- Preface
- Introduction to Cisco vWAAS
- Configuring Cisco vWAAS and Viewing vWAAS Components
- Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ISR-WAAS
- Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi
- Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V
- Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM, KVM on CentOS, and KVM in SUSE Linux
- Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ENCS 5400-W Series
- Cisco vWAAS on Cisco CSP 5000-W Series
- Cisco vWAAS with Cisco Enterprise NFVIS
- Cisco vWAAS with Akamai Connect
- Cisco vWAAS in Cloud Computing Systems
- Troubleshooting Cisco vWAAS
- Cisco vWAAS in Cloud Computing Systems
- Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
- Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
Cisco vWAAS in Cloud Computing Systems
This chapter describes the operation of Cisco vWAAS in the Microsoft Azure and OpenStack cloud computing systems.
Cisco vWAAS in Cloud Computing Systems
Cisco vWAAS is a cloud-ready WAN optimization solution that is fully interoperable with Cisco WAAS appliances, and can be managed by a common Cisco WAAS Central Manager or Cisco vCM. The Cisco vWAAS cloud computing solution includes these features:
Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
This section contains the following topics:
- About Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
- Operating Considerations for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
- Registering the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
- Deploying Cisco vWAAS in Miscrosoft Azure
- Upgrade and Downgrade Guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
About Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure provisions VMs on the Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor. Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure is part of Cisco WAAS support for Microsoft Office 365, and is an end-to-end solution for enterprise branch offices.
- Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure is available for Cisco vWAAS in Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.1x and later.
- Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure is supported for Cisco vWAAS-200, vWAAS-750, vWAAS-1300, vWAAS-2500, vWAAS-6000, and vWAAS-12000.
- Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure is not supported for Cisco vWAAS-50000.
Table 11-1 shows the platforms supported for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure.
Table 11-1 Microsoft Azure VM Sizes for Cisco WAAS vWAAS Models
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Operating Considerations for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Interoperability
Note the following interoperability guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure:
- Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure is available for specified vWAAS models in Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.1 and later.
- You can display and identify vWAAS in Azure device on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager or the Cisco WAAS CLI:
–![]() On the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, choose Manage Devices. The vWAAS in Azure device type is displayed as OE-VWAAS-AZURE.
On the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, choose Manage Devices. The vWAAS in Azure device type is displayed as OE-VWAAS-AZURE.
–![]() On the Cisco WAAS CLI, run either the show version EXEC command or the show hardware EXEC command. Output for both commands includes the device ID, shown as OE-VWAAS-AZURE.
On the Cisco WAAS CLI, run either the show version EXEC command or the show hardware EXEC command. Output for both commands includes the device ID, shown as OE-VWAAS-AZURE.
- Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure communicates with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager in the same way as physical appliances communicate with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
- To display vWAAS in Azure devices, choose Home > Devices > All Devices. The Device Type column shows all WAAS and vWAAS devices. A vWAAS in Azure device is displayed as OE-VWAAS-AZURE.

Note![]() For Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, the supported traffic interception method is PBR; Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure does not support WCCP or AppNav interception methods.
For Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, the supported traffic interception method is PBR; Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure does not support WCCP or AppNav interception methods.
Operating Limitations for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
Note the following operating limitations for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure:
- Cisco vWAAS auto registration is not supported, because Microsoft Azure uses DHCP to configure VMs with IP address and Azure fabric server IP address. There will be operational issues if you deploy a separate DHCP server for auto registration.
Functionality similar to auto registration is available by providing the Cisco WAAS Central Manager IP address during Cisco vWAAS VM provisioning. The Cisco vWAAS VM will try to register with this Cisco WAAS Central Manager during provisioning.
- Microsoft Azure does not support GRE, IPv6, or Jumbo Frames. Therefore Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure does not support these features.

Note![]() For Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, the supported traffic interception method is PBR; Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure does not support WCCP or AppNav interception methods.
For Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, the supported traffic interception method is PBR; Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure does not support WCCP or AppNav interception methods.
Registering the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
Consider the following guidelines for registering the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager:
- If you register the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure with the WAAS Central Manager using a private IP address, follow the Cisco vWAAS registration process described in Configuring Cisco vWAAS Settings of the chapter “Configuring Cisco vWAAS and Viewing vWAAS Components.
- If you register the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager using a public IP address, you must specify the public address of the Cisco vWAAS in the Cisco WAAS Central Manager Device Activation window (choose Devices > device-name > Activation).
After you register the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure device with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, you must configure the public IP address of the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. The Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure device can contact the Cisco WAAS Central Manager only by using the public IP address of the registration. To set the public IP address of the WAAS Central Manager:
1.![]() From the WAAS Central Manager, choose Home > Devices > Primary-CM-Device > Configure > Network > NatSettings.
From the WAAS Central Manager, choose Home > Devices > Primary-CM-Device > Configure > Network > NatSettings.
2.![]() In the NAT IP field, enter the public IP address of the Central Manager.
In the NAT IP field, enter the public IP address of the Central Manager.
Deploying Cisco vWAAS in Miscrosoft Azure
Deployment Options for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
There are two major deployment options for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure:
- A SaaS application, such as an enterprise application, where you control the hosting of the application.
In this type of deployment, both the application server and Cisco vWAAS can be put in the Microsoft Azure cloud just as in a private cloud. The Cisco vWAAS is very close to the server, and tied to the server movement. In such a scenario, the traffic flow is very similar to that in a normal enterprise data center deployment.
- A SaaS application, such as Microsoft Office 365, where you do not control the hosting of the application.
In this type of deployment, you do not have control over the application in the cloud; you control only the Cisco vWAAS. In this case, traffic from the Cisco Cloud Services Router (Cisco CSR) in the branch is tunneled to the Cisco CSR in Microsoft Azure, which is then redirected to the Cisco vWAAS. A Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) is performed to get the traffic back to the Cisco CSR in the Microsoft Azure cloud from the SaaS application. For more information on Microsoft Office 365 with Cisco WAAS, Accelerate Microsoft Office 365 Shared Deployments with Cisco WAAS WAN Optimization.
Provisioning the Cisco vWAAS VM in Microsoft Azure

Note![]() To deploy Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, you need a Microsoft Azure Pay-As-You-Go subscription. Details about the subscription procedure and billing information are available on the Microsoft Azure website.
To deploy Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, you need a Microsoft Azure Pay-As-You-Go subscription. Details about the subscription procedure and billing information are available on the Microsoft Azure website.
To provision the Cisco vWAAS VM in Microsoft Azure, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Login to the Microsoft Azure portal.
Login to the Microsoft Azure portal.
Step 2![]() Choose New > Compute > Virtual Machine > From Gallery.
Choose New > Compute > Virtual Machine > From Gallery.
The Create a Virtual Machine/Choose an Image window is displayed.
Step 3![]() At the Create a Virtual Machine/Choose an Image > My Images window, select the vWAAS Azure image for your system.
At the Create a Virtual Machine/Choose an Image > My Images window, select the vWAAS Azure image for your system.
The Create a Virtual Machine/Virtual Machine Configuration window is displayed.
Step 4![]() In the Virtual Machine Name field, enter the name of the VM you want to create. Use only letters and numbers, up to a maximum of 15 characters.
In the Virtual Machine Name field, enter the name of the VM you want to create. Use only letters and numbers, up to a maximum of 15 characters.
Step 5![]() At the Virtual Machine Tier pane, select Standard.
At the Virtual Machine Tier pane, select Standard.
Step 6![]() From the Size drop-down list, select the Azure VM size for your system. Table 11-2 shows the minimum Azure VM size for each Cisco vWAAS model available for provisioning in the Virtual Machine Tier pane.
From the Size drop-down list, select the Azure VM size for your system. Table 11-2 shows the minimum Azure VM size for each Cisco vWAAS model available for provisioning in the Virtual Machine Tier pane.
Table 11-2 Microsoft Azure VM Sizes for Cisco vWAAS Models
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|

Note![]() Use the Microsoft Azure Virutal Machine Tier pane to select an Azure VM for the Cisco vWAAS models shown in Table 11-2. For vWAAS-6000 and vWAAS-12000, you must use the template to specify the Azure VM. For more information, see Deploying Cisco vWAAS in Miscrosoft Azure. For Azure VM sizes for vWAAS-6000 and vWAAS-12000, see Table 11-1.
Use the Microsoft Azure Virutal Machine Tier pane to select an Azure VM for the Cisco vWAAS models shown in Table 11-2. For vWAAS-6000 and vWAAS-12000, you must use the template to specify the Azure VM. For more information, see Deploying Cisco vWAAS in Miscrosoft Azure. For Azure VM sizes for vWAAS-6000 and vWAAS-12000, see Table 11-1.
Step 7![]() In the New User Name field, enter your user name.
In the New User Name field, enter your user name.
Step 8![]() In the New Password field, enter your password.
In the New Password field, enter your password.
Step 9![]() In the Confirm field, re-enter your password.
In the Confirm field, re-enter your password.
Step 10![]() (Optional) If your system uses SSH key-based authentication:
(Optional) If your system uses SSH key-based authentication:
a.![]() Check the Upload compatible SSH key for authentication checkbox.
Check the Upload compatible SSH key for authentication checkbox.
b.![]() From the Certificate field, browse for the certificate file for your system.
From the Certificate field, browse for the certificate file for your system.
Step 11![]() (Optional) If your system requires a password, check the Provide a password checkbox.
(Optional) If your system requires a password, check the Provide a password checkbox.
Step 12![]() Click the right arrow at the lower right of the window to proceed to the next window.
Click the right arrow at the lower right of the window to proceed to the next window.
The next Create a Virtual Machine/Virtual Machine Configuration window is displayed.
Step 13![]() From the Cloud Service drop-down list, choose Create a Cloud Service.
From the Cloud Service drop-down list, choose Create a Cloud Service.
Step 14![]() In the Cloud Service DNS Name field, enter the name of the VM that you created in Step 4.
In the Cloud Service DNS Name field, enter the name of the VM that you created in Step 4.
When Azure VMs are being named, the DNS name has cloudapp.net automatically appended to it.
Step 15![]() From the Region/Affinity Group/Virtual Network drop-down list, choose a location that is in close proximity to the resources you want to optimize, such as East U.S. or North Europe.
From the Region/Affinity Group/Virtual Network drop-down list, choose a location that is in close proximity to the resources you want to optimize, such as East U.S. or North Europe.
The Region/Affinity Group/Virtual Network setting determines the location of the VM within the Azure cloud data centers.
Step 16![]() From the Storage Account drop-down list, select Use an automatically generated storage account.
From the Storage Account drop-down list, select Use an automatically generated storage account.
Step 17![]() From the Availability Set drop-down list, choose (None).
From the Availability Set drop-down list, choose (None).
Step 18![]() Click the right arrow at the lower right corner of the window to proceed to the next window.
Click the right arrow at the lower right corner of the window to proceed to the next window.
The Virtual Machines/Virtual Machine Instances window is displayed
Step 19![]() By default, the Install the VM Agent check box is checked.
By default, the Install the VM Agent check box is checked.
Step 20![]() In the Endpoints section:
In the Endpoints section:
Step 21![]() Click the check mark at the lower right corner of the window to proceed for provisioning Cisco vWAAS.
Click the check mark at the lower right corner of the window to proceed for provisioning Cisco vWAAS.
The Virtual Machines/Virtual Machine Instances window is displayed, showing the newly-created VM with an initial status of Starting (Provisioning).
The process takes a few minutes before the VM status is displayed as Running.
Step 22![]() Select the Cisco vWAAS VM.
Select the Cisco vWAAS VM.
Step 23![]() Attach the data disks. See Table 11-2 for data disk sizes for Azure VMs.
Attach the data disks. See Table 11-2 for data disk sizes for Azure VMs.
Step 24![]() Stop and then restart the VM, so that it picks up the attached disks.
Stop and then restart the VM, so that it picks up the attached disks.
Your VM is ready to be deployed with an end-to-end setup.
Deploying vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
Deploying Cisco vWAAS VM and Data Disk with the VHD Template
To deploy the Cisco vWAAS VM and data disk with the VHD template, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Copy vwaas.vhd to the storage account using AzCopy.
Copy vwaas.vhd to the storage account using AzCopy.
The AzCopy command parameters are:
Step 2![]() Use the VHD template to deploy the vWAAS VM.
Use the VHD template to deploy the vWAAS VM.
The vWAAS VM is deployed with the data disk.
Step 3![]() Log in with your username and password.
Log in with your username and password.
Step 4![]() (Optional) To verify deployment details such as CMS registration and WAAS Central Manager address, see Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment.
(Optional) To verify deployment details such as CMS registration and WAAS Central Manager address, see Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment.
Deploying vWAAS VM with Template and Custom VHD from the Microsoft ARM Portal
- Verify that the Cisco vWAAS VM is provisioned in Microsoft Azure, including the creation of a storage account and a VM location specified in Microsoft Azure. For more information, see Provisioning the Cisco vWAAS VM in Microsoft Azure.
To deploy the Cisco vWAAS VM with a template and custom VHD from the Microsoft Azure Resource Manager portal (Microsoft ARM portal), follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Copy vwaas.vhd to the storage account using Azcopy.
Copy vwaas.vhd to the storage account using Azcopy.
Step 2![]() Use the VHD template to deploy the Cisco vWAAS VM.
Use the VHD template to deploy the Cisco vWAAS VM.
Step 3![]() At the Microsoft ARM portal, choose New > Template Deployment > Edit Template.
At the Microsoft ARM portal, choose New > Template Deployment > Edit Template.
Step 5![]() Paste the template in the Templates window.
Paste the template in the Templates window.
Step 6![]() For the parameters, enter the values for your system, such as resource group and resource group location, and whether or not to deploy the vWAAS VM in a new or existing virtual network.
For the parameters, enter the values for your system, such as resource group and resource group location, and whether or not to deploy the vWAAS VM in a new or existing virtual network.
Step 7![]() Accept the Terms and Conditions.
Accept the Terms and Conditions.
The Cisco vWAAS VM is deployed.
Step 9![]() Log in with your username and password.
Log in with your username and password.
Step 10![]() (Optional) To verify deployment details such as CMS registration and Cisco WAAS Central Manager address, see Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment.
(Optional) To verify deployment details such as CMS registration and Cisco WAAS Central Manager address, see Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment.
Deploying the Cisco vWAAS VM Using Microsoft Windows PowerShell
- Verify that the Cisco vWAAS VM is provisioned in Microsoft Azure, including the creation of a storage account and a VM location specified in Microsoft Azure. For more information, see Provisioning the Cisco vWAAS VM in Microsoft Azure.
To deploy the Cisco vWAAS VM using Microsoft Windows PowerShell, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Deploy vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V. For information on this deployment procedure, see Chapter 5, “Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V”.
Deploy vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V. For information on this deployment procedure, see Chapter 5, “Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V”.
Step 2![]() Run the azure_predeploy.sh script in Hyper-V, to set the necessary Azure parameters.
Run the azure_predeploy.sh script in Hyper-V, to set the necessary Azure parameters.
Step 3![]() Export the flash VHD from the Microsoft Hyper-V disk location to the storage account in Microsoft Azure, using AzCopy.
Export the flash VHD from the Microsoft Hyper-V disk location to the storage account in Microsoft Azure, using AzCopy.
Step 4![]() Use Microsoft Windows PowerShell commands to specify the following parameters:
Use Microsoft Windows PowerShell commands to specify the following parameters:
Step 5![]() Run the New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name $RGName -Location $locName PowerShell command to create the resource group.
Run the New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name $RGName -Location $locName PowerShell command to create the resource group.
Step 6![]() Run the New-AzureRmResourceGroupDeployment PowerShell cmdlet to deploy Cisco vWAAS in Azure. To complete the deployment, specify values for the following parameters:
Run the New-AzureRmResourceGroupDeployment PowerShell cmdlet to deploy Cisco vWAAS in Azure. To complete the deployment, specify values for the following parameters:
After you enter these parameters, Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure is deployed. The system displays provisioning information, including deployment name, provisioning state, date/time, and mode.
Step 7![]() Log in with your username and password.
Log in with your username and password.
Step 8![]() (Optional) To verify deployment details such as CMS registration and Cisco WAAS Central Manager address, see Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment.
(Optional) To verify deployment details such as CMS registration and Cisco WAAS Central Manager address, see Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment.
Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment
Table 11-3 provides a checklist for verifying the Cisco vWAAS VM deployment in Microsoft Azure.
Table 11-3 Checklist for Verifying the Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure Deployment

Note![]() Whenever ARP caches are cleared or the Cisco vWAAS is rebooted, packets may not be forwarded to the next hop in Microsoft Azure cloud. To ensure that packets are successfully forwarded, use the ping EXEC command to update the ARP cache table.
Whenever ARP caches are cleared or the Cisco vWAAS is rebooted, packets may not be forwarded to the next hop in Microsoft Azure cloud. To ensure that packets are successfully forwarded, use the ping EXEC command to update the ARP cache table.
Upgrade and Downgrade Guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure
Consider the following upgrade and downgrade guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure:
- The procedure for upgrading or downgrading Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure, for all Cisco vWAAS models except Cisco vWAAS-50000, is the same as that for other Cisco WAAS device.
- Downgrading a device or device group for Cisco vWAAS in Microsoft Azure to a version earlier than Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.1 is not supported.
Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
This section contains the following topics:
- Operating Guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
- Upgrade and Downgrade Guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
- Deploying Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
Operating Guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
Consider the following operating guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack:
- Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack is supported for Cisco vWAAS in WAAS Version 6.4.1b and later.
- Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack is supported for all Cisco vWAAS and Cisco vCM models that are supported on RHEL KVM on CentOS.
- On the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, Cisco vWAAS devices in OpenStack are displayed as OE-VWAAS-OPENSTACK.
- All Cisco vWAAS models for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack are deployed with a single, unified OVA. The following are examples of the unified OVA and NPE OVA package filenames for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack:
Upgrade and Downgrade Guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
Consider the following upgrade and downgrade guidelines for Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack:
Deploying Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack
Guidelines for Deploying vWAAS in OpenStack
Consider the following guidelines to deploy Cisco vWAAS in OpenStack:
- vWAAS in OpenStack is deployed for vWAAS on KVM. For more information on vWAAS on KVM, see the chapter “Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM, KVM on CentOS, and KVM in SUSE Linux”.
For Cisco vWAAS on KVM in Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.x and later, Cisco provides a single, unified OVA or NPE OVA package for each hypervisor type, which can be used with all Cisco vWAAS models for that hypervisor. Here are some examples of the unified OVA and NPE OVA package filenames for vWAAS on KVM:
–![]() OVA: Cisco-KVM-vWAAS-Unified-6.4.3c-b-42.tar.
OVA: Cisco-KVM-vWAAS-Unified-6.4.3c-b-42.tar.
–![]() NPE OVA: Cisco-KVM-vWAAS-Unified-6.4.3c-b-42-npe.tar
NPE OVA: Cisco-KVM-vWAAS-Unified-6.4.3c-b-42-npe.tar
For more information about this unified OVA package, see the section Unified OVA Package for Cisco vWAAS on KVM in WAAS Version 6.4.1 and Later.
- After vWAAS in OpenStack is operational on a device, you can use the WAAS CM or the WAAS CLI to display the OpenStack device.
–![]() The Cisco WAAS Central Manager displays the following information for the device:
The Cisco WAAS Central Manager displays the following information for the device:
The OpenStack device is displayed in the Devices > All Devices listing under Device Type as OE-VWAAS-OPENSTACK.
The OpenStack device is displayed in the Devices > device-name > Dashboard as OE-VWAAS-OPENSTACK.
–![]() Run the show hardware command to display the device, as well as other system hardware status information such as startup date and time, the run time since startup, microprocessor type and speed, and a list of disk drives.
Run the show hardware command to display the device, as well as other system hardware status information such as startup date and time, the run time since startup, microprocessor type and speed, and a list of disk drives.
Procedure for Deploying vWAAS in OpenStack
To deploy vWAAS in OpenStack, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Copy the unified OVA to a directory on the host machine.
Copy the unified OVA to a directory on the host machine.
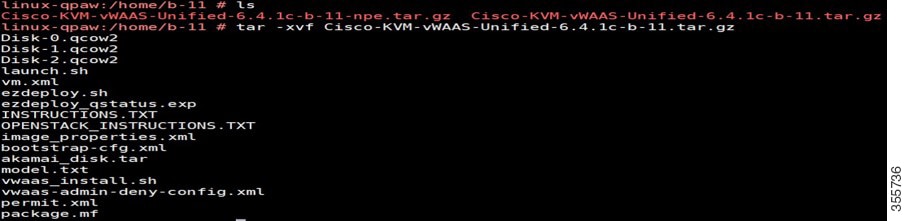
Step 2![]() Untar the OVA using the following command, as shown in Figure 11-1).
Untar the OVA using the following command, as shown in Figure 11-1).
tar -xvf Cisco-KVM-vWAAS-Unified-6.4.1b-b-11.tar.gz
Figure 11-1 Tar Command for vWAAS OpenStack OVA
a.![]() Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose the Compute > Images window (Figure 11-2).
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose the Compute > Images window (Figure 11-2).
Figure 11-2 OpenStack Compute > Images Page
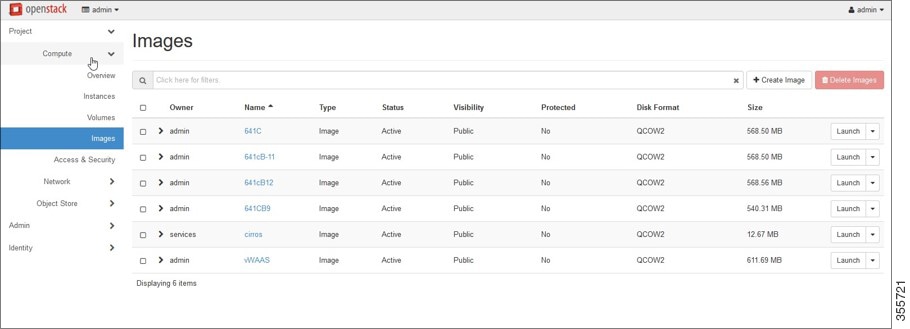
b.![]() From the Images table, choose the image for your system.
From the Images table, choose the image for your system.
c.![]() To create the image, click Create Image.
To create the image, click Create Image.
Step 4![]() Create the bootable volume.
Create the bootable volume.
a.![]() Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Create Volume (Figure 11-3).
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Create Volume (Figure 11-3).
Figure 11-3 OpenStack Create Volume Dialog Box: Creating Bootable Volume
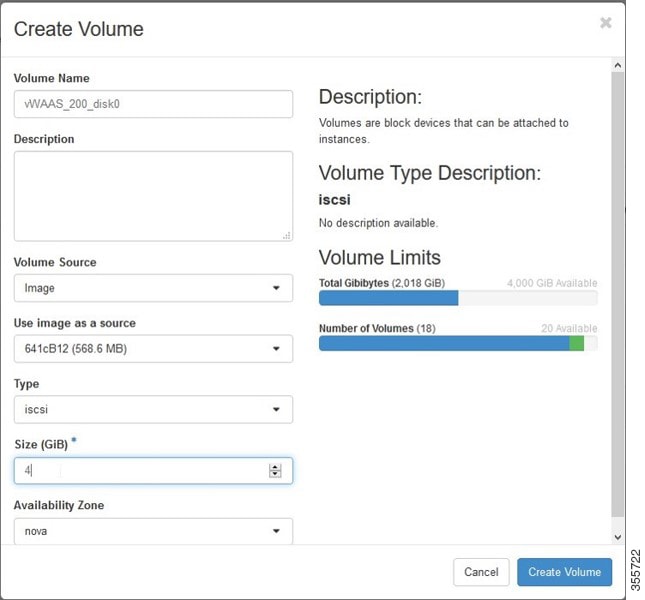
b.![]() In the Volume Name field, enter the name of the Cisco vWAAS model and disk, for example, vWAAS_200_disk0.
In the Volume Name field, enter the name of the Cisco vWAAS model and disk, for example, vWAAS_200_disk0.
c.![]() From the Volume Source drop-down list, choose Image.
From the Volume Source drop-down list, choose Image.
d.![]() From the Use image as a source drop-down list, choose the build number for your system.
From the Use image as a source drop-down list, choose the build number for your system.
e.![]() From the Type drop-down list, choose iscsi.
From the Type drop-down list, choose iscsi.
f.![]() From the Size (GiB) drop-down list, choose the size for this volume, for example, 4.
From the Size (GiB) drop-down list, choose the size for this volume, for example, 4.
g.![]() From the Availability drop-down list, choose nova.
From the Availability drop-down list, choose nova.
Step 5![]() Create nonbootable volumes.
Create nonbootable volumes.
a.![]() Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Create Volume (Figure 11-4).
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Create Volume (Figure 11-4).
Figure 11-4 OpenStack Create Volume Dialog Box: Creating Nonbootable Volumes
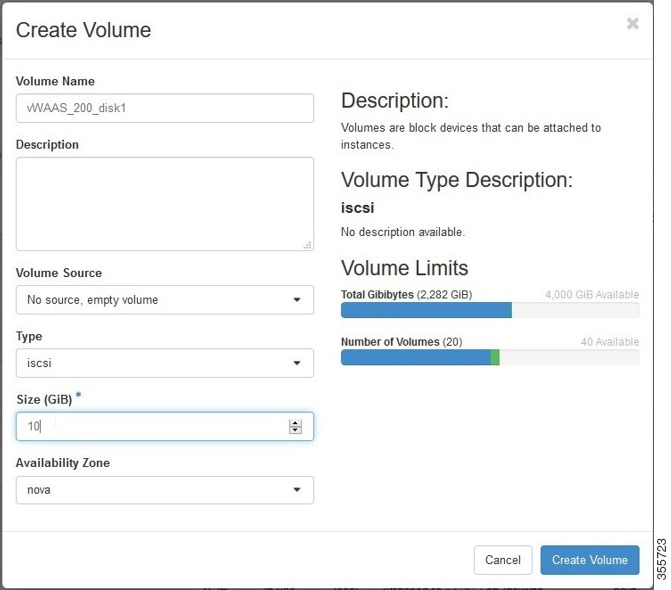
b.![]() In the Volume Name field, enter the name of the Cisco vWAAS model and disk, for example, vWAAS_200_disk1.
In the Volume Name field, enter the name of the Cisco vWAAS model and disk, for example, vWAAS_200_disk1.
c.![]() From the Volume Source drop-down list, choose No source, empty volume.
From the Volume Source drop-down list, choose No source, empty volume.
d.![]() From the Type drop-down list, choose iscsi.
From the Type drop-down list, choose iscsi.
e.![]() From the Size (GiB) drop-down list, choose the size for this volume, for example, 10.
From the Size (GiB) drop-down list, choose the size for this volume, for example, 10.
f.![]() From the Availability drop-down list, choose nova.
From the Availability drop-down list, choose nova.
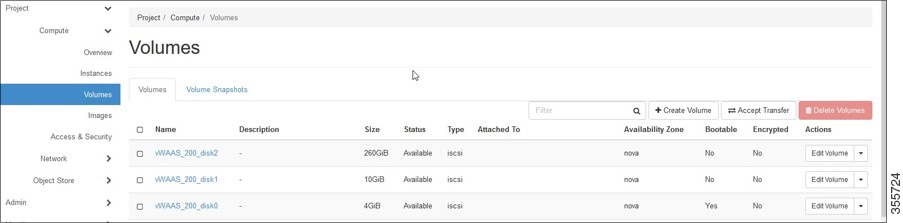
Step 6![]() In the OpenStack Compute > Volumes window, create all the volumes related to your deployed model (Figure 11-5):
In the OpenStack Compute > Volumes window, create all the volumes related to your deployed model (Figure 11-5):
Figure 11-5 Openstack Compute > Volumes Page: Create all Volumes for Deployed Model
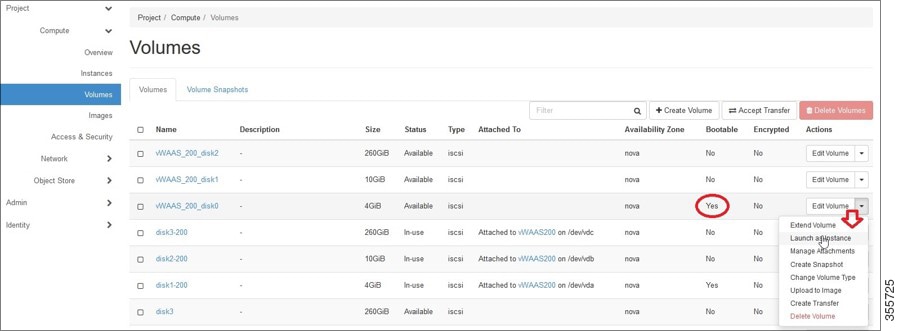
a.![]() In the OpenStack Compute > Volumes page, create an instance with a bootable volume (Figure 11-6).
In the OpenStack Compute > Volumes page, create an instance with a bootable volume (Figure 11-6).
Figure 11-6 OpenStack Compute > Volumes Page: Create Bootable Volume
c.![]() Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Instances > Launch Instance (Figure 11-7).
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Instances > Launch Instance (Figure 11-7).
Figure 11-7 OpenStack Launch Instance > Details Page
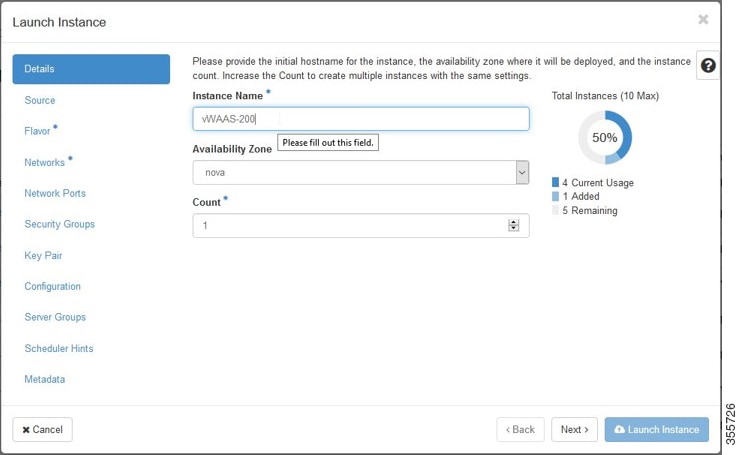
d.![]() In the Instance Name field, enter the name of the Cisco vWAAS model, for example, vWAAS-200.
In the Instance Name field, enter the name of the Cisco vWAAS model, for example, vWAAS-200.
e.![]() From the Availability drop-down list, choose nova.
From the Availability drop-down list, choose nova.
f.![]() From the Count drop-down list, choose 1.
From the Count drop-down list, choose 1.
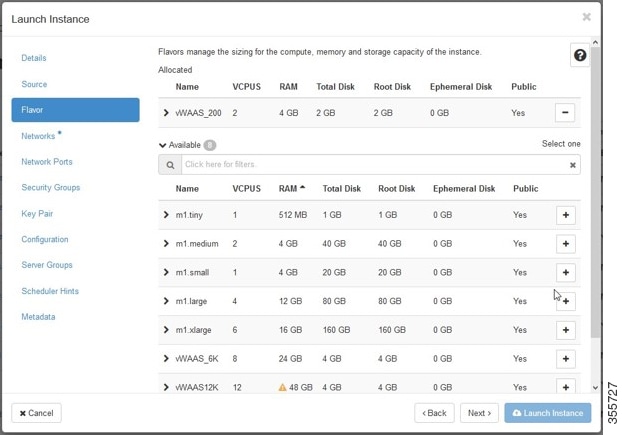
Step 7![]() Specify the flavor suitable for the selected Cisco vWAAS model. As noted on the OpenStack page (Figure 11-8), flavors manage the sizing for the compute, memory, and storage capacity of the instance.
Specify the flavor suitable for the selected Cisco vWAAS model. As noted on the OpenStack page (Figure 11-8), flavors manage the sizing for the compute, memory, and storage capacity of the instance.
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Instances > Launch Instance > Flavor (Figure 11-8).
Figure 11-8 OpenStack Launch Instance > Flavor Page
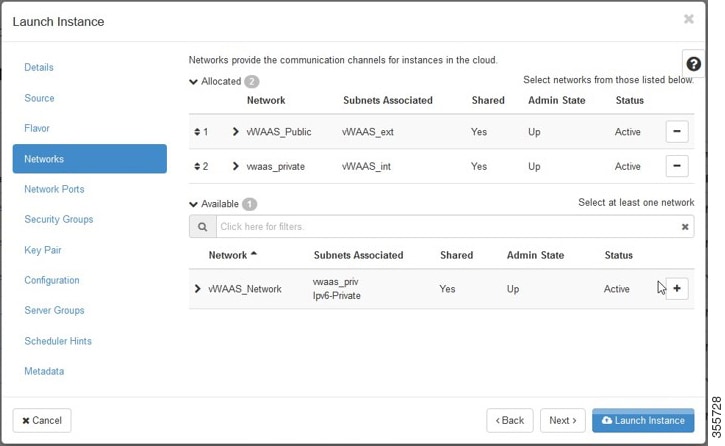
Step 8![]() Select the networks for the vWAAS.
Select the networks for the vWAAS.
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Instances > Launch Instance > Networks (Figure 11-9).
Figure 11-9 OpenStack Launch Instance > Networks Page
Step 9![]() Select the configuration drive to send model parameters.
Select the configuration drive to send model parameters.
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Instances > Launch Instance > Configuration (Figure 11-10).
Figure 11-10 OpenStack Launch Instance > Configuration Page
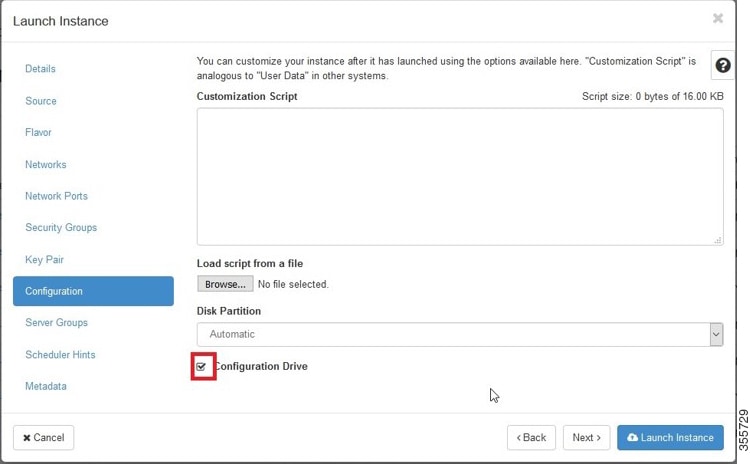
a.![]() From the Disk Partition drop-down list, choose Automatic.
From the Disk Partition drop-down list, choose Automatic.
b.![]() Check the Configuration Drive check box.
Check the Configuration Drive check box.
Step 10![]() Provide model and connection information to deploy vWAAS in OpenStack metadata.
Provide model and connection information to deploy vWAAS in OpenStack metadata.
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Instances > Launch Instance > Metadata (Figure 11-11).
Figure 11-11 OpenStack Launch Instance > Metadata Page
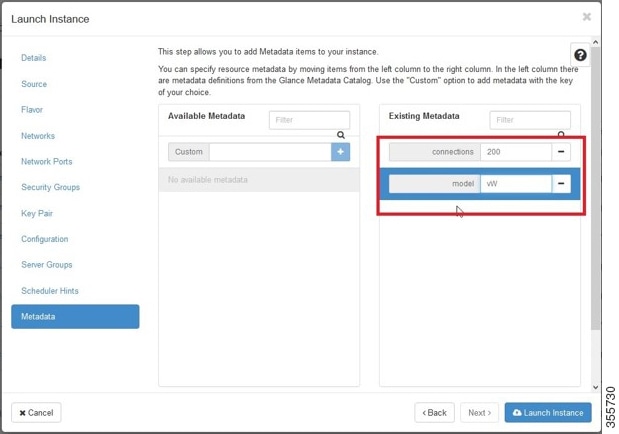
a.![]() Specify resource metadata by selecting and moving items from the Available Metadata column into the Existing Metadata column.
Specify resource metadata by selecting and moving items from the Available Metadata column into the Existing Metadata column.
Step 11![]() Attach disks to the deployed instance.
Attach disks to the deployed instance.
Click the OpenStack Admin tab and choose Compute > Volumes (Figure 11-12).
Figure 11-12 OpenStack Compute > Volumes Page: Attach disks to deployed instance
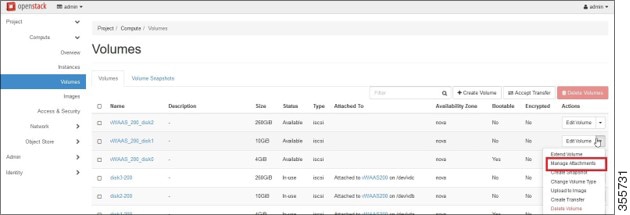
a.![]() From the Edit Volume drop-down list, choose Manage Attachments. The Manage Volume Attachments dialog box appears (Figure 11-13).
From the Edit Volume drop-down list, choose Manage Attachments. The Manage Volume Attachments dialog box appears (Figure 11-13).
Figure 11-13 OpenStack Manage Volume Attachments Dialog Box
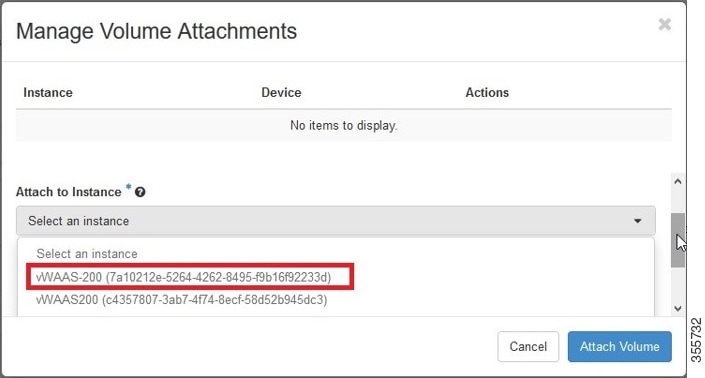
b.![]() From the Select an instance drop-down list, choose the instance to attach to the disk.
From the Select an instance drop-down list, choose the instance to attach to the disk.
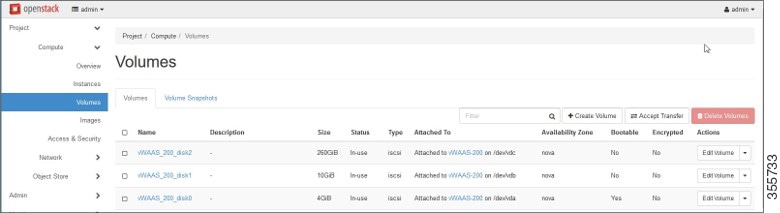
Step 12![]() After attaching the disks, the Compute > Volumes window displays the attached disks (Figure 11-14).
After attaching the disks, the Compute > Volumes window displays the attached disks (Figure 11-14).
Figure 11-14 OpenStack Compute > Volumes Page: List of attached disks
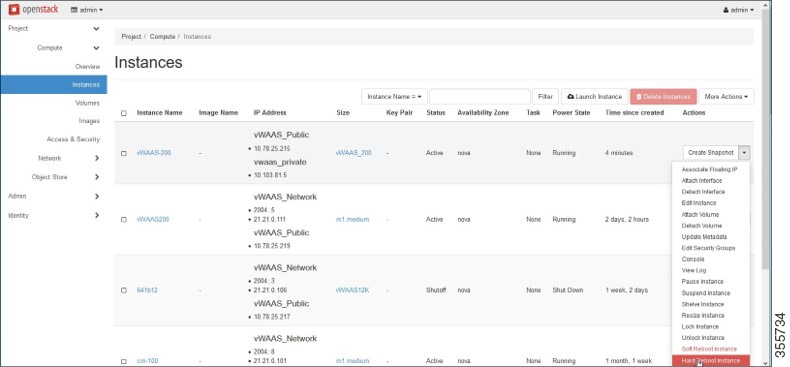
Step 13![]() Reboot the system (hard reboot).
Reboot the system (hard reboot).
a.![]() After the system is rebooted, choose Compute > Instances.
After the system is rebooted, choose Compute > Instances.
b.![]() From the Create Snapshot drop-down list, choose Hard Reboot Instance.
From the Create Snapshot drop-down list, choose Hard Reboot Instance.
c.![]() The Compute > Instances window displays the attached disks (Figure 11-15).
The Compute > Instances window displays the attached disks (Figure 11-15).
Figure 11-15 OpenStack Compute > Instances Page: Attached disks listing
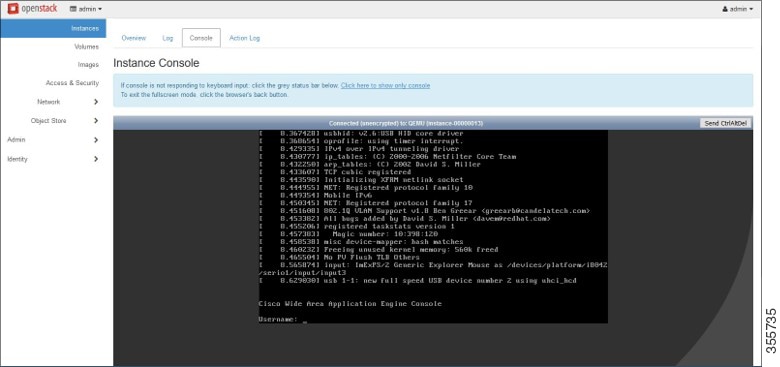
Step 14![]() From the Instances > Instance Console page, connect to the console to work on vWAAS (Figure 11-16).
From the Instances > Instance Console page, connect to the console to work on vWAAS (Figure 11-16).
Figure 11-16 OpenStack Instances > Instance Console Page
 Feedback
Feedback