Information About Configuring NSSA for OSPF
Characteristics of RFC 3101
RFC 3101 describes the following features:
-
Provides an option of importing OSPF summary routes into a Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) as Type-3 summary-Link State Advertisement (LSA).
-
Refines the setting of the forwarding address in Type-7 LSAs.
-
Revises the Type-7 external route calculation.
-
Strengthens the process of translating Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 LSAs.
-
Modifies the process of flushing translated Type-7 LSAs.
-
Defines the P-bit (propagate bit) default as clear.
RFC 1587 Compliance
RFC 3101 compliance is automatically enabled on the devices. Use the compatible rfc1587 command in router configuration mode to revert to route selection that is based on RFC 1587. When you configure the device to be compatible with RFC 1587, the device performs the following actions:
-
Reverts the route selection process to RFC 1587.
-
Configures Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) to configure the P (propagate bit) and zero-forwarding address.
-
Disables always translating Area Border Router (ABR).
ABR as NSSA Link State Advertisement Translator
Use the Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) for Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) feature to simplify administration in a network that connects a central site that uses OSPF to a remote site that is using a different routing protocol.
When the NSSA feature was not implemented, the connection between the border device at the corporate site and the remote device was not established as an OSPF stub area due to following reasons:
-
Routes for the remote site were not redistributed into the stub area.
-
Two routing protocols had to be maintained.
A protocol such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is run to handle the redistribution.
By implementing NSSA, you can extend OSPF to include the remote connection by defining the area between the border device at the corporate site and the remote device as an NSSA.
As with OSPF stub areas, NSSA areas cannot be injected with distributed routes via Type 5 Link State Advertisement (LSA). Route redistribution into an NSSA area is possible only with Type 7 LSA. An NSSA Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) generates the Type 7 LSA , and an NSSA Area Border Router (ABR) translates the Type 7 LSA into a Type 5 LSA. These LSAs can be flooded throughout the OSPF routing domain. Route summarization and filtering are supported during the translation.
Route summarization is the consolidation of advertised addresses. This feature enables an ABR to advertise a single summary route to other areas. If the network numbers in an area are assigned in a way such that they are contiguous, you can configure the ABR to advertise a summary route that covers all the individual networks within the area that fall into the specified range.
When routes from other protocols are redistributed to OSPF area, each route is advertised individually in an external LSA. However, you can configure the Cisco IOS software to advertise a single route with a specified network address and mask for all the redistributed routes that are covered by a specified network address and mask. Thus, the size of the OSPF link-state database decreases.
RFC 3101 allows you to configure an NSSA ABR device as a forced NSSA LSA translator.
 Note |
Even a forced translator might not translate all LSAs; translation depends on the content of each LSA. |
The figure below shows a network diagram in which OSPF Area 1 is defined as the stub area. The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) routes are not propagated into the OSPF domain because routing redistribution is not allowed in the stub area. However, once OSPF Area 1 is defined as an NSSA, an NSSA ASBR can include the EIGRP routes to the OSPF NSSA by generating Type 7 LSAs.
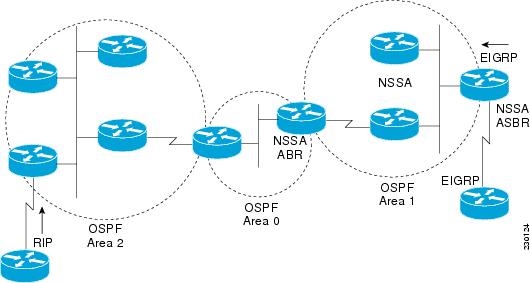
The redistributed routes from the RIP device are not allowed into OSPF Area 1 because NSSA is an extension to the stub area. The stub area characteristics still exist, including the exclusion of Type 5 LSAs.
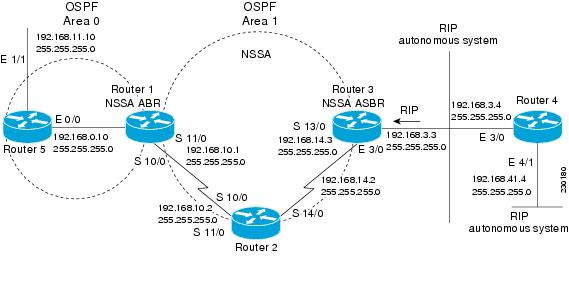
The figure below shows the OSPF stub network with NSSA Area 1. The redistributed routes that Device 4 is propagating from the two RIP networks is translated into Type 7 LSAs by NSSA ASBR Device 3. Device 2, which is configured to be the NSSA ABR, translates the Type 7 LSAs back to Type 5 so that they can be flooded through the rest of the OSPF stub network within OSPF Area 0.
 Feedback
Feedback