Manage Certificates
What is a Certificate?
A certificate is an electronic document that identifies an individual, a server, a company, or another entity, and associates that entity with a public key. When a certificate is created with a public key, a matching private key is also generated. In TLS, the public key is used to encrypt data being sent to the entity and the private key is used to decrypt. A certificate is signed by an issuer or a "parent" certificate (Certificate Authority), that is, signed by the parent's private key. Certificates can also be self-signed. In a TLS exchange, a hierarchy of certificates is used to verify the validity of the certificate's issuer. This hierarchy is called a trust-chain and consists of three types of entities: a root CA certificate (self-signed), possibly multiple levels of intermediate CA certificates, and a server (or client) certificate (end-entity). The intermediate certificates act as a “link of trust” linking the server certificates to the CA’s root certificate and providing additional layers of security. Starting from the root certificate's private key, the private key for each certificate in the trust chain signs and issues the next certificate in the chain until finally signing an end entity certificate. The end-entity certificate is the last certificate in the chain and is used as a client or server certificate.
How are Certificates Used in Cisco Crosswork Planning?
Communication between Cisco Crosswork and devices as well as between various Cisco Crosswork components are secured using the TLS protocol. TLS uses X.509 certificates to securely authenticate devices and encrypt data to ensure its integrity from source to destination. Crosswork uses a mix of generated and client uploaded certificates. Uploaded certificates can be purchased from Certificate authorities (CA) or can be self-signed.
The Certificate Management window () allows you to view and upload, and modify certificates. The following figure displays the default certificates provided by Cisco Crosswork Planning.
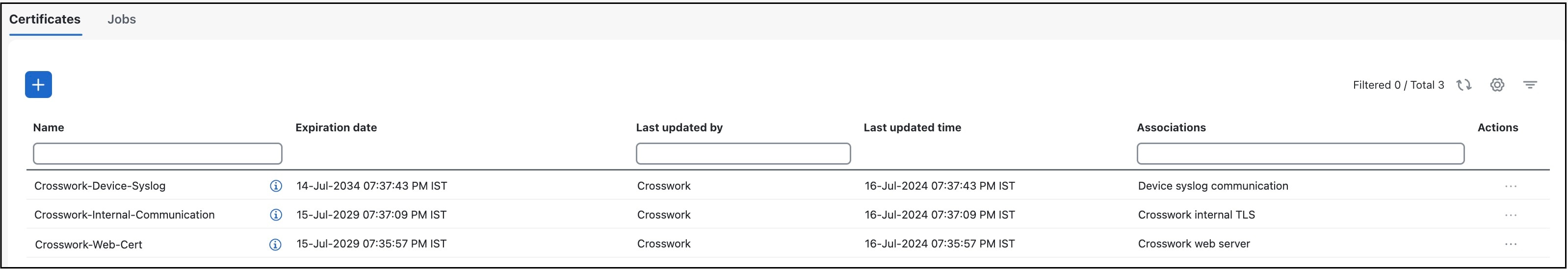
Certificate Types and Usage
These certificates are classified into various roles with different properties depending on their use case as shown in the following table.
|
Role |
UI Name |
Description |
Server |
Client |
Allowed operations |
Default Expiry |
Allowed Expiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Crosswork Internal TLS |
Crosswork-Internal-Communication |
|
Crosswork |
Crosswork |
Download |
5 years |
— |
|
Crosswork Web Server |
Crosswork-Web-Cert Server Authentication |
|
Crosswork Web Server |
User Browser or API Client |
|
5 years |
30 days to 5 years |
|
Crosswork Device Syslog |
Crosswork-Device-Syslog |
|
Device |
Download |
5 years |
— |
There are two category roles in Crosswork:
-
Roles which allow you to upload or download trust chains only.
-
Roles that allow upload or download of both the trust chain and an intermediate certificate and key.
Add a New Certificate
You can add certificates for the following role:
-
Secure LDAP Communication: The user uploads the trust chain of the secure LDAP certificate. This trust chain is used by Crosswork to authenticate the secure LDAP server. Once this trust chain is uploaded and propagated within Crosswork, the user can add the LDAP server (see Manage LDAP Servers) and associate the certificate.
 Note |
Cisco Crosswork does not receive a web certificate directly. It accepts an intermediate CA and intermediate Key to create a new web certificate, and apply it to the Web Gateway. |
Before you begin
-
For information on certificate types and usage, see Certificate Types and Usage.
-
All certificates that are uploaded must be in Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format. Note where these certificates are in the system so that you can navigate to them easily.
-
Trust chain files that are uploaded may contain the entire hierarchy (root CA and intermediate certificates) in the same file. In some cases, multiple chains are also allowed in the same file.
-
Intermediate Keys need to be either PKCS1 or PKCS8 format.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose and click |
||
|
Step 2 |
Enter a unique name for the certificate. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Certificate Role drop-down menu, select the purpose for which the certificate is to be used.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Browse, and navigate to the certificate trustchain. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Click Save.
|
Edit Certificates
You can edit a certificate to add or remove connection destinations, upload, and replace expired or misconfigured certificates. User provided certificates and web certificates can be edited. Other system certificates that are provided by Cisco Crosswork cannot be modified and will not be available for selection.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . and check the certificate that you want to modify. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click |
||
|
Step 3 |
Update the necessary options.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Save. |
Download Certificates
To export certificates, do the following:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Click 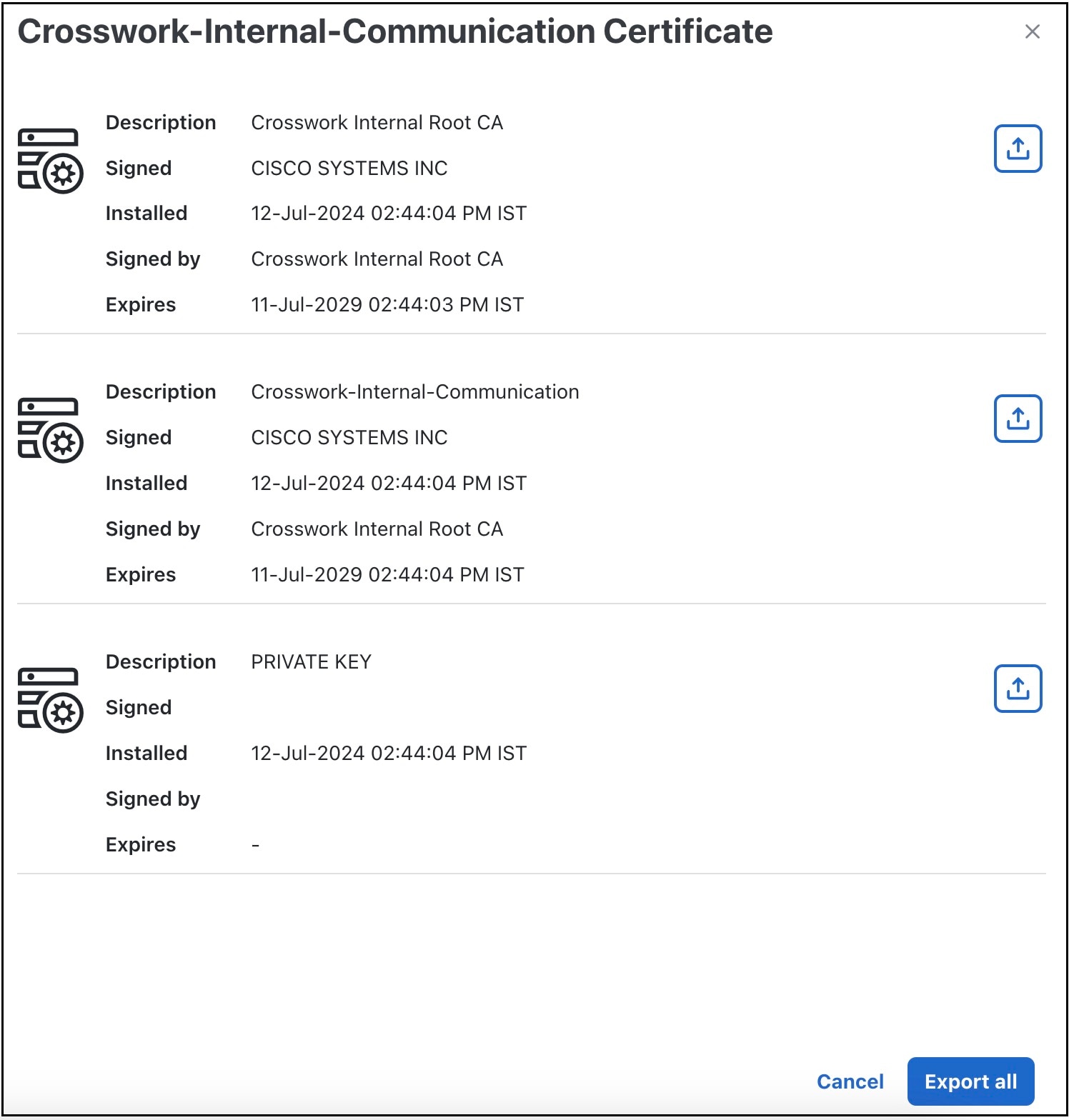
|
|
Step 3 |
To separately download the root certificate, intermediate certificate, and the private key, click |


 Feedback
Feedback