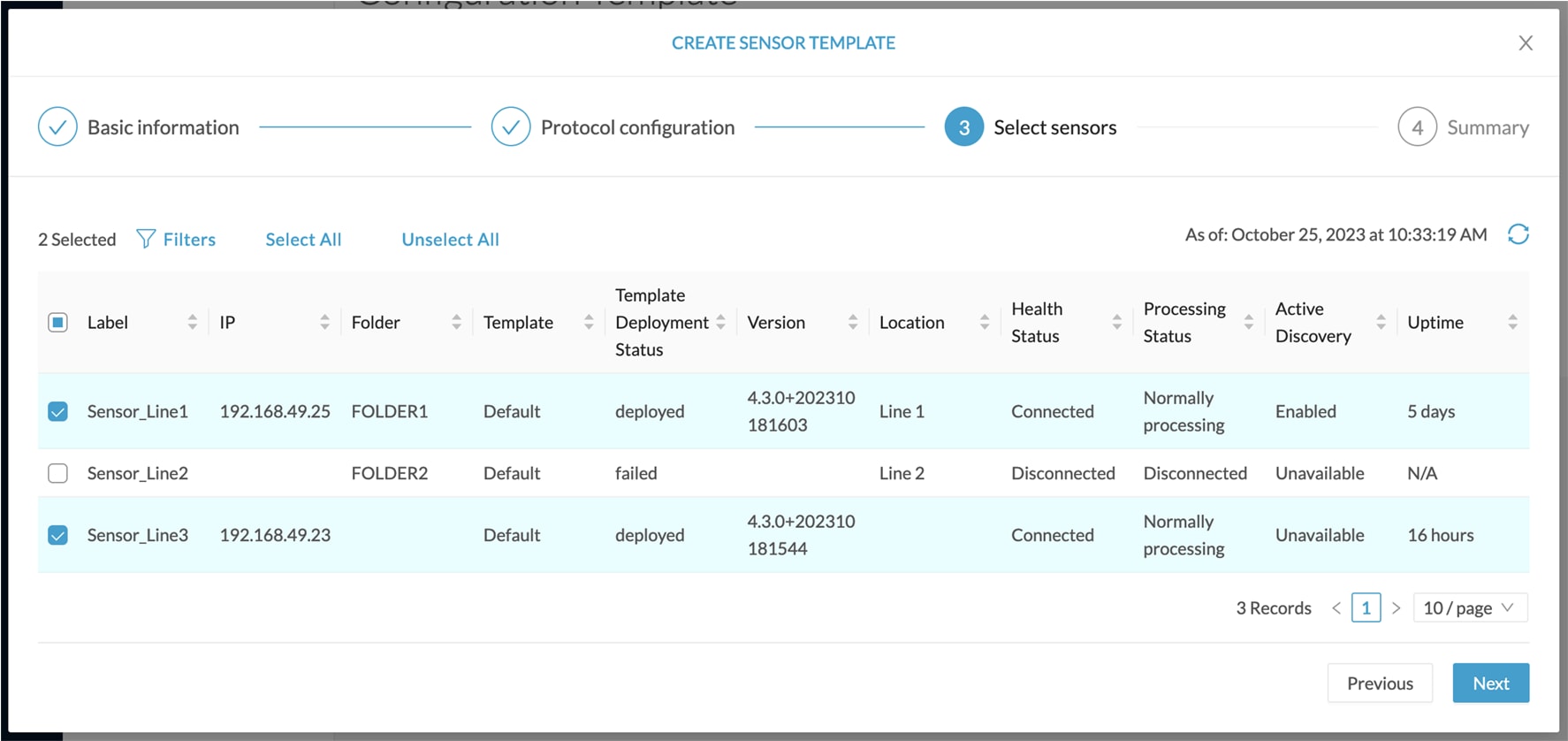
Configure Active Discovery
Once the sensor is connected, you can change the Active Discovery's network interface so it uses the Collection network interface instead, and add several network interfaces for the sensor to perform Active Discovery on several subnetworks at the same time.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the sensor to configure and click the Active Discovery button on its right side panel. The Active Discovery configuration appears with the interface currently set. |
|
Step 2 |
Select Use collection interface for the Active Discovery to use the Collection network interface. |
To add a network interface to Active Discovery for the sensor to perform active monitoring on another subnetwork:
|
Step 3 |
Add a new network interface by clicking the corresponding button. |
|
Step 4 |
Fill the following parameters to set dedicated network interfaces:
|
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. You can add as many network interfaces as needed. |
|
Step 6 |
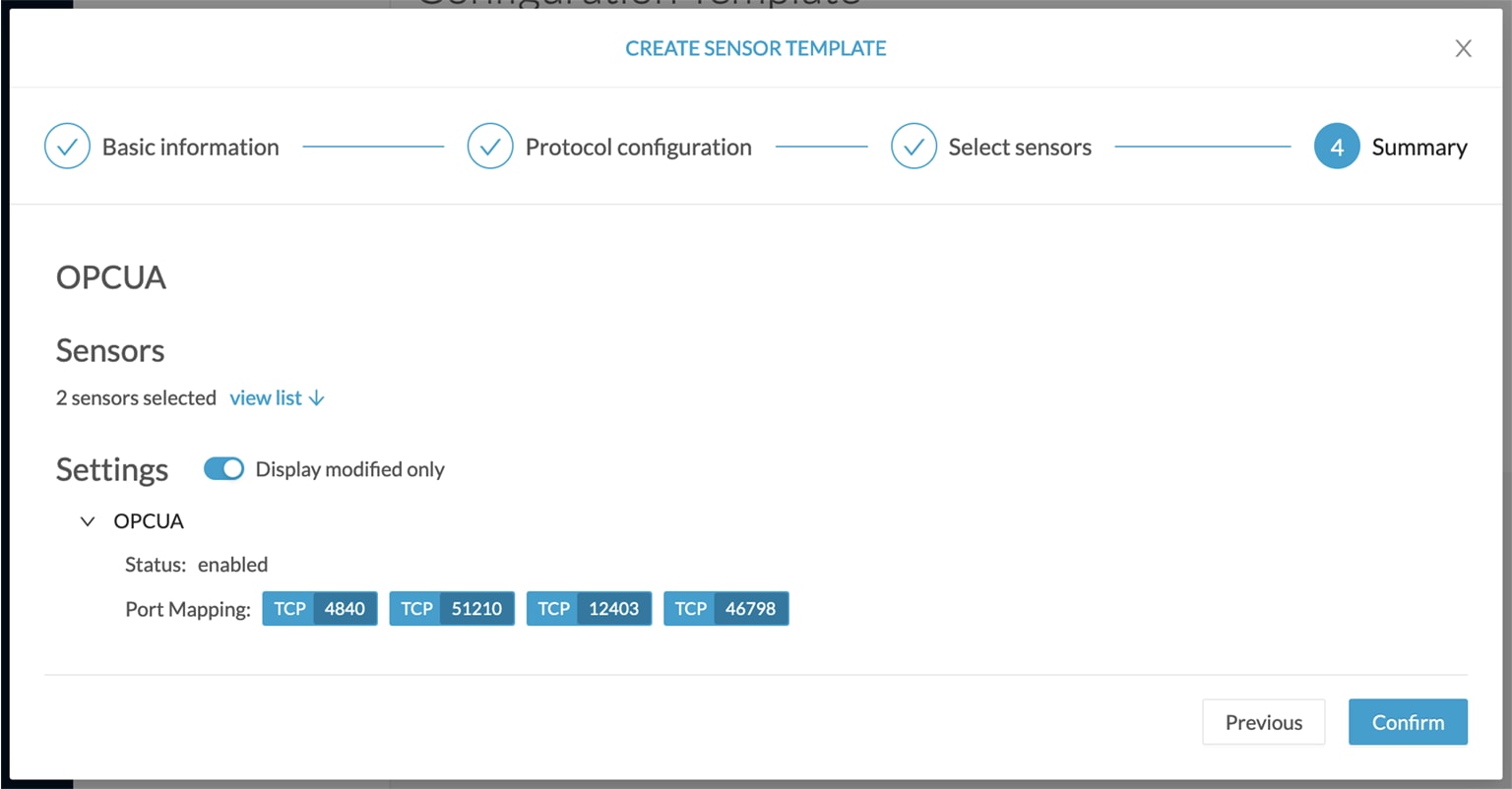
When you are done, click Configure. A message saying that the configuration has been applied successfully appears. |






 Feedback
Feedback