- The ASA FirePOWER Module
- Licensing Requirements for the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Default Settings
- Configuring the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Task Flow for the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Connecting the ASA FirePOWER Management Interface
- (ASA 5512-X through 5555-X) Installing or Reimaging the Software Module
- Changing the ASA FirePOWER Management IP Address
- Configuring Basic ASA FirePOWER Settings at the ASA FirePOWER CLI
- Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center
- Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Redirecting Traffic to the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Managing the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Resetting the Password
- Reloading or Resetting the Module
- Shutting Down the Module
- (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Uninstalling a Software Module Image
- (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Sessioning to the Module From the ASA
- Reimaging the 5585-X ASA FirePOWER Hardware Module
- Upgrading the System Software
- Monitoring the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Configuration Examples for the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Feature History for the ASA FirePOWER Module
ASA FirePOWER (SFR) Module
This chapter describes how to configure the ASA FirePOWER module that runs on the ASA.
- The ASA FirePOWER Module
- Licensing Requirements for the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Default Settings
- Configuring the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Managing the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Monitoring the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Configuration Examples for the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Feature History for the ASA FirePOWER Module
The ASA FirePOWER Module
The ASA FirePOWER module supplies next-generation firewall services, including Next-Generation IPS (NGIPS), Application Visibility and Control (AVC), URL filtering, and Advanced Malware Protection (AMP).You can use the module in single or multiple context mode, and in routed or transparent mode.
The module is also known as ASA SFR.
Although the module has a basic command line interface (CLI) for initial configuration and troubleshooting, you configure the security policy on the device using a separate application, FireSIGHT Management Center, which can be hosted on a separate FireSIGHT Management Center appliance or as a virtual appliance running on a VMware server. (FireSIGHT Management Center is also known as Defense Center.)
- How the ASA FirePOWER Module Works with the ASA
- ASA FirePOWER Management Access
- Compatibility with ASA Features
How the ASA FirePOWER Module Works with the ASA
You can configure your ASA FirePOWER module using one of the following deployment models:
- Inline mode—In an inline deployment, the actual traffic is sent to the ASA FirePOWER module, and the module’s policy affects what happens to the traffic. After dropping undesired traffic and taking any other actions applied by policy, the traffic is returned to the ASA for further processing and ultimate transmission.
- Inline tap monitor-only mode (ASA inline)—In an inline tap monitor-only deployment, a copy of the traffic is sent to the ASA FirePOWER module, but it is not returned to the ASA. Inline tap mode lets you see what the ASA FirePOWER module would have done to traffic, and lets you evaluate the content of the traffic, without impacting the network. However, in this mode, the ASA does apply its policies to the traffic, so traffic can be dropped due to access rules, TCP normalization, and so forth.
Be sure to configure consistent policies on the ASA and the ASA FirePOWER. Both policies should reflect the inline or monitor-only mode of the traffic.
ASA FirePOWER Inline Mode
In inline mode, traffic goes through the firewall checks before being forwarded to the ASA FirePOWER module. When you identify traffic for ASA FirePOWER inspection on the ASA, traffic flows through the ASA and the module as follows:
2.![]() Incoming VPN traffic is decrypted.
Incoming VPN traffic is decrypted.
3.![]() Firewall policies are applied.
Firewall policies are applied.
4.![]() Traffic is sent to the ASA FirePOWER module.
Traffic is sent to the ASA FirePOWER module.
5.![]() The ASA FirePOWER module applies its security policy to the traffic, and takes appropriate actions.
The ASA FirePOWER module applies its security policy to the traffic, and takes appropriate actions.
6.![]() Valid traffic is sent back to the ASA; the ASA FirePOWER module might block some traffic according to its security policy, and that traffic is not passed on.
Valid traffic is sent back to the ASA; the ASA FirePOWER module might block some traffic according to its security policy, and that traffic is not passed on.
7.![]() Outgoing VPN traffic is encrypted.
Outgoing VPN traffic is encrypted.
The following figure shows the traffic flow when using the ASA FirePOWER module in inline mode. In this example, the module blocks traffic that is not allowed for a certain application. All other traffic is forwarded through the ASA.
Figure 24-1 ASA FirePOWER Module Traffic Flow in the ASA
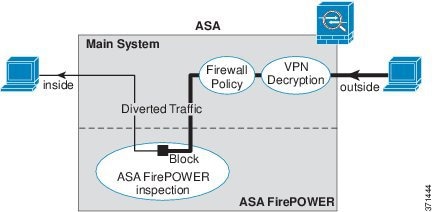

Note![]() If you have a connection between hosts on two ASA interfaces, and the ASA FirePOWER service policy is only configured for one of the interfaces, then all traffic between these hosts is sent to the ASA FirePOWER module, including traffic originating on the non-ASA FirePOWER interface (because the feature is bidirectional).
If you have a connection between hosts on two ASA interfaces, and the ASA FirePOWER service policy is only configured for one of the interfaces, then all traffic between these hosts is sent to the ASA FirePOWER module, including traffic originating on the non-ASA FirePOWER interface (because the feature is bidirectional).
ASA FirePOWER Inline Tap Monitor-Only Mode
This mode sends a duplicate stream of traffic to the ASA FirePOWER module for monitoring purposes only. The module applies the security policy to the traffic and lets you know what it would have done if it were operating in inline mode; for example, traffic might be marked “would have dropped” in events. You can use this information for traffic analysis and to help you decide if inline mode is desirable.

Note![]() You cannot configure both inline tap monitor-only mode and normal inline mode at the same time on the ASA. Only one type of security policy is allowed. In multiple context mode, you cannot configure inline tap monitor-only mode for some contexts, and regular inline mode for others.
You cannot configure both inline tap monitor-only mode and normal inline mode at the same time on the ASA. Only one type of security policy is allowed. In multiple context mode, you cannot configure inline tap monitor-only mode for some contexts, and regular inline mode for others.
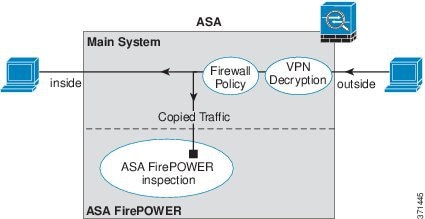
The following figure shows the traffic flow when operating in inline tap mode.
Figure 24-2 ASA FirePOWER Inline Tap Monitor-Only Mode
ASA FirePOWER Management Access
There are two separate layers of access for managing an ASA FirePOWER module: initial configuration (and subsequent troubleshooting) and policy management.
Initial Configuration
For initial configuration, you must use the CLI on the ASA FirePOWER module. For information on the default management addresses, see Default Settings.
To access the CLI, you can use the following methods:
–![]() ASA FirePOWER console port—The console port on the module is a separate external console port.
ASA FirePOWER console port—The console port on the module is a separate external console port.
–![]() ASA FirePOWER Management 1/0 interface using SSH—You can connect to the default IP address or you can use ASDM to change the management IP address and then connect using SSH. The management interface on the module is a separate external Gigabit Ethernet interface.
ASA FirePOWER Management 1/0 interface using SSH—You can connect to the default IP address or you can use ASDM to change the management IP address and then connect using SSH. The management interface on the module is a separate external Gigabit Ethernet interface.

Note![]() You cannot access the ASA FirePOWER hardware module CLI over the ASA backplane using the session command.
You cannot access the ASA FirePOWER hardware module CLI over the ASA backplane using the session command.
–![]() ASA session over the backplane—If you have CLI access to the ASA, then you can session to the module and access the module CLI.
ASA session over the backplane—If you have CLI access to the ASA, then you can session to the module and access the module CLI.
–![]() ASA FirePOWER Management 0/0 interface using SSH—You can connect to the default IP address or you can use ASDM to change the management IP address and then connect using SSH. These models run the ASA FirePOWER module as a software module. The ASA FirePOWER management interface shares the Management 0/0 interface with the ASA. Separate MAC addresses and IP addresses are supported for the ASA and ASA FirePOWER module. You must perform configuration of the ASA FirePOWER IP address within the ASA FirePOWER operating system (using the CLI or ASDM). However, physical characteristics (such as enabling the interface) are configured on the ASA. You can remove the ASA interface configuration (specifically the interface name) to dedicate this interface as an ASA FirePOWER-only interface. This interface is management-only.
ASA FirePOWER Management 0/0 interface using SSH—You can connect to the default IP address or you can use ASDM to change the management IP address and then connect using SSH. These models run the ASA FirePOWER module as a software module. The ASA FirePOWER management interface shares the Management 0/0 interface with the ASA. Separate MAC addresses and IP addresses are supported for the ASA and ASA FirePOWER module. You must perform configuration of the ASA FirePOWER IP address within the ASA FirePOWER operating system (using the CLI or ASDM). However, physical characteristics (such as enabling the interface) are configured on the ASA. You can remove the ASA interface configuration (specifically the interface name) to dedicate this interface as an ASA FirePOWER-only interface. This interface is management-only.
Policy Configuration and Management
After you perform initial configuration, configure the ASA FirePOWER security policy using FireSIGHT Management Center. Then configure the ASA policy for sending traffic to the ASA FirePOWER module using ASDM or Cisco Security Manager.
Compatibility with ASA Features
The ASA includes many advanced application inspection features, including HTTP inspection. However, the ASA FirePOWER module provides more advanced HTTP inspection than the ASA provides, as well as additional features for other applications, including monitoring and controlling application usage.
To take full advantage of the ASA FirePOWER module features, see the following guidelines for traffic that you send to the ASA FirePOWER module:
- Do not configure ASA inspection on HTTP traffic.
- Do not configure Cloud Web Security (ScanSafe) inspection. If you configure both ASA FirePOWER inspection and Cloud Web Security inspection for the same traffic, the ASA only performs ASA FirePOWER inspection.
- Other application inspections on the ASA are compatible with the ASA FirePOWER module, including the default inspections.
- Do not enable the Mobile User Security (MUS) server; it is not compatible with the ASA FirePOWER module.
- If you enable failover, when the ASA fails over, any existing ASA FirePOWER flows are transferred to the new ASA. The ASA FirePOWER module in the new ASA begins inspecting the traffic from that point forward; old inspection states are not transferred.
Licensing Requirements for the ASA FirePOWER Module
|
|
|
|---|---|
The ASA FirePOWER module and FireSIGHT Management Center require additional licenses. See the Licensing chapter of the FireSIGHT System User Guide or the online help in FireSIGHT Management Center for more information.
Guidelines and Limitations
Supported in multiple context mode.
Supported in routed and transparent firewall mode.
Does not support failover directly; when the ASA fails over, any existing ASA FirePOWER flows are transferred to the new ASA. The ASA FirePOWER module in the new ASA begins inspecting the traffic from that point forward; old inspection states are not transferred.
You are responsible for maintaining consistent policies on the ASA FirePOWER modules in the high-availability ASA pair (using FireSIGHT Management Center) to ensure consistent failover behavior.
Does not support clustering directly, but you can use these modules in a cluster. You are responsible for maintaining consistent policies on the ASA FirePOWER modules in the cluster using FireSIGHT Management Center. Do not use different ASA-interface-based zone definitions for devices in the cluster.
- Supported on the ASA 5585-X (as a hardware module) and 5512-X through ASA 5555-X (as a software module). See the Cisco ASA Compatibility Matrix for more information:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/compatibility/asamatrx.html
- For the 5512-X through ASA 5555-X, you must install a Cisco solid state drive (SSD). For more information, see the ASA 5500-X hardware guide.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
- See Compatibility with ASA Features.
- You cannot change the software type installed on the hardware module; if you purchase an ASA FirePOWER module, you cannot later install other software on it.
- You cannot configure both normal inline mode and inline tap monitor-only mode at the same time on the ASA. Only one type of security policy is allowed. In multiple context mode, you cannot configure inline tap monitor-only mode for some contexts, and regular inline mode for others.
Default Settings
The following table lists the default settings for the ASA FirePOWER module.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
– – |
|
Configuring the ASA FirePOWER Module
This section describes how to configure the ASA FirePOWER module.
- Task Flow for the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Connecting the ASA FirePOWER Management Interface
- (ASA 5512-X through 5555-X) Installing or Reimaging the Software Module
- Changing the ASA FirePOWER Management IP Address
- Configuring Basic ASA FirePOWER Settings at the ASA FirePOWER CLI
- Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center
- Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Redirecting Traffic to the ASA FirePOWER Module
Task Flow for the ASA FirePOWER Module
Configuring the ASA FirePOWER module is a process that includes configuration of the ASA FirePOWER security policy on the ASA FirePOWER module and then configuration of the ASA to send traffic to the ASA FirePOWER module. To configure the ASA FirePOWER module, perform the following steps:
Step 1![]() Cable the ASA FirePOWER management interfaces and optionally, the console interface. See Connecting the ASA FirePOWER Management Interface.
Cable the ASA FirePOWER management interfaces and optionally, the console interface. See Connecting the ASA FirePOWER Management Interface.
Step 2![]() (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Install the software module. See (ASA 5512-X through 5555-X) Installing or Reimaging the Software Module.
(ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Install the software module. See (ASA 5512-X through 5555-X) Installing or Reimaging the Software Module.
Step 3![]() (ASA 5585-X) Configure the ASA FirePOWER module management IP address for initial SSH access. See Changing the ASA FirePOWER Management IP Address.
(ASA 5585-X) Configure the ASA FirePOWER module management IP address for initial SSH access. See Changing the ASA FirePOWER Management IP Address.
Step 4![]() On the ASA FirePOWER module, configure basic settings. See Configuring Basic ASA FirePOWER Settings at the ASA FirePOWER CLI.
On the ASA FirePOWER module, configure basic settings. See Configuring Basic ASA FirePOWER Settings at the ASA FirePOWER CLI.
Step 5![]() Identify the FireSIGHT Management Center that will manage the device. See Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
Identify the FireSIGHT Management Center that will manage the device. See Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
Step 6![]() On the ASA FirePOWER module, configure the security policy using FireSIGHT Management Center. See Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA FirePOWER Module.
On the ASA FirePOWER module, configure the security policy using FireSIGHT Management Center. See Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA FirePOWER Module.
Step 7![]() On the ASA, identify traffic to divert to the ASA FirePOWER module. See Redirecting Traffic to the ASA FirePOWER Module.
On the ASA, identify traffic to divert to the ASA FirePOWER module. See Redirecting Traffic to the ASA FirePOWER Module.
Connecting the ASA FirePOWER Management Interface
In addition to providing management access to the ASA FirePOWER module, the ASA FirePOWER management interface needs access to an HTTP proxy server or a DNS server and the Internet for signature updates and more. This section describes recommended network configurations. Your network may differ.
ASA 5585-X (Hardware Module)
The ASA FirePOWER module includes a separate management and console interface from the ASA. For initial setup, you can connect with SSH to the ASA FirePOWER Management 1/0 interface using the default IP address. If you cannot use the default IP address, you can either use the console port or use ASDM to change the management IP address so you can use SSH. (See Changing the ASA FirePOWER Management IP Address.)
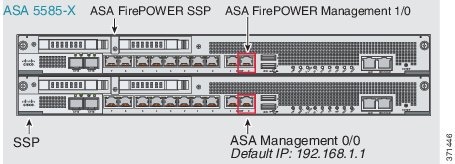
If you have an inside router, you can route between the management network, which can include both the ASA Management 0/0 and ASA FirePOWER Management 1/0 interfaces, and the ASA inside network for Internet access. Be sure to also add a route on the ASA to reach the Management network through the inside router.

If you do not have an inside router
If you have only one inside network, then you cannot also have a separate management network, which would require an inside router to route between the networks. In this case, you can manage the ASA from the inside interface instead of the Management 0/0 interface. Because the ASA FirePOWER module is a separate device from the ASA, you can configure the ASA FirePOWER Management 1/0 address to be on the same network as the inside interface.

ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X (Software Module)
These models run the ASA FirePOWER module as a software module, and the ASA FirePOWER management interface shares the Management 0/0 interface with the ASA. For initial setup, you can connect with SSH to the ASA FirePOWER default IP address. If you cannot use the default IP address, you can either session to the ASA FirePOWER over the backplane or use ASDM to change the management IP address so you can use SSH.

If you have an inside router, you can route between the Management 0/0 network, which includes both the ASA and ASA FirePOWER management IP addresses, and the inside network for Internet access. Be sure to also add a route on the ASA to reach the Management network through the inside router.

If you do not have an inside router
If you have only one inside network, then you cannot also have a separate management network. In this case, you can manage the ASA from the inside interface instead of the Management 0/0 interface. If you remove the ASA-configured name from the Management 0/0 interface, you can still configure the ASA FirePOWER IP address for that interface. Because the ASA FirePOWER module is essentially a separate device from the ASA, you can configure the ASA FirePOWER management address to be on the same network as the inside interface.
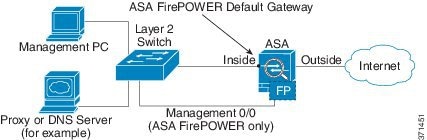

Note![]() You must remove the ASA-configured name for Management 0/0; if it is configured on the ASA, then the ASA FirePOWER address must be on the same network as the ASA, and that excludes any networks already configured on other ASA interfaces. If the name is not configured, then the ASA FirePOWER address can be on any network, for example, the ASA inside network.
You must remove the ASA-configured name for Management 0/0; if it is configured on the ASA, then the ASA FirePOWER address must be on the same network as the ASA, and that excludes any networks already configured on other ASA interfaces. If the name is not configured, then the ASA FirePOWER address can be on any network, for example, the ASA inside network.
(ASA 5512-X through 5555-X) Installing or Reimaging the Software Module
If you purchase the ASA with the ASA FirePOWER module, the module software and required solid state drives (SSDs) come pre-installed and ready to configure. If you want to add the ASA FirePOWER software module to an existing ASA, or need to replace the SSD, you need to install the ASA FirePOWER boot software, partition the SSD, and install the system software according to this procedure.
Reimaging the module is the same procedure, except you should first uninstall the ASA FirePOWER module. You would reimage a system if you replace an SSD.
For information on how to physically install the SSD, see the ASA hardware guide.
Prerequisites
- The free space on flash (disk0) should be at least 3GB plus the size of the boot software.
- In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
- You must shut down any other software module that you might be running; the device can run a single software module at a time. You must do this from the ASA CLI. For example, the following commands shut down and uninstall the IPS software module, and then reload the ASA; the commands to remove the CX module are the same, except use the cxsc keyword instead of ips.

Note![]() If you have an active service policy redirecting traffic to an IPS or CX module, you must remove that policy. For example, if the policy is a global one, you would use no service-policy ips_policy global. You can remove the policies using CLI or ASDM.
If you have an active service policy redirecting traffic to an IPS or CX module, you must remove that policy. For example, if the policy is a global one, you would use no service-policy ips_policy global. You can remove the policies using CLI or ASDM.
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Download the boot image to the device. Do not transfer the system software; it is downloaded later to the SSD. You have the following options:
Download the boot image to the device. Do not transfer the system software; it is downloaded later to the SSD. You have the following options:
- ASDM—First, download the boot image to your workstation, or place it on an FTP, TFTP, HTTP, HTTPS, SMB, or SCP server. Then, in ASDM, choose Tools > File Management, and then choose the appropriate File Transfer command, either Between Local PC and Flash or Between Remote Server and Flash. Transfer the boot software to disk0 on the ASA.
- ASA CLI—First, place the boot image on a TFTP, FTP, HTTP, or HTTPS server, then use the copy command to download it to flash. The following example uses TFTP; replace <TFTP Server> with your server’s IP address or host name.
Step 2![]() Download the ASA FirePOWER system software from Cisco.com to an HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP server accessible from the ASA FirePOWER management interface.
Download the ASA FirePOWER system software from Cisco.com to an HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP server accessible from the ASA FirePOWER management interface.
Step 3![]() Set the ASA FirePOWER module boot image location in ASA disk0 by entering the following command:
Set the ASA FirePOWER module boot image location in ASA disk0 by entering the following command:

Note![]() If you get a message like “ERROR: Another service (cxsc) is running, only one service is allowed to run at any time,” it means that you already have a different software module configured. You must shut it down and remove it to install a new module as described in the prerequisites section above.
If you get a message like “ERROR: Another service (cxsc) is running, only one service is allowed to run at any time,” it means that you already have a different software module configured. You must shut it down and remove it to install a new module as described in the prerequisites section above.
Step 4![]() Load the ASA FirePOWER boot image by entering the following command:
Load the ASA FirePOWER boot image by entering the following command:
Step 5![]() Wait approximately 5-15 minutes for the ASA FirePOWER module to boot up, and then open a console session to the now-running ASA FirePOWER boot image. You might need to press enter after opening the session to get to the login prompt. The default username is admin and the default password is Admin123.
Wait approximately 5-15 minutes for the ASA FirePOWER module to boot up, and then open a console session to the now-running ASA FirePOWER boot image. You might need to press enter after opening the session to get to the login prompt. The default username is admin and the default password is Admin123.

Tip If the module boot has not competed, the session command will fail with a message about not being able to connect over ttyS1. Wait and try again.
Step 6![]() Use the setup command to configure the system
Use the setup command to configure the system![]() so that you can install the system software package.
so that you can install the system software package.
You are prompted for the following. Note that the management address and gateway, and DNS information, are the key settings to configure.
- Host name—Up to 65 alphanumeric characters, no spaces. Hyphens are allowed.
- Network address—You can set static IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, or use DHCP (for IPv4) or IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration.
- DNS information—You must identify at least one DNS server, and you can also set the domain name and search domain.
- NTP information—You can enable NTP and configure the NTP servers, for setting system time.
Step 7![]() Install the System Software image using the system
Install the System Software image using the system![]() install command:
install command:
system install [ noconfirm ] url
Include the noconfirm option if you do not want to respond to confirmation messages. Use an HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP URL; if a username and password are required, you will be prompted to supply them.
When installation is complete, the system reboots. Allow 10 or more minutes for application component installation and for the ASA FirePOWER services to start. (The show module sfr output should show all processes as Up.)
Step 8![]() Open a session to the ASA FirePOWER module. You will see a different login prompt because you are logging into the fully functional module.
Open a session to the ASA FirePOWER module. You will see a different login prompt because you are logging into the fully functional module.
Step 9![]() Log in with the username admin and the password Sourcefire.
Log in with the username admin and the password Sourcefire.
Step 10![]() Complete the system configuration as prompted.
Complete the system configuration as prompted.
You must first read and accept the end user license agreement (EULA). Then change the admin password, then configure the management address and DNS settings, as prompted. You can configure both IPv4 and IPv6 management addresses. For example:
Step 11![]() Identify the FireSIGHT Management Center appliance that will manage this device using the configure manager add command.
Identify the FireSIGHT Management Center appliance that will manage this device using the configure manager add command.
You come up with a registration key, which you will then use in FireSIGHT Management Center when you add the device to its inventory. The following example shows the simple case. When there is a NAT boundary, the command is different; see Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
Step 12![]() Log into the FireSIGHT Management Center using an HTTPS connection in a browser, using the hostname or address entered above. For example, https://DC.example.com.
Log into the FireSIGHT Management Center using an HTTPS connection in a browser, using the hostname or address entered above. For example, https://DC.example.com.
Use the Device Management (Devices > Device Management) page to add the device. For more information, see the online help or the Managing Devices chapter in the FireSIGHT System User Guide.

Tip You also configure NTP and time settings through FireSIGHT Management Center. Use the Time Synchronization settings when editing the local policy from the System > Local > System Policy page.
Changing the ASA FirePOWER Management IP Address
If you cannot use the default management IP address, then you can set the management IP address from the ASA. After you set the management IP address, you can access the ASA FirePOWER module using SSH to perform additional setup.
If you already configured the management address during initial system setup through the ASA FirePOWER CLI, as described in Configuring Basic ASA FirePOWER Settings at the ASA FirePOWER CLI, then it is not necessary to configure it through the ASA CLI or ASDM.

Note![]() For a software module, you can access the ASA FirePOWER CLI to perform setup by sessioning from the ASA CLI; you can then set the ASA FirePOWER management IP address as part of setup. For a hardware module, you can complete the initial setup through the Console port.
For a software module, you can access the ASA FirePOWER CLI to perform setup by sessioning from the ASA CLI; you can then set the ASA FirePOWER management IP address as part of setup. For a hardware module, you can complete the initial setup through the Console port.
Guidelines
In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
Detailed Steps
Configuring Basic ASA FirePOWER Settings at the ASA FirePOWER CLI
You must configure basic network settings and other parameters on the ASA FirePOWER module before you can configure your security policy. This procedure assumes you have the full system software installed (not just the boot image), either after you installed it directly, or because it is already installed on a hardware module.

Tip![]() This procedure also assumes that you are performing an initial configuration. During initial configuration, you are prompted for these settings. If you need to change these settings later, use the various configure network commands to change the individual settings. For more information on the configure network commands, use the ? command for help, and see the FireSIGHT System User Guide, or the online help in FireSIGHT Management Center.
This procedure also assumes that you are performing an initial configuration. During initial configuration, you are prompted for these settings. If you need to change these settings later, use the various configure network commands to change the individual settings. For more information on the configure network commands, use the ? command for help, and see the FireSIGHT System User Guide, or the online help in FireSIGHT Management Center.
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Do one of the following:
Do one of the following:
- (All models) Use SSH to connect to the ASA FirePOWER management IP address.
- (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Open a session to the module from the ASA CLI (see the “Getting Started” chapter in the general operations configuration guide to access the ASA CLI). In multiple context mode, session from the system execution space.
Step 2![]() Log in with the username admin and the password Sourcefire.
Log in with the username admin and the password Sourcefire.
Step 3![]() Complete the system configuration as prompted.
Complete the system configuration as prompted.
You must first read and accept the end user license agreement (EULA). Then change the admin password, then configure the management address and DNS settings, as prompted. You can configure both IPv4 and IPv6 management addresses. The configuration is complete when you see the message that says the sensor must be managed by a FireSIGHT Management Center.
Step 4![]() Now you must identify the FireSIGHT Management Center that will manage this device, as explained in Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
Now you must identify the FireSIGHT Management Center that will manage this device, as explained in Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center
You must register the ASA FirePOWER module to a FireSIGHT Management Center, which is the application you use to configure the policies on the module. FireSIGHT Management Center is also known as Defense Center.
To register a device, use the configure manager add command. A unique alphanumeric registration key is always required to register a device to a FireSIGHT Management Center. This is a simple key that you specify, and is not the same as a license key.
In most cases, you must provide the FireSIGHT Management Center’s hostname or the IP address along with the registration key, for example:
However, if the device and the FireSIGHT Management Center are separated by a NAT device, enter a unique NAT ID along with the registration key, and specify DONTRESOLVE instead of the hostname, for example:
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Do one of the following:
Do one of the following:
- (All models) Use SSH to connect to the ASA FirePOWER management IP address.
- (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Open a session to the module from the ASA CLI (see the “Getting Started” chapter in the general operations configuration guide to access the ASA CLI). In multiple context mode, session from the system execution space.
Step 2![]() Log in with the username admin or another username that has the CLI configuration (Administrator) access level.
Log in with the username admin or another username that has the CLI configuration (Administrator) access level.
Step 3![]() At the prompt, register the device to a FireSIGHT Management Center using the configure manager add command, which has the following syntax:
At the prompt, register the device to a FireSIGHT Management Center using the configure manager add command, which has the following syntax:
configure manager add { hostname | IPv4_address | IPv6_address | DONTRESOLVE } reg_key [ nat_id ]
- { hostname | IPv4_address | IPv6_address | DONTRESOLVE } specifies either the fully qualified host name or IP address of the FireSIGHT Management Center. If the FireSIGHT Management Center is not directly addressable, use DONTRESOLVE.
- reg_key is the unique alphanumeric registration key required to register a device to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
- nat_id is an optional alphanumeric string used during the registration process between the FireSIGHT Management Center and the device. It is required if the hostname is set to DONTRESOLVE.
Step 4![]() Log into the FireSIGHT Management Center using an HTTPS connection in a browser, using the hostname or address entered above. For example, https://DC.example.com.
Log into the FireSIGHT Management Center using an HTTPS connection in a browser, using the hostname or address entered above. For example, https://DC.example.com.
Use the Device Management (Devices > Device Management) page to add the device. For more information, see the online help or the Managing Devices chapter in the FireSIGHT System User Guide.
Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA FirePOWER Module
You use FireSIGHT Management Center to configure the security policy on the ASA FirePOWER module. The security policy controls the services provided by the module, such as Next Generation IPS filtering and application filtering. You cannot configure the policy through the ASA FirePOWER CLI, the ASA CLI, or ASDM.
To open FireSIGHT Management Center, use a web browser to open the following URL:
Where DC_address is the DNS name or IP address of the manager you defined in Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center. For example, https://dc.example.com.
For information about how to configure the security policy, see the FireSIGHT System User Guide or the online help in FireSIGHT Management Center.

Tip![]() You can also open FireSIGHT Management Center from the ASA FirePOWER Status dashboard in ASDM. Choose Home > ASA FirePOWER Status, and click the link at the bottom of the dashboard.
You can also open FireSIGHT Management Center from the ASA FirePOWER Status dashboard in ASDM. Choose Home > ASA FirePOWER Status, and click the link at the bottom of the dashboard.
Redirecting Traffic to the ASA FirePOWER Module
Redirect traffic to the ASA FirePOWER module by creating a service policy that identifies specific traffic that you want to send. ASA policies, such as access rules, are applied to the traffic before it is redirected to the module.
You can configure your device in either an inline or inline tap monitor-only deployment.
- In an inline deployment, the actual traffic is sent to the device, and the device’s policy affects what happens to the traffic. After dropping undesired traffic and taking any other actions applied by policy, the traffic is returned to the ASA for further processing and ultimate transmission.
- In an inline tap deployment, a copy of the traffic is sent to the device, but it is not returned to the ASA. Inline tap mode lets you see what the device would have done to traffic, and lets you evaluate the content of the traffic, without impacting the network.

Note![]() You cannot configure both monitor-only mode and normal inline mode at the same time on the ASA. Only one type of security policy is allowed. In multiple context mode, you cannot configure monitor-only mode for some contexts, and regular inline mode for others.
You cannot configure both monitor-only mode and normal inline mode at the same time on the ASA. Only one type of security policy is allowed. In multiple context mode, you cannot configure monitor-only mode for some contexts, and regular inline mode for others.
Prerequisites
- If you have an active service policy redirecting traffic to an IPS or CX module (that you replaced with the ASA FirePOWER), you must remove that policy before you configure the ASA FirePOWER service policy.
- Be sure to configure consistent policies on the ASA and the ASA FirePOWER. Both policies should reflect the inline or inline tap mode of the traffic.
- In multiple context mode, perform this procedure within each security context.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
Creates a class map to identify the traffic for which you want to send to the module. If you want to send multiple traffic classes to the module, you can create multiple class maps for use in the security policy. |
|
|
|
Specifies the traffic in the class map. See Identifying Traffic (Layer 3/4 Class Maps) for more information. |
|
|
|
Adds or edits a policy map that sets the actions to take with the class map traffic. |
|
|
|
Identifies the class map you created at the start of this procedure. |
|
sfr { fail-close | fail-open } [ monitor-only ] |
Specifies that the traffic should be sent to the ASA FirePOWER module. The fail-close keyword sets the ASA to block all traffic if the ASA FirePOWER module is unavailable. The fail-open keyword sets the ASA to allow all traffic through, uninspected, if the module is unavailable. Specify monitor-only to send a read-only copy of traffic to the module, i.e. inline tap mode. If you do not include the keyword, the traffic is sent in inline mode. See ASA FirePOWER Inline Tap Monitor-Only Mode for more information. |
|
|
|
If you created multiple class maps for ASA FirePOWER traffic, you can specify another class for the policy. See Feature Matching Within a Service Policy for detailed information about how the order of classes matters within a policy map. Traffic cannot match more than one class map for the same action type. |
|
| sfr { fail-close | fail-open } [ monitor-only ] |
Specifies that the second class of traffic should be sent to the ASA FirePOWER module. |
|
service-policy policymap_name {global | interface interface_name } hostname(config)# service-policy sfr_policy interface outside |
Activates the policy map on one or more interfaces. The global keyword applies the policy map to all interfaces, and interface applies the policy to one interface. Only one global policy is allowed. You can override the global policy on an interface by applying a service policy to that interface. You can only apply one policy map to each interface. |
Managing the ASA FirePOWER Module
This section includes procedures that help you manage the module.
- Resetting the Password
- Reloading or Resetting the Module
- Shutting Down the Module
- (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Uninstalling a Software Module Image
- (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Sessioning to the Module From the ASA
- Reimaging the 5585-X ASA FirePOWER Hardware Module
- Upgrading the System Software
Resetting the Password
If you forget the password for admin user, another user with CLI Configuration permissions can log in and change the password.
If there are no other users with the required permissions, you can reset the admin password from the ASA using the session do command.

Tip![]() The password-reset option on the ASA hw-module and sw-module commands does not work with ASA FirePOWER.
The password-reset option on the ASA hw-module and sw-module commands does not work with ASA FirePOWER.
Guidelines
In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
Detailed Steps
Reloading or Resetting the Module
To reload or reset the module, enter one of the following commands at the ASA CLI.
Guidelines
In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
Detailed Steps
Shutting Down the Module
Shutting down the module software prepares the module to be safely powered off without losing configuration data. To gracefully shut down the module, perform the following steps at the ASA CLI.

Note![]() If you reload the ASA, the module is not automatically shut down, so we recommend shutting down the module before reloading the ASA.
If you reload the ASA, the module is not automatically shut down, so we recommend shutting down the module before reloading the ASA.
Guidelines
In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|---|---|
For a hardware module (ASA 5585-X): For a software module (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X): |
(ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Uninstalling a Software Module Image
To uninstall a software module image and associated configuration, perform the following steps.
Guidelines
In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
Detailed Steps
(ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Sessioning to the Module From the ASA
To access the ASA FirePOWER software module CLI from the ASA, you can session from the ASA. You can either session to the module (using Telnet) or create a virtual console session. A console session might be useful if the control plane is down and you cannot establish a Telnet session.
Use the ASA FirePOWER CLI to configure basic network settings and to troubleshoot the module.
Guidelines
- In multiple context mode, perform this procedure in the system execution space.
- You can log in with any username configured on the ASA FirePOWER. Initially, the admin username is the only one configured (and it is always available). The initial default username is Sourcefire for the full image, and Admin123 for the boot image.
Detailed Steps
Reimaging the 5585-X ASA FirePOWER Hardware Module
If you need to reimage the ASA FirePOWER hardware module in an ASA 5585-X appliance for any reason, you need to install both the Boot Image and a System Software package, in that order. You must install both packages to have a functioning system. Under normal circumstances, you do not need to reimage the system to install upgrade packages.
To install the boot image, you need to TFTP boot the image from the Management-0 port on the ASA FirePOWER SSP by logging into the module’s Console port. Because the Management-0 port is on an SSP in the first slot, it is also known as Management1/0, but rommon recognizes it as Management-0 or Management0/1.
To accomplish a TFTP boot, you must:
- Place the software image on a TFTP server that can be accessed through the Management1/0 interface on the ASA FirePOWER.
- Connect Management1/0 to the network. You must use this interface to TFTP boot the Boot Image.
- Configure rommon variables. Press Esc to interrupt the auto-boot process so that you can configure rommon variables.
Once the boot image is installed, you install the System Software package. You must place the package on an HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP server that is accessible from the ASA FirePOWER.
The following procedure explains how to install the boot image and then install the System Software package.
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Connect to the Console port. Use the console cable included with the ASA product to connect your PC to the console using a terminal emulator set for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control. See the hardware guide for your ASA for more information about the console cable.
Connect to the Console port. Use the console cable included with the ASA product to connect your PC to the console using a terminal emulator set for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control. See the hardware guide for your ASA for more information about the console cable.
Step 2![]() Enter the system
Enter the system![]() reboot command to reload the system
reboot command to reload the system![]() .
.
Step 3![]() When prompted, break out of the boot by pressing Esc. If you see grub start to boot the system, you have waited too long.
When prompted, break out of the boot by pressing Esc. If you see grub start to boot the system, you have waited too long.
This will place you at the rommon prompt.
Step 4![]() At the rommon prompt, enter set and configure the following parameters:
At the rommon prompt, enter set and configure the following parameters:
- ADDRESS—The management IP address of the module.
- SERVER—The IP address of the TFTP server.
- GATEWAY—The gateway address to the TFTP server. If the TFTP server is directly attached to Management1/0, use the IP address of the TFTP server. If the TFTP server and management address are on the same subnet, do not configure the gateway or TFTP boot will fail.
- IMAGE—The Boot Image path and image name on the TFTP server. For example, if you place the file on the TFTP server in /tftpboot/images/filename.img, the IMAGE value is images/filename.img.
Step 5![]() Enter sync to save the settings.
Enter sync to save the settings.
Step 6![]() Enter tftp to initiate the download and boot process.
Enter tftp to initiate the download and boot process.
You will see ! marks to indicate progress. When the boot completes after several minutes, you will see a login prompt.
Step 7![]() Log in as admin, with the password Admin123.
Log in as admin, with the password Admin123.
Step 8![]() Use the setup command to configure the system
Use the setup command to configure the system![]() so that you can install the system software package.
so that you can install the system software package.
You are prompted for the following. Note that the management address and gateway, and DNS information, are the key settings to configure.
- Host name—Up to 65 alphanumeric characters, no spaces. Hyphens are allowed.
- Network address—You can set static IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, or use DHCP (for IPv4) or IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration.
- DNS information—You must identify at least one DNS server, and you can also set the domain name and search domain.
- NTP information—You can enable NTP and configure the NTP servers, for setting system time.
Step 9![]() Install the System Software image using the system
Install the System Software image using the system![]() install command:
install command:
system install [ noconfirm ] url
Include the noconfirm option if you do not want to respond to confirmation messages.
When installation is complete, the system reboots. Allow 10 or more minutes for application component installation and for the ASA FirePOWER services to start.
Step 10![]() When the boot completes, log in as admin with the password Sourcefire.
When the boot completes, log in as admin with the password Sourcefire.
Complete the system configuration as prompted.
You must first read and accept the end user license agreement (EULA). Then change the admin password, then configure the management address and DNS settings, as prompted. You can configure both IPv4 and IPv6 management addresses.
Step 11![]() Identify the FireSIGHT Management Center appliance that will manage this device using the configure manager add command.
Identify the FireSIGHT Management Center appliance that will manage this device using the configure manager add command.
You come up with a registration key, which you will then use in FireSIGHT Management Center when you add the device to its inventory. The following example shows the simple case. When there is a NAT boundary, the command is different; see Adding ASA FirePOWER to the FireSIGHT Management Center.
Step 12![]() Log into the FireSIGHT Management Center using an HTTPS connection in a browser, using the hostname or address entered above. For example, https://DC.example.com.
Log into the FireSIGHT Management Center using an HTTPS connection in a browser, using the hostname or address entered above. For example, https://DC.example.com.
Use the Device Management (Devices > Device Management) page to add the device. For more information, see the Managing Devices chapter in the FireSIGHT System User Guide or the online help in FireSIGHT Management Center.
Upgrading the System Software
Use FireSIGHT Management Center to apply upgrade images to the ASA FirePOWER module. Before applying an upgrade, ensure that the ASA is running the minimum required release for the new version; you might need to upgrade the ASA prior to upgrading the module.
For more information about applying upgrades, see the FireSIGHT System User Guide or the online help in FireSIGHT Management Center.
Monitoring the ASA FirePOWER Module
- Showing Module Status
- Showing Module Statistics
- Monitoring Module Connections
- Capturing Module Traffic

Note![]() For ASA FirePOWER-related syslog messages, see the syslog messages guide. ASA FirePOWER syslog messages start with message number 434001.
For ASA FirePOWER-related syslog messages, see the syslog messages guide. ASA FirePOWER syslog messages start with message number 434001.
Showing Module Status
To check the status of a module, enter one of the following commands:
Examples
The following is sample output from the show module command for an ASA 5585-X with an ASA FirePOWER SSP hardware module installed:
The following example shows the details for a software module. Note that DC Addr indicates the address of the FireSIGHT Management Center that manages this device.
The following example shows the location of the ASA FirePOWER boot image that was used with the sw-module module sfr recover command when installing the module.
Showing Module Statistics
To show module statistics, enter the following command:
|
|
|
|---|---|
Displays statistics and status for each service policy that includes the sfr command. Use clear service-policy to clear the counters. |
Examples
The following example shows the ASA FirePOWER service policy and the current statistics as well as the module status:
The following example shows a monitor-only policy. In this case, you should see packet input counters increasing, but the packet output counter should stay zero, because no traffic is passing back to the ASA.
Monitoring Module Connections
To show connections through the ASA FirePOWER module, enter one of the following commands:
Drop Reasons
The show asp drop command can include the following drop reasons related to the ASA FirePOWER module.
- sfr-bad-tlv-received—This occurs when ASA receives a packet from FirePOWER without a Policy ID TLV. This TLV must be present in non-control packets if it does not have the Standby/Active bit set in the actions field.
- sfr-request—The frame was requested to be dropped by FirePOWER due a policy on FirePOWER whereby FirePOWER would set the actions to Deny Source, Deny Destination, or Deny Pkt. If the frame should not have been dropped, review the policies on the module that are denying the flow.
- sfr-fail-close—The packet is dropped because the card is not up and the policy configured was ‘fail-close’ (rather than ‘fail-open’ which allows packets through even if the card was down). Check card status and attempt to restart services or reboot it.
- sfr-fail—The FirePOWER configuration was removed for an existing flow and we are not able to process it through FirePOWER it will be dropped. This should be very unlikely.
- sfr-malformed-packet—The packet from FirePOWER contains an invalid header. For instance, the header length may not be correct.
- sfr-ha-request—This counter is incremented when the security appliance receives a FirePOWER HA request packet, but could not process it and the packet is dropped.
- sfr-invalid-encap—This counter is incremented when the security appliance receives a FirePOWER packet with invalid message header, and the packet is dropped.
- sfr-bad-handle-received—Received Bad flow handle in a packet from FirePOWER Module, thus dropping flow. This counter is incremented, flow and packet are dropped on ASA as the handle for FirePOWER flow has changed in flow duration.
- sfr-rx-monitor-only—This counter is incremented when the security appliance receives a FirePOWER packet when in monitor-only mode, and the packet is dropped.
Examples
The following is sample output from the show asp table classify domain sfr command:
Capturing Module Traffic
To configure and view packet captures for the module, enter one of the following commands:
|
|
|
|---|---|
Captures packets between module and the ASA on the backplane. |
|

Note![]() Captured packets contain an additional AFBP header that your PCAP viewer might not understand; be sure to use the appropriate plug-in to view these packets.
Captured packets contain an additional AFBP header that your PCAP viewer might not understand; be sure to use the appropriate plug-in to view these packets.
Configuration Examples for the ASA FirePOWER Module
The following example diverts all HTTP traffic to the ASA FirePOWER module, and blocks all HTTP traffic if the module fails for any reason:
The following example diverts all IP traffic destined for the 10.1.1.0 network and the 10.2.1.0 network to the ASA FirePOWER module, and allows all traffic through if the module fails for any reason.
Feature History for the ASA FirePOWER Module
The following table lists each feature change and the platform release in which it was implemented. ASDM is backwards-compatible with multiple platform releases, so the specific ASDM release in which support was added is not listed.
 Feedback
Feedback