Configuration

The Configuration menu in the Admin UI is used to configure and manage various Secure Malware Analytics Appliance configuration settings, including:
|
Section |
Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication | |
|
Describes how to configure LDAP and RADIUS authentication for logging into the Secure Malware Analytics Appliance Admin UI. |
|
|
Describes how to add CA certificate for outbound SSL connections for the appliance to trust the Cisco Secure Endpoint Private Cloud. |
|
|
Describes how to change your Admin UI password. |
|
|
Describes how to configure SSH to setup some key elements via SSH. |
|
|
Describes how to set up SSH keys to provide access to the Admin TUI via SSH. |
|
|
Describes how to configure SSL certificates to support Secure Malware Analytics Appliance connections with Email Security Appliance (ESA), Web Security Appliance (WSA), Secure Endpoint Private Cloud, and other integrations; replacing SSL certificates. |
|
|
Application Settings |
|
|
Describes how to configure third-party detection and enrichment services (OpenDNS, TitaniumCloud, VirusTotal); enable or disable ClamAV automatic updates. |
|
|
Describes how to upload your Secure Malware Analytics Appliance license or retrieve it from the server. |
|
|
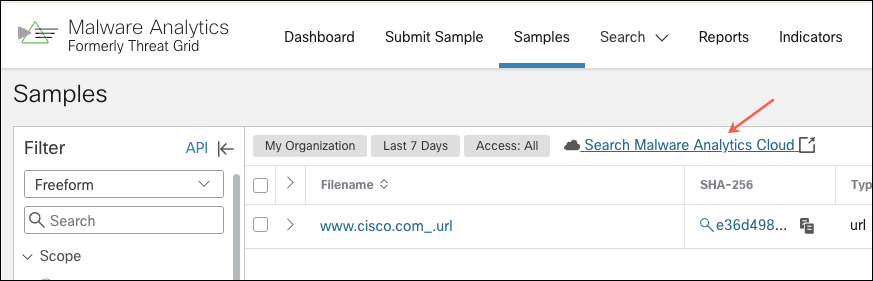
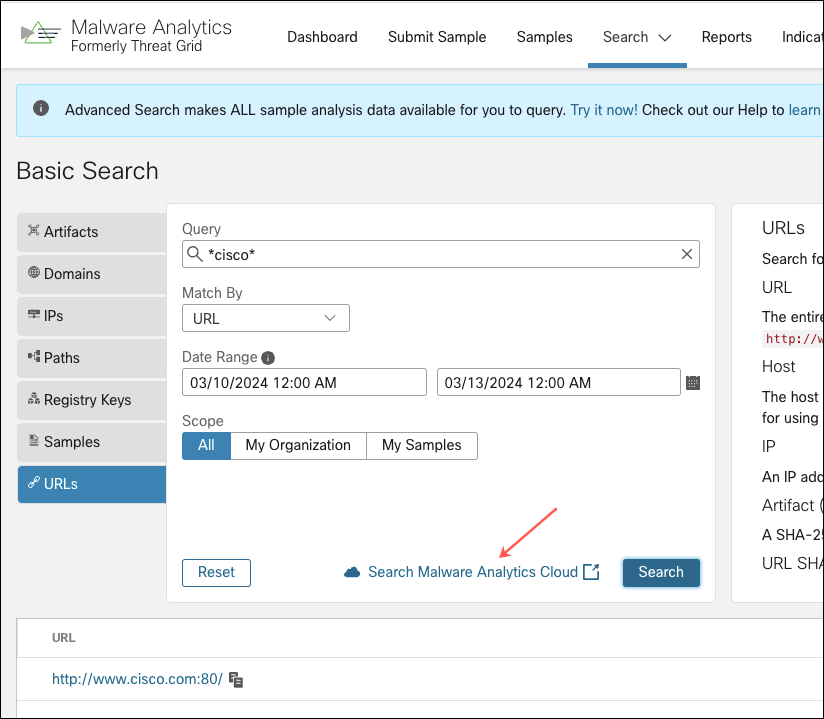
Describes how to configure the network exit options that are available in the Secure Malware Analytics portal when submitting samples for analysis. |
|
|
Describes how to configure the SOCKS5 proxy to download the updates. |
|
|
General |
|
|
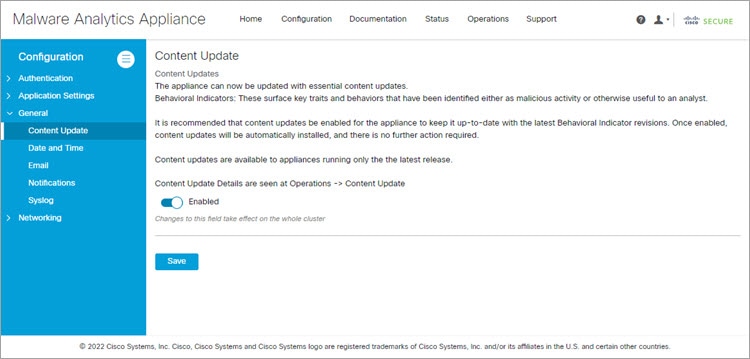
Describes how to enable Content Update. |
|
|
Describes how to add Network Time Protocol (NTP) server to configure date and time. |
|
|
Describes how to configure your email settings (SMTP) for system notifications. |
|
|
Describes how to manage notification recipients. |
|
|
Describes how to configure a system log server to receive syslog messages and notifications. |
|
|
Networking |
|
|
Describes how to adjust the IP assignment from DHCP to your permanent static IP addresses, and how to configure DNS. |
|
|
Describes appliance backup, including NFS requirements, backup storage requirements, backup expectations, and configuring the strict retention period limits; how to perform a backup. |
|
|
Describes features, limitations, and requirements of clustering Secure Malware Analytics Appliances; network and NFS storage requirements; how to build a cluster, join appliances to the cluster, remove cluster nodes, and designate a tie-breaker node; failure tolerances and failure recovery; API and operational usage and characteristics for clusters, and sample deletion. |
|
 Note |
|
 Important |
The Admin UI uses HTTPS and you must enter this in the browser address bar; pointing to only the Admin IP is not sufficient. Enter the following address in your browser: https://adminIP/ OR https://adminHostname/ |






























 Feedback
Feedback