VXLAN EVPN TE - Multi-Site Egress Load-Balancing Overview
The VXLAN EVPN TE - Multi-Site Egress Load-Balancing feature facilitates traffic steering and enables load balancing for the data sent between different fabrics across multi-site links.
The traffic engineering and load-balancing functionality operate across an IP-based underlay network, usually referred to as Inter-Site Network (ISN). Therefore, this essentially serves as IP Traffic Engineering that is applicable to any overlay-encapsulated traffic sent over the underlay.
The VXLAN EVPN TE - Multi-Site Egress Load-Balancing typically provides improved utilization of inter-Data Center (DC) links.

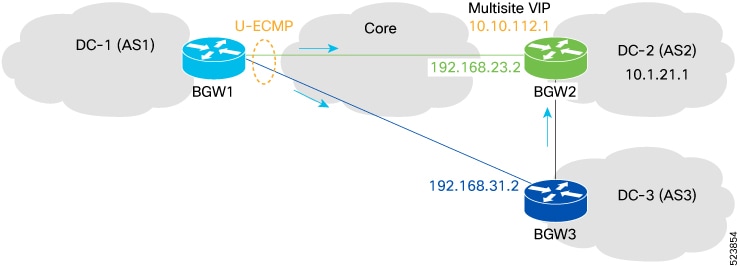
The topology above shows three VXLAN EVPN fabrics part of the same Multi-Site domain. Each fabric connects to the remote sites through a local tier of Border Gateway devices (BGWs) that essentially represent the interface of the fabric with the rest of the network infrastructure. Various types of BGWs, such as Anycast BGWs, vPC BGWs, and Border Gateway Spines, can coexist within this deployment. They may be interconnected through different connectivity options, including direct BGW-to-BGW links or through a generic Core infrastructure (ISN).
-
Typically, the paths designated in orange are used as the best path or multipath for intersite communication between endpoints belonging to Site-1 and Site-2.
-
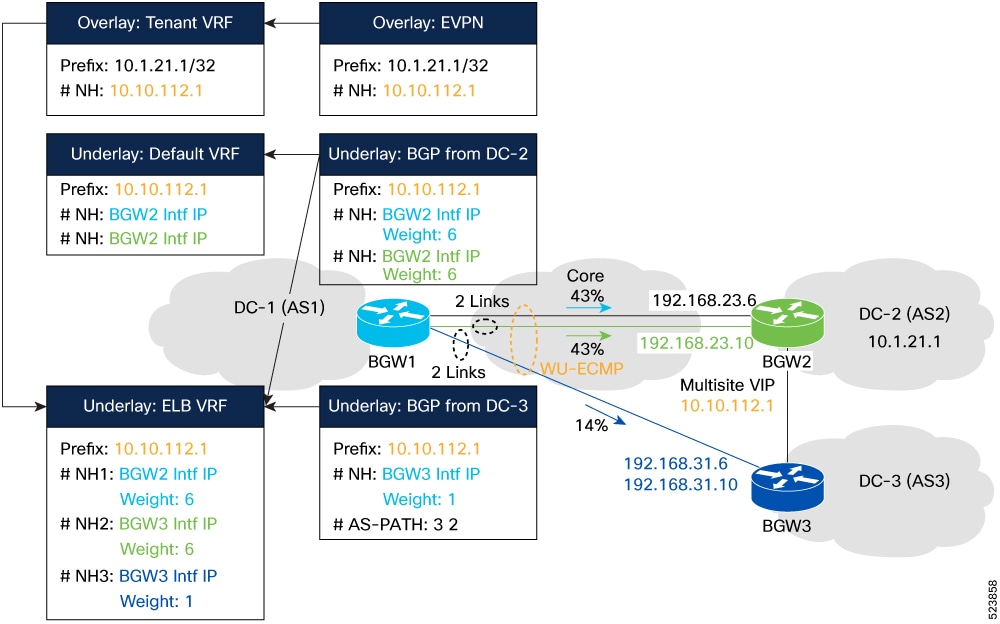
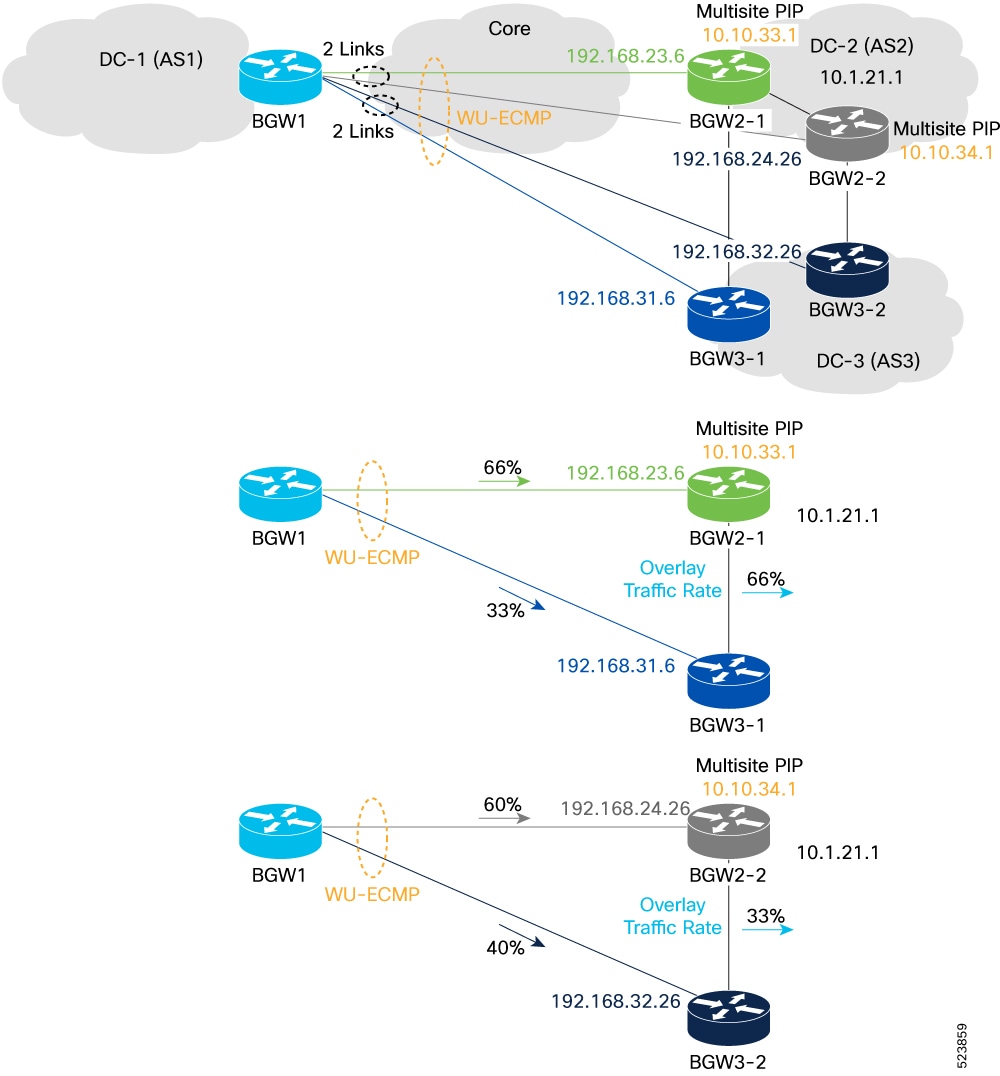
By enabling the VXLAN EVPN TE - Multi-Site Egress Load-Balancing feature, additional paths for traffic distribution are available beyond the best path. This includes alternative routes such as those through an intermediary location, referred to as Site-3 (highlighted in blue), as well as paths that traverse through a generic Core infrastructure (highlighted in green). These alternative paths can be used as part of Unequal Equal-Cost Multipath (uECMP) or Weighted Unequal Equal-Cost Multipath (wuECMP).






 Feedback
Feedback