- Overview
- Adding and Deleting Location Servers
- Synchronizing Location Servers with Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Cisco WCS
- Editing Location Server Properties
- Managing Location Server Users and Groups
- Configuring Event Notifications
- Location Planning and Verification
- Monitoring Location Servers and Site
- Performing Maintenance Operations
Overview
This chapter describes the role of the location appliance within the Cisco Unified Wireless Network and its overall functionality.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•![]() Location Appliance Functionality
Location Appliance Functionality
•![]() Configuration and Administration
Configuration and Administration
•![]() Location Server Synchronization
Location Server Synchronization
•![]() Location Planning and Verification
Location Planning and Verification
Location Appliance Functionality
The Cisco Wireless Location Appliance is a component of the Cisco Unified Wireless Network (CUWN).
The location appliance uses Cisco wireless LAN controllers and Cisco Aironet lightweight access points to simultaneously track the physical location of up to 2,500 802.11 wireless devices. For those areas requiring very high fidelity and deterministic location, chokepoint-based notifications are supported for Cisco Compatible Extensions Wi-Fi tags.
Figure 1-1 illustrates the relationship of the location appliance with other components of the CUWN.
Figure 1-1 Cisco Unified Wireless Network
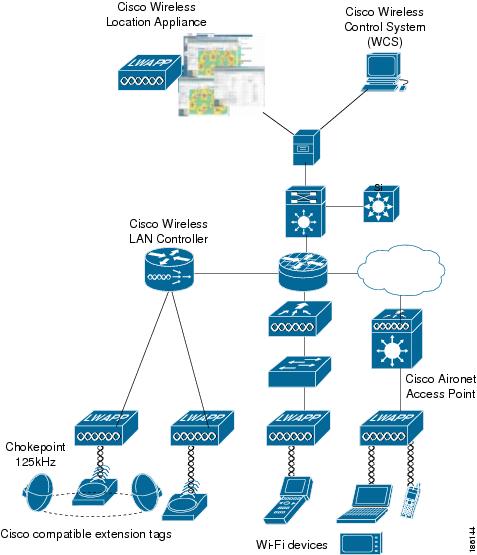
Viewing Location Data
The collected location data can be viewed in GUI format in the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), the centralized WLAN management platform.

Note ![]() However, before you can use Cisco WCS, initial configuration for the location server is required using a command-line (CLI) console session. Details are described in the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance Getting Started Guide at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6386/prod_installation_guides_list.html
However, before you can use Cisco WCS, initial configuration for the location server is required using a command-line (CLI) console session. Details are described in the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance Getting Started Guide at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6386/prod_installation_guides_list.html
After its installation and initial configuration is complete, the location server communicates with the Cisco wireless LAN controller to which it was assigned to collect operator-defined location data. You can then use the associated Cisco WCS server to communicate with each location server to transfer and display selected data.
You can configure location appliances to collect data for Cisco Wireless LAN Solution clients, rogue access points, rogue clients, mobile stations, and RFID asset tags at separate intervals. The interval frequency is a user-configurable setting.
Event Notification
Location servers provide the functionality for sending event notifications to registered listeners over the following transport mechanisms:
•![]() Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
•![]() Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) mail
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) mail
•![]() Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
•![]() SysLog
SysLog

Note ![]() WCS can act as a listener receiving event notifications over SNMP. Without event notification, Cisco WCS and third-party applications will need to periodically request location information from location servers. (Figure 1-2).
WCS can act as a listener receiving event notifications over SNMP. Without event notification, Cisco WCS and third-party applications will need to periodically request location information from location servers. (Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-2 Pull Communication Model
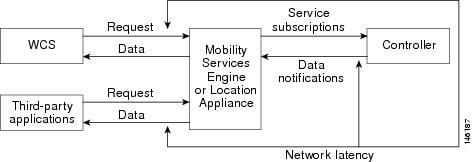
The pull communication model, however, is not suitable for applications that require more real-time updates to location information. For these applications, you can configure location servers to send event notifications (push) when certain conditions are met by the registered listeners.
Configuration and Administration
You can use Cisco WCS to perform different configuration and administrative tasks, including adding and removing location servers, configuring location server properties, and managing users and groups as summarized below.
Adding and Deleting Location Servers
You can use Cisco WCS to add and delete location servers within the network. Refer to Chapter 2, "Adding and Deleting Location Servers" for configuration details.
Editing Location Server Properties
You can use Cisco WCS to configure the following parameters on the location appliance. Refer to Chapter 4, "Configuring and Viewing System Properties" for configuration details.
•![]() General Properties: Enables you to assign a contact name, user name, password and HTTPS for the location appliance.
General Properties: Enables you to assign a contact name, user name, password and HTTPS for the location appliance.
•![]() Tracking Parameters: Enables you define which element locations you want to actively track (client stations, active asset tags; and rogue clients and access points), set limits on how many of a specific element you want to track, and disable tracking and reporting of ad hoc rogue clients and access points.
Tracking Parameters: Enables you define which element locations you want to actively track (client stations, active asset tags; and rogue clients and access points), set limits on how many of a specific element you want to track, and disable tracking and reporting of ad hoc rogue clients and access points.
•![]() Filtering Parameters: Enables you to define filters to exclude probing clients and elements based on their MAC addresses.
Filtering Parameters: Enables you to define filters to exclude probing clients and elements based on their MAC addresses.
–![]() Probing clients are clients that are associated to another controller but whose probing activity causes them to be seen by another controller and counted as an element by the "probed" controller as well as its primary controller.
Probing clients are clients that are associated to another controller but whose probing activity causes them to be seen by another controller and counted as an element by the "probed" controller as well as its primary controller.
•![]() History Parameters: Enables you to specify how often the location appliance collects historical data on client station, rogue access point, and asset tags from controllers to manage the amount of data stored on the location appliance hard drive.
History Parameters: Enables you to specify how often the location appliance collects historical data on client station, rogue access point, and asset tags from controllers to manage the amount of data stored on the location appliance hard drive.
•![]() Advanced Parameters: Enables you to set the number of days events are kept, set session time out values, set an absent data interval cleanup interval and enable or disable Advanced Debug.
Advanced Parameters: Enables you to set the number of days events are kept, set session time out values, set an absent data interval cleanup interval and enable or disable Advanced Debug.
•![]() Location Parameters: Enables you to specify whether the location server retains its calculation times and how soon the location server deletes its collected RSSI measurement times. It also enables you to apply varying smoothing rates to manage location movement of an element.
Location Parameters: Enables you to specify whether the location server retains its calculation times and how soon the location server deletes its collected RSSI measurement times. It also enables you to apply varying smoothing rates to manage location movement of an element.
•![]() NMSP Parameters: Enables you to modify Network Mobility Services Protocol (NMSP) parameters such as echo and neighbor dead intervals as well as response and retransmit periods. NMSP is the protocol that manages communication between the location server and the controller. Transport of telemetry, emergency, and chokepoint information between the location server and the controller is managed by this protocol.
NMSP Parameters: Enables you to modify Network Mobility Services Protocol (NMSP) parameters such as echo and neighbor dead intervals as well as response and retransmit periods. NMSP is the protocol that manages communication between the location server and the controller. Transport of telemetry, emergency, and chokepoint information between the location server and the controller is managed by this protocol.
Managing Location Server Users and Groups
You can use Cisco WCS to add, delete, and edit user session and user group parameters as well as add and delete host access records. Refer to Chapter 5, "Managing Location Server Users and Groups" for configuration details.
Location Server Synchronization
To maintain accurate location information, you can use Cisco WCS to configure location servers so that they are synchronized with network design, event group, and controller elements. Cisco WCS provides you with two ways to synchronize these elements and locations servers: manual and automatic (auto-sync). Additionally, you need to set the time zone for the associated controller to ensure continued synchronization. Refer to Chapter 3, "Synchronizing Location Servers with Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Cisco WCS"for specifics.
Location Planning and Verification
To plan and optimize access point deployment, you can use Cisco WCS to use either apply location readiness or calibration to examine location quality. Additionally, you can analyze the location accuracy of non-rogue and rogue clients and asset tags using testpoints on an area or floor map; and, use chokepoints to enhance location accuracy for tags.
To further refine location calculation, you can define those areas which should be included in location calculations (inclusion regions) and those areas that should not be included (exclusion regions). Rail areas which represent conveyors within a building can also be defined. Refer to Chapter 7, "Location Planning and Verification" for specifics.
Monitoring Capability
You can use Cisco WCS to monitor alarms, events and logs generated by location servers. You can also monitor the status of location servers, clients, and tagged asset status. Additionally, you can generate a location server utilization report to determine CPU and memory utilization as well as counts for clients, tags, and rogue elements (access points and clients). Refer to Chapter 8, "Monitoring Location Servers and Site"for specifics.
Maintenance Operations
You can use Cisco WCS to import and export asset location information, recover a password, back up the location server to a predefined FTP folder on any Cisco WCS server at defined intervals, and restore the location server data from that Cisco WCS Server. Other location server maintenance operations that you can perform include downloading new application code to all associated location server from any Cisco WCS server, a defragment the Cisco WCS database, restarting location servers, shutting down location servers, and clearing location server configurations. Refer to Chapter 9, "Performing Maintenance Operations" for specifics.
System Compatibility

Note ![]() Refer to the location appliance release notes for the latest system (controller, WCS, location appliance) compatibility information, feature support and operational notes for your current release at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6386/prod_release_notes_list.html
Refer to the location appliance release notes for the latest system (controller, WCS, location appliance) compatibility information, feature support and operational notes for your current release at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6386/prod_release_notes_list.html
Backwards Compatibility of Location Server Software
Location server software is backwards compatible with the previous two location server releases. Therefore, you can only upgrade two releases forward. For example, you can directly upgrade from release 5.1 to 6.0 but you cannot directly upgrade to release 6.0 from releases 1.1, 1.2, 2.0, 2.1, 3.0, 3.1 or 4.0.

Note ![]() There is no release 3.2 or 5.0 for location appliances.
There is no release 3.2 or 5.0 for location appliances.
 Feedback
Feedback