- Preface
- New and Changed Information
- Overview
- Configuring Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring N Port Virtualization
- Configuring VSAN Trunking
- Configuring SAN Port Channel
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Advanced Fibre Channel Features and Concepts
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Index
Configuring Port Tracking
This chapter contains the following sections:
Configuring Port Tracking
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches offer the port tracking feature on physical Fibre Channel interfaces (but not on virtual Fibre Channel interfaces). This feature uses information about the operational state of the link to initiate a failure in the link that connects the edge device. This process of converting the indirect failure to a direct failure triggers a faster recovery process towards redundant links. When enabled, the port tracking feature brings down the configured links based on the failed link and forces the traffic to be redirected to another redundant link.
- Information About Port Tracking
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Displaying Port Tracking Information
- Default Port Tracking Settings
Information About Port Tracking
Generally, hosts can instantly recover from a link failure on a link that is immediately (direct link) connected to a switch. However, recovering from an indirect link failure between switches in a WAN or MAN fabric with a keepalive mechanism is dependent on several factors such as the timeout values (TOVs) and on registered state change notification (RSCN) information.
In the following figure, when the direct link 1 to the host fails, recovery can be immediate. However, when the ISL 2 fails between the two switches, recovery depends on TOVs, RSCNs, and other factors.
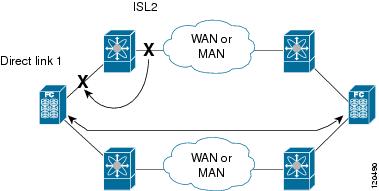
The port tracking feature monitors and detects failures that cause topology changes and brings down the links connecting the attached devices. When you enable this feature and explicitly configure the linked and tracked ports, the switch software monitors the tracked ports and alters the operational state of the linked ports on detecting a link state change.
The following terms are used in this chapter:
-
Tracked ports—A port whose operational state is continuously monitored. The operational state of the tracked port is used to alter the operational state of one or more ports. Fibre Channel, VSAN, SAN port channel, or a Gigabit Ethernet port can be tracked. Generally, ports in E and TE port modes can also be F ports.
-
Linked ports—A port whose operational state is altered based on the operational state of the tracked ports. Only physical Fibre Channel ports can be linked ports.
Port tracking has the following features:
-
The application brings the linked port down when the tracked port goes down. When the tracked port recovers from the failure and comes back up again, the linked port is also brought up automatically (unless otherwise configured).
-
You can forcefully continue to keep the linked port down, even though the tracked port comes back up. In this case, you must explicitly bring up the linked port when required.
Configuring Port Tracking
Before configuring port tracking, consider the following guidelines:
-
Verify that the tracked ports and the linked ports are on the same Cisco switch.
-
Be aware that the linked port is automatically brought down when the tracked port goes down.
-
Do not track a linked port back to itself (for example, Port fc2/2 to Port fc2/4 and back to Port fc2/2) to avoid recursive dependency.
- Enabling Port Tracking
- About Configuring Linked Ports
- Operationally Binding a Tracked Port
- About Tracking Multiple Ports
- Tracking Multiple Ports
- About Monitoring Ports in a VSAN
- Monitoring Ports in a VSAN
- About Forceful Shutdown
- Forcefully Shutting Down a Tracked Port
Enabling Port Tracking
The port tracking feature is disabled by default in Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. When you enable this feature, port tracking is globally enabled for the entire switch.
To configure port tracking, enable the port tracking feature and configure the linked ports for the tracked port.
To enable port tracking, perform this task:
1.
switch# configuration terminal
2.
switch(config)# port-track enable
3.
switch(config)# no port-track enable
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
About Configuring Linked Ports
You can link ports using one of two methods:
Operationally Binding a Tracked Port
When you configure the first tracked port, operational binding is automatically in effect. When you use this method, you have the option to monitor multiple ports or monitor ports in one VSAN.
To operationally bind a tracked port, perform this task:
1.
switch# configuration terminal
2.
switch(config)# interface fc
slot/port
3.
switch(config-if)# port-track interface fc
slot/port |
san-port-channel
port
4.
switch(config-if)# no port-track interface fc
slot/port |
san-port-channel
port
DETAILED STEPS
About Tracking Multiple Ports
You can control the operational state of the linked port based on the operational states of multiple tracked ports. When more than one tracked port is associated with a linked port, the operational state of the linked port will be set to down only if all the associated tracked ports are down. Even if one tracked port is up, the linked port will stay up.
In the following figure, only if both ISLs 2 and 3 fail, will the direct link 1 be brought down. Direct link 1 will not be brought down if either 2 or 3 are still functioning as desired.

Tracking Multiple Ports
To track multiple ports, perform this task:
1.
switch# configuration terminal
2.
switch(config)# interface fc
slot/port
3.
switch(config-if)# port-track interface interface fc
slot/port |
san-port-channel
port
DETAILED STEPS
About Monitoring Ports in a VSAN
You can optionally configure one VSAN from the set of all operational VSANs on the tracked port with the linked port by specifying the required VSAN. This level of flexibility provides higher granularity in tracked ports. In some cases, when a tracked port is a TE port, the set of operational VSANs on the port can change dynamically without bringing down the operational state of the port. In such cases, the port VSAN of the linked port can be monitored on the set of operational VSANs on the tracked port.
If you configure this feature, the linked port is up only when the VSAN is up on the tracked port.
The specified VSAN does not have to be the same as the port VSAN of the linked port.
Monitoring Ports in a VSAN
To monitor a tracked port in a specific VSAN, perform this task :
1.
switch# configuration terminal
2.
switch(config)# interface fc
slot/port
3.
switch(config-if)# port-track interface san-port-channel 1 vsan 2
4.
switch(config-if)# no port-track interface san-port-channel 1 vsan 2
DETAILED STEPS
About Forceful Shutdown
If a tracked port flaps frequently, then tracking ports using the operational binding feature may cause frequent topology change. In this case, you may choose to keep the port in the down state until you are able to resolve the reason for these frequent flaps. Keeping the flapping port in the down state forces the traffic to flow through the redundant path until the primary tracked port problems are resolved. When the problems are resolved and the tracked port is back up, you can explicitly enable the interface.
If you configure this feature, the linked port continues to remain in the shutdown state even after the tracked port comes back up. You must explicitly remove the forced shut state (by administratively bringing up this interface) of the linked port once the tracked port is up and stable.
Forcefully Shutting Down a Tracked Port
To forcefully shut down a tracked port, perform this task:
1.
switch# configuration terminal
2.
switch(config)# interface fc
slot/port
3.
switch(config-if)# port-track force-shut
4.
switch(config-if)# no port-track force-shut
DETAILED STEPS
Displaying Port Tracking Information
The show commands display the current port tracking settings for the switch.
The following example shows how to display tracked port configuration for a specific interface:
switch# show interface fc2/1
fc2/1 is down (Administratively down)
Hardware is Fibre Channel, FCOT is short wave laser w/o OFC (SN)
Port WWN is 20:01:00:05:30:00:0d:de
Admin port mode is FX
Port vsan is 1
Receive data field Size is 2112
Beacon is turned off
Port tracked with interface fc2/2 (down)
Port tracked with interface san-port-channel 1 vsan 2 (down)
5 minutes input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
...
The following example shows how to display tracked port configuration for a SAN port channel:
switch# show interface san-port-channel 1
port-channel 1 is down (No operational members)
Hardware is Fibre Channel
Port WWN is 24:01:00:05:30:00:0d:de
Admin port mode is auto, trunk mode is on
Port vsan is 2
Linked to 1 port(s)
Port linked to interface fc2/1
...
The following example shows how to display the port track mode:
switch# show interface fc 2/4
fc2/4 is up
Hardware is Fibre Channel, FCOT is short wave laser
...
Transmit B2B Credit is 64
Receive B2B Credit is 16
Receive data field Size is 2112
Beacon is turned off
Port track mode is force_shut <-- this port remains shut even if the tracked port is back up
Default Port Tracking Settings
The following table lists the default settings for port tracking parameters.
|
Parameters |
Default |
|---|---|
|
Port tracking |
Disabled |
|
Operational binding |
Enabled along with port tracking |
 Feedback
Feedback