- Preface
- Product Overview
- Command-line Interfaces
- Configuring the Switch for the First Time
- Administering the Switch
- Configuring the Cisco IOS In Service Software Upgrade Process
- Configuring Interfaces
- Checking Port Status and Connectivity
- Configuring Supervisor Engine Redundancy Using RPR and SSO
- Configuring Cisco NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- Environmental Monitoring and Power Management
- Configuring Power over Ethernet
- Configuring the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch with Cisco Network Assistant
- Configuring VLANs, VTP, and VMPS
- Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface
- Configuring Layer 2 Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring SmartPort Macros
- Configuring STP and MST
- Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Optional STP Features
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and Filtering
- Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
- Configuring 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring LLDP and LLDP-MED
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring Unidirectional Ethernet
- Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Cisco Express Forwarding
- Configuring Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding
- Configuring IP Multicast
- Configuring ANCP Client
- Configuring Policy-Based Routing
- Configuring VRF-lite
- Configuring Quality of Service
- Configuring Voice Interfaces
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Configuring 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring PPPoE Intermediate Agent
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Control Plane Policing
- Configuring DHCP Snooping, IP Source Guard, and IPSG for Static Hosts
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Port Unicast and Multicast Flood Blocking
- Configuring Storm Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring NetFlow
- Configuring Ethernet CFM and OAM
- Configuring Y.1731 (AIS and RDI)
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring RMON
- Performing Diagnostics
- Configuring WCCP Version 2 Services
- ROM Monitor
- Configuring MIB Support
- Acronyms
- Index
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface
This chapter discusses the IP Unnumbered Interface feature, which allows you to enable IP processing on an interface without assigning an explicit IP address.
This chapter contains these sections:
•![]() Overview of IP Unnumbered Support
Overview of IP Unnumbered Support
•![]() Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support with DHCP Server
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support with DHCP Server
•![]() Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support with Connected Host Polling
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support with Connected Host Polling
•![]() Displaying IP Unnumbered Interface Settings
Displaying IP Unnumbered Interface Settings
•![]() Troubleshooting IP Unnumbered
Troubleshooting IP Unnumbered

Note ![]() For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Command Reference and related publications at this location:
For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Command Reference and related publications at this location:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122sr/cr/index.htm
Related Documents
Overview of IP Unnumbered Support
Before you configure VLANs and LAN interfaces with IP unnumbered interfaces, you should understand the following concepts:
•![]() IP Unnumbered Interface Support with DHCP Server and Relay Agent
IP Unnumbered Interface Support with DHCP Server and Relay Agent
•![]() IP Unnumbered with Connected Host Polling
IP Unnumbered with Connected Host Polling
IP Unnumbered Interface Support with DHCP Server and Relay Agent
The IP unnumbered interface configuration allows you to enable IP processing on an interface without assigning it an explicit IP address. The IP unnumbered interface can "borrow" the IP address from another interface that is already configured on the Catalyst 4500 series switch, thereby conserving network and address space. When employed with the DHCP server/relay agent, this feature allows a host address assigned by the DHCP server to be learned dynamically at the DHCP relay agent.
Figure 14-1 shows a sample network topology implementing the IP Unnumbered Interface feature. In this topology, IP routes are dynamically established by the aggregation switch when the DHCP server assigns IP addresses to the hosts.
Figure 14-1
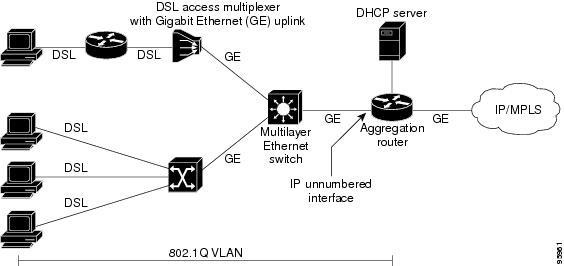
Sample Network Topology Using the VLANs over IP Unnumbered Interfaces Feature
DHCP Option 82
DHCP provides a framework for passing configuration information to hosts on a TCP/IP network. Configuration parameters and other control information are carried in tagged data items that are stored in the options field of the DHCP message. The data items are also called options. Option 82 is organized as a single DHCP option that contains information known by the relay agent.
The IP Unnumbered Interface feature communicates information to the DHCP server using a suboption of the DHCP relay agent information option called agent remote ID. The information sent in the agent remote ID includes an IP address identifying the relay agent and information about the interface and the connection over which the DHCP request entered. The DHCP server can use this information to make IP address assignments and security policy decisions.
Figure 14-2 shows the agent remote ID suboption format that is used with the IP Unnumbered Interfaces feature.
Figure 14-2 Format of the Agent Remote ID Suboption
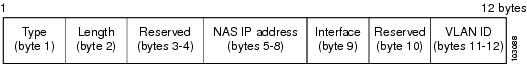
Table 14-1 describes the agent remote ID suboption fields displayed in Figure 14-2.
IP Unnumbered with Connected Host Polling

Note ![]() This feature option is applicable to LAN and VLAN interfaces only.
This feature option is applicable to LAN and VLAN interfaces only.
In some cases, the host IP address is assigned statically. The IP Unnumbered Interfaces feature can learn the static host IP address dynamically.
Limitations and Restrictions
Limitations and restrictions include:
•![]() For IP unnumbered interfaces, the following features are not supported:
For IP unnumbered interfaces, the following features are not supported:
–![]() Dynamic routing protocols
Dynamic routing protocols
–![]() HSRP/VRRP
HSRP/VRRP
–![]() Static arp
Static arp
–![]() Unnumbered interface and Numbered interface in different VRFs
Unnumbered interface and Numbered interface in different VRFs
•![]() The option to add dhcp host routes as connected routes is available in Cisco IOS. When using connected mode, however, the clear ip route * command deletes the dhcp host connected routes permanently.
The option to add dhcp host routes as connected routes is available in Cisco IOS. When using connected mode, however, the clear ip route * command deletes the dhcp host connected routes permanently.
Workarounds:
–![]() For a layer 3 interface (SVI), enter shut then no shut.
For a layer 3 interface (SVI), enter shut then no shut.
–![]() To enable IP unnumbered to use static routes, enter the ip dhcp route static command.
To enable IP unnumbered to use static routes, enter the ip dhcp route static command.
•![]() IP Redirect is not sent by an interface configured with IP unnumbered. (CSCse75660).
IP Redirect is not sent by an interface configured with IP unnumbered. (CSCse75660).
•![]() An IP unnumbered interface is unable to forward multicast source packets. (CSCse61766)
An IP unnumbered interface is unable to forward multicast source packets. (CSCse61766)
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support with DHCP Server

Note ![]() DHCP must be configured and operational.
DHCP must be configured and operational.
This section contains the following procedures:
•![]() Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support on LAN and VLAN Interfaces
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support on LAN and VLAN Interfaces
•![]() Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support on a Range of Ethernet VLANs
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support on a Range of Ethernet VLANs
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support on LAN and VLAN Interfaces
To configure IP unnumbered interface support on a single LAN or VLAN interface, perform this task.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() interface [fastethernet | gigabitethernet | tengigabitethernet | vlan vlan} port-channel | loopback]
interface [fastethernet | gigabitethernet | tengigabitethernet | vlan vlan} port-channel | loopback]
4. ![]() ip unnumbered type number
ip unnumbered type number
DETAILED STEPS
In the following example, Ethernet VLAN 10 is configured as an IP unnumbered interfaces:
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip unnumbered Lookback 0
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support on a Range of Ethernet VLANs
To configure IP unnumbered interface support on a range of Ethernet VLAN interfaces, perform this task.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() interface range {{fastethernet | gigabitethernet | vlan vlan} slot/interface {fastethernet | gigabitethernet | vlan vlan} slot/interface macro macro-name}
interface range {{fastethernet | gigabitethernet | vlan vlan} slot/interface {fastethernet | gigabitethernet | vlan vlan} slot/interface macro macro-name}
4. ![]() ip unnumbered type number
ip unnumbered type number
DETAILED STEPS
In the following example, Vlan in the range from 1 to 10 are configured as IP unnumbered interfaces, sharing ip address of fastethernet 3/1:
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface range vlan 1 - 10
Switch(config-if)# ip unnumbered fastethernet 3/1
Switch(config-if)# exit
Switch(config)# end
Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface Support
with Connected Host Polling
To configure IP unnumbered interface support with connected host polling, perform this task:
The following example shows how to enable IP processing and connected host polling on Fast Ethernet interface 6/2. It also shows how to set the global backlog queue to 2000 and the maximum number of arp requests to 500:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastEthernet 6/2
Switch(config-if)# no switchport
Switch(config-if)# ip unnumbered loopback 0 poll
Warning: dynamic routing protocols will not work on non-point-to-point interfaces with IP unnumbered configured.
Switch(config-if)# exit
Switch(config)# ip arp poll queue 2000
Switch(config)# ip arp poll rate 500
Switch(config)# end
Displaying IP Unnumbered Interface Settings
Use the show ip interface [type number] unnumbered [detail] command to display status of an unnumbered interface with connected host polling for the switch.
To display status of an unnumbered interface, perform one or more of these tasks:
|
|
|
|---|---|
Switch# show ip interface [type number] |
Displays the status of unnumbered interface with connected host polling for the Catalyst 4500 series switch. |
The following example shows how to display the status of unnumbered interface with connected host polling:
Switch# show ip interface loopback 0 unnumbered detail
Number of unnumbered interfaces with polling: 1
Number of IP addresses processed for polling: 2
10.1.1.7
10.1.1.8
Number of IP addresses in queue for polling: 2(high water mark: 3)
10.1.1.17
10.1.1.18
To display key statistic for the backlog of unnumbered interface with connected host polling for the switch, use the show ip arp poll command.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Switch# show ip arp poll [detail] |
display key statistic for the backlog of unnumbered interface with connected host polling for the switch |
The following example shows how to display key statistic for the backlog of unnumbered interface with connected host polling:
Switch# show ip arp poll
Number of IP addresses processed for polling: 439
Number of IP addresses in queue for polling: 3 (high water mark: 0, max: 1000)
Number of requests dropped:
Queue was full: 0
Request was throttled by incomplete ARP: 0
Duplicate request was found in queue: 0
To clear the key statistic for the backlog of unnumbered interface, use the clear ip arp poll statistic command, as follows:
Switch# clear ip arp poll statistic
Switch# show ip arp poll
Number of IP addresses processed for polling: 0
Number of IP addresses in queue for polling: 0 (high water mark: 0, max: 1000)
Number of requests dropped:
Queue was full: 0
Request was throttled by incomplete ARP: 0
Duplicate request was found in queue: 0
Troubleshooting IP Unnumbered
To understand how to debug connect host polling, see the IOS documentation of the debug arp command on cisco.com.
When an IP unnumbered interface shares the IP address of a loopback interface whose prefix is advertised in an OSPF network, you must modify the loopback interface as a point to point interface. Otherwise, only the loopback interface host route will be advertised to an OSPF neighbor.
Switch(config)# int loopback 0
Switch(config-if)# ip address
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.0.0 Switch(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point Switch(config-if)# end
 Feedback
Feedback