- Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Interoperability
- Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
- Configuring Conferencing and Transcoding for Voice Gateway Routers
- Configuring MGCP PRI Backhaul and T1 CAS Support
- Configuring MGCP-Controlled Backhaul of BRI Signaling
- Configuring Tone Download to MGCP Gateways
- Configuring MCID for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
- Configuring RSVP Agent
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
- Restrictions for Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
- Information about MGCP Gateway Support
- How to Configure MGCP Gateway Support
- Enabling MGCP on Cisco IOS Gateways
- Verifying MGCP Configuration on the Cisco IOS Gateway
- Configuring Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Configuring MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
- Verifying Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Configuring POTS Dial Peers on MGCP Gateways
- Verifying Dial Peer Configuration for MGCP Gateways
- Verifying Single-Point Configuration for MGCP Gateways
- Configuring Multicast Music-on-Hold
- Verifying Music-on-Hold
- Configuring MLPP Service on Cisco MGCP Gateways
- Configuring Fallback when Using MLPP on T1 CAS
- Verifying MLPP Configuration
- Configuration Examples for MGCP Gateway Support
- Where to Go Next
- Additional References
Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
This chapter describes the basic tasks for configuring Cisco IOS MGCP gateways to interoperate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Feature History for MLPP for Cisco IOS Voice Gateways
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.3(8)XY |
This feature was introduced. |
| 12.3(11)T |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T. |
Feature History for MGCP Generic Configuration Support for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.2(2)XN |
This feature was introduced. |
| 12.2(11)T |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T. |
Feature History for Multicast Music-on-Hold
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.2(2)XN |
This feature was introduced. |
| 12.2(11)T |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T. |
Feature History for MGCP Support for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.1(3)T |
This feature was introduced for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 3.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 3.0). |
| 12.1(5)XM |
H.323 support was added for E1 and T1 PRI, E&M, E1-CAS, and BRI. Analog support for MGCP and analog DID were added. |
| 12.2(2)XA |
Support was added for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 3.0(8) (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 3.0(8)). |
| 12.2(2)XN |
Support was added for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 3.1 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 3.1). New MGCP features included ISDN PRI Backhaul and T1 CAS, Single-Point Configuration, MGCP Gateway Fallback, and Multicast Music-on-Hold (MOH). |
| 12.2(11)T |
Support was added for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 3.2 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 3.2). |
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn . You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
For more information about this and related Cisco IOS voice features, see the following:
- "Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco IOS Interoperability" on page 13 .
- Entire Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library--including library preface and glossary, other feature documents, and troubleshooting documentation--at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios123/123cgcr/voice_c/vcl.htm .
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
- Cisco IOS gateway is configured for VoIP.
- Voice interface card or network module is installed.
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 3.2 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager version 3.2) or later is used.
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 4.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager version 4.0) or later version is used.
Restrictions for Configuring MGCP Gateway Support
- Integrated access is not supported when you control voice traffic using MGCP and Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Integrated access is when the channels on a T1 or E1 interface are divided between a group used for voice and another group used for WAN access.
- T1 and E1 protocols, such as E1 R2, T1 FGD, and PRI NFAS, are not supported with MGCP.
 Note |
Any configuration update that affects MGCP should be performed during a planned maintenance window while MGCP is disabled; otherwise, updating the configuration could disrupt MGCP functionality. Before making any configuration changes, disable MGCP using the no mgcp command. After all configuration changes are completed, use the mgcp command to enable MGCP. |
Information about MGCP Gateway Support
- MGCP Gateways and Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
- Gateway Single-Point Configuration for MGCP Gateways
- MLPP Service on Cisco MGCP Gateway
- Multicast Music-on-Hold
MGCP Gateways and Cisco Unified Communications Manager
MGCP enables the remote control and management of voice and data communications devices at the edge of multiservice IP packet networks. Because of its centralized architecture, MGCP overcomes the distributed configuration and administration problems inherent in the use of protocols such as H.323. MGCP simplifies the configuration and administration of voice gateways and supports multiple (redundant) call agents, eliminating the potential for a single point of failure in controlling the Cisco IOS gateway in the network.
MGCP can be configured as a master or slave protocol to ensure that the gateway receives and executes the configuration, control, and management commands that are issued by Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The MGCP gateway is under the control of Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
MGCP uses endpoints and connections to construct a call. Endpoints are sources of or destinations for data and can be physical or logical locations identifying a device. The voice ports on the Cisco MGCP gateway are its endpoints. Connections can be point-to-point or multipoint. Cisco Unified Communications Manager acts as the MGCP call agent, managing connections between endpoints and controlling how the Cisco IOS gateway functions.
The figure below shows a typical MGCP gateway that is controlled by an MGCP call agent.
| Figure 1 | MGCP Gateway Controlled by Cisco Unified Communications Manager |
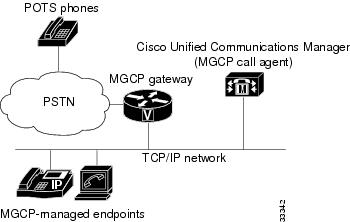
The MGCP gateway receives most of its required configuration from the call agent. To configure an MGCP gateway, you simply identify the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server associated with the gateway and identify the gateway to the call agent. The MGCP gateway handles the translation between voice signals and the packet network and interacts with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server. The server performs signal and call processing.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
This section describes how to configure Cisco Unified Communications Manager failover capabilities on the MGCP gateway.
- Switchover
- Switchback
- MGCP Gateway Fallback
- MGCP Gateway Registration with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Benefits of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
Switchover
Cisco IOS gateways can maintain links to up to two backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers in addition to a primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager. This redundancy enables a voice gateway to switchover to a backup if the gateway loses communication with the primary. The backup server takes control of the devices that are registered with the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The second backup takes control of the registered devices if both the primary and first backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager fail. The gateway preserves existing connections during a switchover to a backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
When the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager server becomes available again, control reverts to that server. Reverting to the primary server can occur immediately, after a configurable amount of time, or only when all connected sessions are released.
Switchback
Switchback is the process a voice gateway uses to reestablish communication with the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager server when the server becomes available again. Switchback can occur immediately, at a specified time after the last active call ends, or after a specified length of time.
MGCP Gateway Fallback
The MGCP gateway maintains a remote connection to a centralized Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster by sending MGCP keepalive messages to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server at 15-second intervals. If the active Cisco Unified Communications Manager server fails to acknowledge receipt of the keepalive message within 30 seconds, the gateway attempts to switch over to the next available Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
If none of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers respond, the gateway switches into fallback mode and reverts to the default H.323 session application for basic call control. H.323 is a standardized communication protocol that enables dissimilar devices to communicate with each other through use of a common set of codecs, call setup and negotiating procedures, and basic data transport methods. The gateway processes calls on its own using H.323 until one of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager connections is restored.
The figure below illustrates a typical VoIP network topology in which MGCP gateway fallback is supported.
| Figure 2 | Typical VoIP Network Topology Supporting the MGCP Gateway Fallback Feature |
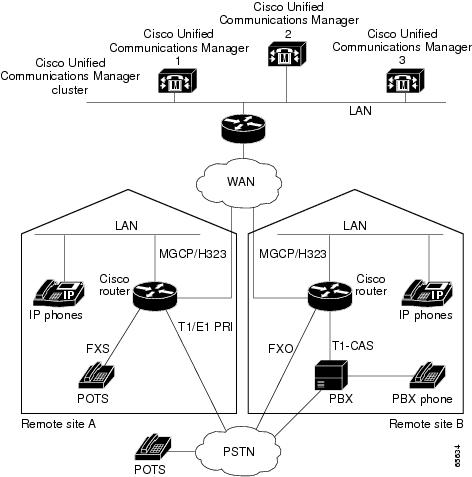
The MGCP Gateway Fallback feature provides the following functionality:
- MGCP gateway fallback support--All active MGCP analog and T1 CAS calls are maintained during the fallback transition. Callers are unaware of the fallback transition, and the active MGCP calls are cleared only when the communicating callers hang up. Active MGCP PRI backhaul calls are released during fallback.
Any transient MGCP calls (that is, calls that are not in the connected state) are cleared at the onset of the fallback transition and must be attempted again later.
- Basic connection services in fallback mode--Provides basic connection services for IP telephony traffic that passes through the gateway. When the local MGCP gateway transitions into fallback mode, the default H.323 session application assumes responsibility for handling new calls. Only basic two-party voice calls are supported during the fallback period.
Except for ISDN T1 and E1 PRI calls, all the MGCP calls that are active at the time of fallback are preserved, but transient calls are released. When a user completes (hangs up) an active MGCP call, the MGCP application handles the on-hook event and clears all call resources.
- Rehome support--Provides a rehome function in the gateway fallback mode that detects the restoration of a WAN TCP connection to the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
When the fallback mode is in effect, the affected MGCP gateway repeatedly tries to open a TCP connection to a Cisco Unified Communications Manager server in the prioritized list of call agents. This process continues until one of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers in the prioritized list responds.
The TCP open request from the MGCP gateway is honored, and the gateway reverts to MGCP mode. The gateway sends a Restart-in-Progress (RSIP) message to begin registration with the responding Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
All currently active calls that are initiated and set up during the fallback period are maintained by the default H.323 session application, except ISDN T1 and E1 PRI calls. Transient calls are released. After rehome occurs, the new Cisco Unified Communications Manager assumes responsibility for controlling new IP telephony activity.
The following types of interfaces on the gateway are supported:
MGCP Gateway Registration with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
The table below describes what can happen when either the gateway loses connection to the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager or the gateway also loses connection to all backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers.
| Table 1 | Registration Scenarios |
| Terminology |
Connection |
Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Gateway Connection to Primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager |
||
| Failover (also called switchover) |
Gateway loses connection to primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager. |
Gateway switches over to a backup. |
| Switchback |
Gateway reconnects to primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager. |
Gateway switches back to the primary. |
| Gateway connection to all Cisco Unified Communications Manager Servers |
||
| Fallback |
Gateway loses connection to primary and all backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers. |
Gateway falls back to H.323 call processing. |
| Rehome |
Gateway reconnects to one of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers. |
Gateway rehomes, resuming MGCP call processing. |
Any calls at the time of reregistration (even those in a transient state such as call setup) remain undisturbed. The newly registered Cisco Unified Communications Manager determines the status of existing calls and maintains or deletes them as appropriate.
Benefits of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Eliminates a potential single point of failure in the VoIP network by allowing you to designate up to two backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers. Your MGCP voice gateways can continue working if the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager server fails.
- Ensures greater stability in the voice network by preserving existing connections during a switchover to a backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
- Prevents call-processing interruptions or dropped calls in the event of a Cisco Unified Communications Manager or WAN failure.
MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
Cisco Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) provides Cisco Unified Communications Manager with fallback support for Cisco IP phones that are attached to a Cisco router on your local network. Cisco SRST enables routers to provide call-handling support for Cisco IP phones when they lose connection to remote primary, secondary, or tertiary Cisco Unified Communications Manager installations or when the WAN connection is down.
MGCP gateway fallback is a different feature than SRST, and when MGCP gateway fallback is configured as an individual feature, it can be used by a PSTN gateway if you configure H.323 (or some other voice application) as a backup service. To use SRST as your fallback mode on an MGCP gateway, you must configure SRST and MGCP fallback on the same gateway. MGCP and SRST have had the capability to be configured on the same gateway since Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)T.
- Cisco SRST Description
- Configuring MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
- Enabling SRST on an MGCP Gateway
Cisco SRST Description
Cisco Unified Communications Manager supports Cisco IP phones at remote sites that are attached to Cisco multiservice routers across the WAN. Prior to Cisco SRST, when the WAN connection between a router and the Cisco Unified Communications Manager failed or when connectivity with Cisco Unified Communications Manager was lost for some reason, Cisco Unified IP phones on the network became unusable for the duration of the failure. Cisco SRST overcomes this problem and ensures that Cisco Unified IP phones offer continuous (although minimal) service by providing call-handling support for Cisco Unified IP phones directly from the Cisco SRST router. The system automatically detects a failure and uses Simple Network Auto Provisioning (SNAP) technology to autoconfigure the branch office router to provide call processing for Cisco Unified IP phones that are registered with the router. When the WAN link or connection to the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager is restored, call handling reverts back to the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
For more information on Cisco SRST, see Overview of Cisco IOS SRST .
Configuring MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
To make outbound calls while in SRST mode on your MGCP gateway, you must configure two fallback commands on the MGCP gateway. These two commands allow SRST to assume control over the voice port and over call processing on the MGCP gateway. With Cisco IOS releases prior to 12.3(14)T, you must configure MGCP gateway fallback by using the ccm-manager fallback-mgcp and call application alternate commands. With Cisco IOS releases after 12.3(14)T, you must configure MGCP gateway fallback by using the ccm-manager fallback-mgcp and service commands.
 Note |
You must configure both commands. For instance, your configuration will not work if you only configure the ccm-manager fallback-mgcp command. |
Enabling SRST on an MGCP Gateway
To use SRST as your fallback mode with an MGCP gateway, you must configure both SRST and MGCP fallback on the same gateway. The following configuration allows SRST to assume control over the voice port and over call processing on the MGCP gateway.
Gateway Single-Point Configuration for MGCP Gateways
When you configure MGCP gateways to support Cisco Unified Communications Manager, you can use a centralized TFTP boot directory on a host device in your network to automatically download most of the configuration in the XML files. Each MGCP gateway in your VoIP network has an associated gateway-specific configuration that is stored in the centralized TFTP boot directory. A tailored XML file can be created and downloaded from the TFTP server to your designated MGCP gateway. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager server can be configured concurrently as a TFTP server.
When you make changes to the configuration in the database, a message is sent by Cisco Unified Communications Manager to the affected MGCP gateway, instructing the gateway devices to download the new XML configuration file. Each device has an XML parser that interprets the XML file according to its device-specific requirements. Cisco MGCP gateways, for example, translate the content of the XML file into specific Cisco IOS commands for local execution.
When an MGCP gateway is first started up, it is preconfigured with the following information or it obtains the information through Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP):
- A unique device identifier, which can be either of the following:
- IP address of the TFTP server in the network and routing information required for access
- Sufficient information for configuration of an IP interface on the device
With this configuration information available at startup, the MGCP gateway downloads the XML file from the TFTP server. The gateway parses the XML file, converts the information to appropriate Cisco IOS configuration commands, and configures itself to run in the VoIP network. Finally, the gateway registers itself with Cisco Unified Communications Manager using an RSIP message. At that point, the MGCP gateway is ready for service in the network.
After a successful configuration download, the MGCP gateway saves the running configuration to nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM), which updates the startup configuration. Any manually-added configuration parameters are also saved to NVRAM if they were not previously saved. Manually-added configuration parameters are updates to the configuration that were made using the command-line interface (CLI). Manual configuration updates are separate from the automatic configuration updates made during the configuration download process.
In the event of a configuration failure, the MGCP gateway attempts to restore its current configuration by copying the startup configuration from NVRAM into the running configuration. Because this overwrites the running configuration, any manually-added configuration parameters could be lost if they were not saved to NVRAM before running the automatic configuration-download process.
| Figure 3 | Single-Point Configuration for Cisco MGCP Gateways |
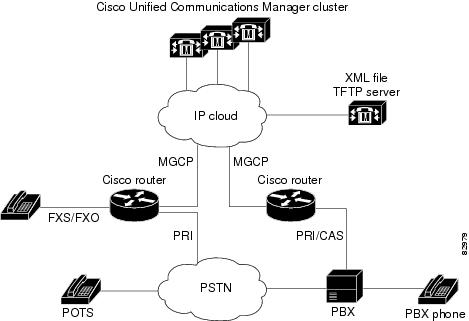
MLPP Service on Cisco MGCP Gateway
Multilevel Precedence and Preemption (MLPP) is a service that allows authorized users to preempt lower priority voice calls to targeted stations or fully subscribed shared resources such as TDM trunks or conference bridges. This capability ensures high-ranking personnel of communication to critical organizations and personnel during network stress situations such as a national emergency. MLPP enables the voice gateway to interoperate with other MLPP-capable networks for call preemption and precedence. MLPP is supported only for MGCP endpoints over T1 CAS (E&M wink start) and T1 PRI using the backhaul feature.
MLPP service applies only to the subscribers and network resources within a specific domain. Connections and resources for a call from an MLPP subscriber are marked with a precedence level and domain identifier. A call can only be preempted by calls of higher precedence from MLPP users in the same domain. The Cisco Communications Manager or defense switched network (DSN) switch sets the maximum precedence level of a subscriber at subscription time.
For more information about MLPP, see the "Multilevel Precedence and Preemption" chapter in the Cisco CallManager Features and Services Guide , Release 4.0(1).
MLPP Call Treatment During Cisco Unified Communications Manager Switchover
When a Cisco Unified Communications Manager server fails during the processing of an MLPP call, the call is treated as a transient call and is dropped. The gateway releases the trunks and does a switchover to the backup Cisco Communications Manager server or falls back to H.323 mode, depending on the availability of the backup server. All currently connected MLPP calls are preserved during the switchover, switchback, or fallback process. After the gateway reregisters with Cisco Communications Manager, call precedence and domain are preserved. During fallback, an incoming MLPP call is treated as a routine priority call.
Multicast Music-on-Hold
The Music-on-Hold (MOH) feature enables you to subscribe to a music streaming service when you are using a Cisco IOS MGCP voice gateway. Music streams from an MOH server to the voice interfaces of on-net and off-net callers that have been placed on hold. Cisco Communications Manager supports the capability to place callers on hold with music supplied from a streaming multicast MOH server. This integrated multicast capability is implemented through the H.323 signaling in Cisco Communications Manager.
By means of a preconfigured multicast address on the gateway, the gateway can "listen" for Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) packets that are broadcast from a default router in the network and can relay the packets to designated voice interfaces in the network. Whenever a called party places a calling party on hold, Cisco Communications Manager requests the MOH server to stream RTP packets to the "on-hold" interface through the preconfigured multicast address. In this way, RTP packets are relayed to appropriately configured voice interfaces that have been placed on hold. When you configure a multicast address on a gateway, the gateway sends an Internet Gateway Management Protocol (IGMP) "join" message to the default router, indicating to the default router that the gateway is ready to receive RTP multicast packets.
Multiple MOH servers can be present in the same network, but each server must have a different Class D IP address, and the address must be configured in Cisco Communications Manager and the MGCP voice gateways.
How to Configure MGCP Gateway Support
- Enabling MGCP on Cisco IOS Gateways
- Verifying MGCP Configuration on the Cisco IOS Gateway
- Configuring Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Configuring MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
- Verifying Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
- Configuring POTS Dial Peers on MGCP Gateways
- Verifying Dial Peer Configuration for MGCP Gateways
- Verifying Single-Point Configuration for MGCP Gateways
- Configuring Multicast Music-on-Hold
- Verifying Music-on-Hold
- Configuring MLPP Service on Cisco MGCP Gateways
- Configuring Fallback when Using MLPP on T1 CAS
- Verifying MLPP Configuration
Enabling MGCP on Cisco IOS Gateways
Perform this task to enable MGCP on a Cisco IOS gateway to support Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying MGCP Configuration on the Cisco IOS Gateway
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | show running-config Use the show running-config command to verify that MGCP is enabled on the voice gateway: Example:
Router# show running-config
...
hostname voice-3640
!
...
mgcp
mgcp call-agent 10.0.0.21 service-type mgcp version 0.1
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band
!
ccm-manager mgcp
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 10.10.2.23 255.255.255.0
half-duplex
|
||
| Step 2 | show interfaces ethernet Use the show interfaces ethernet command to verify that an Ethernet interface is configured to communicate with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server, for example: Example:
Router# show interfaces ethernet 4/2
Ethernet4/2 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is cxBus Ethernet, address is 0000.0c02.d0ce (bia 0000.0c02.d0ce)
Internet address is 10.10.7.1, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 4:00:00
Last input 0:00:00, output 0:00:09, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 0:56:40
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
Five minute input rate 3000 bits/sec, 4 packets/sec
Five minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
4961 packets input, 715381 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 2014 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
567 packets output, 224914 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 168 collisions, 0 interface resets, 0 restarts
0 babbles, 2 late collision, 7 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
|
||
| Step 3 | show mgcp Use the show mgcp command to display the MGCP settings on the Cisco IOS gateway: Example:
Router# show mgcp
MGCP Admin State ACTIVE, Oper State ACTIVE - Cause Code NONE
!MGCP call agent with IP address for Cisco Unified Communications Manager:
MGCP call-agent: 10.0.0.21 2427 Initial protocol service is MGCP, v. 0.1
MGCP block-newcalls DISABLED
MGCP send RSIP for SGCP is DISABLED
MGCP quarantine mode discard/step
MGCP quarantine of persistent events is ENABLED
!DTMF-relay voip codec parameters:
MGCP dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band
MGCP dtmf-relay for VoAAL2 disabled for all codec types
MGCP voip modem passthrough mode: CISCO, codec: g711ulaw, redundancy: DISABLED,
MGCP voaal2 modem passthrough mode: NSE, codec: g711ulaw
MGCP TSE payload: 0
MGCP Network (IP/AAL2) Continuity Test timer: 200
MGCP 'RTP stream loss' timer: 5
MGCP request timeout 500, MGCP request retries 3
MGCP rtp unreachable timeout 1000
MGCP gateway port: 2427, MGCP maximum waiting delay 3000
MGCP restart delay 0, MGCP vad DISABLED
MGCP simple-sdp DISABLED
MGCP undotted-notation DISABLED
MGCP codec type g711ulaw, MGCP packetization period 20
MGCP JB threshold lwm 30, MGCP JB threshold hwm 150
MGCP LAT threshold lmw 150, MGCP LAT threshold hwm 300
MGCP PL threshold lwm 1000, MGCP PL threshold hwm 10000
MGCP CL threshold lwm 1000, MGCP CL threshold hwm 10000
MGCP playout mode is adaptive 60, 4, 200 in msec
MGCP IP ToS low delay disabled, MGCP IP ToS high throughput disabled
MGCP IP ToS high reliability disabled, MGCP IP ToS low cost disabled
MGCP IP RTP precedence 5, MGCP signaling precedence: 3
MGCP default package: line-package
MGCP supported packages: gm-package dtmf-package trunk-package line-package
hs-package rtp-package ms-package dt-package sst-packagc-package
MGCP VoAAL2 ignore-lco-codec DISABLED
MGCP T.38 Fax is DISABLED
|
Configuring Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ccm-manager redundant-host 10.0.0.50 |
Identifies up to two backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ccm-manager switchback immediate |
Configures switchback mode for returning control to the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ccm-manager fallback-mgcp |
Enables the MGCP fallback feature. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# call application alternate |
Specifies that the default voice application takes over if the MGCP application is not available. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router# ccm-manager switchover-to-backup |
Manually redirects the MGCP gateway to the backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager server. The switchover to the backup Cisco Unified Communications Manager server occurs immediately.
|
Configuring MGCP Gateway Fallback and Cisco SRST
 Note |
Effective with Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T, the call application alternate command has been replaced by the service command. You can use the service command cin all releases after Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T. Both commands are reflected in Step 4 . |
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enters privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. |
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ccm-mananger fallback-mgcp |
Enables the gateway fallback feature and allows an MGCP voice gateway to provide call processing services through SRST or other configured applications when Cisco Unified Communications Manager is unavailable. |
|
|
Example: service [alternate|default] service-name location Example: Router(config)# call application alternate Example: Router(config)# service default |
With Cisco IOS releases prior to 12.3(14)T, the call application alternatecommand specifies that the default voice application takes over if the MGCP application is not available. The application-name argument is optional and indicates the name of the specific voice application to use if the application dial peer fails. If a specific application name is not entered, the gateway uses the DEFAULT application. or With Cisco IOS releases after 12.3(14)T, the service command loads and configures a specific, standalone application on a dial peer. The keywords and arguments are as follows:
|
|
|
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Verifying Switchover and MGCP Gateway Fallback
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | show running-config Use the show running-config command to verify configuration of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager failover options, for example: Example:
Router# show running-config
...
ccm-manager switchback immediate
ccm-manager fallback-mgcp
ccm-manager redundant-host 10.0.0.50
ccm-manager mgcp
.
.
.
call application alternate DEFAULT
! |
||
| Step 2 | show ccm-manager Use the show ccm-manager command to verify the Cisco Unified Communications Manager failover options. The following example shows one Cisco Unified Communications Manager backup server is configured. Switchback mode is set for immediate return to the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager server as soon as the server is available. Example:
Router# show ccm-manager
MGCP Domain Name: router.cisco.com
Total number of host: 2
Priority Status Host
===================================================
Primary Registered 10.0.0.201
First backup Backup polling 10.0.0.50
Second backup Undefined
Current active Communications Manager: 10.0.0.201
Current backup Communications Manager: 10.0.0.50
Redundant link port: 2428
Failover Interval: 30 seconds
Keepalive Interval: 15 seconds
Last keepalive sent: 00:20:18 (elapsed time: 00:00:06)
Last MGCP traffic time: 00:20:18 (elapsed time: 00:00:06)
Last switchover time: None
Switchback mode: Immediate
|
||
| Step 3 | show ccm-manager fallback-mgcp Use the show ccm-manager fallback-mgcp command to verify whether MGCP fallback is enabled and whether it is active or not (on or off), for example: Example:
Router# show ccm-manager fallback-mgcp
Current active Communications Manager: 10.00.71.29
MGCP Fallback mode: Enabled/OFF
Last MGCP Fallback start time: 00:00:00
Last MGCP Fallback end time: 00:00:00
|
Configuring POTS Dial Peers on MGCP Gateways
Perform this task to enable the POTS dial peers on your MGCP gateway to communicate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
When you have finished this procedure, the voice gateway is ready to communicate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager. It periodically sends out messages attempting to establish a connection. When the Cisco Unified Communications Manager configuration is complete, the connection should automatically establish itself. You should not have to make any further changes on the MGCP gateway.
 Note |
|
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config)# dial-peer voice 101 pots |
Designates the specified dial peer as a POTS device and enters dial-peer configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# application mgcpapp |
Enables MGCP on the dial peer.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# direct-inward-dial |
(Optional) Enables the direct inward dialing (DID) call treatment for an incoming called number.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# port 1/0/1 |
Binds the MGCP application to the specified voice port.
|
||
|
|
Example: Router(config-dial-peer)# exit |
Exits dial-peer configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. |
Verifying Dial Peer Configuration for MGCP Gateways
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
show running-config Use the show running-config command to verify the dial peer configuration. The following example shows two Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) ports and one Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) port that are configured to run under MGCP control. Slot numbering and port numbering begin at 0. Example: ! FXO port dial-peer voice 1 pots application mgcpapp port 1/0/0 ! ! FXO port dial-peer voice 2 pots application mgcpapp port 1/0/1 ! ! FXS port dial-peer voice 3 pots application mgcpapp port 1/1/0 The following example shows a configuration on MGCP voice gateways for T1 CAS with e&m-wink-start emulation. Example: ccm-manager switchback immediate ccm-manager fallback-mgcp ccm-manager mgcp ! controller T1 1/0 framing esf linecode b8zs ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-24 type e&m-wink-start ! voice-port 1/0:1 ! dial-peer voice 1 pots application mgcpapp destination-pattern 91.......... port 1/0:1 The following example shows a configuration on MGCP voice gateways for FXS ports. Example: dial-peer voice 1 pots application mgcpapp destination-pattern 555-1212 port 1/0/0 The following example shows a configuration on MGCP voice gateways for FXO ports. Example: dial-peer voice 2 pots application mgcpapp destination-pattern 527.... prefix 527 port 1/1/1 The following example shows a configuration on MGCP gateways for VoIP calls, when the fallback feature is used. Example: dial-peer voice 555 voip application mgcpapp destination pattern 555... incoming-called-number 444... session-target ipv4:172.20.21.8 codec g711ulaw
|
||
| Step 2 |
show dial-peer voice Use the show dial-peer voice command to verify the configuration of the POTS dial peer, for example: Example: Router# show dial-peer voice 1000 VoiceEncapPeer1000 information type = voice, description = `', tag = 1000, destination-pattern = `', answer-address = `', preference=0, numbering Type = `unknown' group = 1000, Admin state is up, Operation state is down, incoming called-number = `', connections/maximum = 0/unlimited, DTMF Relay = disabled, huntstop = disabled, in bound application associated: 'mgcpapp' out bound application associated: '' dnis-map = permission :both incoming COR list:maximum capability outgoing COR list:minimum requirement type = pots, prefix = `', forward-digits default session-target = `', voice-port = `', direct-inward-dial = disabled, digit_strip = enabled, register E.164 number with GK = TRUE Connect Time = 0, Charged Units = 0, Successful Calls=0, Failed Calls=0, Incomplete Calls=0 Accepted Calls = 0, Refused Calls = 0, Last Disconnect Cause is "", Last Disconnect Text is "", Last Setup Time = 0. |
||
| Step 3 |
show voice port Use the show voice port command to verify that the voice port is operational. The following is sample output from a Cisco 3600 series router with an FXS analog voice port: Example: Router# show voice port 1/0/0 Foreign Exchange Office 1/0/0 Slot is 1, Sub-unit is 0, Port is 0 Type of VoicePort is FXO Operation State is DORMANT Administrative State is UP No Interface Down Failure Description is not set Noise Regeneration is enabled Non Linear Processing is enabled Non Linear Mute is disabled Non Linear Threshold is -21 dB Music On Hold Threshold is Set to -38 dBm In Gain is Set to 0 dB Out Attenuation is Set to 3 dB Echo Cancellation is enabled Echo Cancellation NLP mute is disabled Echo Cancellation NLP threshold is -21 dB Echo Cancel Coverage is set to 8 ms Playout-delay Mode is set to default Playout-delay Nominal is set to 60 ms Playout-delay Maximum is set to 200 ms Playout-delay Minimum mode is set to default, value 40 ms Playout-delay Fax is set to 300 ms Connection Mode is normal Connection Number is not set Initial Time Out is set to 10 s Interdigit Time Out is set to 10 s Call Disconnect Time Out is set to 60 s Ringing Time Out is set to 180 s Wait Release Time Out is set to 30 s Companding Type is u-law Region Tone is set for US Analog Info Follows: Currently processing none Maintenance Mode Set to None (not in mtc mode) Number of signaling protocol errors are 0 Impedance is set to 600r Ohm Station name None, Station number None Translation profile (Incoming): Translation profile (Outgoing): Voice card specific Info Follows: Signal Type is loopStart Number Of Rings is set to 1 Supervisory Disconnect is inactive Answer Supervision is inactive Hook Status is On Hook Ring Detect Status is inactive Ring Ground Status is inactive Tip Ground Status is inactive Dial Type is dtmf Digit Duration Timing is set to 100 ms InterDigit Duration Timing is set to 100 ms Pulse Rate Timing is set to 10 pulses/second InterDigit Pulse Duration Timing is set to 750 ms Percent Break of Pulse is 60 percent GuardOut timer is 2000 ms
|
Verifying Single-Point Configuration for MGCP Gateways
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | show running-config Use the show running-config command to verify the single-point download configuration, for example: Example: Router# show running-config ... ccm-manager switchback immediate ccm-manager fallback-mgcp ccm-manager redundant-host 10.10.10.1 ccm-manager mgcp ccm-manager music-on-hold ccm-manager config server 10.10.1.10 ccm-manager config ! |
||
| Step 2 | show ccm-manager config-download Use the show ccm-manager config-download command to verify the download status. The output indicates that four downloads were successful. Example:
Router# show ccm-manager config-download
Configuration Auto-download Information
=======================================
Current version-id: {1645327B-F59A-4417-8E01-7312C61216AE}
Last config-downloaded:00:00:49
Current state: Waiting for commands
Configuration Download statistics:
Download Attempted : 4
Download Successful : 4
Download Failed : 0
Configuration Attempted : 1
Configuration Successful : 1
Configuration Failed(Parsing): 0
Configuration Failed(config) : 0
Last config download command: New Registration
|
Configuring Multicast Music-on-Hold
This section describes how to configure your gateway to provide music to customers on hold.
The default router in the network for handling multicast traffic must have the following enabled:
- Multicast routing
- A multicast routing protocol, for example Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) or Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP)
- An IP routing protocol, for example Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 3.1 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 3.1) or higher
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ccm-manager music-on-hold |
Enables music-on-hold. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# ccm-manager music-on-hold bind async |
(Optional) Binds the multicast MOH feature to a designated interface. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode. |
Verifying Music-on-Hold
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | show running-config Use the show running-config command to verify the MOH configuration, for example: Example:
Router# show running-config
...
ccm-manager redundant-host 10.0.0.21
ccm-manager mgcp
ccm-manager music-on-hold
ccm-manager config server 10.0.0.21
ccm-manager config
! |
||
| Step 2 | show ccm-manager music-on-hold Use the show ccm-manager music-on-hold command to display information about the currently active MOH sessions, for example: Example:
Router#
show ccm-manager music-on-hold
Multicast RTP Packets Call Incoming
Address Port In/Out ID Protocol Interface
10.10.20.22 16256 3000/3000 1 IGMP fe0/0
|
Configuring MLPP Service on Cisco MGCP Gateways
Perform this task to configure the MGCP package capability for MLPP.
 Note |
If you downloaded the default configuration file from TFTP, you do not need to manually configure MLPP on the MGCP gateway. The MLPP configuration is contained in the default configuration. |
- Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T or later
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 4.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 4.0) or later
- DSPWare 4.0
- Telogy DSP4 (Catalyst 6000 switches)
- Preemptions and precedences should be configured in Cisco Communications Manager. Interfaces, dial peers, voice ports, controllers, framing, and line codes should also be configured.
- Cisco Catalyst 6500 series and Cisco 7600 series Communication Media Module (CMM) requires WS-SVC-CMM-6T1 port adapter.
 Note |
|
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# mgcp package-capability pre-package |
Enables MLPP as an MGCP package capability type on the voice gateway. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring Fallback when Using MLPP on T1 CAS
When the gateway is in fallback mode, the precedence digit must be stripped from the dial string for T1 CAS calls. Perform this task to configure SRST to handle stripping the precedence digit.
 Note |
For information on configuring digit stripping options for your specific dial plan, see the "Setting Up Call Handling" chapter in the Cisco Survivable Remote Site Telephony Version 3.2 System Administration Guide . |
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
|
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: Router(config)# call-manager-fallback |
Enters call-manager-fallback configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: Router(config-cm-fallback)# ip source-address 10.10.200.23 port 2000 |
Enables the voice gateway to receive messages from the Cisco IP phones through the specified IP addresses and provides for strict IP address verification. |
|
|
Example: Router(config-cm-fallback)# max-dn 12 |
Sets the maximum number of directory numbers or virtual voice ports that can be supported by the voice gateway. The maximum number is platform dependent. |
|
|
Example: Router(config-cm-fallback)# max-ephones 10 |
Configures the maximum number of Cisco IP phones that can be supported by the voice gateway. The maximum number is platform dependent. |
|
|
Example: Router(config-cm-fallback)# dialplan-pattern 1 [A-D].... extension-length 4 |
Creates a global prefix that can be used to expand the abbreviated extension numbers into fully qualified E.164 numbers. |
|
|
Example: Router(config-cm-fallback)# translate calling 1 |
Applies a translation rule to modify the phone number dialed or received by any Cisco IP phone user while Cisco Communications Manager fallback is active. |
|
|
Example: Router(config-cm-fallback)# end |
Exits to privileged EXEC mode. |
Verifying MLPP Configuration
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | Use the show running-config command to verify the configuration of the MGCP package, for example: Example: Router# show running-config ... mgcp mgcp call-agent OTHERCLUSTER 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1 mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 action notify mgcp package-capability rtp-package no mgcp package-capability res-package mgcp package-capability sst-package no mgcp package-capability fxr-package mgcp package-capability pre-package no mgcp timer receive-rtcp mgcp sdp simple no mgcp validate domain-name mgcp fax t38 inhibit mgcp rtp payload-type g726r16 static ! mgcp profile default ! |
| Step 2 | Use the show mgcp command to display the MGCP configuration details, for example: Example: Router# show mgcp MGCP Admin State ACTIVE, Oper State ACTIVE - Cause Code NONE MGCP call-agent: 172.18.195.147 2300 Initial protocol service is SGCP 1.5 MGCP block-newcalls DISABLED MGCP send SGCP RSIP:forced/restart/graceful DISABLED, disconnected ENABLED MGCP quarantine mode discard/step MGCP quarantine of persistent events is ENABLED MGCP dtmf-relay for VoIP disabled for all codec types MGCP dtmf-relay voaal2 codec all MGCP voip modem passthrough mode: NSE, codec: g711ulaw, redundancy: DISABLED, MGCP voaal2 modem passthrough mode: NSE, codec: g711ulaw MGCP TSE payload: 100 MGCP T.38 Named Signalling Event (NSE) response timer: 200 MGCP Network (IP/AAL2) Continuity Test timer: 3000 MGCP 'RTP stream loss' timer: 2 MGCP request timeout 500 MGCP maximum exponential request timeout 4000 MGCP gateway port: 2427, MGCP maximum waiting delay 3000 MGCP restart delay 0, MGCP vad DISABLED MGCP rtrcac DISABLED MGCP system resource check DISABLED MGCP xpc-codec: DISABLED, MGCP persistent hookflash: DISABLED MGCP persistent offhook: ENABLED, MGCP persistent onhook: DISABLED MGCP piggyback msg DISABLED, MGCP endpoint offset DISABLED MGCP simple-sdp DISABLED MGCP undotted-notation DISABLED MGCP codec type g711ulaw, MGCP packetization period 20 MGCP JB threshold lwm 30, MGCP JB threshold hwm 150 MGCP LAT threshold lmw 150, MGCP LAT threshold hwm 300 MGCP PL threshold lwm 1000, MGCP PL threshold hwm 10000 MGCP CL threshold lwm 1000, MGCP CL threshold hwm 10000 MGCP playout mode is adaptive 60, 4, 200 in msec MGCP IP ToS low delay disabled, MGCP IP ToS high throughput disabled MGCP IP ToS high reliability disabled, MGCP IP ToS low cost disabled MGCP IP RTP precedence 5, MGCP signaling precedence: 3 MGCP default package: line-package MGCP supported packages: gm-package dtmf-package trunk-package line-package hs-package atm-package ms-package dt-package res-package mt-package pre-package |
Configuration Examples for MGCP Gateway Support
 Note |
To view relevant configuration examples, go to the Cisco Systems Technologies website at http://cisco.com/en/US/tech/index.html . From the website, select Voice > IP Telephony/VoIP, then click Technical Documentation > Configuration Examples. |
- MGCP Gateway with T1 CAS Example
- MGCP Gateway with T1 PRI Example
- Multicast Music-on-Hold Example
- MLPP on Cisco 2801 Example
- MLPP on Cisco 2621 Example
MGCP Gateway with T1 CAS Example
The following example shows MGCP fallback configured on a voice gateway with T1 CAS.
Current configuration : 2181 bytes
!
version 12.2
no service single-slot-reload-enable
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Test-3640a
!
logging rate-limit console 10 except errors
!
memory-size iomem 25
voice-card 3
!
ip subnet-zero
!
no ip domain-lookup
ip domain-name test.com
!
no ip dhcp-client network-discovery
frame-relay switching
mgcp
mgcp call-agent 10.0.0.21 service-type mgcp version 0.1
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band
mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000
mgcp package-capability rtp-package
no mgcp timer receive-rtcp
call rsvp-sync
!
ccm-manager switchback immediate
ccm-manager fallback-mgcp
ccm-manager redundant-host 10.0.0.21
ccm-manager mgcp
!
controller T1 3/0
framing esf
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1 type e&m-wink-start
!
controller T1 3/1
framing sf
linecode ami
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.224
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.224
encapsulation frame-relay
no keepalive
frame-relay interface-dlci 300
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
clockrate 2000000
!
interface Ethernet2/0
ip address 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.224
half-duplex
!
interface TokenRing2/0
no ip address
shutdown
ring-speed 16
!
ip classless
ip route 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.0 14.0.0.1
ip route 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.0 14.0.0.1
ip route 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.0 14.0.0.1
ip route 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.0 14.0.0.1
ip route 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.255 Ethernet2/0
ip route 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.255 Ethernet2/0
no ip http server
!
snmp-server manager
!
voice-port 1/0/0
!
voice-port 1/0/1
!
voice-port 1/1/0
!
voice-port 1/1/1
!
voice-port 3/0:1
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
dial-peer voice 44 pots
application mgcpapp
destination-pattern 4301
port 1/1/0
!
dial-peer voice 55 pots
application mgcpapp
destination-pattern 4302
port 1/1/1
!
dial-peer voice 85 voip
destination-pattern 805....
session target ipv4:10.0.0.21
codec g711ulaw
!
dial-peer voice 33 pots
application mgcpapp
destination-pattern 807....
port 3/0:1
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
end
 Note |
If the ccm-manager config command is enabled and you separate the MGCP and H.323 dial peers under different tags, make sure that the MGCP dial peers are configured before the H.323 dial peers. |
MGCP Gateway with T1 PRI Example
The following example shows MGCP fallback configured on a voice gateway with T1 PRI ports.
version 12.2 no parser cache no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname voice-3640 ! logging rate-limit console 10 except errors ! voice-card 1 ! ip subnet-zero ! no ip domain-lookup ! no ip dhcp-client network-discovery mgcp mgcp call-agent 172.16.240.124 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1 mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 action notify mgcp modem passthrough voip mode cisco mgcp package-capability rtp-package mgcp package-capability sst-package no mgcp timer receive-rtcp ! ccm-manager fallback-mgcp ccm-manager redundant-host CM-B ccm-manager mgcp ccm-manager music-on-hold ccm-manager config server cm-a ccm-manager config ! controller T1 1/0 framing esf linecode b8zs pri-group timeslots 1-24 service mgcp ! controller T1 1/1 framing esf linecode b8zs pri-group timeslots 1-24 service mgcp ! interface Serial1/0:23 no ip address no logging event link-status isdn switch-type primary-ni isdn incoming-voice voice isdn T306 30000 isdn bind-l3 ccm-manager no cdp enable ! voice-port 1/0:23 ! dial-peer voice 9991023 pots application mgcpapp direct-inward-dial port 1/0:23 ! dial-peer voice 9991123 pots application mgcpapp direct-inward-dial port 1/1:23 ! dial-peer voice 1640001 pots destination-pattern 16..... direct-inward-dial port 1/0:23 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! end
 Note |
DID is required for T1/E1 PRI dial peers. |
Multicast Music-on-Hold Example
The following example shows multicast MOH configured for an MGCP voice gateway:
version 12.2 no parser cache no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname voice-3640 ! logging rate-limit console 10 except errors ! memory-size iomem 10 voice-card 1 ! ip subnet-zero ! ip domain-name test.com ! no ip dhcp-client network-discovery mgcp mgcp call-agent 10.0.0.21 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1 mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 mgcp modem passthrough voip mode cisco mgcp package-capability rtp-package mgcp package-capability sst-package no mgcp timer receive-rtcp call rsvp-sync ! ccm-manager redundant-host 10.0.0.21 ccm-manager mgcp ccm-manager music-on-hold ccm-manager config server 10.0.0.21 ccm-manager config ! controller T1 2/0 framing sf linecode ami ds0-group 0 timeslots 1 type e&m-wink-start ! controller T1 2/1 framing sf linecode ami ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.0 no ip mroute-cache duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ! voice-port 1/0/0 ! voice-port 1/0/1 ! voice-port 2/0:0 ! dial-peer cor custom ! dial-peer voice 125 pots application mgcpapp port 1/0/0 ! dial-peer voice 150 pots application mgcpapp port 2/0:0 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! no scheduler max-task-time scheduler allocate 4000 4000 ! end
MLPP on Cisco 2801 Example
The following configuration includes both MLPP T1 CAS and T1 PRI.
Current configuration :1851 bytes ! version 12.3 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname 2801_router ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no network-clock-participate wic 1 network-clock-participate wic 2 no network-clock-participate wic 3 no network-clock-participate wic 4 mmi polling-interval 60 no mmi auto-configure no mmi pvc mmi snmp-timeout 180 no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! ! no ftp-server write-enable isdn switch-type primary-ni voice-card 0 ! ! ! ccm-manager mgcp ccm-manager music-on-hold ccm-manager config server 192.168.12.125 ! ! controller T1 2/0 framing esf clock source internal linecode b8zs ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-3 type e&m-wink-start ! controller T1 2/1 framing esf linecode b8zs pri-group timeslots 1,24 service mgcp ! ! ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.38 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial2/1:23 no ip address isdn switch-type primary-ni isdn incoming-voice voice isdn bind-l3 ccm-manager no cdp enable ! ip classless ip http server ! ! ! control-plane ! ! voice-port 1/0 ! voice-port 1/1 ! voice-port 2/0:1 ! voice-port 2/1:23 ! mgcp mgcp call-agent 192.168.12.125 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1 mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 action notify mgcp package-capability rtp-package no mgcp package-capability res-package mgcp package-capability sst-package no mgcp package-capability fxr-package no mgcp timer receive-rtcp mgcp sdp simple mgcp fax t38 inhibit mgcp rtp payload-type g726r16 static ! mgcp profile default ! ! ! dial-peer voice 1 pots application mgcapp port 2/0:1 ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! end
MLPP on Cisco 2621 Example
Current configuration :2530 bytes
!
version 12.3
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 2621-other
!
boot-start-marker
boot system flash:c2600-ipvoice-mz
boot-end-marker
!
logging buffered 10000000 debugging
enable password lab
!
voice-card 1
!
no aaa new-model
ip subnet-zero
ip tcp synwait-time 13
!
!
ip domain name sample-vlan200.cisco.com
ip host demo 10.69.1.129
ip name-server 10.10.100.100
no ftp-server write-enable
isdn switch-type primary-ni
!
!
voice call carrier capacity active
!
!
ccm-manager fallback-mgcp
ccm-manager mgcp
ccm-manager music-on-hold
ccm-manager config server OTHER
ccm-manager config
!
!
controller T1 1/0
framing esf
crc-threshold 320
clock source internal
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-23 type e&m-wink-start
!
controller T1 1/1
framing esf
crc-threshold 320
clock source internal
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-23 type e&m-wink-start
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.200.23 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/0
ip http server
!
control-plane
!
!
call application alternate default
!
!
voice-port 1/0:1
!
voice-port 1/1:1
!
mgcp
mgcp call-agent OTHER 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1
mgcp dtmf-relay voip codec all mode out-of-band
mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 action notify
mgcp package-capability rtp-package
no mgcp package-capability res-package
mgcp package-capability sst-package
no mgcp package-capability fxr-package
mgcp package-capability pre-package
no mgcp timer receive-rtcp
mgcp sdp simple
no mgcp validate domain-name
mgcp fax t38 inhibit
mgcp rtp payload-type g726r16 static
!
mgcp profile default
!
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
!
dial-peer voice 999101 pots
application mgcpapp
port 1/0:1
!
dial-peer voice 999111 pots
application mgcpapp
port 1/1:1
!
dial-peer voice 999222 pots
preference 1
destination-pattern 100.
direct-inward-dial
port 1/0:1
forward-digits all
!
!
call-manager-fallback
max-conferences 4
ip source-address 10.10.200.23 port 2000
max-ephones 10
max-dn 10
dialplan-pattern 1 [A-D].... extension-length 4
translate calling 1
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
exec-timeout 0 0
no exec
transport input all
line vty 0 4
password lab
login
!
exception core-file core_2621 compress
exception region-size 65536
exception dump 10.10.100.101
!
!
end
Where to Go Next
- To configure conferencing, transcoding, and MTP support on a Cisco IOS gateway, see "Configuring Enhanced Conferencing and Transcoding for Voice Gateway Routers" on page 67 .
- To enable MGCP PRI backhaul support, see "Configuring MGCP PRI Backhaul and T1 CAS Support for Cisco Unified Communications Manager" on page 113 .
- To enable MGCP BRI backhaul support, see "Configuring MGCP-Controlled Backhaul of BRI Signaling in Conjunction with Cisco Unified Communications Manager" on page 129 .
- To download region-specific tones and their associated frequencies, amplitudes, and cadences, see "Configuring Tone Download to MGCP Gateways" on page 145 .
Additional References
- "Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco IOS Interoperability" on page 13 --Describes basics of underlying technology and lists related documents.
- Configuring Media Gateway Control Protocol and Related Protocols --Describes MGCP concepts and configuration procedures.
- Configuring the Cisco IOS MGCP Gateway --Describes the basics of configuring an MGCP gateway to support Cisco Communications Manager.
- How to Configure MGCP with Digital PRI and Cisco Unified Communications Manager --Describes how to configure MGCP with PRI.
- MGCP Gateway Fallback Transition to Default H.323 Session Application --Describes how to enable an MGCP gateway to fallback to an H323 session application when the WAN connection to the primary Cisco Communications Manager server is lost, and no backup Cisco Communications Manager server is available.
- MGCP with Digital CAS and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Configuration Example --Describes how to use MGCP between a Cisco IOS gateway and a Cisco Communications Manager Media Convergence Server (MCS).
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback