- Preface
- Introduction to Cisco vWAAS
- Configuring Cisco vWAAS and Viewing vWAAS Components
- Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ISR-WAAS
- Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi
- Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V
- Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM and KVM CentOS
- Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ENCS 5400-W Series
- Cisco vWAAS on Cisco CSP 5000-W Series
- Cisco vWAAS with Cisco Enterprise NFVIS
- Cisco vWAAS with Akamai Connect
- Cisco vWAAS in Cloud Computing Systems
- Troubleshooting Cisco vWAAS
- About Cisco vWAAS
- Cisco vWAAS and WAAS Interoperability
- Cisco vWAAS and vCM Model Profiles
- DRE Disk, Object Cache, and Akamai Connect Cache Capacity
- vWAAS Resizing for WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later
Introduction to Cisco vWAAS
This chapter provides an overview of the Cisco Virtual Wide Area Applications Services (vWAAS) solution and describes the main features that enable Cisco vWAAS to overcome the most common challenges in transporting data over a wide area network.
This chapter contains the following sections:
- About Cisco vWAAS
- Cisco vWAAS and WAAS Interoperability
- Cisco vWAAS and vCM Model Profiles
- DRE Disk, Object Cache, and Akamai Connect Cache Capacity
- vWAAS Resizing for WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later
- OVA Package Files for vWAAS and vCM Models
- Cisco Hardware Platforms Supported for vWAAS
- Hypervisors Supported for Cisco vWAAS and vCM
- Hypervisor OVA Packages for vWAAS
- Cloud Platforms Supported for vWAAS
About Cisco vWAAS
Cisco Virtual WAAS (vWAAS) is a virtual appliance—for both enterprises and service providers—that accelerates business applications delivered from private and virtual private cloud infrastructure. Cisco vWAAS enables you to rapidly create WAN optimization services with minimal network configuration or disruption. Cisco vWAAS can be deployed in the physical data center and in private clouds and in virtual private clouds offered by service providers.
Cisco vWAAS service is associated with application server virtual machines as they are instantiated or moved. This approach helps enable cloud providers to offer rapid delivery of WAN optimization services with little network configuration or disruption in cloud-based environments.
Cisco vWAAS enables migration of business applications to the cloud, reducing the negative effect on performance of cloud-based application delivery to end-users. It enables service providers to offer an excellent application experience over the WAN as a value-added service in their catalogs of cloud services.
ISR-WAAS is the specific implementation of vWAAS running in a Cisco IOS-XE Software container on a Cisco ISR 4000 Series router (ISR-4321, ISR-4331, ISR-4351, ISR-4431, ISR-4451, ISR-4461). In this context, “container” refers to the hypervisor that runs virtualized applications on a Cisco ISR 4000 Series router.

Note![]() ISR-4461 is supported for vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1b and later.
ISR-4461 is supported for vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1b and later.
Table 1-1 shows the hypervisors supported for Cisco vWAAS. For more information on each of these hypervisors, see Hypervisors Supported for Cisco vWAAS and vCM in this chapter, and in the chapters listed in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 Hypervisors Supported for Cisco vWAAS
|
|
|
|---|---|
Chapter 3, “Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ISR-WAAS” |
|
Chapter 4, “Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi” |
|
Chapter 5, “Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V” |
|
Chapter 6, “Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM and KVM CentOS” |
|
Chapter 6, “Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM and KVM CentOS” |
|
Chapter 8, “Cisco vWAAS with Cisco Enterprise NFVIS” |
Cisco vWAAS supports WAN optimization in a cloud environment where physical WAE devices cannot usually be deployed. Virtualization also provides various benefits like elasticity, ease of maintenance, and a reduction of branch office and data center footprint.
The following hardware and cloud platforms are supported for Cisco vWAAS. For more information on each of these supported platforms, see Cisco Hardware Platforms Supported for vWAAS.
- Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS)
- Cisco UCS E-Series Servers
- Cisco UCS E-Series Network Compute Engines (NCEs)
- Cisco ISR-4000 Series
- Cisco ENCS 5400 Series
- Microsoft Azure Cloud
For details on the interoperability of the hypervisors and platforms supported for vWAAS, see Table 1-12.
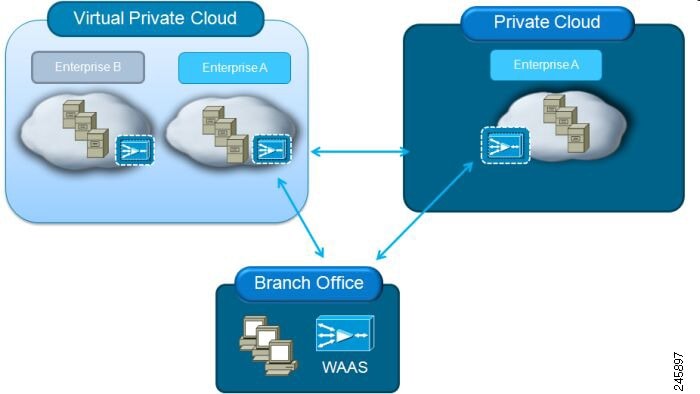
As shown in Figure 1-1, you can enable vWAAS at the branch and/or the data center:
- At the branch—with Cisco ENCS 5400 Series, Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) E-Series servers and E-Series Network Compute Engines (NCEs), on either the Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) or Cisco ISR G2 branch router.
- At the data center—with a Cisco UCS server.
vWAAS supports on-demand provisioning and teardown, which reduces the branch office and data center footprint. Cisco vWAAS software follows the VMware ESXi standard as the preferred platform to deploy data center applications and services.
Figure 1-1 vWAAS in Virtual Private Cloud at WAN Edge, in Branch Office and Data Center
Benefits of Cisco vWAAS
The following are some of the benefits of deploying Cisco vWAAS on your system:
- On-demand orchestration of WAN optimization
- Fault tolerance with virtual machine (VM) mobility awareness
- Lower operating expenses for customers who are migrating their applications to the cloud
- Private and virtual private cloud environments:
–![]() Use vWAAS to create value-added WAN optimization services on a per-application basis, for optimized delivery to remote branch-office users.
Use vWAAS to create value-added WAN optimization services on a per-application basis, for optimized delivery to remote branch-office users.
–![]() Associate vWAAS services with application server virtual machines as they are moved in response to dynamic load demand in the cloud, to offer rapid delivery of WAN optimization services, with minimal network configuration or disruption.
Associate vWAAS services with application server virtual machines as they are moved in response to dynamic load demand in the cloud, to offer rapid delivery of WAN optimization services, with minimal network configuration or disruption.
–![]() Deploy vWAAS in public clouds, with the Cisco Nexus 1000V Series, to obtain benefits similar to benefits vWAAS produces in private cloud environments.
Deploy vWAAS in public clouds, with the Cisco Nexus 1000V Series, to obtain benefits similar to benefits vWAAS produces in private cloud environments.
Cisco vWAAS and WAAS Interoperability
Consider the following guidelines when using Cisco vWAAS with WAAS:
- For vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.1.x and later—The vWAAS and vCM devices require both virtual (network) interfaces to be present, but both need not be active. If only one virtual interface is active, the vWAAS and vCM devices will not be operational after power up
- Cisco WAAS Central Manager interoperability—In a mixed version Cisco WAAS network, the Central Manager must be running the highest version of the Cisco WAAS software, and associated Cisco WAAS devices must be running Version 5.1.x or later.
- Cisco WAAS system interoperability—Cisco WAAS Version 5.2.1 is not supported running in a mixed version Cisco WAAS network in which any Cisco WAAS device is running a software version earlier than Version 5.1.x. Directly upgrading a device from a version earlier than Version 5.5.3 to 5.2.1 is not supported.
Cisco vWAAS and vCM Model Profiles
This section contains the following topics:
- Cisco vWAAS Models: CPUs, Memory, and Disk Storage
- Cisco vWAAS-150000 for WAAS 6.4.1a
- VMware VMFS Block Size and vWAAS Disk Size
- Cisco vCM Models: Managed Nodes, vCPUs, Memory, and Disk Storage
Cisco vWAAS Models: CPUs, Memory, and Disk Storage
Table 1-2 shows the default number of vCPUs, memory capacity, and disk storage for each vWAAS model for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1 and earlier. Table 1-8 shows the resizing capability for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a and later.
Table 1-2 CPUs, Memory, and Disk Storage for vWAAS Models
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
For the vWAAS models noted below, follow these operating guidelines for CPU, memory, and disk storage:
- When using vWAAS-150 or vWAAS-200 with the KVM hypervisor, you must increase the default memory of 3 GB to 4 GB.
- When vWAAS-6000, 1300, 12000, or 50000 are used with Akamai Connect and when connections are more than 70% of TFO, response time will be on the higher side. Adding CPUs to these models when used with Akamai Connect may improve response time.
- Table 1-3 shows where to find more information on specific vWAAS models and their applications.
Table 1-3 For More Information on Specific vWAAS Models
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco vWAAS-150000 for WAAS 6.4.1a
Cisco vWAAS-150000, available for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a, supports 150,000 connections. Table 1-4 shows specifications for Cisco vWAAS-150000.
Consider the following operating guidelines for Cisco vWAAS-150000:
- Cisco vWAAS-150000 replaces Cisco WAVE-8541, which has end-of-sale (EOS) and end-of-life (EOL) dates. For more information on WAVE-8541 EOS/EOL dates, see the End-of-Sale and End-of-Life Announcement for the Cisco WAVE 294, 594, 694, 7541, 7571 and 8541.
- For vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.4.1a, the supported hypervisor for vWAAS-150000 is VMware ESXi Version 5.5 or later. For more information on vWAAS on the VMware ESXi hypervisor, see Chapter 4, “Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi” .
- Traffic interception methods used with vWAAS-150000 are AppNav, Policy-Based Routing (PBR), and Web Cache Communications Protocol (WCCP).
- Upgrading vWAAS-150000 to a version later than vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a is supported.
- Downgrading vWAAS-150000 to a version earlier than vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a is not supported.
Table 1-4 vWAAS-150000 Specifications
|
|
|
|---|---|
VMware ESXi Version 5.5 or later For more information on VMware ESXi, see Chapter 4, “Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi” . |
|
Cisco-WAAS-Unified-6.41a-b-6.ova For more information on Cisco unified OVA files, see Hypervisor-wise Unified OVA Package Format for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.x and Later. |
|
Cisco UCS C240 M4/M5 Rack Server 
Note For more information, the Cisco UCS C220 M5 Rack Server, see the Cisco UCS C240 M4 Data Sheet and the Cisco UCS C240 M5 Data Sheet. |
|
vWAAS-150000 for WAAS Version 6.4.1a supports the following traffict interception methods: WCCP, AppNav, and PBR. |
VMware VMFS Block Size and vWAAS Disk Size
Table 1-5 shows the VMware Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) block size and associated vWAAS maximum disk file size. For more information on VMware and vWAAS interoperability, see Table 1-12.
Table 1-5 VMware VMFS Block Size and vWAAS Maximum File Size
|
|
|
|---|---|

Note![]() For vWAAS models that have a disk size greater than 256 GB, a VMFS block size greater than 1 MB is required.
For vWAAS models that have a disk size greater than 256 GB, a VMFS block size greater than 1 MB is required.
Cisco vCM Models: Managed Nodes, vCPUs, Memory, and Disk Storage
Table 1-6 shows the number of managed nodes and disk storage for each vCM model, as well as the required and recommended number of vCPUs and the required and recommended memory capacity.

Note![]() Cisco vWAAS installation packages are configured with the minimal required amounts of CPU and memory resources to accommodate the various hypervisor setups. These minimal requirements are sufficient for initial setup and a limited number of nodes.
Cisco vWAAS installation packages are configured with the minimal required amounts of CPU and memory resources to accommodate the various hypervisor setups. These minimal requirements are sufficient for initial setup and a limited number of nodes.
However, as the number of managed devices on your system increases, the Central Manager service can experience intermittent restarts or flapping—device states when under resource shortage. To remedy this, please configure the recommended values for number of CPUs and memory shown in Table 1-6.
Table 1-6 vCM Models: Managed Nodes, vCPUs, Memory, and Disk Storage
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
DRE Disk, Object Cache, and Akamai Connect Cache Capacity
This section contains the following topics:
- Table 1-7 shows the DRE disk capacity, default object cache capacity, and default Akamai Connect Cache capacity by WAVE model.
- Table 1-8 shows the DRE disk capacity, default object cache capacity, and default Akamai Connect Cache capacity by vWAAS model.
- For information on default and resized DRE disk capacity, object cache capacity, and Akamai Connect Cache capacity by vWAAS model, see Table 1-9.
Table 1-7 DRE Disk, Default OC, and Default Akamai Connect Cache by WAVE Model
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
vWAAS Resizing for WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later
This section contains the following topics:
- About vWAAS Resizing
- Resizing Guidelines: Upgrading to WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later
- Resizing Guidelines: Installing WAAS 6.4.1a
- Resizing Guidelines by Hypervisor for WAAS 6.4.1b and Later
About vWAAS Resizing
vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a and later requires additional resources, so we highly recommend that you resize CPU and memory resources, as shown in Table 1-8, and resize DRE object cache and Akamai Connect Cache, as shown in Table 1-9.

For vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1b, you cannot deploy vWAAS-12000 or vWAAS-50000 in Microsoft Hyper-V with the original resources. For a successful deployment of vWAAS 12000 or vWAAS-50000 in Microsoft Hyper-V with original resources, do a new deployment with WAAS Version 6.4.1 or earlier, and then perform the bin upgrade to WAAS Version 6.4.1b.

Note![]() ISR-WAAS and vCM are not resized for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a.
ISR-WAAS and vCM are not resized for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1a.
Resizing vWAAS on the recommended platforms enables vWAAS to scale to optimized TCP connections for the associated device, and to reduce CPU and RAM utilization.

Note![]() For optimum performance, we recommend you use the SSD disk with the UCS models listed in Table 1-8.
For optimum performance, we recommend you use the SSD disk with the UCS models listed in Table 1-8.
Table 1-8 Resized vWAAS CPU and Memory Specifications for WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Table 1-9 shows the default and resized DRE disk capacity, object cache capacity, and Akamai Connect cache capacity, by vWAAS model.
Table 1-9 Default and Resized DRE, OC, and Akamai Connect Cache, by vWAAS Model
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Resizing Guidelines: Upgrading to WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later
Upgrading to WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later with Existing CPU and Memory
You can use the CLI or the Central Manager to upgrade to WAAS Version 6.4.1a, with existing CPU and memory:
Using the CLI to perform the upgrade with existing CPU and memory:
1.![]() During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, you will be prompted to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, you will be prompted to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
2.![]() You can continue the upgrade procedure and retain the existing vWAAS resources.
You can continue the upgrade procedure and retain the existing vWAAS resources.

Note![]() For vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1a only, after the upgrade there will be undersized-resource alarms for vCPU and memory for the vWAAS device. Use the show alarms command to display information undersized alarms for the vWAAS model.
For vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1a only, after the upgrade there will be undersized-resource alarms for vCPU and memory for the vWAAS device. Use the show alarms command to display information undersized alarms for the vWAAS model.
Using the Central Manager to perform the upgrade with existing CPU and memory:
1.![]() During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, there will be an informational note on the upgrade page, but there will not be a prompt to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, there will be an informational note on the upgrade page, but there will not be a prompt to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
2.![]() You can continue the upgrade procedure and retain the existing vWAAS resources.
You can continue the upgrade procedure and retain the existing vWAAS resources.

Note![]() For vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1a only, after the upgrade there will be undersized-resource alarms for vCPU and memory for the vWAAS device. Use the show alarms command to display information undersized alarms for the vWAAS model.
For vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1a only, after the upgrade there will be undersized-resource alarms for vCPU and memory for the vWAAS device. Use the show alarms command to display information undersized alarms for the vWAAS model.
Upgrading to WAAS Version 6.4.1a and Later with Resized CPU and Memory
You can use the CLI or the Central Manager to upgrade to WAAS Version 6.4.1a, with resized CPU and memory:
Using the CLI to perform the upgrade with resized CPU and memory:
1.![]() During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, you will be prompted to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, you will be prompted to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
2.![]() You can then cancel the upgrade procedure.
You can then cancel the upgrade procedure.
3.![]() After shutting down the vWAAS instance, manually increase the vCPU and memory, from the hypervisor, to meet your specifications.
After shutting down the vWAAS instance, manually increase the vCPU and memory, from the hypervisor, to meet your specifications.
- To change settings in VMware ESXi: Navigate to Edit Settings... > Hardware tab.
- To change settings in Microsoft Hyper-V: Navigate to Virtual Machine > Settings... > Hardware.
- To change settings in RHEL KVM/CentOS:
b.![]() Navigate to Virtual Machine > CPUs.
Navigate to Virtual Machine > CPUs.
c.![]() Navigate to Virtual Machine > Memory.
Navigate to Virtual Machine > Memory.
a.![]() Navigate to VM Life Cycle > Image Repository > Profiles and add another profile with: resized CPU, memory, and same disk size.
Navigate to VM Life Cycle > Image Repository > Profiles and add another profile with: resized CPU, memory, and same disk size.
b.![]() Navigate to VM Life Cycle > Deploy > VM Details and select the resized profile created.
Navigate to VM Life Cycle > Deploy > VM Details and select the resized profile created.

Note If you use the Route Manager Debugging (RMD) process with vBranch: To ensure that the RMD process will start successfully in vBranch deployment, you must manually connect both the interfaces before starting the vWAAS.
a.![]() Navigate to Deployments > Microsoft Template Overview > Custom Deployment,
Navigate to Deployments > Microsoft Template Overview > Custom Deployment,
b.![]() Navigate to Home > Virtual Machines > vWAAS Instance > Size.
Navigate to Home > Virtual Machines > vWAAS Instance > Size.
4.![]() Restart the upgrade procedure. With the resized vCPU and memory, the host should have sufficient resources for a successful upgrade.
Restart the upgrade procedure. With the resized vCPU and memory, the host should have sufficient resources for a successful upgrade.
5.![]() Resources will not change automatically in subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system change, manual intervention is required to change the resource.
Resources will not change automatically in subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system change, manual intervention is required to change the resource.
Using the Central Manager to perform the upgrade with resized CPU and memory:
1.![]() During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, there will be an informational note on the upgrade page, but there will not be a prompt to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.
During the upgrade, if the vCPU and memory resources are undersized, there will be an informational note on the upgrade page, but there will not be a prompt to resize these vWAAS parameters before the upgrade.

Note![]() You cannot cancel the upgrade procedure, in process, from the Central Manager.
You cannot cancel the upgrade procedure, in process, from the Central Manager.
2.![]() Resources will not change in subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system.
Resources will not change in subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system.
Resizing Guidelines: Installing WAAS 6.4.1a
New Installation with Existing CPU and Memory
1.![]() Install the vWAAS OVA with a WAAS version earlier than WAAS Version 6.4.1a, which, by default, will deploy with resized resource.
Install the vWAAS OVA with a WAAS version earlier than WAAS Version 6.4.1a, which, by default, will deploy with resized resource.
2.![]() Upgrade to WAAS Version 6.4.1a and retain existing CPU and memory resources.
Upgrade to WAAS Version 6.4.1a and retain existing CPU and memory resources.
3.![]() After installation is complete, there will be undersized-resource alarms for CPU and memory for the vWAAS device. You use the show alarms command to display information about undersized alarms for the vWAAS model.
After installation is complete, there will be undersized-resource alarms for CPU and memory for the vWAAS device. You use the show alarms command to display information about undersized alarms for the vWAAS model.
4.![]() After resources are upgraded, there will not be any automatic change in resources for subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system.
After resources are upgraded, there will not be any automatic change in resources for subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system.
New Installation with Resized CPU and Memory
1.![]() Install vWAAS OVA with version WAAS 6.4.1a.
Install vWAAS OVA with version WAAS 6.4.1a.
2.![]() The host should have sufficient resources of resized CPU and resized memory for a successful deployment.
The host should have sufficient resources of resized CPU and resized memory for a successful deployment.
3.![]() After resources are upgraded, there will not be any automatic change in resources for subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system.
After resources are upgraded, there will not be any automatic change in resources for subsequent upgrades/downgrades of the system.
Resizing Guidelines by Hypervisor for WAAS 6.4.1b and Later
Resizing for vWAAS on VMware ESXi
To resize CPU and memory for vWAAS on VMware ESXi, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the vSphere Client, choose Deploy OVF Template > Deployment Configuration (Figure 1-2).
From the vSphere Client, choose Deploy OVF Template > Deployment Configuration (Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-2 vSphere Client Deployment Configuration Screen
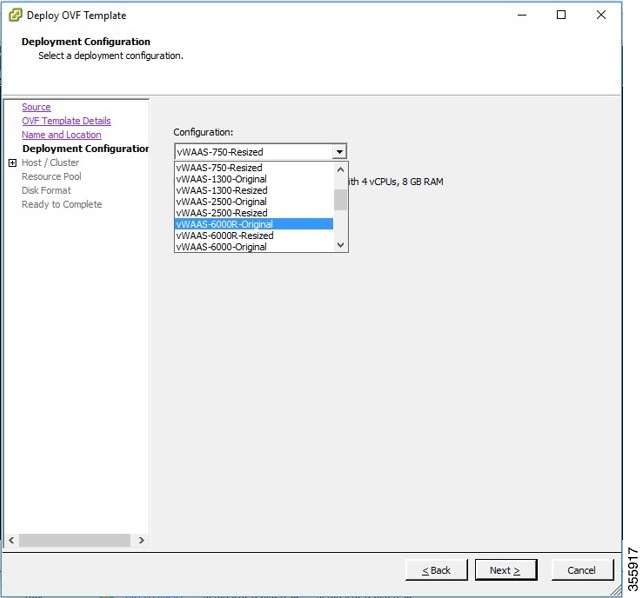
Step 2![]() At the Configuration drop-down list, choose the vWAAS model for this hypervisor (Figure 1-2).
At the Configuration drop-down list, choose the vWAAS model for this hypervisor (Figure 1-2).
For example, if you are choosing vWAAS-6000, you can choose vWAAS-6000-Original or vWAAS-6000-Resized.
Resizing for vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V
To resize CPU and memory for vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Login to the WAAS Installer for Microsoft Hyper-V, which displays a list of supported WAAS models (Figure 1-3).
Login to the WAAS Installer for Microsoft Hyper-V, which displays a list of supported WAAS models (Figure 1-3).
Figure 1-3 vWAAS and vCM Resources for vWAAS on Hyper-V
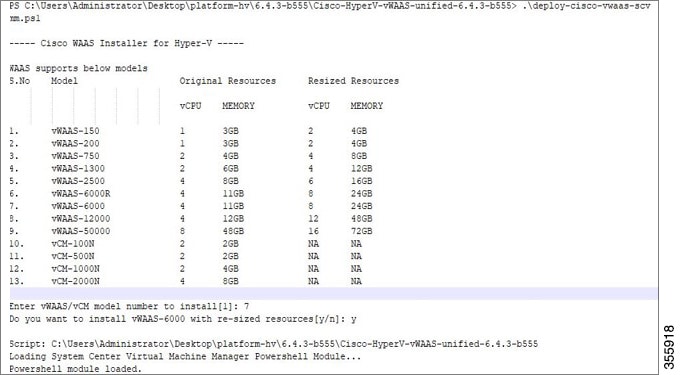
Step 2![]() At the Enter vWAAS/vCM model to install prompt, enter the line number for the model you want to install. For example, from the listing shown in Figure 1-3. entering 7 would select vWAAS-6000.
At the Enter vWAAS/vCM model to install prompt, enter the line number for the model you want to install. For example, from the listing shown in Figure 1-3. entering 7 would select vWAAS-6000.
Step 3![]() At the Do you want to install vWAAS-6000 with resized resources [y/n] prompt, enter Y to select resized resources.
At the Do you want to install vWAAS-6000 with resized resources [y/n] prompt, enter Y to select resized resources.
Step 4![]() After you select Y, the system displays the associated script, for example:
After you select Y, the system displays the associated script, for example:
Resizing for vWAAS on RHEL CentOS or SUSE Linux
To resize CPU and memory for vWAAS on RHEL CentOS or on SUSE Linux, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() At the root@localhost screen, enter the resizing launch script:
At the root@localhost screen, enter the resizing launch script:
Step 2![]() The system displays original and resized resources for each vWAAS model (Figure 1-4):
The system displays original and resized resources for each vWAAS model (Figure 1-4):
Figure 1-4 vWAAS and vCM Resources on CentOS or SUSE Linux
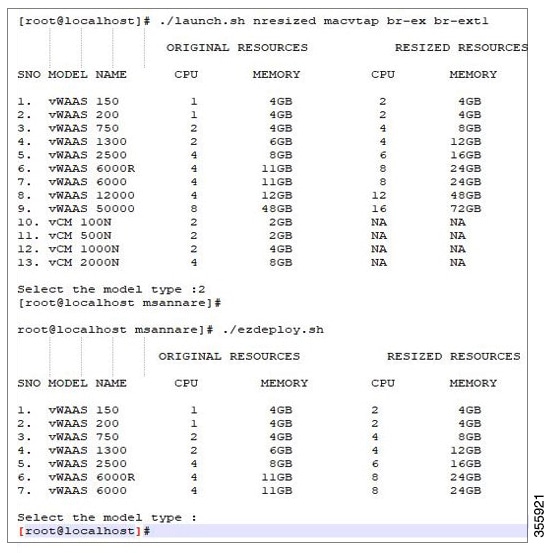
Step 3![]() At the Select the model type prompt, enter the line number of the model type for your system. For example, selecting 7 will select vWAAS-6000.
At the Select the model type prompt, enter the line number of the model type for your system. For example, selecting 7 will select vWAAS-6000.
The system displays the message:
Step 4![]() Launch the EzDeploy script:
Launch the EzDeploy script:
The EzDeploy script also displays both the original and resized resources as shown in Figure 1-4.
Step 5![]() The system deploys the selected model, with resized resources.
The system deploys the selected model, with resized resources.
Resizing for vWAAS on NFVIS
For resizing for vWAAS on NFVIS, install the vWAAS OVA with version WAAS 6.4.1b. Figure 1-5 shows the NFVIS Profiles listing for original and resized vWAAS resources.
Figure 1-5 vWAAS Profiles Listing on vWAAS on NFVIS
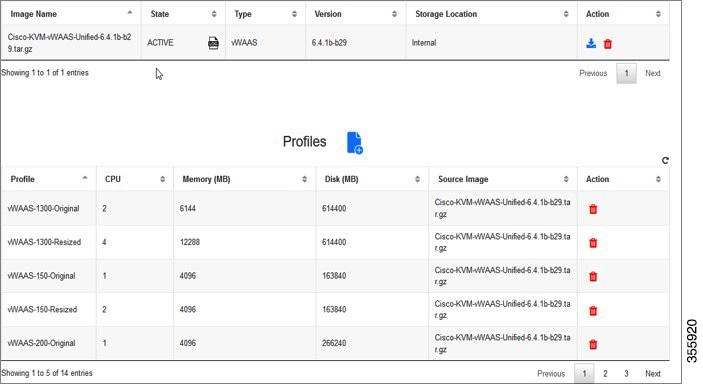
For information on resizing vWAAS on NFVIS, see the Cisco Enterprise Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure Configuration Guide.
OVA Package Files for vWAAS and vCM Models
Table 1-10 shows the OVA and NPE OVA file for each vWAAS model:
Table 1-10 OVA Package Files for vWAAS Models
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 1-11 shows the OVA and NPE OVA file for each vCM model (all models are available with WAAS version 4.3.1 and later, except as noted):
Table 1-11 OVA Package Files for vCM Models
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Cisco Hardware Platforms Supported for vWAAS
This section contains the following topics:
- Platforms Supported for vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
- Components for Deploying vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
- Components for Managing vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
- Cisco UCS E-Series Servers and NCEs
- Cisco ENCS 5400 Series
Platforms Supported for vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
For each hypervisor used with vWAAS, Table 1-12 shows the types of platforms supported for vWAAS, including minimum WAAS version, host platform, and disk type.

Note![]() ISR-4321 with IOS-XE 16.9.x is supported for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1b and later.
ISR-4321 with IOS-XE 16.9.x is supported for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1b and later.
Table 1-12 Platforms Supported for vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Components for Deploying vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
For each hypervisor used with vWAAS, Table 1-13 shows the components used to deploy vWAAS, including package format, deployment tool, pre-configuration tool (if needed), and network driver.
Table 1-13 Components for Deploying vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|

Note![]() Cisco Virtual Interface Cards (VICs) are not qualified for vWAAS.
Cisco Virtual Interface Cards (VICs) are not qualified for vWAAS.
Components for Managing vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
For each hypervisor used with vWAAS, Table 1-14 shows the components used to manage vWAAS, including vCM model, vWAAS model, number of instances supported, and traffic interception method used.
Table 1-14 Components for Managing vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cisco UCS E-Series Servers and NCEs
vWAAS and Cisco UCS E-Series Interoperability
Cisco UCS E-Series servers and UCS E-Series Network Compute Engines (NCEs) provide platforms for Cisco vWAAS and Cisco ISR routers. Table 1-15 shows the supported operating systems, Hypervisors, Cisco ISR routers, and minimum version of IOS-XE used.
Table 1-15 vWAAS and UCS E-Series Interoperability
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
vWAAS and Cisco UCS E-Series Memory Guidelines and Requirements
Table 1-16 shows memory and disk storage capacity for Cisco UCS E-Servers NCEs. When calculating memory requirements for your vWAAS system, include the following parameters:
- A minimum of 2 GB of memory is needed for VMware v5.0, v5.1, or v6.0.
- A minimum of 4 GB of memory is needed for VMware v5.5.
- You must also allocate memory overhead for vCPU memory. The amount is dependent on the number of vCPUs for your system: 1, 2, 4, or 8 vCPUs.

Note![]() For information on vCPUs, ESXi server datastore memory, and disk space by vWAAS model and vCM model, see Table 4-3 and Table 4-4 in Chapter 4, “Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi”.
For information on vCPUs, ESXi server datastore memory, and disk space by vWAAS model and vCM model, see Table 4-3 and Table 4-4 in Chapter 4, “Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi”.
Example1: A deployment of vWAAS-750 on the UCS-E140S, using VMware v6.0.
1.![]() UCS-E140S has a default value of 8 GB memory (which can be expanded to 48 GB).
UCS-E140S has a default value of 8 GB memory (which can be expanded to 48 GB).
2.![]() vWAAS-750 requires 6 GB memory + VMware v6.0 requires 2 GB memory = 6 GB memory, which is below the default memory capacity of the UCS-E140S.
vWAAS-750 requires 6 GB memory + VMware v6.0 requires 2 GB memory = 6 GB memory, which is below the default memory capacity of the UCS-E140S.
3.![]() You can deploy vWAAS-750 on the UCS-E140S without adding additional memory to the UCS-E140S DRAM.
You can deploy vWAAS-750 on the UCS-E140S without adding additional memory to the UCS-E140S DRAM.
Example1: A deployment of vWAAS-1300 on the UCS-E140S, using VMware v6.0.
1.![]() UCS-E140S has a default value of 8 GB DRAM, (which can be expanded to 48 GB).
UCS-E140S has a default value of 8 GB DRAM, (which can be expanded to 48 GB).
2.![]() vWAAS-1300 requires 6 GB memory + VMware v6.0 requires 2 GB DRAM = 8 GB memory, which equals the memory capacity of UCS-E140S.
vWAAS-1300 requires 6 GB memory + VMware v6.0 requires 2 GB DRAM = 8 GB memory, which equals the memory capacity of UCS-E140S.
3.![]() To deploy vWAAS-1300 on the UCS-E140S, you must add additional memory to the UCS-E140S memory.
To deploy vWAAS-1300 on the UCS-E140S, you must add additional memory to the UCS-E140S memory.

Note![]() For the vWAAS datastore, you can use either SAN storage or local storage on the ESXi server. NAS (Network-Attached Storage) storage should only be used in nonproduction scenarios (for test purposes, for example).
For the vWAAS datastore, you can use either SAN storage or local storage on the ESXi server. NAS (Network-Attached Storage) storage should only be used in nonproduction scenarios (for test purposes, for example).
Table 1-16 Memory and Disk Storage for Cisco UCS E-Servers NCEs
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Cisco ENCS 5400 Series
About the Cisco ENCS 5400 Series
The Cisco Enterprise Network Compute System (ENCS) 5400 Series is designed for the Cisco Enterprise Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) solution, and is available for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1 and later.
The ENCS 5400 Series—ENCS-5406/K9, 5408/K9, and 5412/K9—is an x86 hybrid platform for branch deployment and for hosting WAAS applications. This high-performance unit achieves this goal by providing the infrastructure to deploy virtualized network functions while at the same time acting as a server that addresses processing, workload, and storage challenges.
For more information on the Cisco ENCS 5400 series, see the Cisco 5400 Enterprise Network Compute System Data Sheet.
For information on vWAAS with NFVIS on the ENCS 5400 Series, see Chapter 7, “Cisco vWAAS with Cisco Enterprise NFVIS” .
ENCS 5400 Series Hardware Features and Specifications
Table 1-17 shows specifications that apply to all three ENCS 5400 series models. For views of the Cisco ENCS 5400 Series and further information, see the Cisco 5400 Enterprise Network Compute System Data Sheet.
Table 1-17 ENCS 5400 Series Features and Specifications
Hypervisors Supported for Cisco vWAAS and vCM
Here is an overview of hypervisors are supported for Cisco vWAAS and vCM.
ISR-WAAS is the specific implementation of vWAAS running in a Cisco IOS-XE Software container on a Cisco ISR 4000 Series router (ISR-4321, ISR-4331, ISR-4351, ISR-4431, ISR-4451, ISR-4461). In this context, “container” refers to the hypervisor that runs virtualized applications on a Cisco ISR 4000 Series router.

Note![]() ISR-4461 is supported for vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1b and later.
ISR-4461 is supported for vWAAS for WAAS 6.4.1b and later.
For more information, see Chapter 3, “Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ISR-WAAS” .
Cisco vWAAS for VMware ESXi provides cloud-based application delivery service over the WAN in ESX/ESXi-based environments. Cisco vWAAS on VMware vSphere ESXi is delivered an OVA file. The vSphere client takes the OVA file for a specified vWAAS model, and deploys an instance of that vWAAS model.
For more information, see Chapter 4, “Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi” .
Microsoft Hyper-V, available for vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.1.x and later, provides virtualization services through hypervisor-based emulations.
Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V extends Cisco networking benefits to Microsoft Windows Server Hyper-V deployments.
Microsoft HyperV, Chapter 5, “Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V” .
Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM (Red Hat Enterprise Linux Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a virtual WAAS appliance that runs on a RHEL KVM hypervisor. Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM extends the capabilities of ISR-WAAS and vWAAS running on the Cisco UCS E-Series Servers.
–![]() Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM is available for vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.2.1 and later,
Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM is available for vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.2.1 and later,
–![]() Cisco vWAAS on KVM on CentOS (Linux Community Enterprise Operating System) is available for vWAAS with WAAS version 6.2.3x and later.
Cisco vWAAS on KVM on CentOS (Linux Community Enterprise Operating System) is available for vWAAS with WAAS version 6.2.3x and later.

Note![]() Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM can also be deployed as a tar archive (tar.gz) to deploy Cisco vWAAS on Cisco Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure Software (NFVIS). The NFVIS portal is used to select the tar.gz file to deploy vWAAS.
Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM can also be deployed as a tar archive (tar.gz) to deploy Cisco vWAAS on Cisco Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure Software (NFVIS). The NFVIS portal is used to select the tar.gz file to deploy vWAAS.
For more information, see Chapter 6, “Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM and KVM CentOS” .
Cisco Enterprise NFV Infrastructure Software (NFVIS) offers flexibility and choice in deployment and platform options for the Cisco Enterprise NFV solution. By virtualizing and abstracting the network services from the underlying hardware, NFVIS allows virtual network functions (VNFs) to be managed independently and to be provisioned dynamically.
–![]() For vWAAS on WAAS Version 5.x to 6.2.x, Cisco NFVIS is available for vWAAS running on Cisco UCS E-Series Servers.
For vWAAS on WAAS Version 5.x to 6.2.x, Cisco NFVIS is available for vWAAS running on Cisco UCS E-Series Servers.
–![]() For vWAAS on WAAS Version 6.4.1 and later, Cisco NFVIS is available for vWAAS running on Cisco UCS E-Series Servers and the Cisco ENCS 5400 Series.
For vWAAS on WAAS Version 6.4.1 and later, Cisco NFVIS is available for vWAAS running on Cisco UCS E-Series Servers and the Cisco ENCS 5400 Series.
For more information, see Chapter 9, “Cisco vWAAS with Cisco Enterprise NFVIS” .
Hypervisor OVA Packages for vWAAS
This section contains the following topics:
- Hypervisor OVA Package Format for vWAAS for WAAS Versions 5.x to 6.2.x
- Hypervisor-wise Unified OVA Package Format for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.x and Later
Hypervisor OVA Package Format for vWAAS for WAAS Versions 5.x to 6.2.x
For vWAAS for WAAS Versions 5.x to 6.2.x, Cisco provides an OVA package for an NPE and non-NPE version for each vWAAS model connection profile.
For a listing of hypervisor-wise NPE and non-NPE OVA files for vWAAS or vCM, see the Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Download Software Page and select the WAAS software version used with your vWAAS instance.
Table 1-18 shows the file formats for hypervisors supported for vWAAS and vCM, for WAAS Version 5.x to 6.2.x.
Table 1-18 File Formats for OVA Packages for vWAAS and vCM for WAAS Version 5.x to 6.2.x
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
Hypervisor-wise Unified OVA Package Format for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.x and Later
For vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.4.x and later, Cisco provides a single unified OVA package, one each for the NPE and non-NPE version of the WAAS image for all the vWAAS and vCM models for that Hypervisor.
Each unified OVA package file provides an option to select a vWAAS or vCM model and other required parameters to launch vWAAS or vCM with WAAS in the required configuration.
Table 1-19 shows the unified OVA filename formats supported for hypervisors, appliances, vWAAS models, and vCM models.

Note![]() On VMware ESXi, the OVA deployment for WAAS Version 6.4.1 and later must be done only through VMware vCenter.
On VMware ESXi, the OVA deployment for WAAS Version 6.4.1 and later must be done only through VMware vCenter.
For a listing of hypervisor-wise NPE and non-NPE OVA files for vWAAS or vCM, see the Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) Download Software Page and select the WAAS software version for your vWAAS instance.
Table 1-19 Unified OVA Filename Format Supported for Hypervisors, Appliances, vWAAS Models, and vCM Models
Cloud Platforms Supported for vWAAS
Cisco vWAAS supports the following cloud computing platforms:
- Microsoft Azure—Used with vCM and vWAAS models supported on Microsoft Hyper-V. Cisco vWAAS in Azure is supported for vWAAS with WAAS Version 6.2.1x and later.
- OpenStack—Used with vCM and vWAAS models supported on KVM on CentOS, Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack is supported for vWAAS for WAAS Version 6.4.1b and later.
For more information, see Chapter 11, “Cisco vWAAS in Cloud Computing Systems”.
 Feedback
Feedback