect Path dialog box appears, stating that it is about to force the traffic from the working path to the protect path for the terminal nodes.
Click Next. The Force Traffic to Protect Path dialog box appears, stating that it is about to force the traffic from the working path to the protect path for the terminal nodes.
Step 12 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
Step 13 ![]() Follow each step as instructed by the wizard as it guides you through the process of refibering the working path between nodes and forcing the traffic back to the working path. The final dialog box informs you when you have completed the procedure of upgrading from terminal to linear protection.
Follow each step as instructed by the wizard as it guides you through the process of refibering the working path between nodes and forcing the traffic back to the working path. The final dialog box informs you when you have completed the procedure of upgrading from terminal to linear protection.
Step 14 ![]() Click Finish.
Click Finish.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-E99 Convert a Point-to-Point to a Linear ADM Manually

Note ![]() Optical transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in the specifications section for each card in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.
Optical transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in the specifications section for each card in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.

Note ![]() In a point-to-point configuration, two OC-N cards are connected to two OC-N cards on a second node.
In a point-to-point configuration, two OC-N cards are connected to two OC-N cards on a second node.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at either of the point-to-point nodes. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at either of the point-to-point nodes. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31.
Complete the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31.
Step 3 ![]() In network view, double-click the node that will be added to the point-to-point configuration.
In network view, double-click the node that will be added to the point-to-point configuration.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the new node has four OC-N ports at the same rate as the point-to-point node.
Verify that the new node has four OC-N ports at the same rate as the point-to-point node.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "NTP-E32 Verify Node Turn-Up" procedure on page 5-2 for the new node.
Complete the "NTP-E32 Verify Node Turn-Up" procedure on page 5-2 for the new node.
Step 6 ![]() Physically connect the fibers between the point-to-point node you are logged into and the new node.
Physically connect the fibers between the point-to-point node you are logged into and the new node.
Step 7 ![]() On the new node, create a 1+1 protection group for the OC-N cards that will connect to the point-to-point node. See the "NTP-E25 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" procedure on page 4-7 for instructions.
On the new node, create a 1+1 protection group for the OC-N cards that will connect to the point-to-point node. See the "NTP-E25 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" procedure on page 4-7 for instructions.
Step 8 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E114 Provision Section DCC Terminations" task on page 17-14 for the working OC-N ports in the new node that will connect to the linear ADM network. (Alternatively, if additional bandwidth is needed for CTC management, complete the "DLP-E189 Provision Line DCC Terminations" task on page 17-68.) Make sure to set the port state in the Create SDCC Termination dialog box to IS.
Complete the "DLP-E114 Provision Section DCC Terminations" task on page 17-14 for the working OC-N ports in the new node that will connect to the linear ADM network. (Alternatively, if additional bandwidth is needed for CTC management, complete the "DLP-E189 Provision Line DCC Terminations" task on page 17-68.) Make sure to set the port state in the Create SDCC Termination dialog box to IS.

Note ![]() DCC failure alarms appear until you create DCC terminations in the point-to-point node during Step 13.
DCC failure alarms appear until you create DCC terminations in the point-to-point node during Step 13.
Step 9 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go To Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go To Network View.
Step 10 ![]() Double-click the point-to-point node that will connect to the other side of the new node.
Double-click the point-to-point node that will connect to the other side of the new node.
Step 11 ![]() Ensure that this point-to-point node has OC-N cards installed that can connect to the new node.
Ensure that this point-to-point node has OC-N cards installed that can connect to the new node.
Step 12 ![]() Create a 1+1 protection group for the OC-N ports that will connect to the new node. See the "NTP-E25 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" procedure on page 4-7 for instructions.
Create a 1+1 protection group for the OC-N ports that will connect to the new node. See the "NTP-E25 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" procedure on page 4-7 for instructions.
Step 13 ![]() Create DCC terminations on the working OC-N port that will connect to the new node. See the "DLP-E114 Provision Section DCC Terminations" task on page 17-14 or the "DLP-E189 Provision Line DCC Terminations" task on page 17-68. In the Create SDCC Termination dialog box, set the port state to IS.
Create DCC terminations on the working OC-N port that will connect to the new node. See the "DLP-E114 Provision Section DCC Terminations" task on page 17-14 or the "DLP-E189 Provision Line DCC Terminations" task on page 17-68. In the Create SDCC Termination dialog box, set the port state to IS.
Step 14 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go To Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go To Network View.
Step 15 ![]() Double-click the new node.
Double-click the new node.
Step 16 ![]() Complete the "NTP-E24 Set Up Timing" procedure on page 4-6 for the new node. If the new node is using line timing, make the working OC-N card the timing source.
Complete the "NTP-E24 Set Up Timing" procedure on page 4-6 for the new node. If the new node is using line timing, make the working OC-N card the timing source.
Step 17 ![]() Display the network view to verify that the newly created linear ADM configuration is correct. A single green span line should appear between each linear node.
Display the network view to verify that the newly created linear ADM configuration is correct. A single green span line should appear between each linear node.
Step 18 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-E157 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 17-46 for instructions.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-E157 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 17-46 for instructions.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 19 ![]() Repeat the procedure for each node that you want to add to the linear ADM.
Repeat the procedure for each node that you want to add to the linear ADM.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-E100 Convert a Point-to-Point or Linear ADM to a Two-Fiber BLSR Manually


Note ![]() Optical transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.
Optical transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at one of the nodes that you want to convert from a point-to-point or ADM to a bidirectional line switched ring (BLSR). If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at one of the nodes that you want to convert from a point-to-point or ADM to a bidirectional line switched ring (BLSR). If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31.
Complete the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31.
Step 3 ![]() Right-click a span adjacent to the node you are logged into.
Right-click a span adjacent to the node you are logged into.
Step 4 ![]() From the shortcut menu, choose Circuits. The Circuits on Span window appears.
From the shortcut menu, choose Circuits. The Circuits on Span window appears.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the total number of active synchronous transport signal (STS) circuits does not exceed 50 percent of the span bandwidth. In the Circuits column there is a block titled "Unused." This number should exceed 50 percent of the span bandwidth.
Verify that the total number of active synchronous transport signal (STS) circuits does not exceed 50 percent of the span bandwidth. In the Circuits column there is a block titled "Unused." This number should exceed 50 percent of the span bandwidth.

Note ![]() If the span is an OC-48, no more than 24 STSs can be provisioned on the span. If the span is an OC-192, no more than 96 STSs can be provisioned on the span.
If the span is an OC-48, no more than 24 STSs can be provisioned on the span. If the span is an OC-192, no more than 96 STSs can be provisioned on the span.

Step 6 ![]() Repeat Steps 3 through 5 at each node in the point-to-point or linear ADM that you will convert to the BLSR. If all nodes comply with Step 5, continue with Step 7.
Repeat Steps 3 through 5 at each node in the point-to-point or linear ADM that you will convert to the BLSR. If all nodes comply with Step 5, continue with Step 7.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E108 Verify that a 1+1 Working Port is Active" task on page 17-8 for every 1+1 protection group that supports a span in the point-to-point or linear ADM network.
Complete the "DLP-E108 Verify that a 1+1 Working Port is Active" task on page 17-8 for every 1+1 protection group that supports a span in the point-to-point or linear ADM network.
Step 8 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E87 Delete a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 16-91 at each node that supports the point-to-point or linear ADM span.
Complete the "DLP-E87 Delete a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 16-91 at each node that supports the point-to-point or linear ADM span.
Step 9 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E115 Change the Service State for a Port" task on page 17-16 to put the protect ports out of service at each node that supports the point-to-point or linear ADM span.
Complete the "DLP-E115 Change the Service State for a Port" task on page 17-16 to put the protect ports out of service at each node that supports the point-to-point or linear ADM span.
Step 10 ![]() (Linear ADM only) Physically remove the protect fibers from all nodes in the linear ADM. For example, in Figure 12-3 you could remove the fiber running from Node 2/Slot 13/Port 1 to Node 3/Slot 13/Port 1.
(Linear ADM only) Physically remove the protect fibers from all nodes in the linear ADM. For example, in Figure 12-3 you could remove the fiber running from Node 2/Slot 13/Port 1 to Node 3/Slot 13/Port 1.
Figure 12-3 Linear ADM to BLSR Conversion
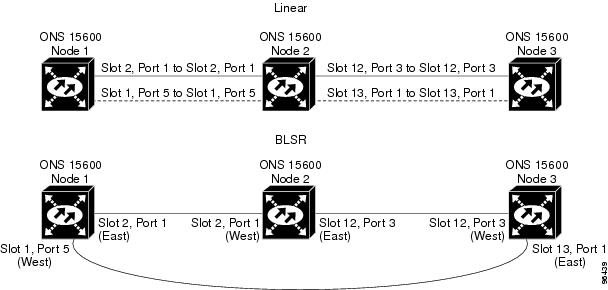
Step 11 ![]() Create the ring by connecting the protect fiber from one end node to the protect port on the other end node. For example, the fiber between Node 1/Slot 1/Port 5 and Node 2/Slot 1/Port 5 (Figure 12-3) can be rerouted to connect Node 1/Slot 1/Port 5 to Node 3/Slot 13/Port 1.
Create the ring by connecting the protect fiber from one end node to the protect port on the other end node. For example, the fiber between Node 1/Slot 1/Port 5 and Node 2/Slot 1/Port 5 (Figure 12-3) can be rerouted to connect Node 1/Slot 1/Port 5 to Node 3/Slot 13/Port 1.

Note ![]() If you need to physically remove any OC-N cards, do so now. In this example, cards in Node 2/Slots 1 and 13 can be removed. See the "NTP-E14 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure on page 2-8.
If you need to physically remove any OC-N cards, do so now. In this example, cards in Node 2/Slots 1 and 13 can be removed. See the "NTP-E14 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure on page 2-8.
Step 12 ![]() In network view, click the Circuits tabs and complete the "DLP-E265 Export CTC Data" task on page 18-84 to save the circuit data to a file on your hard drive.
In network view, click the Circuits tabs and complete the "DLP-E265 Export CTC Data" task on page 18-84 to save the circuit data to a file on your hard drive.
Step 13 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E114 Provision Section DCC Terminations" task on page 17-14 at the end nodes to provision the slot in each node that is not already in the SDCC Terminations list.
Complete the "DLP-E114 Provision Section DCC Terminations" task on page 17-14 at the end nodes to provision the slot in each node that is not already in the SDCC Terminations list.
Step 14 ![]() For circuits provisioned on an STS that is now part of the protection bandwidth (STSs 25 to 48 for an OC-48 BLSR, and STSs 97 to 192 for an OC-192 BLSR), delete and recreate each circuit:
For circuits provisioned on an STS that is now part of the protection bandwidth (STSs 25 to 48 for an OC-48 BLSR, and STSs 97 to 192 for an OC-192 BLSR), delete and recreate each circuit:

Note ![]() Deleting circuits is service-affecting.
Deleting circuits is service-affecting.
a. ![]() Complete the "DLP-E163 Delete Circuits" task on page 17-49 for one circuit.
Complete the "DLP-E163 Delete Circuits" task on page 17-49 for one circuit.
b. ![]() Create the circuit on STSs 1 to 24 for an OC-48 BLSR, or 1 to 96 for an OC-192 BLSR on the fiber that served as the protect fiber in the linear ADM. See the "NTP-E161 Create a Manually Routed Optical Circuit" procedure on page 6-9 for instructions.
Create the circuit on STSs 1 to 24 for an OC-48 BLSR, or 1 to 96 for an OC-192 BLSR on the fiber that served as the protect fiber in the linear ADM. See the "NTP-E161 Create a Manually Routed Optical Circuit" procedure on page 6-9 for instructions.
c. ![]() Repeat Steps a and b for each circuit residing on a BLSR protect STS.
Repeat Steps a and b for each circuit residing on a BLSR protect STS.
Step 15 ![]() Complete the "NTP-E164 Create a BLSR" procedure on page 5-9 to put the nodes into a BLSR.
Complete the "NTP-E164 Create a BLSR" procedure on page 5-9 to put the nodes into a BLSR.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-E166 Convert a Two-Fiber BLSR to a Four-Fiber BLSR Automatically

Note ![]() BLSR dual-ring interconnect (DRI) configurations do not support in-service topology upgrades.
BLSR dual-ring interconnect (DRI) configurations do not support in-service topology upgrades.

Note ![]() Span upgrades are not supported.
Span upgrades are not supported.

Note ![]() Two card and four card four-fiber BLSR configurations are supported. East and west ports must be configured on separate cards; however, working and protect ports can be on the same card or separate cards. The following modes are supported on separate cards: East-Working, East-Protect, West-Working, and West-Protect. The following modes are supported on the same card: East-Working, and East-Protect on card 1, and West-Working, West-Protect on card 2.
Two card and four card four-fiber BLSR configurations are supported. East and west ports must be configured on separate cards; however, working and protect ports can be on the same card or separate cards. The following modes are supported on separate cards: East-Working, East-Protect, West-Working, and West-Protect. The following modes are supported on the same card: East-Working, and East-Protect on card 1, and West-Working, West-Protect on card 2.

Note ![]() BLSR protection channel access (PCA) circuits, if present, will remain in their existing STSs. Therefore, they will be located on the working path of the four-fiber BLSR and will have full BLSR protection. To route PCA circuits on protection channels in the four-fiber BLSR, delete and recreate the circuits after the upgrade. For example, if you upgrade a two-fiber OC-48 BLSR to four-fiber, PCA circuits on the protection STSs (STSs 25 to 48) in the two-fiber BLSR will remain in their existing STSs, which are working STSs in the four-fiber BLSR. Deleting and recreating the OC-48 PCA circuits moves the circuits to STSs 1 to 24 in the protect bandwidth of the four-fiber BLSR. To delete circuits, see the "DLP-E163 Delete Circuits" task on page 17-49. To create circuits, see Chapter 6, "Create Circuits."
BLSR protection channel access (PCA) circuits, if present, will remain in their existing STSs. Therefore, they will be located on the working path of the four-fiber BLSR and will have full BLSR protection. To route PCA circuits on protection channels in the four-fiber BLSR, delete and recreate the circuits after the upgrade. For example, if you upgrade a two-fiber OC-48 BLSR to four-fiber, PCA circuits on the protection STSs (STSs 25 to 48) in the two-fiber BLSR will remain in their existing STSs, which are working STSs in the four-fiber BLSR. Deleting and recreating the OC-48 PCA circuits moves the circuits to STSs 1 to 24 in the protect bandwidth of the four-fiber BLSR. To delete circuits, see the "DLP-E163 Delete Circuits" task on page 17-49. To create circuits, see Chapter 6, "Create Circuits."

Note ![]() Before beginning this procedure, optical transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.
Before beginning this procedure, optical transmit and receive levels should be in their acceptable range as shown in Table 2-2 on page 2-10.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at one of the two-fiber nodes that you want to convert.
Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at one of the two-fiber nodes that you want to convert.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31.
Complete the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "NTP-E11 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-4 to install the additional OC-48 or OC-192 cards at each two-fiber BLSR node. The newly installed OC-N cards must have the same port rate as the two-fiber BLSR.
Complete the "NTP-E11 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-4 to install the additional OC-48 or OC-192 cards at each two-fiber BLSR node. The newly installed OC-N cards must have the same port rate as the two-fiber BLSR.
Step 4 ![]() Connect the fiber to the new ports. Use the same east-west connection scheme that was used to create the two-fiber connections. See the "DLP-E234 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations" task on page 18-47.
Connect the fiber to the new ports. Use the same east-west connection scheme that was used to create the two-fiber connections. See the "DLP-E234 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations" task on page 18-47.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E115 Change the Service State for a Port" task on page 17-16 to put in service the ports for each new OC-N card.
Complete the "DLP-E115 Change the Service State for a Port" task on page 17-16 to put in service the ports for each new OC-N card.
Step 6 ![]() Test the new fiber connections using procedures standard for your site.
Test the new fiber connections using procedures standard for your site.
Step 7 ![]() Convert the BLSR:
Convert the BLSR:
a. ![]() Display the network view and click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Display the network view and click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
b. ![]() Choose the two-fiber BLSR you want to convert and then click the Upgrade to 4 Fiber button.
Choose the two-fiber BLSR you want to convert and then click the Upgrade to 4 Fiber button.
c. ![]() In the Upgrade BLSR dialog box, set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path after the condition that caused the switch has been resolved. The default is 5 minutes.
In the Upgrade BLSR dialog box, set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path after the condition that caused the switch has been resolved. The default is 5 minutes.
d. ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
e. ![]() Assign the east and west protection ports:
Assign the east and west protection ports:
•![]() West Protect—Select the west BLSR port that will connect to the west protect fiber from the drop-down list.
West Protect—Select the west BLSR port that will connect to the west protect fiber from the drop-down list.
•![]() East Protect—Select the east BLSR port that will connect to the east protect fiber from the drop-down list.
East Protect—Select the east BLSR port that will connect to the east protect fiber from the drop-down list.
f. ![]() Click Finish.
Click Finish.
The fibers that were divided into working and protect bandwidths for the two-fiber BLSR are now fully allocated for working BLSR traffic.
Step 8 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-E157 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 17-46 as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-E157 Disable Alarm Filtering" task on page 17-46 as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Step 9 ![]() Complete the "NTP-E165 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test" procedure on page 5-12.
Complete the "NTP-E165 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test" procedure on page 5-12.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-E103 Modify a BLSR
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at a node in the BLSR you want to modify. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-E26 Log into CTC" task on page 16-39 at a node in the BLSR you want to modify. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Check the BLSR for outstanding alarms and conditions. See the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31 for instructions.
Check the BLSR for outstanding alarms and conditions. See the "DLP-E137 Check the Network for Alarms and Conditions" task on page 17-31 for instructions.

Note ![]() Some or all of the following alarms appear during BLSR setup: E-W-MISMATCH, RING-MISMATCH, APSC-IMP, APSCDFLTK, and BLSROSYNC. The alarms clear after you configure all the nodes in the BLSR. For definitions of these alarms, refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide.
Some or all of the following alarms appear during BLSR setup: E-W-MISMATCH, RING-MISMATCH, APSC-IMP, APSCDFLTK, and BLSROSYNC. The alarms clear after you configure all the nodes in the BLSR. For definitions of these alarms, refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 3 ![]() To change the BLSR ring ID or the ring or span reversion times, complete the following steps. If you want to change a node ID, continue with Step 4.
To change the BLSR ring ID or the ring or span reversion times, complete the following steps. If you want to change a node ID, continue with Step 4.
a. ![]() In network view, click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
In network view, click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
b. ![]() Click the BLSR that you want to modify and click Edit.
Click the BLSR that you want to modify and click Edit.
c. ![]() In the BLSR window, change any of the following:
In the BLSR window, change any of the following:
•![]() Ring ID—If needed, change the BLSR ring ID (a BLSR ring ID is a 6-character string that includes letters and numbers). Do not choose an ID that is already assigned to another BLSR.
Ring ID—If needed, change the BLSR ring ID (a BLSR ring ID is a 6-character string that includes letters and numbers). Do not choose an ID that is already assigned to another BLSR.
•![]() Reversion time—If needed, change the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path after a ring switch.
Reversion time—If needed, change the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path after a ring switch.
d. ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
If you changed the ring ID, the BLSR window closes automatically. If you only changed a reversion time, close the window by choosing Close from the File menu.
Step 4 ![]() To change a BLSR node ID, complete the following steps; otherwise, continue with Step 5.
To change a BLSR node ID, complete the following steps; otherwise, continue with Step 5.
a. ![]() On the network map, double-click the node with the node ID you want to change.
On the network map, double-click the node with the node ID you want to change.
b. ![]() Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
c. ![]() Choose a Node ID number. Do not choose a number already assigned to another node in the same BLSR.
Choose a Node ID number. Do not choose a number already assigned to another node in the same BLSR.
d. ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the following:
Verify the following:
•![]() A green span line appears between all BLSR nodes.
A green span line appears between all BLSR nodes.
•![]() All E-W-MISMATCH, RING-MISMATCH, APSC-IMP, APSCDFLTK, BLSROSYNC, and APSCNMIS alarms are cleared.
All E-W-MISMATCH, RING-MISMATCH, APSC-IMP, APSCDFLTK, BLSROSYNC, and APSCNMIS alarms are cleared.

Note ![]() For definitions of these alarms, refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide.
For definitions of these alarms, refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 Troubleshooting Guide.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
 Feedback
Feedback