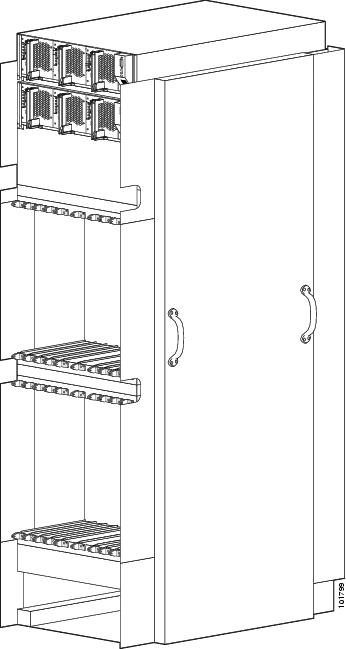
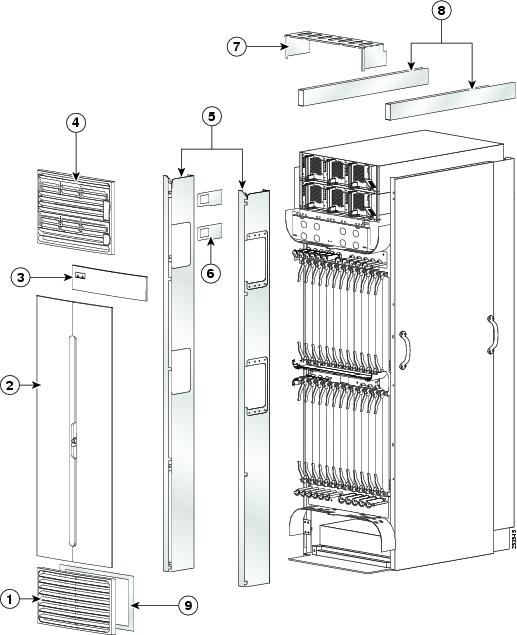
About the CRS 16-Slot Line Card Chassis
The 16 slots in the Cisco CRS 16-slot Line Card Chassis (LCC) can contain the following:
- Modular services cards (MSCs)
- Forwarding processor (FPs) cards
- Label switch processor (LSP) cards
 Note |
MSCs, FPs, and LSPs are referred to as line cards. |
- Associated physical layer interface modules (PLIMs)
- SPA Interface Processors (SIPs)
Each slot has the capacity of up to 200 gigabits per second (Gbps) ingress and 200 Gbps egress, for a total routing capacity per chassis of 6400 Gbps or 6.4 terabits per second (Tbps). (A terabit is 1 x 1012 bits or 1000 gigabits.)
The LCC supports 40G, 140G, and 400G fabric cards, as follows:
- The Cisco CRS-1 Carrier Routing System uses fabric cards designed for 40 G operation (CRS-16-FC/S or CRS-16-FC/M cards).
- The Cisco CRS-3 Carrier Routing System uses fabric cards designed for 140G operation (CRS-16-FC140/S or CRS-16-FC140/M cards).
- The Cisco CRS-X Carrier Routing System uses fabric cards designed for 200G operation (CRS-16-FC400/S or CRS-16-FC400/M cards in 200G mode).
A mixture of 40G, 140G, and 400G fabric cards is not supported except during migration.
 Note |
Throughout this document, the generic term Cisco CRS Carrier Routing system refers to the Cisco CRS-1, Cisco CRS-3, and Cisco CRS-X Carrier Routing Systems, unless otherwise specified. |
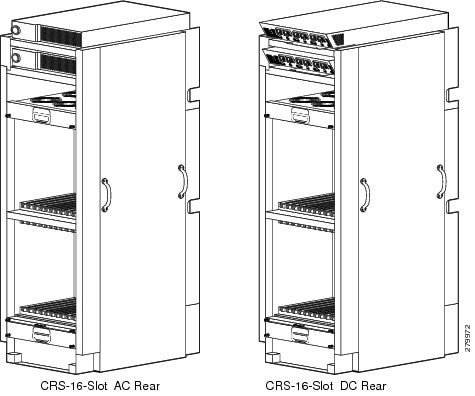
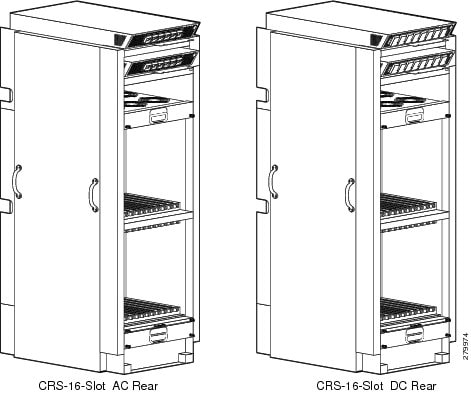
The chassis has an integrated rack and does not require an external rack. The chassis is bolted to the facility floor. It contains its own power and cooling systems. Two types of power systems are available: fixed and modular. Both power configurations use either AC or DC power.
This system description is not a planning, an installation, or a configuration guide.







 Feedback
Feedback