BUM Ingress Replication for EVPN E-LAN
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
BUM Ingress Replication for EVPN E-LAN |
Release 24.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700) (select variants only*) * The BUM ingress replication functionality is now extended to the Cisco 8712-MOD-M routers. |
|
BUM Ingress Replication for EVPN E-LAN |
Release 24.3.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200, 8700); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100]) (select variants only*) * The BUM ingress replication functionality is now extended to:
|
|
BUM Ingress Replication for EVPN E-LAN |
Release 24.2.11 |
Introduced in this release on: Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100]) (select variants only*) * The BUM ingress replication functionality is now extended to routers with the 88-LC1-36EH line cards. |
|
BUM Ingress Replication for EVPN E-LAN |
Release 7.11.1 |
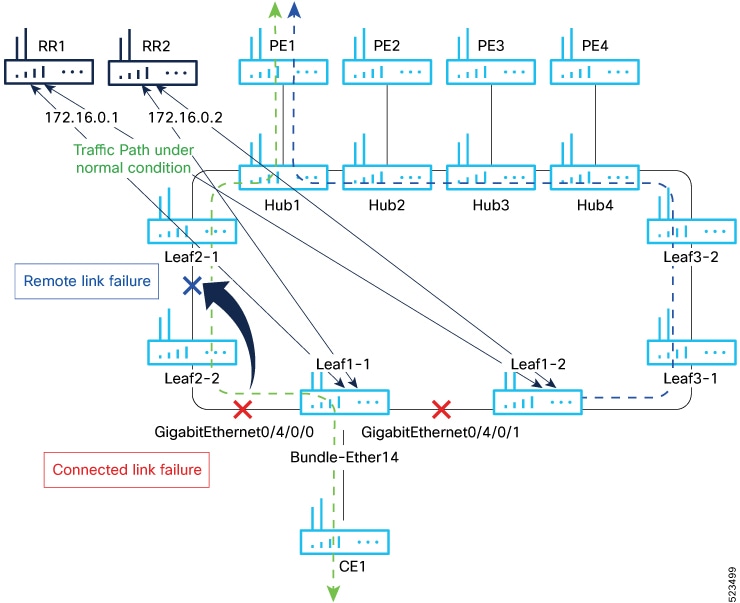
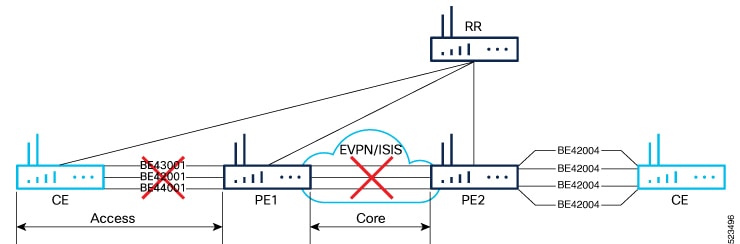
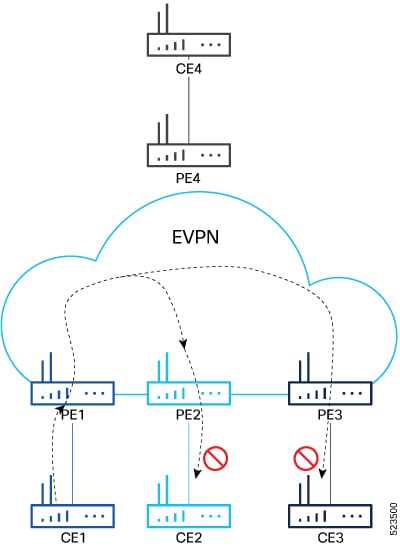
You can optimize Broadcast, Unknown Unicast, and Multicast (BUM) traffic by ensuring that traffic that a device receives is replicated and forwarded to only those CE devices in an EVPN network, if and when they require it. This reduction in the unnecessary forwarding of BUM traffic prevents the flooding of BUM traffic to all devices on the EVPN network. This feature is supported only on Q200-based line cards. This feature is enabled by default. |
EVPN BUM ingress replication handles the forwarding of BUM traffic within the network. When the router receives BUM traffic from a particular source, it replicates and forwards that traffic to all the relevant destinations. EVPN BUM ingress replication involves replicating the BUM traffic at the ingress (source) device and forwarding it to the appropriate egress (destination) devices.
The EVPN protocol uses MAC advertisement routes and control plane signaling to enable routers to selectively forward traffic to the intended recipient devices, preventing flooding the entire EVPN network.
Here's How it Works
-
The ingress router learns MAC addresses associated with BUM traffic and also gathers information about multicast group membership for multicast traffic.
-
Instead of flooding the BUM traffic across all ports in the EVPN, the ingress router replicates the traffic to the specific EVPN instances or Virtual Routing and Forwarding instances (VRFs) where it is needed. This ensures that BUM traffic is forwarded solely to the appropriate destinations.
-
BGP signals and distributes MAC addresses and multicast information to other routers in the EVPN network. Ingress router replicates and transmits the BUM traffic to the designated locations.
Feature Highlights
-
EVPN BUM ingress replication optimizes resource allocation by forwarding BUM traffic to necessary EVPN instances or VRFs, minimizing traffic flooding, reducing congestion, and preserving bandwidth. Thereby, reducing the overhead and potential performance issues within a broadcast domain.
-
Effective BUM traffic management is vital for sustaining network scalability. EVPN BUM ingress replication guarantees directed BUM traffic distribution, supporting network scaling without overwhelming broadcast or multicast traffic.
-
EVPN BUM ingress replication improves network security by selectively duplicating BUM traffic to the designated recipients, thus limiting sensitive traffic exposure to unintended devices and unauthorized access risks.
-
In traditional Ethernet networks, broadcast storms occur when broadcast traffic is flooded throughout the network. EVPN BUM ingress replication reduces this risk by forwarding traffic only to the intended devices, preventing broadcast storms and network disruptions.



 Feedback
Feedback