Configuring MSDP
This chapter describes how to configure Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) on a Cisco NX-OS switch.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Information About MSDP
You can use MSDP to exchange multicast source information between multiple BGP-enabled Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) sparse-mode domains. For information about PIM, see Chapter3, “Configuring PIM” For information about BGP, see the
Cisco Nexus 3000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide
.
When a receiver for a group matches the group transmitted by a source in another domain, the rendezvous point (RP) sends PIM join messages in the direction of the source to build a shortest path tree. The designated router (DR) sends packets on the source-tree within the source domain, which may travel through the RP in the source domain and along the branches of the source-tree to other domains. In domains where there are receivers, RPs in those domains can be on the source-tree. The peering relationship is conducted over a TCP connection.
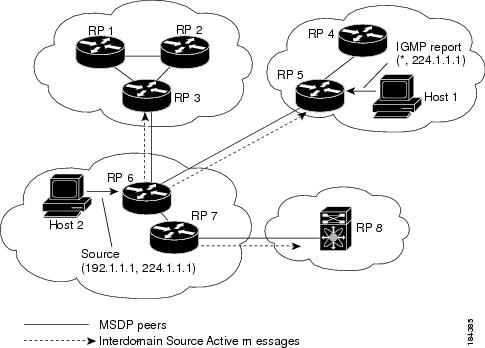
Figure 5-1 shows four PIM domains. The connected RPs (routers) are called MSDP peers because each RP maintains its own set of multicast sources. Source host 1 sends the multicast data to group 224.1.1.1. On RP 6, the MSDP process learns about the source through PIM register messages and generates Source-Active (SA) messages to its MSDP peers that contain information about the sources in its domain. When RP 3 and RP 5 receive the SA messages, they forward them to their MSDP peers. When RP 5 receives the request from host 2 for the multicast data on group 224.1.1.1, it builds a shortest path tree to the source by sending a PIM join message in the direction of host 1 at 192.1.1.1.
Figure 5-1 MSDP Peering Between RPs in Different PIM Domains
When you configure MSDP peering between each RP, you create a full mesh. Full MSDP meshing is typically done within an autonomous system, as shown between RPs 1, 2, and 3, but not across autonomous systems. You use BGP to do loop suppression and MSDP peer-RPF to suppress looping SA messages. For more information about mesh groups, see the “MSDP Mesh Groups” section.
Note You do not need to configure MSDP in order to use Anycast-RP (a set of RPs that can perform load balancing and failover) within a PIM domain. For more information, see the “Configuring a PIM Anycast-RP Set” section.
For detailed information about MSDP, see
RFC 3618
.
This section includes the following topics:
SA Messages and Caching
MSDP peers exchange Source-Active (SA) messages that the MSDP software uses to propagate information about active sources. SA messages contain the following information:
-
Source address of the data source
-
Group address that the data source uses
-
IP address of the RP or the configured originator ID
When a PIM register message advertises a new source, the MSDP process reencapsulates the message in an SA message that is immediately forwarded to all MSDP peers.
The SA cache holds the information for all sources learned through SA messages. Caching reduces the join latency for new receivers of a group because the information for all known groups can be found in the cache. You can limit the number of cached source entries by configuring the SA limit peer parameter. You can limit the number of cached source entries for a specific group prefix by configuring the group limit global parameter.
The MSDP software sends SA messages for each group in the SA cache every 60 seconds or at the configured SA interval global parameter. An entry in the SA cache is removed if an SA message for that source and group is not received within SA interval plus 3 seconds.
MSDP Peer-RPF Forwarding
MSDP peers forward the SA messages that they receive away from the originating RP. This action is called peer-RPF flooding. The router examines the BGP routing table to determine which peer is the next hop in the direction of the originating RP of the SA message. This peer is called a reverse path forwarding (RPF) peer.
If the MSDP peer receives the same SA message from a non-RPF peer in the direction of the originating RP, it drops the message. Otherwise, it forwards the message to all its MSDP peers.
MSDP Mesh Groups
You can use MSDP mesh groups to reduce the number of SA messages that are generated by peer-RPF flooding. In Figure 5-1, RPs 1, 2, and 3 receive SA messages from RP 6. By configuring a peering relationship between all the routers in a mesh and then configuring a mesh group of these routers, the SA messages that originate at a peer are sent by that peer to all other peers. SA messages received by peers in the mesh are not forwarded. An SA message that originates at RP 3 is forwarded to RP 1 and RP 2, but these RPs do not forward those messages to other RPs in the mesh.
A router can participate in multiple mesh groups. By default, no mesh groups are configured.
Virtualization Support
You can define multiple virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instances. The MSDP configuration applies to the selected VRF.
You can use the
show
commands with a VRF argument to provide a context for the information displayed. The default VRF is used if no VRF argument is supplied.
For information about configuring VRFs, see the
Cisco Nexus 3000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide
.
Licensing Requirements for MSDP
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
|
|
|
DCNM
|
<Feature-1> requires no license. Any feature not included in a license package is bundled with the Cisco DCNM and is provided at no charge to you. For a complete explanation of the DCNM licensing scheme, see the
Cisco DCNM Licensing Guide
.
|
DCNM
|
<Feature-1> requires a LAN Enterprise license. For a complete explanation of the DCNM licensing scheme and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the
Cisco DCNM Licensing Guide.
|
Cisco NX-OS
|
MSDP requires a LAN Base Services license. For a complete explanation of the Cisco NX-OS licensing scheme and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the
Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide
.
|
Prerequisites for MSDP
MSDP has the following prerequisites:
-
You are logged onto the switch.
-
For global commands, you are in the correct virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) mode. The default configuration mode shown in the examples in this chapter applies to the default VRF.
-
You configured PIM for the networks where you want to configure MSDP.
-
You configured BGP for the PIM domains where you want to configure MSDP.
Default Settings
Table 5-1
lists the default settings for MSDP parameters.
Table 5-1 Default MSDP Parameters
|
|
|
Description
|
Peer has no description
|
Administrative shutdown
|
Peer is enabled when it is defined
|
MD5 password
|
No MD5 password is enabled
|
SA policy IN
|
All SA messages are received
|
SA policy OUT
|
All registered sources are sent in SA messages
|
SA limit
|
No limit is defined
|
Originator interface name
|
RP address of the local system
|
Group limit
|
No group limit is defined
|
SA interval
|
60 seconds
|
Configuring MSDP
You can establish MSDP peering by configuring the MSDP peers within each PIM domain.
To configure MSDP peering, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the routers to act as MSDP peers.
Step 2 Enable the MSDP feature. See the “Enabling the MSDP Feature” section.
Step 3 Configure the MSDP peers for each router identified in Step 1. See the “Configuring MSDP Peers” section.
Step 4 Configure the optional MSDP peer parameters for each MSDP peer. See the “Configuring MSDP Peer Parameters” section.
Step 5 Configure the optional global parameters for each MSDP peer. See the “Configuring MSDP Global Parameters” section.
Step 6 Configure the optional mesh groups for each MSDP peer. See the “Configuring MSDP Mesh Groups” section.
Note The MSDP commands that you enter before you enable MSDP are cached and then run when MSDP is enabled. Use the ip msdp peer or ip msdp originator-id command to enable MSDP.
This section includes the following topics:
Note If you are familiar with the Cisco IOS CLI, be aware that the Cisco NX-OS commands for this feature might differ from the Cisco IOS commands that you would use.
Enabling the MSDP Feature
Before you can access the MSDP commands, you must enable the MSDP feature.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure terminal
2.
feature msdp
3. (Optional)
show running-configuration | grep
feature
4. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
Step 2
|
feature msdp
Example:
switch# feature msdp
|
Enables the MSDP feature so that you can enter MSDP commands. By default, the MSDP feature is disabled.
|
Step 3
|
show running-configuration | grep
feature
Example:
switch# show running-configuration | grep feature
|
(Optional) Shows
feature
commands that you specified.
|
Step 4
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Configuring MSDP Peers
You can configure an MSDP peer when you configure a peering relationship with each MSDP peer that resides either within the current PIM domain or in another PIM domain. MSDP is enabled on the router when you configure the first MSDP peering relationship.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Ensure that you have installed the LAN Base Services license and enabled PIM and MSDP.
Ensure that you configured BGP and PIM in the domains of the routers that you will configure as MSDP peers.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip msdp peer
peer-ip-address
connect-source
interface
[
remote-as
as-number
]
3. Repeat Step 2 for each MSDP peering relationship.
4. (Optional)
show ip msdp summary
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
5. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
Step 2
|
ip msdp peer
peer-ip-address
connect-source
interface
[
remote-as
as-number
]
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp peer 192.168.1.10 connect-source ethernet 2/1 remote-as 8
|
Configures an MSDP peer with the specified peer IP address. The software uses the source IP address of the interface for the TCP connection with the peer. The interface can take the form of
type slot/port
. If the AS number is the same as the local AS, then the peer is within the PIM domain; otherwise, this peer is external to the PIM domain. By default, MSDP peering is disabled.
Note MSDP peering is enabled when you use this command.
|
Step 3
|
Repeat Step 2 for each MSDP peering relationship by changing the peer IP address, the interface, and the AS number as appropriate.
|
—
|
Step 4
|
show ip msdp summary
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
Example:
switch# show ip msdp summary
|
(Optional) Displays a summary of MDSP peers.
|
Step 5
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Configuring MSDP Peer Parameters
You can configure the optional MSDP peer parameters described in
Table 5-2
. You configure these parameters in global configuration mode for each peer based on its IP address.
Table 5-2 MSDP Peer Parameters
|
|
|
Description
|
Description string for the peer. By default, the peer has no description.
|
Administrative shutdown
|
Method to shut down the MSDP peer. The configuration settings are not affected by this command. You can use this parameter to allow configuration of multiple parameters to occur before making the peer active. The TCP connection with other peers is terminated by the shutdown. By default, a peer is enabled when it is defined.
|
MD5 password
|
MD5-shared password key used for authenticating the peer. By default, no MD5 password is enabled.
|
SA policy IN
|
Route-map policy for incoming SA messages. By default, all SA messages are received.
|
SA policy OUT
|
Route-map policy
1
for outgoing SA messages. By default, all registered sources are sent in SA messages.
|
SA limit
|
Number of (S, G) entries accepted from the peer and stored in the SA cache. By default, there is no limit.
|
For information about configuring multicast route maps, see the “Configuring Route Maps to Control RP Information Distribution” section.
Note For information about configuring mesh groups, see the “Configuring MSDP Mesh Groups” section.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Ensure that you have installed the LAN Base Services license and enabled PIM and MSDP.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip msdp description
peer-ip-address string
ip msdp shutdown
peer-ip-address
ip msdp password
peer-ip-address password
ip msdp sa-policy
peer-ip-address policy-name
in
ip msdp sa-policy
peer-ip-address policy-name
out
ip msdp sa-limit
peer-ip-address limit
3. (Optional)
show ip msdp peer
[
peer-address
] [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
4. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
|
Step 2
|
ip msdp description
peer-ip-address
string
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp description 192.168.1.10 peer in Engineering network
|
Sets a description string for the peer. By default, the peer has no description.
|
ip msdp shutdown
peer-ip-address
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp shutdown 192.168.1.10
|
Shuts down the peer. By default, the peer is enabled when it is defined.
|
ip msdp password
peer-ip-address
password
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp password 192.168.1.10 my_md5_password
|
Enables an MD5 password for the peer. By default, no MD5 password is enabled.
|
ip msdp sa-policy
peer-ip-address
policy-name
in
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp sa-policy 192.168.1.10 my_incoming_sa_policy in
|
Enables a route-map policy for incoming SA messages. By default, all SA messages are received.
|
ip msdp sa-policy
peer-ip-address
policy-name
out
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp sa-policy 192.168.1.10 my_outgoing_sa_policy out
|
Enables a route-map policy for outgoing SA messages. By default, all registered sources are sent in SA messages.
|
ip msdp sa-limit
peer-ip-address
limit
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp sa-limit 192.168.1.10 5000
|
Sets a limit on the number of (S, G) entries accepted from the peer. By default, there is no limit.
|
Step 3
|
show ip msdp peer
[
peer-address
] [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
Example:
switch# show ip msdp peer 1.1.1.1
|
(Optional) Displays detailed MDSP peer information.
|
Step 4
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Configuring MSDP Global Parameters
You can configure the optional MSDP global parameters described in
Table 5-3
.
Table 5-3 MSDP Global Parameters
|
|
|
Originator interface name
|
IP address used in the RP field of an SA message entry. When Anycast RPs are used, all RPs use the same IP address. You can use this parameter to define a unique IP address for the RP of each MSDP peer. By default, the software uses the RP address of the local system.
|
Group limit
|
Maximum number of (S, G) entries that the software creates for the specified prefix. The software ignores groups when the group limit is exceeded and logs a violation. By default, no group limit is defined.
|
SA interval
|
Interval at which the software transmits Source-Active (SA) messages. The range is from 60 to 65,535 seconds. The default is 60 seconds.
|
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Ensure that you have installed the LAN Base Services license and enabled PIM and MSDP.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip msdp originator-id
interface
ip msdp group-limit
limit
source
source-prefix
ip msdp sa-interval
seconds
3. (Optional)
show ip msdp summary
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
4. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
|
Step 2
|
ip msdp originator-id
interface
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp originator-id loopback0
|
Sets the IP address used in the RP field of an SA message entry. The interface can take the form of
type slot/port
. By default, the software uses the RP address of the local system.
Note We recommend that you use a loopback interface for the RP address.
|
ip msdp group-limit
limit
source
source-prefix
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp group-limit 1000 source 192.168.1.0/24
|
Maximum number of (S, G) entries that the software creates for the specified prefix. The software ignores groups when the group limit is exceeded and logs a violation. By default, no group limit is defined.
|
ip msdp sa-interval
seconds
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp sa-interval 80
|
Interval at which the software transmits Source-Active (SA) messages. The range is from 60 to 65,535 seconds. The default is 60 seconds.
|
Step 3
|
show ip msdp summary
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
Example:
switch# show ip msdp summary
|
(Optional) Displays a summary of the MDSP configuration.
|
Step 4
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Remote Multicast Source Support
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(3)U2(1), if multicast traffic is received from a source which is not attached, the (S,G) route is not formed and all traffic continuously hits the CPU. You can enable the remote multicast source support to redirect the traffic.
When this feature is enabled, static mroute to the source is configured using the
ip mroute
src-ip next-hop
command and when the prebuild spt is enabled using the
ip pim pre-build-spt
command, the (S,G) route is formed without traffic hitting the CPU. Also, for these sources, register messages are sent periodically and MSDP SA messages are sent to the peer.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip mfwd mstatic register
3. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
Step 2
|
ip mfwd mstatic register
Example:
switch(config)# ip mfwd mstatic register
|
Enables the remote multicast source support.
|
Step 3
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Configuring MSDP Mesh Groups
You can configure optional MDSP mesh groups in global configuration mode by specifying each peer in the mesh. You can configure multiple mesh groups on the same router and multiple peers per mesh group.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Ensure that you have installed the LAN Base Services license and enabled PIM and MSDP.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip msdp mesh-group
peer-ip-addr mesh-name
3. Repeat Step 2 for each MSDP peer in the mesh.
4. (Optional)
show ip msdp mesh-group
[
mesh-group
] [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
5. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
Step 2
|
ip msdp mesh-group
peer-ip-addr mesh-name
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp mesh-group 192.168.1.10 my_mesh_1
|
Configures an MSDP mesh with the peer IP address specified. You can configure multiple meshes on the same router and multiple peers per mesh group. By default, no mesh groups are configured.
|
Step 3
|
Repeat Step 2 for each MSDP peer in the mesh by changing the peer IP address.
|
—
|
Step 4
|
show ip msdp mesh-group
[
mesh-group
] [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
Example:
switch# show ip msdp summary
|
(Optional) Displays information about the MDSP mesh group configuration.
|
Step 5
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Restarting the MSDP Process
You can restart the MSDP process and optionally flush all routes.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Ensure that you have installed the LAN Base Services license and enabled PIM and MSDP.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
restart msdp
2.
configure terminal
3.
ip msdp flush-routes
4. (Optional)
show running-configuration | include flush-routes
5. (Optional)
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
Step 1
|
restart msdp
Example:
switch# restart msdp
|
Restarts the MSDP process.
|
Step 2
|
configure terminal
Example:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)#
|
Enters configuration mode.
|
Step 3
|
ip msdp flush-routes
Example:
switch(config)# ip msdp flush-routes
|
Removes routes when the MSDP process is restarted. By default, routes are not flushed.
|
Step 4
|
show running-configuration | include flush-routes
Example:
switch(config)# show running-configuration | include flush-routes
|
(Optional) Shows flush-routes configuration lines in the running configuration.
|
Step 5
|
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves configuration changes.
|
Verifying the MSDP Configuration
To display the MSDP configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
|
|
|
show ip msdp count
[
as-number
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays MSDP (S, G) entry and group counts by the AS number.
|
show ip msdp mesh-group
[
mesh-group
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays the MSDP mesh group configuration.
|
show ip msdp peer
[
peer-address
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays MSDP information for the MSDP peer.
|
show ip msdp rpf
[
rp-address
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays next-hop AS on the BGP path to an RP address.
|
show ip msdp sources
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays the MSDP-learned sources and violations of configured group limits.
|
show ip msdp summary
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays a summary of the MSDP peer configuration.
|
show system internal mfwd mroute status
|
Displays the status of multicast forwarding (MFWD) static routes.
|
show ip igmp snooping
|
Displays whether vPC multicast optimization is enabled or disabled.
|
For detailed information about the fields in the output from these commands, see the
Cisco Nexus 3000 Series Command Reference,
.
Displaying Statistics
You can display and clear MSDP statistics by using the features in this section.
This section has the following topics:
Displaying Statistics
You can display MSDP statistics using the commands listed in
Table 5-4
.
Table 5-4 MSDP Statistics Commands
|
|
|
show ip msdp
[
as-number
]
internal event-history
{
errors
|
messages
}
|
Displays memory allocation statistics.
|
show ip msdp policy statistics sa-policy
peer-address
{
in
|
out
} [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Displays the MSDP policy statistics for the MSDP peer.
|
show ip msdp
{
sa-cache
|
route
}
[
source-address
]
[
group-address
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
] [
asn-number
] [
peer
peer-address
]
|
Displays the MSDP SA route cache. If you specify the source address, all groups for that source are displayed. If you specify a group address, all sources for that group are displayed.
|
Clearing Statistics
You can clear the MSDP statistics using the commands listed in
Table 5-5
.
Table 5-5 MSDP Clear Statistics Commands
|
|
|
clear ip msdp peer
[
peer-address
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
]
|
Clears the TCP connection to an MSDP peer.
|
clear ip msdp policy statistics sa-policy
peer-address
{
in
|
out
} [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
]
|
Clears statistics counters for MSDP peer SA policies.
|
clear ip msdp statistics
[
peer-address
] [
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
]
|
Clears statistics for MSDP peers.
|
clear ip msdp
{
sa-cache
|
route
}
[
group-address
]
[
vrf
vrf-name
|
known-vrf-name
|
all
]
|
Clears the group entries in the SA cache.
|
Configuration Examples for MSDP
To configure MSDP peers, some of the optional parameters, and a mesh group, follow these steps for each MSDP peer:
Step 1 Configure the MSDP peering relationship with other routers.
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# ip msdp peer 192.168.1.10 connect-source ethernet 1/0 remote-as 8
Step 2 Configure the optional peer parameters.
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# ip msdp password 192.168.1.10 my_peer_password_AB
Step 3 Configure the optional global parameters.
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# ip msdp sa-interval 80
Step 4 Configure the peers in each mesh group.
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# ip msdp mesh-group 192.168.1.10 mesh_group_1
This example shows how to configure a subset of the MSDP peering that is shown in Figure 5-1.
-
RP 3: 192.168.3.10 (AS 7)
ip msdp peer 192.168.1.10 connect-source ethernet 1/1 ip msdp peer 192.168.2.10 connect-source ethernet 1/2 ip msdp peer 192.168.6.10 connect-source ethernet 1/3 remote-as 9 ip msdp password 192.168.6.10 my_peer_password_36 ip msdp mesh-group 192.168.1.10 mesh_group_123 ip msdp mesh-group 192.168.2.10 mesh_group_123 ip msdp mesh-group 192.168.3.10 mesh_group_123
-
RP 5: 192.168.5.10 (AS 8)
ip msdp peer 192.168.4.10 connect-source ethernet 1/1 ip msdp peer 192.168.6.10 connect-source ethernet 1/2 remote-as 9 ip msdp password 192.168.6.10 my_peer_password_56
-
RP 6: 192.168.6.10 (AS 9)
ip msdp peer 192.168.7.10 connect-source ethernet 1/1 ip msdp peer 192.168.3.10 connect-source ethernet 1/2 remote-as 7 ip msdp peer 192.168.5.10 connect-source ethernet 1/3 remote-as 8 ip msdp password 192.168.3.10 my_peer_password_36 ip msdp password 192.168.5.10 my_peer_password_56
This example shows how to display information about IGMP snooping information on a switch that runs Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(3)U2(1) and shows the status of multicast optimization on a virtual Port Channel (vPC):
switch# show ip igmp snooping Global IGMP Snooping Information: Optimised Multicast Flood (OMF) disabled IGMPv1/v2 Report Suppression enabled IGMPv3 Report Suppression disabled Link Local Groups Suppression enabled VPC Multicast optimization disabled IGMP Snooping information for vlan 1 Optimised Multicast Flood (OMF) disabled IGMP querier present, address: 10.1.1.7, version: 2, interface Ethernet1/13 IGMPv3 Explicit tracking enabled IGMPv2 Fast leave disabled IGMPv1/v2 Report suppression enabled IGMPv3 Report suppression disabled Link Local Groups suppression enabled Router port detection using PIM Hellos, IGMP Queries Number of router-ports: 1
This example shows how to display the status of the configured MFWD static routes:
switch# show system internal mfwd mroute status
Additional References
For additional information related to implementing MSDP, see the following sections:
Related Documents
|
|
|
CLI commands
|
Cisco Nexus 3000 Series Command Reference,
|
Standards
|
|
|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
|
—
|
Feature History for IGMP
Table 5-6
lists the release history for this feature.
Table 5-6 Feature History for MSDP
|
|
|
|
MSDP
|
5.0(3)U1(1)
|
This feature was introduced.
|




 Feedback
Feedback