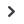6
Cybersecurity in ASEAN: An Urgent Call to Action
State-sponsored cyberattacks, such as those from North Korea, are another threat. This
combination of criminal and state-sponsored threats increases ASEAN’s risk profile, creating
obstacles for foreign investment and hampering the growth of the digital economy.
1.2 Policy preparedness is still nascent with a lack of institutional
oversight and limited funding to fortify digital economies
The region’s cyber resilience is low, particularly around policy, governance, and cybersecurity
capabilities. The absence of a unifying regional governance framework makes it difficult
to collaborate and share intelligence within and across countries. Businesses have also
underestimated the value-at-risk, resulting in a lack of adequate spending on cybersecurity.
1.2.1 Varying levels of cyber readiness, with some countries lacking a strategicmindset
about cybersecurity policy andgovernance
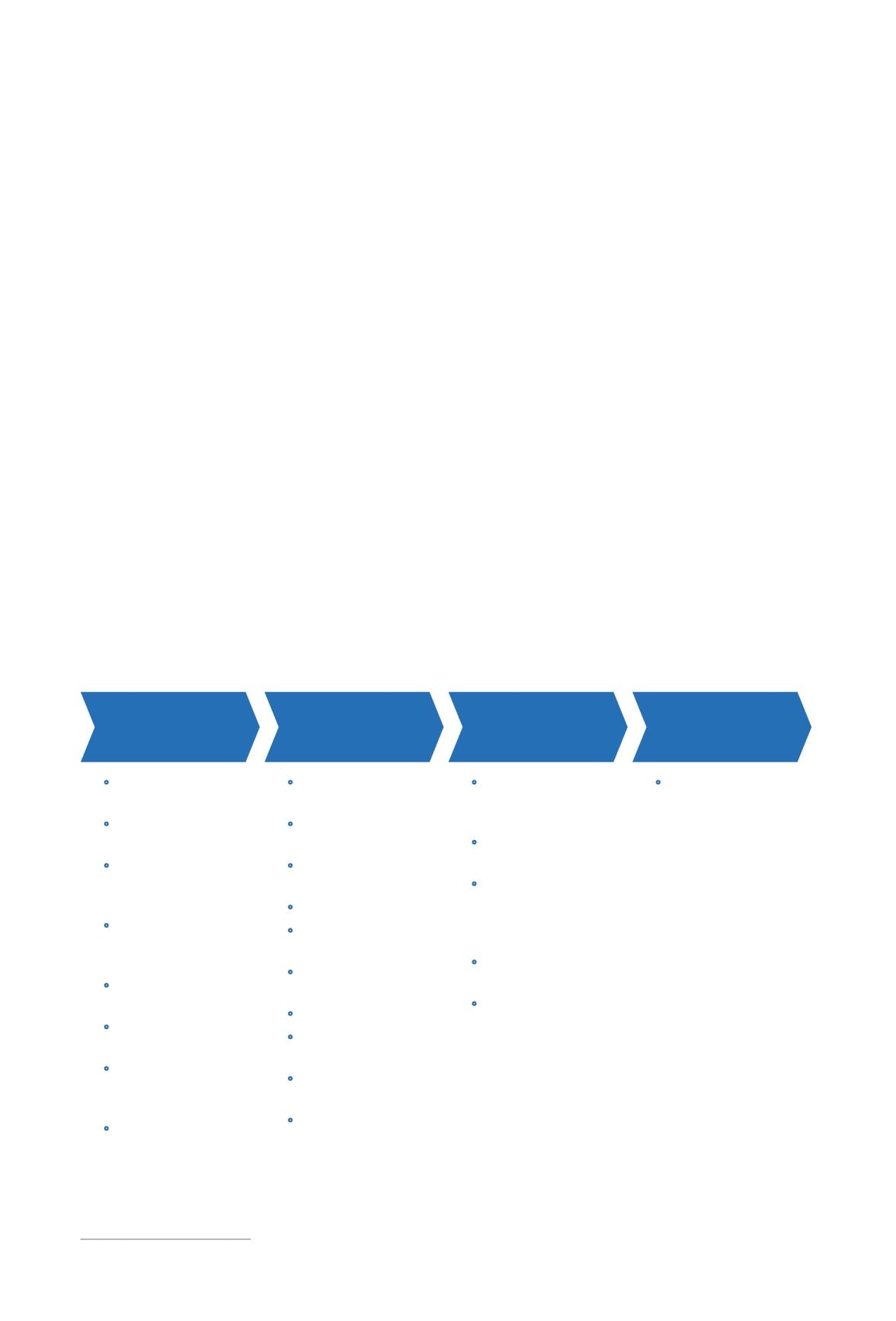
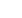
The Good Practice Guide from the European Network Information Security Agency (ENISA) cites
four steps in defining and implementing a sound national cybersecurity strategy (see figure 4).
A look at the regional cybersecurity policy landscape reveals varying levels of cyber readiness,
particularly around strategy definition and implementation, legislation, and governance (see
figure 5 on page 7).
9
See the appendix for more about the current situation.
Sources: European Union Agency for Network and Information Security; A.T. Kearney analysis
Figure
Four-phased approach to national cybersecurity strategy development
•
Deine the vision,
scope, and objectives
•
Follow a risk
assessment approach
•
Deine and identify
crucial information
infrastructure
•
Take stock of existing
policies, regulations,
and capabilities
•
Set a clear
governance structure
•
Identify and
engage stakeholders
•
Establish trusted
information sharing
mechanisms
•
Develop national
cyber-contingency plans
•
Organize cybersecurity
exercises
•
Establish baseline
security measures
•
Establish incident
reporting mechanisms
•
Raise user awareness
•
Strengthen training and
educational programs
•
Establish an incident
response capability
•
Address cybercrime
•
Engage in international
cooperation
•
Establish public–private
partnerships
•
Provide incentives for the
private sector to invest
in security measures
•
Deine the evaluation
approach, including
objectives and frequency
•
Identify an
independent entity
•
Adopt a quantitative
and qualitative approach
with emphasis on impact
and results
•
Create a data
collection scheme
•
Prepare an
evaluation approach
•
Continuously review
and update the strategy
Develop the
strategy
1
Execute the
strategy
2
Evaluate the
strategy
3
Maintain the
strategy
4
9
Based on available information in the public domain