Cisco Umbrella Auto Tunnel
Domain Name System (DNS) is an internet protocol often used in attacks. 90% of malware uses DNS (Source: Cisco Security Research Report). However, many organizations do not monitor their DNS or use DNS-focused security.
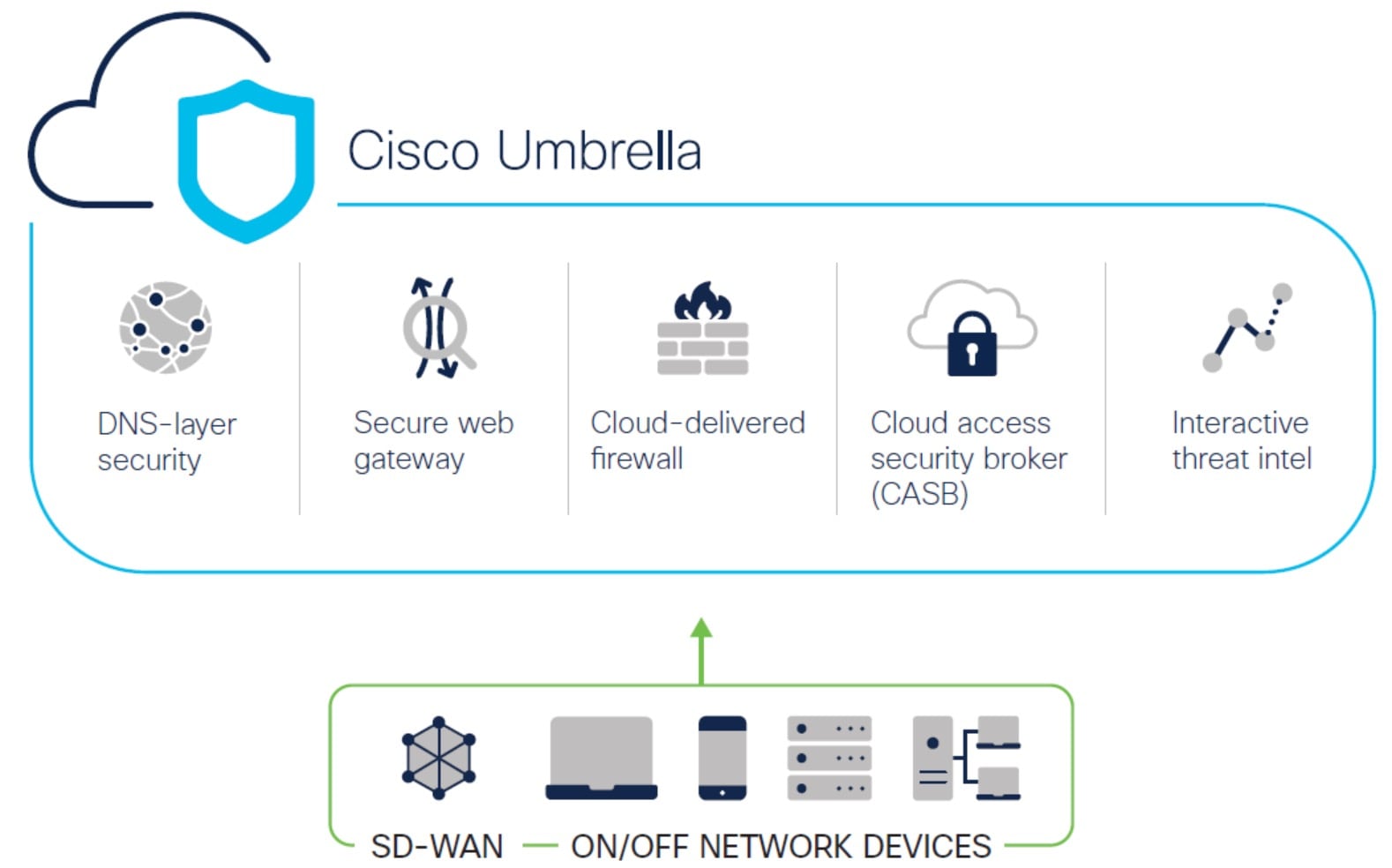
Cisco Umbrella is a cloud based secure internet gateway platform that provides multiple levels of defense against internet based threats. Umbrella integrates DNS layer security, Cloud Access Security Border (CASB) functionality, cloud-delivered firewall, and secure web gateway to deliver highly scalable security regardless of branch resources. Internet bound traffic can be sent securely automatically from the branch to the nearest Umbrella point of presence for inspection prior to being allowed or denied access to the internet.
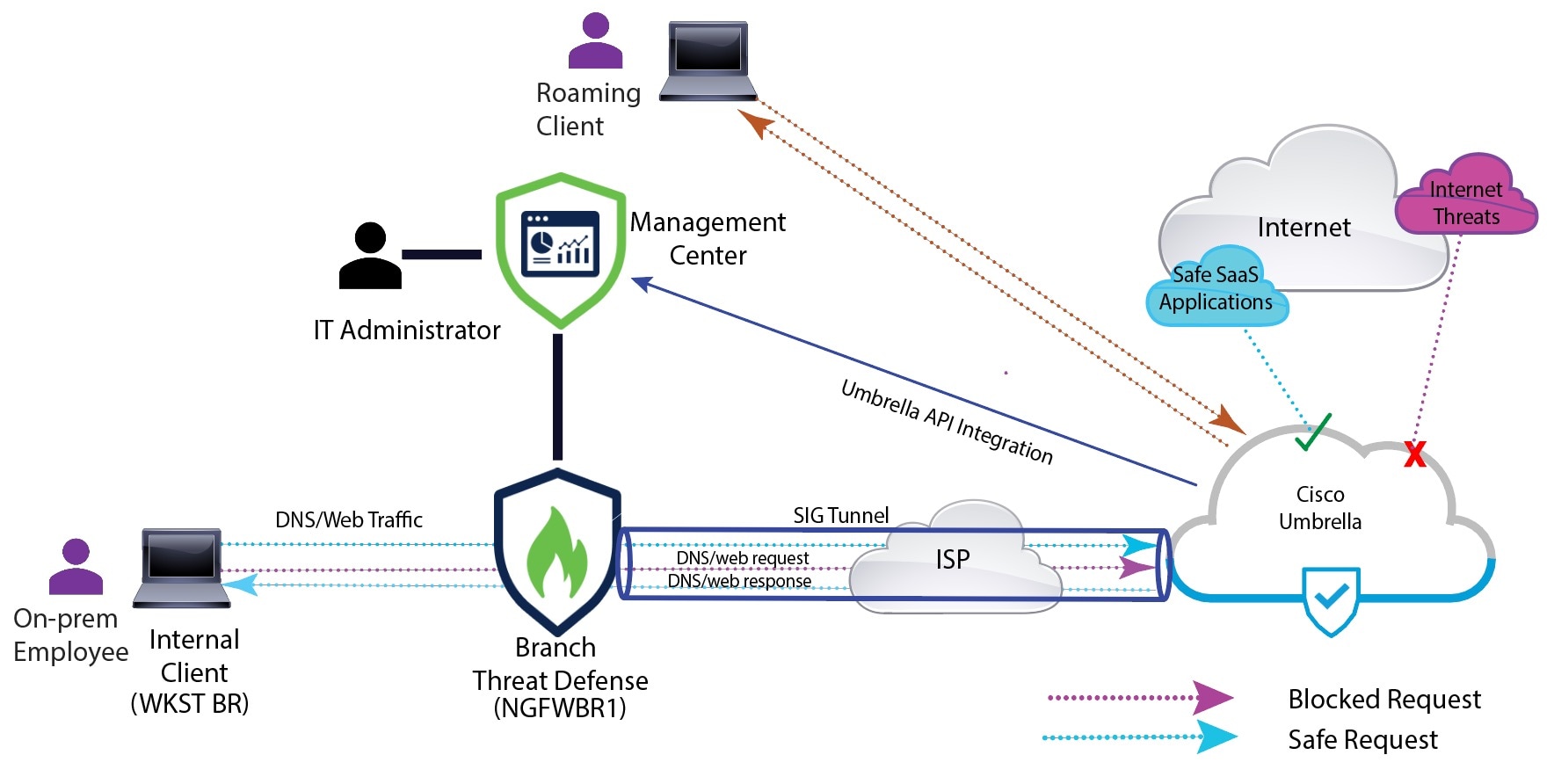
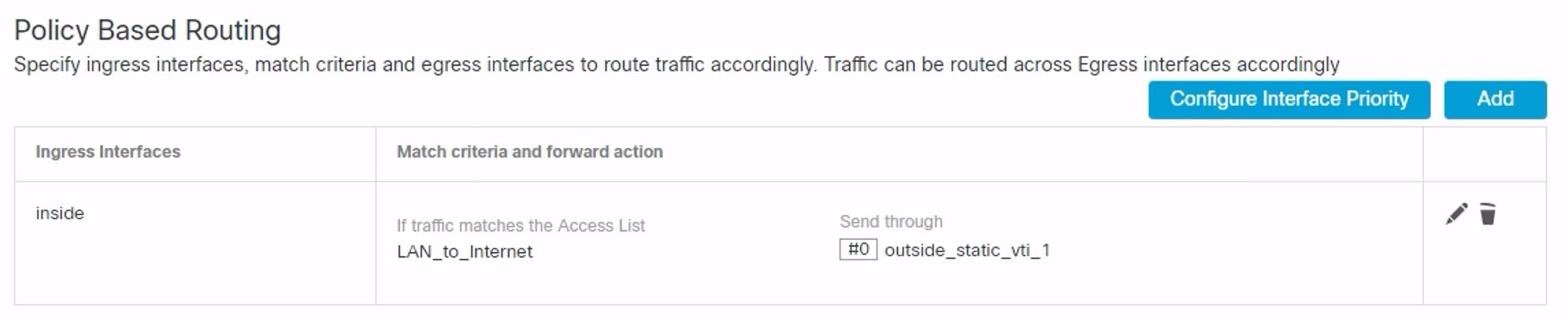
From Release 7.3, the Secure Firewall Management Center supports Auto Tunnel configuration for Umbrella Secure Internet Gateway (SIG) integration that enables a network device to forward DNS and web traffic to Umbrella SIG for inspection and filtering through the SIG tunnel.
DNS and web policies defined within Cisco Umbrella can be applied to connections through Secure Firewall This enables you to apply and validate requests based on their domain names.
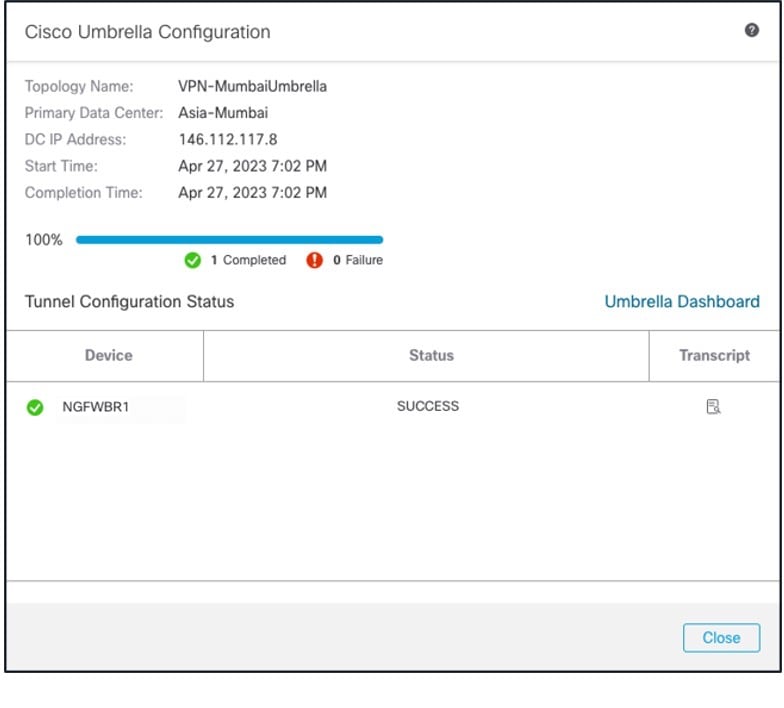
The management center provides a new simplified intuitive wizard-based interface to build this tunnel thus minimizing the configuration steps on Firewall Threat Defense and Cisco Umbrella.
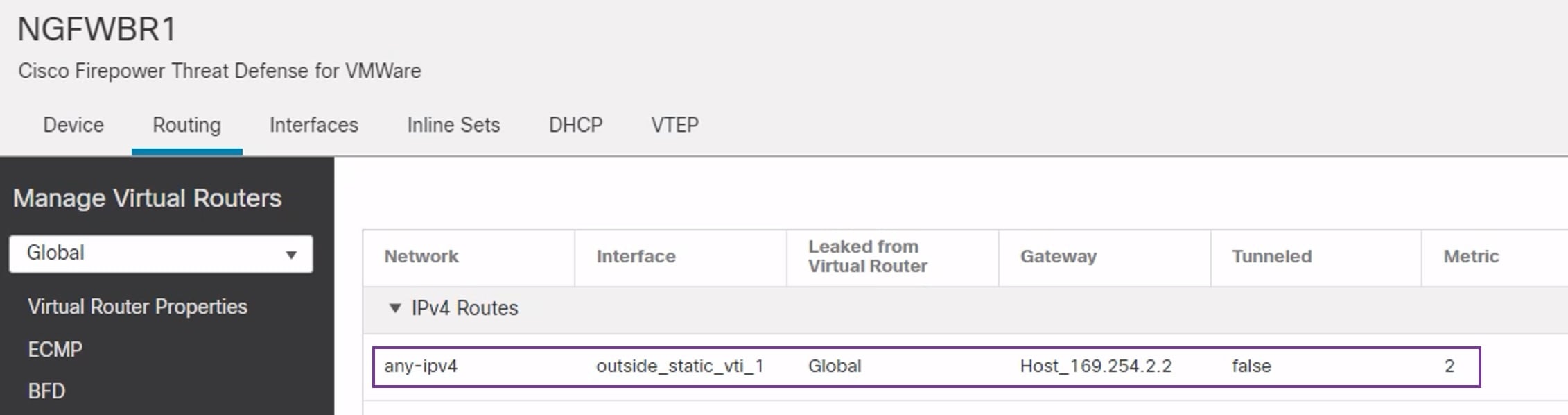
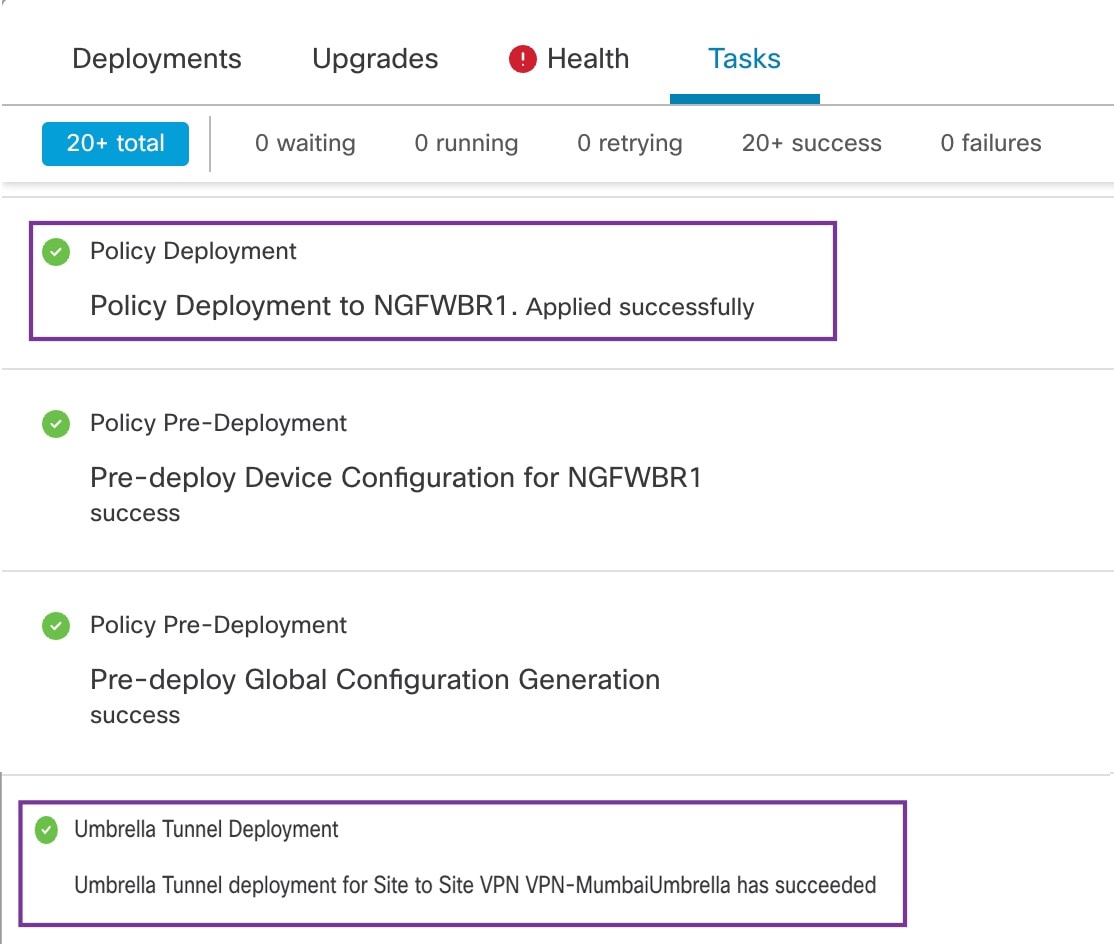
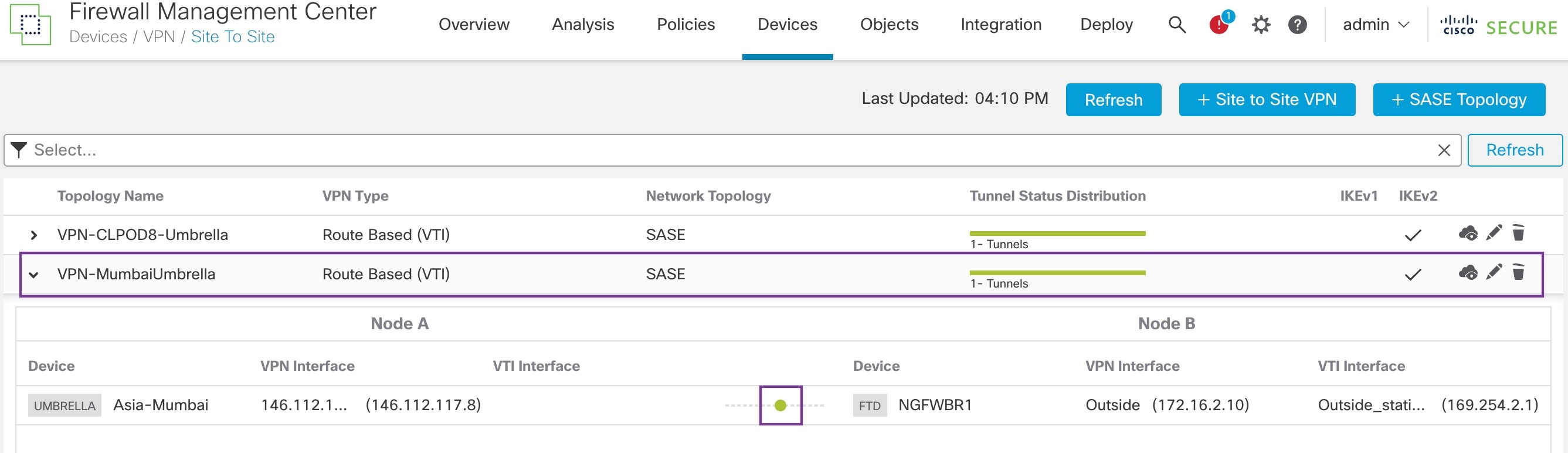
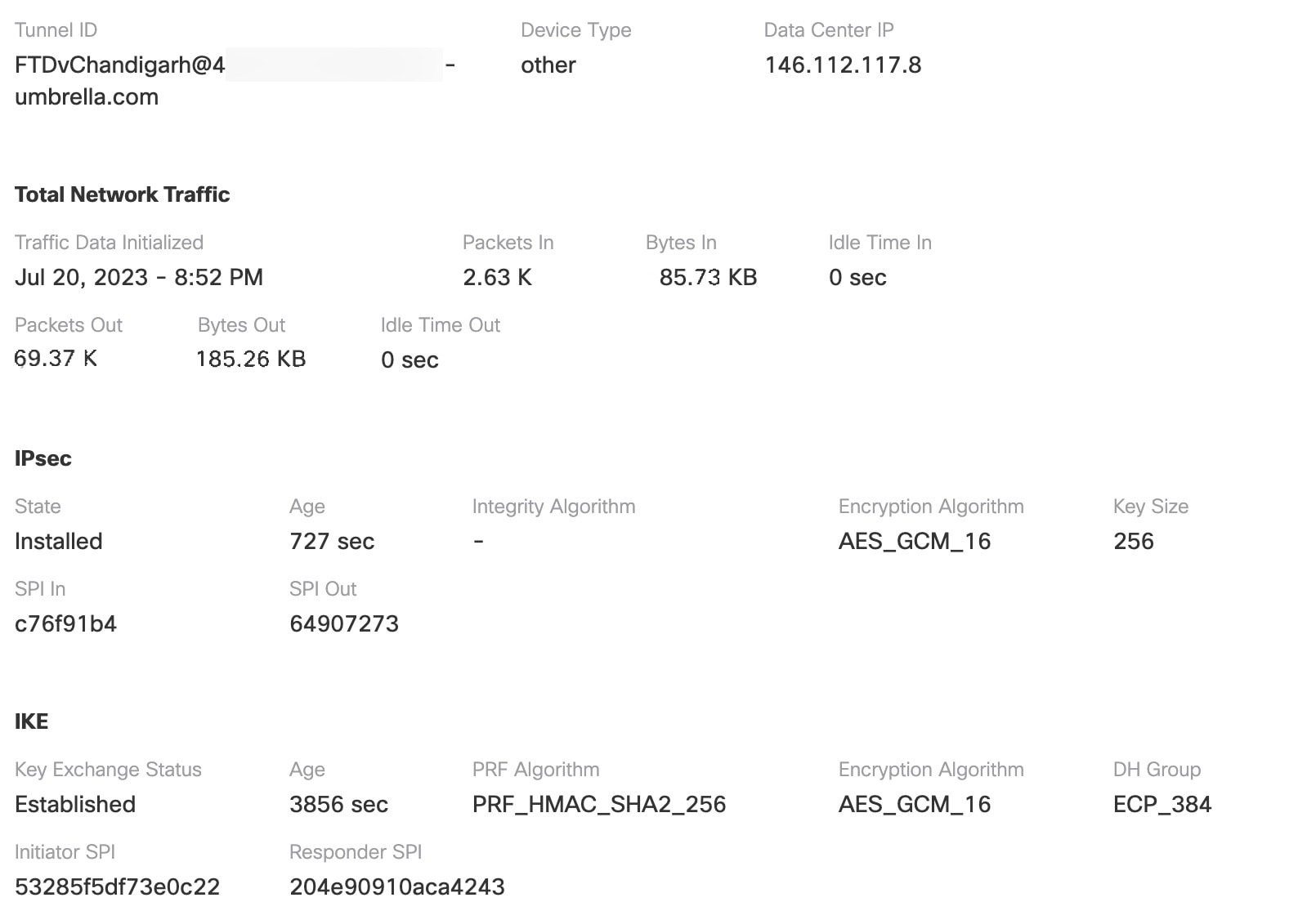
The management center leverages uses Umbrella APIs to configure the network tunnels using parameters in the Cisco Umbrella Connection configuration. Then management center fetches the list of Umbrella datacenters and displays them in the user interface for selection as a hub in the SASE Topology. The network tunnel is deployed on the threat defense device and automatically created on Cisco Umbrella after the deployment is complete in the management center. This helps to apply uniform DNS and web policies for on premise users and roaming users.








 Feedback
Feedback