Cisco NCS 6008 Product Overview
Cisco Network Convergence System 6000 Series
-
support elastic capacity at the lowest total ownership cost
-
deliver high-bandwidth mobile, video, and cloud services
-
enhance application service offerings
-
increase provisioning speed
-
optimize network economics
The Cisco NCS 6000 Series System is engineered for environmental efficiency, with the use of adaptable power consumption. The Cisco NCS 6000 Series System is powered by the Cisco nPower Network Processor Units (NPU). These technologies aid the Cisco NCS 6000 Series the lowest carbon footprint in service provider routing.
Cisco Network Convergence System 6008 Router
The Cisco NCS 6008 router, part of the Cisco NCS 6000 Series System, is the next-generation core router that provides industry-leading 8 Tbps of full-duplex network bandwidth through eight line cards.
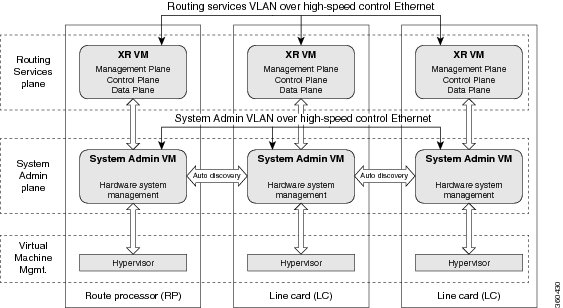
The Cisco NCS 6008 router runs on Cisco IOS XR software, with Linux as the underlying host operating system. A Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) hypervisor provides a virtualized environment to independently run system administration and routing functions on separate virtual machines. This provision makes the new system versatile and robust, providing immense flexibility for future expansion without the need for a complete system overhaul.
A multi-slice architecture of line cards enables the system to be configured to operate in a mixed operating mode, simultaneously supporting traffic at 10 Gbps and 100 Gbps on slice-level granularity.
 Feedback
Feedback