Local Redundancy (HA) Process Overview
The local redundancy configuration provides an automatic failover solution in the event of software or hardware failures without the need to reconfigure IP addresses or DNS entries on your switched/routed network.
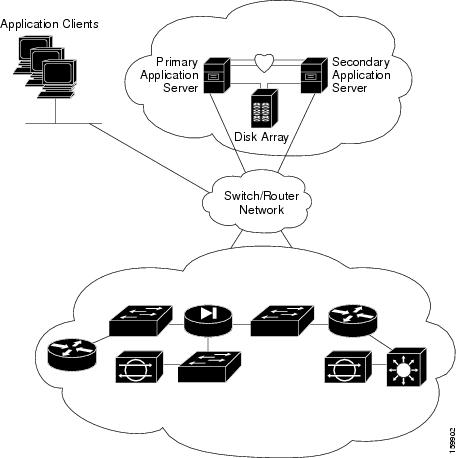
The figure illustrates the local redundancy HA configuration.
 Note |
The servers in the figure optionally contain mirrored internal boot disks. We recommend that they be the same make, model, and storage capacity. We recommend a fault-tolerant switched/routed network for communicating with the HA servers. |
Local Redundancy (HA) Configuration Steps
The following table lists the steps required to configure a locally redundant installation of Cisco Security Manager.
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
Make physical connections. |
|
|
Step 2 |
Install Microsoft Windows Server and all necessary drivers. |
|
|
Step 3 |
Make storage connections. |
|
|
Step 4 |
Install and configure the Veritas products and components. |
|
|
Step 5 |
Mirror the boot disk. |
|
|
Step 6 |
Setup required volumes on the shared array. |
|
|
Step 7 |
Install Cisco Security Manager on the shared volume on the primary server. |
|
|
Step 8 |
Install Cisco Security Manager on the spare (dummy) volume on the secondary server. |
|
|
Step 9 |
Update permissions on secondary server. |
|
|
Step 10 |
Create and configure clusters. |
|
 Feedback
Feedback