In an inline IPS deployment, you configure the Firepower System
transparently on a network segment by binding two ports together. This allows
the system to be installed in any network environment without the configuration
of adjacent network devices. Inline interfaces receive all traffic
unconditionally, but all traffic received on these interfaces is retransmitted
out of an inline set unless explicitly dropped.

Note
|
For the system to
affect traffic, you must deploy relevant configurations to managed devices
using routed, switched, or transparent interfaces, or inline interface pairs.
|
You can configure the interfaces on your managed device to route traffic between a host on your network and external hosts
through different inline interface pairs, depending on whether the device traffic is inbound or outbound. This is an asynchronous routing configuration. If you deploy asynchronous routing but you include only one interface pair in an inline set, the device might
not correctly analyze your network traffic because it might see only half of the traffic.
Adding multiple inline interface pairs to the same inline interface set allows the system to identify the inbound and outbound
traffic as part of the same traffic flow. For passive interfaces only, you can also achieve this by including the interface
pairs in the same security zone.
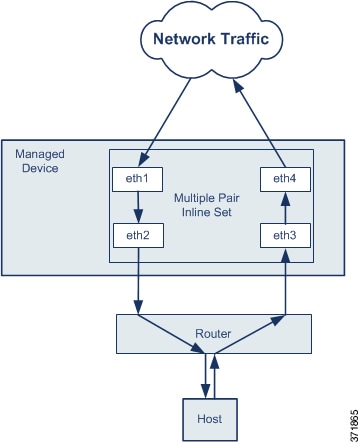
When the system generates a connection event from traffic
passing through an asynchronous routing configuration, the event may identify
an ingress and egress interface from the same inline interface pair. The
configuration in the following diagram, for example, would generate a
connection event identifying
eth3 as the ingress interface and
eth2 as the egress interface. This is expected
behavior in this configuration.

Note
|
If you assign multiple interface pairs to a single inline
interface set but you experience issues with duplicate traffic, reconfigure to
help the system uniquely identify packets. For example, you could reassign your
interface pairs to separate inline sets or modify your security zones.
|
For devices with inline sets, a software bridge is automatically
set up to transport packets after the device restarts. If the device is
restarting, there is no software bridge running anywhere. If you enable bypass
mode on the inline set, it goes into hardware bypass while the device is
restarting. In that case, you may lose a few seconds of packets as the system
goes down and comes back up, due to renegotiation of link with the device.
However, the system will pass traffic while Snort is restarting.


 )
)
 )
) Feedback
Feedback