- Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Interoperability
- Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
- Configuring Conferencing and Transcoding for Voice Gateway Routers
- Configuring MGCP PRI Backhaul and T1 CAS Support
- Configuring MGCP-Controlled Backhaul of BRI Signaling
- Configuring Tone Download to MGCP Gateways
- Configuring MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Configuring RSVP Agent
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Restrictions for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Information About MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- How to Configure MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Configuration Examples for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
Configuring MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
The MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways feature supports the Malicious Call Identification (MCID) supplementary service that enables Cisco Unified Communications Manager to identify the source of malicious calls.
Feature History for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.3(8)XY |
This feature was introduced. |
| 12.3(11)T |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T. |
| 12.3(14)T |
Support was added for the new Cisco IOS command structure for voice applications in the HTTP Client API for TCL IVR feature. |
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn . You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
For more information about this and related Cisco IOS voice features, see the following:
- "Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco IOS Interoperability" on page 13 .
- Entire Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library--including library preface and glossary, other feature documents, and troubleshooting documentation--at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios123/123cgcr/voice_c/vcl.htm .
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Restrictions for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Information About MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- How to Configure MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Configuration Examples for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- MCID must be configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager 4.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 4.0) or later. For information, see the "Malicious Call Identification" chapter in the Cisco Unified CallManager Features and Services Guide, Release 4.0(1).
- Your platform must support MCID and TCL IVR 2.0.
- You must either use the script app_mcid.2.0.0.40.tcl or a later version, or write your own TCL IVR 2.0 script that implements MCID. To download the script, go to the Software Download site at http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/tclware . To write your own script, see the TCL IVR API Version 2.0 Programming Guide .
- If you require an MCID service log in RADIUS, you can write a script that supports the RADIUS service and uses the aaa accounting update command to generate an accounting record.
- Cisco Catalyst 6500 series and Cisco 7600 series Communication Media Module (CMM) requires WS-SVC-CMM-6T1, WS-SVC-CMM-6E1, or WS-SVC-CMM-24 FXS port adapter in H.323 environment.
Restrictions for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Supported only for NET5 switches that have MCID functionality enabled. Other switch types are not supported.
- Supported only for incoming calls from the ISDN network.
- MCID requests from the central office are ignored by Cisco Unified Communications Manager and are not supported by the Cisco voice gateway.
- Service provider on the time-division multiplexing (TDM) side of the PSTN must have MCID functionality enabled.
- ISDN interface on the voice gateway must have the ISDN switch type set to primary-net5 with the isdn switch-type command and operate in user-side mode (default).
- Voice gateways with PRI interfaces should provide the following capabilities:
- Receive MCID requests relating to the call from upper layers and relay them to the connected network using the PRI protocol specified for the MCID service.
- Receive MCID related response signals and information from the connected network using the PRI protocol specified for the MCID service. Cisco Unified Communications Manager ignores the signals and information.
- Not supported on the Access Gateway Module (AGM).
Information About MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
MCID
Malicious Call Identification (MCID) is a supplementary service that enables Cisco Unified Communications Manager to identify the source of malicious calls. A user who receives a malicious call from another network, typically the PSTN, can select a softkey on the IP phone which immediately notifies the system administrator, flags the call detail record (CDR) for the Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster, and notifies the PSTN of the malicious nature of the call, allowing the offnet system to take action, such as notifying legal authorities.
The figure below shows an example of the MCID call flow. After receiving an MCID request from an endpoint device (victim), Cisco Unified Communications Manager sends an H.225 Facility message with the MCID information element (IE) to the voice gateway. The gateway sends a Q.931 Facility message with the MCID IE to the ISDN network (central office).
| Figure 1 | MCID Functionality |
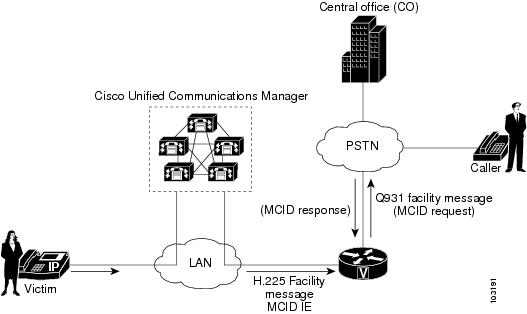
A called party invokes MCID by pressing the appropriate softkey on the IP phone. A configurable timer is available when awaiting a response after sending a Facility message to the PSTN. If a response is not received within the specified time, the TCL IVR script is notified. Depending on how the script is written, it could try to reinvoke MCID or perform some other action, for example, playing a message to the user that the MCID attempt did not work.
How to Configure MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Enabling the ISDN Interface to Send MCID Requests
- Configuring MCID on the Voice Gateway in Cisco IOS Release 12.3T
- Configuring MCID on the Voice Gateway in Earlier Release
Enabling the ISDN Interface to Send MCID Requests
Perform this task to enable an ISDN interface to send MCID requests and to set the timer.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring MCID on the Voice Gateway in Cisco IOS Release 12.3T
Use this procedure to define the MCID application on a voice gateway that is running Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T or later. To verify your release, use the show version command.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# application |
Enters application configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-app)# service mcid flash:app_mcid.2.0.0.40.tcl |
Specifies the name and location of the MCID script. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-app-param)# param mcid-release-timer 30 |
(Optional) Number of seconds the script waits before releasing both call legs after it receives a disconnect message. Default is 60 seconds. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-app-param)# param retry-count 3 |
(Optional) Maximum number of times the called party can trigger MCID if all previous attempts failed. Default is 0, which means the user can invoke MCID as many times as needed. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-app-param)# exit |
Exits to global configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# dial-peer voice 250 pots |
Configures incoming dial peer and enters dial-peer configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# service mcid |
Configures the incoming dial peer to use the MCID application. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# incoming called-number 222.... |
Configures the incoming called number for the MCID application. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# direct-inward-dial |
Configures direct-inward-dial (DID) for the MCID application. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# port 3/0:23 |
Configures the port for the MCID application.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# exit |
Exits to global configuration mode. |
Configuring MCID on the Voice Gateway in Earlier Release
Use this procedure to define the MCID application on a voice gateway that is running Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T. To verify your release, use the show version command.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# call application voice mcid flash:app_mcid.2.0.0.40.tcl |
Specifies the name and location of the MCID script. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# call application voice mcid mcid-release-timer 30 |
(Optional) Number of seconds the script waits to release both call legs after it receives a disconnect message. Default is 60 seconds. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# dial-peer voice 250 pots |
Configures incoming dial peer and enters dial-peer configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# application mcid |
Configures the incoming dial peer to use the MCID application. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# incoming called-number 222.... |
Configures the incoming called number for the MCID application. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# direct-inward-dial |
Configures direct-inward-dial (DID) for the MCID application. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# port 3/0:23 |
Configures the port for the MCID application.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# exit |
Exits to global configuration mode. |
Configuration Examples for MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
Configuring MCID on Cisco 2801 Example
The following example is for Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T:
Current configuration : 1695 bytes ! version 12.3 no service timestamps debug uptime no service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname router_2801 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 40960 debugging no logging console ! no aaa new-model ! resource manager ! network-clock-participate wic 2 mmi polling-interval 60 no mmi auto-configure no mmi pvc mmi snmp-timeout 180 ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! no ip dhcp use vrf connected ! ! no ip domain lookup no ftp-server write-enable isdn switch-type primary-net5 ! voice-card 0 ! ! ! application service mcid flash:app_mcid.2.0.0.40.tcl param mcid-release-timer 10 param retry-count 3 ! ! controller T1 0/2/0 framing esf clock source internal linecode b8zs pri-group timeslots 1-24 ! controller T1 0/2/1 framing esf linecode b8zs ! ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 9.1.0.102 255.255.0.0 duplex auto speed auto no keepalive ! interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/2/0:23 no ip address isdn switch-type primary-net5 isdn incoming-voice voice isdn supp-service mcid isdn T-Activate 5000 no cdp enable ! ip classless ! ip http server ! disable-eadi ! ! control-plane ! ! voice-port 0/2/0:23 ! ccm-manager music-on-hold ! ! dial-peer voice 500 pots service mcid destination-pattern 111111.... incoming called-number 555555.... direct-inward-dial port 0/2/0:23 prefix 111111 ! dial-peer voice 600 voip destination-pattern 555555.... session target ipv4:9.1.0.2 incoming called-number 111111.... playout-delay minimum low codec g711ulaw no vad ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! end
Configuring MCID on Cisco 3745 Example
The following exampl is for Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T :
Current configuration : 1492 bytes ! version 12.3 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname router_3745 ! ! voice-card 3 dspfarm ! no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ! ! ip domain name cisco.com mpls ldp logging neighbor-changes no ftp-server write-enable isdn switch-type primary-4ess no scripting tcl init no scripting tcl encdir ! ! no voice hpi capture buffer no voice hpi capture destination ! ! controller T1 3/0 framing esf linecode b8zs pri-group timeslots 1-24 ! controller T1 3/1 framing sf linecode ami ! ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.4.175.116 255.255.0.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet0/1 shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial3/0:23 no logging event link-status isdn switch-type primary-net5 isdn incoming-voice voice isdn supp-service mcid no cdp enable ! ip default-gateway 10.4.0.1 ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/0 ! ip http server ! ! control-plane ! ! call application voice mcid flash:app_mcid.2.0.0.40.tcl call application voice mcid mcid-release-timer 10 ! voice-port 3/0:23 ! mgcp call-agent 10.4.175.2 service-type mgcp version 0.1 ! mgcp profile default ! ! dial-peer voice 1 pots application mcid destination-pattern 2010 incoming called-number 2000 direct-inward-dial port 3/0:23 forward-digits all ! dial-peer voice 2 voip destination-pattern 2000 session target ipv4:10.4.175.2 ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! end
Where to Go Next
- To configure conferencing, transcoding, and MTP support on a Cisco IOS gateway, see "Configuring Enhanced Conferencing and Transcoding for Voice Gateway Routers" on page 67 .
- To enable MGCP PRI backhaul support, see "Configuring MGCP PRI Backhaul and T1 CAS Support for Cisco Unified Communications Manager" on page 113 .
- To enable MGCP BRI backhaul support, see "Configuring MGCP-Controlled Backhaul of BRI Signaling in Conjunction with Cisco Unified Communications Manager" on page 129 .
Additional References
- "Malicious Call Identification" chapter in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Features and Services Guide --Describes how to configure MCID in Cisco Unified Communications Manager 4.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 4.0).
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback