- Cisco Unified Border Element Enterprise Protocol-Independent Features and Setup
- SIP-to-SIP Extended Feature Functionality for Session Border Controllers
- Bandwidth-Based Call Admission Control
- Interworking Between RSVP Capable and RSVP Incapable Networks
- Cisco Resource Reservation Protocol Agent
- SIP INFO Method for DTMF Tone Generation
- DTMF Events through SIP Signaling
- Call Progress Analysis Over IP-to-IP Media Session
- Codec Preference Lists
- AAC-LD MP4A-LATM Codec Support on Cisco UBE
- Multicast Music-on-Hold Support on Cisco UBE
- Network-Based Recording
- Video Recording - Additional Configurations
- TDoS Attack Mitigation
- Cisco Unified Communications Gateway Services--Extended Media Forking
- Dynamic Payload Type Interworking for DTMF and Codec Packets for SIP-to-SIP Calls
- iLBC Support for SIP and H.323
- DSP-Based Functionality on the Cisco UBE Enterprise Including Transcoding and Transrating
- Acoustic Shock Protection
- Noise Reduction
- SIP Ability to Send a SIP Registration Message on a Border Element
- SIP Profiles
- Session Refresh with Reinvites
- SIP Stack Portability
- VoIP for IPv6
- Interworking of Secure RTP calls for SIP and H.323
- Cisco UBE Support for SRTP-RTP Internetworking
- Support for SRTP Termination
- WebEx Telepresence Media Support Over Single SIP Session
- SIP SRTP Fallback to Nonsecure RTP
- Support for Software Media Termination Point
- Cisco Unified Communication Trusted Firewall Control
- Cisco Unified Communication Trusted Firewall Control-Version II
- Finding Feature Information
- Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- URI-Based Dialing Enhancements
- Additional References
- Glossary
Contents
- Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Feature Information for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Restrictions for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Information About Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- How to Configure Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Configuring Domain-Based Routing at Global Level
- Configuring Domain-Based Routing at Dial Peer Level
- Verifying and Troubleshooting Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Configuration Examples for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Example Configuring Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
First Published: June 15, 2011
Last Updated: July 22, 2011
The Domain-based routing feature provides support for matching an outbound dial peer based on the domain name or IP address provided in the request URI of the incoming SIP message or an inbound dial peer.
Domain-based routing enables for calls to be routed on the outbound dialpeer based on the domain name or IP address provided in the request Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) of incoming Session IP message.
- Feature Information for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Restrictions for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Information About Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- How to Configure Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Configuration Examples for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
Feature Information for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn . An account on Cisco.com is not required.
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Domain Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE |
15.2(1)T |
The domain-based routing enables for calls to be routed on the outbound dial peer based on the domain name or IP address provided in the request URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) of incoming SIP message. The following commands were introduced or modified: call-route, voice-class sip call-route. |
|
Domain Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S |
The domain-based routing enables for calls to be routed on the outbound dial peer based on the domain name or IP address provided in the request URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) of incoming SIP message. The following commands were introduced or modified: call-route, voice-class sip call-route. |
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental. © 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved
Restrictions for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
Domain-based routing support is available only for SIP-SIP call flows.
Information About Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
When a dial peer has an application configured as a session application, then only the user parameter of the request URI is used and is sent from the inbound SIP SPI to the application. The session application performs a match on an outbound dial peer based on the user parameter of the request URI sent from the inbound dial peer. In the figure below, 567 is the user portion of the request-URI that is passed from the inbound dial peer to the application and the matching outbound dial-peer found is 1000.
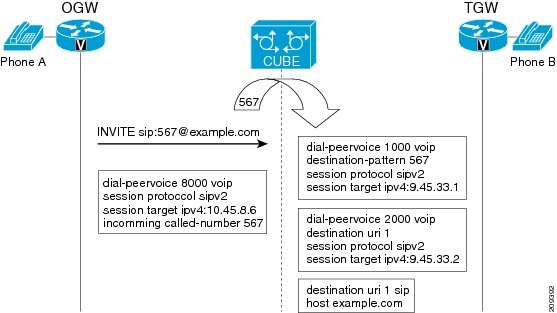
With the introduction of the domain-based routing feature, all parameters including the domain name of the request URI will be sent to the application and the outbound dial peer can be matched with any parameter. In Figure 1, when the domain name example.com is used to match an outbound dial peer the resulting dial peer is 2000. The call route url command is used for configuring domain-based routing.
How to Configure Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
- Configuring Domain-Based Routing at Global Level
- Configuring Domain-Based Routing at Dial Peer Level
- Verifying and Troubleshooting Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
Configuring Domain-Based Routing at Global Level
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
voice
service
voip
4.
sip
5.
call-route
url
6.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Domain-Based Routing at Dial Peer Level
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
dial-peer
voice
dial-peer
tag
voip
4.
voice-class
sip
call-route
url
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying and Troubleshooting Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
1.
enable
2.
debug
ccsip
all
3.
debug
voip
dialpeer
inout
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
Example Configuring Domain-Based Routing Support on the Cisco UBE
The following example shows how to enable domain-based routing support on the Cisco UBE:
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# voice service voip Device(conf-voi-serv)# sip Device(conf-serv-sip)# call-route url Device(conf-serv-sip)# exit Device(config)# dial-peer voice 2 voip Device(config-dial-peer)# voice-class sip call-route url Device(config-dial-peer)# exit