- About this Guide
- Chapter 1, Install Shelf and Backplane Hardware
- Chapter 2, Install Cards and Fiber-Optic Cable
- Chapter 3, Set Up PC and Log Into the GUI
- Chapter 4, Turn Up Node
- Chapter 5, Turn Up DWDM Node
- Chapter 6, Turn Up Network
- Chapter 7, Turn Up DWDM Network
- Chapter 8, Create Circuits and VT Tunnels
- Chapter 9, Manage Alarms
- Chapter 10, Monitor Performance
- Chapter 11, Manage Circuits
- Chapter 12, Change Node Settings
- Chapter 13, Change Card Settings
- Chapter 14, Upgrade Cards and Spans
- Chapter 15, Convert Network Configurations
- Chapter 16, Add and Remove Nodes
- Chapter 17, Maintain the Node
- Chapter 18, Power Down Node
- Appendix A, CTC Information and Shortcuts
- Appendix B, Specifications
- Before You Begin
- NTP-A35 Verify Node Turn Up
- NTP-A124 Provision a Point-to-Point Network
- NTP-A173 Point-to-Point Network Acceptance Test
- NTP-A38 Provision a Linear ADM Network
- NTP-A174 Linear ADM Network Acceptance Test
- NTP-A40 Provision BLSR Nodes
- NTP-A126 Create a BLSR
- NTP-A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test
- NTP-A176 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test
- NTP-A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes
- NTP-A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test
- NTP-A216 Provision a Traditional Path Protection Dual Ring Interconnect
- NTP-A217 Provision an Integrated Path Protection Interconnect
- NTP-A224 Provision an Open-Ended Path Protection
- NTP-A225 Open-Ended Path Protection Acceptance Test
- NTP-A46 Subtend a Path Protection from a BLSR
- NTP-A47 Subtend a BLSR from a Path Protection
- NTP-A48 Subtend a BLSR from a BLSR
- NTP-A172 Create a Logical Network Map
Turn Up Network
This chapter explains how to turn up and test Cisco ONS 15454 networks, including point-to-point networks, linear add-drop multiplexers (ADMs), path protection, and bidirectional line switched rings (BLSRs).

Note ![]() The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration. Rather, these terms, as well as "Path Protected Mesh Network" and "PPMN," refer generally to Cisco's path protection feature, which may be used in any topological network configuration. Cisco does not recommend using its path protection feature in any particular topological network configuration.
The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration. Rather, these terms, as well as "Path Protected Mesh Network" and "PPMN," refer generally to Cisco's path protection feature, which may be used in any topological network configuration. Cisco does not recommend using its path protection feature in any particular topological network configuration.
Before You Begin
This section lists the chapter procedures (NTPs). Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
1. ![]() A35 Verify Node Turn Up—Complete this procedure before beginning network turn up.
A35 Verify Node Turn Up—Complete this procedure before beginning network turn up.
2. ![]() A124 Provision a Point-to-Point Network—Complete as needed.
A124 Provision a Point-to-Point Network—Complete as needed.
3. ![]() A173 Point-to-Point Network Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you provision a point-to-point network.
A173 Point-to-Point Network Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you provision a point-to-point network.
4. ![]() A38 Provision a Linear ADM Network—Complete as needed.
A38 Provision a Linear ADM Network—Complete as needed.
5. ![]() A174 Linear ADM Network Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you provision a linear ADM.
A174 Linear ADM Network Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you provision a linear ADM.
6. ![]() A40 Provision BLSR Nodes—Complete this procedure to provision ONS 15454s in a two-fiber or four-fiber bidirectional line switched ring (BLSR).
A40 Provision BLSR Nodes—Complete this procedure to provision ONS 15454s in a two-fiber or four-fiber bidirectional line switched ring (BLSR).
7. ![]() A126 Create a BLSR—Complete this procedure after you provision the BLSR nodes.
A126 Create a BLSR—Complete this procedure after you provision the BLSR nodes.
8. ![]() A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you create a two-fiber BLSR.
A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you create a two-fiber BLSR.
9. ![]() A176 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you create a four-fiber BLSR.
A176 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you create a four-fiber BLSR.
10. ![]() A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes—Complete as needed.
A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes—Complete as needed.
11. ![]() A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you create a path protection.
A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test—Complete this procedure after you create a path protection.
12. ![]() A216 Provision a Traditional Path Protection Dual Ring Interconnect—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision a path protection.
A216 Provision a Traditional Path Protection Dual Ring Interconnect—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision a path protection.
13. ![]() A217 Provision an Integrated Path Protection Interconnect—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision a path protection.
A217 Provision an Integrated Path Protection Interconnect—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision a path protection.
14. ![]() A224 Provision an Open-Ended Path Protection—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision a path protection.
A224 Provision an Open-Ended Path Protection—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision a path protection.
15. ![]() A225 Open-Ended Path Protection Acceptance Test—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision an open-ended path protection.
A225 Open-Ended Path Protection Acceptance Test—As needed, complete this procedure after you provision an open-ended path protection.
16. ![]() A46 Subtend a Path Protection from a BLSR—Complete as needed.
A46 Subtend a Path Protection from a BLSR—Complete as needed.
17. ![]() A47 Subtend a BLSR from a Path Protection—Complete as needed.
A47 Subtend a BLSR from a Path Protection—Complete as needed.
18. ![]() A48 Subtend a BLSR from a BLSR—Complete as needed.
A48 Subtend a BLSR from a BLSR—Complete as needed.
19. ![]() A172 Create a Logical Network Map—Complete as needed.
A172 Create a Logical Network Map—Complete as needed.
NTP-A35 Verify Node Turn Up
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on the network you will test. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on the network you will test. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If alarms appear, investigate and resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide for procedures.
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the SW Version and Defaults shown in the node view status area match the software version and NE defaults shown in your site plan. If either is not correct, complete the following procedures as needed:
Verify that the SW Version and Defaults shown in the node view status area match the software version and NE defaults shown in your site plan. If either is not correct, complete the following procedures as needed:
•![]() If the software is not the correct version, install the correct version from the ONS 15454 software CD. Upgrade procedures are located in the Cisco ONS 15454 Upgrade Guide. Follow the upgrade procedures appropriate to the software currently installed on the node. TCC2 cards can also be ordered with the latest software release.
If the software is not the correct version, install the correct version from the ONS 15454 software CD. Upgrade procedures are located in the Cisco ONS 15454 Upgrade Guide. Follow the upgrade procedures appropriate to the software currently installed on the node. TCC2 cards can also be ordered with the latest software release.
•![]() If the node defaults are not correct, import the network element defaults. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Network Element Defaults for Software R4.6.
If the node defaults are not correct, import the network element defaults. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Network Element Defaults for Software R4.6.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Provisioning > General tabs. Verify that all general node information settings match the settings of your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A81 Change Node Management Information" procedure on page 12-2.
Click the Provisioning > General tabs. Verify that all general node information settings match the settings of your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A81 Change Node Management Information" procedure on page 12-2.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Timing tabs. Verify that timing settings match the settings of your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A85 Change Node Timing" procedure on page 12-23.
Click the Provisioning > Timing tabs. Verify that timing settings match the settings of your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A85 Change Node Timing" procedure on page 12-23.
Step 6 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Network tabs. Ensure that the IP settings and other CTC network access information is correct. If not, see the "NTP-A201 Change CTC Network Access" procedure on page 12-4.
Click the Provisioning > Network tabs. Ensure that the IP settings and other CTC network access information is correct. If not, see the "NTP-A201 Change CTC Network Access" procedure on page 12-4.
Step 7 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs. Verify that all protection groups have been created according to your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A203 Modify or Delete Card Protection Settings" procedure on page 12-15.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs. Verify that all protection groups have been created according to your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A203 Modify or Delete Card Protection Settings" procedure on page 12-15.
Step 8 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Security tabs. Verify that all users have been created and their security levels and policies match the settings indicated by your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A205 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 12-25.
Click the Provisioning > Security tabs. Verify that all users have been created and their security levels and policies match the settings indicated by your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A205 Modify Users and Change Security" procedure on page 12-25.
Step 9 ![]() If SNMP is provisioned on the node, click the Provisioning > SNMP tabs. Verify that all SNMP settings match the settings of your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A87 Change SNMP Settings" procedure on page 12-33.
If SNMP is provisioned on the node, click the Provisioning > SNMP tabs. Verify that all SNMP settings match the settings of your site plan. If not, see the "NTP-A87 Change SNMP Settings" procedure on page 12-33.
Step 10 ![]() Provision the network using the applicable procedure shown in the "Before You Begin" section.
Provision the network using the applicable procedure shown in the "Before You Begin" section.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A124 Provision a Point-to-Point Network
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on an ONS 15454 in the network where you want to provision a point-to-point configuration. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on an ONS 15454 in the network where you want to provision a point-to-point configuration. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs. Verify that 1+1 protection is created for the OC-N cards. Complete the "DLP-A73 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 4-30 if protection has not been created.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs. Verify that 1+1 protection is created for the OC-N cards. Complete the "DLP-A73 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 4-30 if protection has not been created.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for the second point-to-point node.
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for the second point-to-point node.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the working and protect cards in the 1+1 protection groups correspond to the physical fiber connections between the nodes, that is, verify that the working card in one node connects to the working card in the other node, and that the protect card in one node connects to the protect card in the other node.
Verify that the working and protect cards in the 1+1 protection groups correspond to the physical fiber connections between the nodes, that is, verify that the working card in one node connects to the working card in the other node, and that the protect card in one node connects to the protect card in the other node.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for the working OC-N port on both point-to-point nodes.
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for the working OC-N port on both point-to-point nodes.

Note ![]() DCC terminations are not provisioned on the protect ports.
DCC terminations are not provisioned on the protect ports.

Note ![]() If the point-to-point nodes are not connected to a LAN, you will need to create the DCC terminations using a direct (craft) connection to the node. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
If the point-to-point nodes are not connected to a LAN, you will need to create the DCC terminations using a direct (craft) connection to the node. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A214 Change the Service State for a Port" task to put the protect card in-service.
Complete the "DLP-A214 Change the Service State for a Port" task to put the protect card in-service.
Step 7 ![]() Verify that timing is set up at both point-to-point nodes. If not, complete the "NTP-A28 Set Up Timing" procedure on page 4-22 for one or both of the nodes. If a node uses line timing, make its working OC-N card the timing source. The system will automatically choose the corresponding protect OC-N card the protect timing source. This will be visible in the Maintenance > Timing tab.
Verify that timing is set up at both point-to-point nodes. If not, complete the "NTP-A28 Set Up Timing" procedure on page 4-22 for one or both of the nodes. If a node uses line timing, make its working OC-N card the timing source. The system will automatically choose the corresponding protect OC-N card the protect timing source. This will be visible in the Maintenance > Timing tab.
Step 8 ![]() Complete the "A173 Point-to-Point Network Acceptance Test" procedure.
Complete the "A173 Point-to-Point Network Acceptance Test" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations

Note ![]() When SDCC is provisioned, an LDCC termination is allowed on the same port, but is not recommended. Using SDCC and LDCC on the same port is only needed during a software upgrade if the software version does not support LDCC. You can provision SDCCs and LDCCs on different ports in the same node.
When SDCC is provisioned, an LDCC termination is allowed on the same port, but is not recommended. Using SDCC and LDCC on the same port is only needed during a software upgrade if the software version does not support LDCC. You can provision SDCCs and LDCCs on different ports in the same node.
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > DCC/GCC/OSC > SDCC tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > DCC/GCC/OSC > SDCC tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click Create.
Click Create.
Step 3 ![]() In the Create SDCC Terminations dialog box click the ports where you want to create the DCC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key or the Ctrl key.
In the Create SDCC Terminations dialog box click the ports where you want to create the DCC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key or the Ctrl key.

Note ![]() SDCC refers to the Section DCC, which is used for ONS 15454 DCC terminations. The SONET Line DCCs and the Section DCC (when not used as a DCC termination by the ONS 15454) can be provisioned as DCC tunnels. See the "DLP-A313 Create a DCC Tunnel" task on page 8-93.
SDCC refers to the Section DCC, which is used for ONS 15454 DCC terminations. The SONET Line DCCs and the Section DCC (when not used as a DCC termination by the ONS 15454) can be provisioned as DCC tunnels. See the "DLP-A313 Create a DCC Tunnel" task on page 8-93.
Step 4 ![]() In the Port State area, click the Set to IS radio button.
In the Port State area, click the Set to IS radio button.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the Disable OSPF on DCC Link check box is unchecked.
Verify that the Disable OSPF on DCC Link check box is unchecked.
Step 6 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.

Note ![]() EOC (DCC Termination Failure) and LOS (Loss of Signal) alarms appear until you create all network DCC terminations and put the DCC termination OC-N ports in service.
EOC (DCC Termination Failure) and LOS (Loss of Signal) alarms appear until you create all network DCC terminations and put the DCC termination OC-N ports in service.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A355 Provision SONET LDCC Terminations

Note ![]() When LDCC is provisioned, an SDCC termination is allowed on the same port, but is not recommended. Using SDCC and LDCC on the same port is only needed during a software upgrade if the software version does not support LDCC. You can provision SDCCs and LDCCs on different ports in the same node.
When LDCC is provisioned, an SDCC termination is allowed on the same port, but is not recommended. Using SDCC and LDCC on the same port is only needed during a software upgrade if the software version does not support LDCC. You can provision SDCCs and LDCCs on different ports in the same node.
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > DCC/GCC/OSC > LDCC tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > DCC/GCC/OSC > LDCC tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click Create.
Click Create.
Step 3 ![]() In the Create LDCC Terminations dialog box click the ports where you want to create the LDCC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key or the Ctrl key.
In the Create LDCC Terminations dialog box click the ports where you want to create the LDCC termination. To select more than one port, press the Shift key or the Ctrl key.

Note ![]() LDCC refers to the Line DCC, which is used for ONS 15454 DCC terminations. The SONET Line DCCs and the Section DCC (when not used as a DCC termination by the ONS 15454) can be provisioned as DCC tunnels. See the "DLP-A313 Create a DCC Tunnel" task on page 8-93.
LDCC refers to the Line DCC, which is used for ONS 15454 DCC terminations. The SONET Line DCCs and the Section DCC (when not used as a DCC termination by the ONS 15454) can be provisioned as DCC tunnels. See the "DLP-A313 Create a DCC Tunnel" task on page 8-93.
Step 4 ![]() In the Port State area, click the Set to IS radio button.
In the Port State area, click the Set to IS radio button.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the Disable OSPF on DCC Link check box is unchecked.
Verify that the Disable OSPF on DCC Link check box is unchecked.
Step 6 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.

Note ![]() EOC-L (Line DCC Termination Failure) and LOS (Loss of Signal) alarms appear until you create all network DCC terminations and put the DCC termination OC-N ports in service.
EOC-L (Line DCC Termination Failure) and LOS (Loss of Signal) alarms appear until you create all network DCC terminations and put the DCC termination OC-N ports in service.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A214 Change the Service State for a Port

Note ![]() To provision Ethernet ports, see the "DLP-A220 Provision E-Series Ethernet Ports" task on page 8-66 or the "DLP-A222 Provision G-Series Ethernet Ports" task on page 8-86.
To provision Ethernet ports, see the "DLP-A220 Provision E-Series Ethernet Ports" task on page 8-66 or the "DLP-A222 Provision G-Series Ethernet Ports" task on page 8-86.
Step 1 ![]() In node view on the shelf graphic, double-click the card with the port(s) you want to put in or out of service. The card view appears.
In node view on the shelf graphic, double-click the card with the port(s) you want to put in or out of service. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
Step 3 ![]() In the State area, choose one of the following:
In the State area, choose one of the following:
•![]() IS—The port is in-service.
IS—The port is in-service.
•![]() OOS—The port is out-of-service. Traffic is not passed on the port until the service state is changed to IS, OOS_MT, or OOS_AINS.
OOS—The port is out-of-service. Traffic is not passed on the port until the service state is changed to IS, OOS_MT, or OOS_AINS.
•![]() OOS_MT—The port is in a maintenance state. The maintenance state does not interrupt traffic flow, but alarm reporting is suppressed and loopbacks are allowed. Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command. Use OOS_MT for testing or to suppress alarms temporarily. Change the state to IS, OOS, or OOS_AINS when testing is complete.
OOS_MT—The port is in a maintenance state. The maintenance state does not interrupt traffic flow, but alarm reporting is suppressed and loopbacks are allowed. Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command. Use OOS_MT for testing or to suppress alarms temporarily. Change the state to IS, OOS, or OOS_AINS when testing is complete.
•![]() OOS_AINS—The port is in an auto-inservice state; alarm reporting is suppressed, but traffic is carried and loopbacks are allowed. After the soak period passes, the port changes to IS. Raised fault conditions, whether their alarms are reported or not, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command.
OOS_AINS—The port is in an auto-inservice state; alarm reporting is suppressed, but traffic is carried and loopbacks are allowed. After the soak period passes, the port changes to IS. Raised fault conditions, whether their alarms are reported or not, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command.
Step 4 ![]() If you set State to OOS-AINS, set the soak period time in the AINS Soak field. This is the amount of time that the port will stay in OOS-AINS after a signal is continuously received. When the soak period elapses, the port changes to IS.
If you set State to OOS-AINS, set the soak period time in the AINS Soak field. This is the amount of time that the port will stay in OOS-AINS after a signal is continuously received. When the soak period elapses, the port changes to IS.
Step 5 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 6 ![]() As needed, repeat this task for each port.
As needed, repeat this task for each port.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A173 Point-to-Point Network Acceptance Test

Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at one of the point-to-point nodes. The node (default) view appears. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at one of the point-to-point nodes. The node (default) view appears. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export alarm data.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export alarm data.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the condition information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the condition information.
Step 5 ![]() On the network map, double-click a point-to-point node to open it in node view.
On the network map, double-click a point-to-point node to open it in node view.
Step 6 ![]() Create a test circuit from the login node to the other point-to-point node:
Create a test circuit from the login node to the other point-to-point node:
•![]() For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
Step 7 ![]() Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
•![]() DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3. Next, choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3. Next, choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
Step 8 ![]() Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector the other to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before going to Step 9.
Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector the other to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before going to Step 9.
Step 9 ![]() Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Step 10 ![]() At the circuit source card:
At the circuit source card:
a. ![]() Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the receive (Rx) connector on the circuit source card.
Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the receive (Rx) connector on the circuit source card.
b. ![]() Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector on the circuit source card.
Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector on the circuit source card.
Step 11 ![]() Verify that the test set has a clean signal. If a clean signal is not present, repeat Steps 6 through 10 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Verify that the test set has a clean signal. If a clean signal is not present, repeat Steps 6 through 10 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Step 12 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
Step 13 ![]() Inject BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, indicating a complete end-to-end circuit.
Inject BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, indicating a complete end-to-end circuit.
Step 14 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Step 15 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Step 16 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A88 Optical 1+1 Protection Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A88 Optical 1+1 Protection Test" task.
Step 17 ![]() Set up and complete a BER Test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for the specified length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Set up and complete a BER Test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for the specified length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Step 18 ![]() Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Step 19 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 20 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarms information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarms information.
Step 21 ![]() Repeat Steps 9 through 20 for the other point-to-point node.
Repeat Steps 9 through 20 for the other point-to-point node.
Step 22 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
Step 23 ![]() Delete the test circuit. See the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18.
Delete the test circuit. See the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18.
After all tests are successfully completed and no alarms exist in the network, the network is ready for service application.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Conditions tab. Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Click the Conditions tab. Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 4 ![]() On the network map, double-click the node containing the TCC2 cards you are testing to open it in node view.
On the network map, double-click the node containing the TCC2 cards you are testing to open it in node view.
Step 5 ![]() Make a note of which TCC2 is active and which is standby by examining the LEDs on the shelf graphic. TCC2 cards are installed in Slot 7 and Slot 11. The active TCC2 has a green ACT LED, and the standby TCC2 has an amber SBY LED.
Make a note of which TCC2 is active and which is standby by examining the LEDs on the shelf graphic. TCC2 cards are installed in Slot 7 and Slot 11. The active TCC2 has a green ACT LED, and the standby TCC2 has an amber SBY LED.
Step 6 ![]() On the shelf graphic, right-click the active TCC2 and choose Reset from the shortcut menu.
On the shelf graphic, right-click the active TCC2 and choose Reset from the shortcut menu.
Step 7 ![]() In the Resetting Card dialog box, click Yes. After 20 to 40 seconds, a "lost node connection, changing to network view" message appears.
In the Resetting Card dialog box, click Yes. After 20 to 40 seconds, a "lost node connection, changing to network view" message appears.
Step 8 ![]() Click OK. On the network view map, the node where you reset the TCC2 will be gray.
Click OK. On the network view map, the node where you reset the TCC2 will be gray.
Step 9 ![]() After the node icon turns green (within 1 to 2 minutes), double-click it. On the shelf graphic, observe the following:
After the node icon turns green (within 1 to 2 minutes), double-click it. On the shelf graphic, observe the following:
•![]() The previous standby TCC2 has a green ACT LED.
The previous standby TCC2 has a green ACT LED.
•![]() The previous active TCC2 LEDs go through the following LED sequence: NP (card not present), Ldg (software is loading), amber SBY LED (TCC2 is in standby mode). The LEDs should complete this sequence within 5 to 10 minutes.
The previous active TCC2 LEDs go through the following LED sequence: NP (card not present), Ldg (software is loading), amber SBY LED (TCC2 is in standby mode). The LEDs should complete this sequence within 5 to 10 minutes.
Step 10 ![]() Verify that traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. If a traffic interruption occurs, do not continue, refer to your next level of support.
Verify that traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. If a traffic interruption occurs, do not continue, refer to your next level of support.
Step 11 ![]() Repeat Steps 2 through 10 to return the active/standby TCC2 cards to their configuration at the start of the procedure.
Repeat Steps 2 through 10 to return the active/standby TCC2 cards to their configuration at the start of the procedure.
Step 12 ![]() Verify that the TCC2 cards appear as noted in Step 5.
Verify that the TCC2 cards appear as noted in Step 5.
Step 13 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test

Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Conditions tab. Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Click the Conditions tab. Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 4 ![]() On the network map, double-click the node containing the cross-connect cards you are testing to open it in node view.
On the network map, double-click the node containing the cross-connect cards you are testing to open it in node view.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Maintenance > Cross-Connect tabs.
Click the Maintenance > Cross-Connect tabs.
Step 6 ![]() In the Cross-Connect Cards area, make a note of the active and standby slots.
In the Cross-Connect Cards area, make a note of the active and standby slots.
Step 7 ![]() On the shelf graphic, verify that the active cross-connect card has a green ACT LED and the standby cross-connect card has an amber SBY LED. If these conditions are not present, review the "DLP-A37 Install the XC, XCVT, or XC10G Cards" task on page 2-9 or contact your next level of support.
On the shelf graphic, verify that the active cross-connect card has a green ACT LED and the standby cross-connect card has an amber SBY LED. If these conditions are not present, review the "DLP-A37 Install the XC, XCVT, or XC10G Cards" task on page 2-9 or contact your next level of support.
Step 8 ![]() Click Switch.
Click Switch.
Step 9 ![]() In the Confirm Switch dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm Switch dialog box, click Yes.
Step 10 ![]() Verify that the active slot noted in Step 6 becomes the standby slot, and that the standby slot becomes the active slot. The switch should appear within 1 to 2 seconds.
Verify that the active slot noted in Step 6 becomes the standby slot, and that the standby slot becomes the active slot. The switch should appear within 1 to 2 seconds.
Step 11 ![]() Verify that traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. Some bit errors are normal, but traffic flow should not be interrupted. If a traffic interruption occurs, do not continue. Refer to your next level of support.
Verify that traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. Some bit errors are normal, but traffic flow should not be interrupted. If a traffic interruption occurs, do not continue. Refer to your next level of support.
Step 12 ![]() Wait 60 seconds, then repeat Steps 7 through 9 to return the active/standby slots to their configuration at the start of the procedure.
Wait 60 seconds, then repeat Steps 7 through 9 to return the active/standby slots to their configuration at the start of the procedure.
Step 13 ![]() Verify that the cross-connect card appears as you noted in Step 6.
Verify that the cross-connect card appears as you noted in Step 6.
Step 14 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A88 Optical 1+1 Protection Test
Purpose |
This task verifies that a 1+1 protection group will switch traffic properly. |
Tools/Equipment |
The test set specified by the acceptance test procedure. |
Prerequisite Procedures |
DLP-A60 Log into CTC, page 3-24; a test circuit created as part of the topology acceptance test. |
Required/As Needed |
Required |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Conditions tab. Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Click the Conditions tab. Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 4 ![]() On the network map, double-click the node containing the 1+1 protection group you are testing to open it in node view.
On the network map, double-click the node containing the 1+1 protection group you are testing to open it in node view.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Maintenance > Protection tabs.
Click the Maintenance > Protection tabs.
Step 6 ![]() Initiate a Force switch on the working port:
Initiate a Force switch on the working port:
a. ![]() In the Protection Groups area, click the 1+1 protection group.
In the Protection Groups area, click the 1+1 protection group.
b. ![]() Click the working port. Next to Switch Commands, click Force.
Click the working port. Next to Switch Commands, click Force.
c. ![]() In the Confirm Force Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm Force Operation dialog box, click Yes.
d. ![]() In the Selected Group area, verify that the following appears:
In the Selected Group area, verify that the following appears:
•![]() Protect port - Protect/Active [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_PROTECT] [PORT STATE]
Protect port - Protect/Active [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_PROTECT] [PORT STATE]
•![]() Working port - Working/Standby [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_PROTECT], [PORT STATE]
Working port - Working/Standby [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_PROTECT], [PORT STATE]
Step 7 ![]() Verify that traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. Some bit errors are normal, but traffic flow should not be interrupted. If a traffic interruption occurs, complete Step 8, then refer to your next level of support. If a traffic interruption does not occur, complete Steps 8 through 12.
Verify that traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. Some bit errors are normal, but traffic flow should not be interrupted. If a traffic interruption occurs, complete Step 8, then refer to your next level of support. If a traffic interruption does not occur, complete Steps 8 through 12.
Step 8 ![]() Clear the switch on the working port:
Clear the switch on the working port:
a. ![]() Next to Switch Commands, click Clear.
Next to Switch Commands, click Clear.
b. ![]() In the Confirm Clear Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm Clear Operation dialog box, click Yes.
Step 9 ![]() Initiate a Force switch on the protect port:
Initiate a Force switch on the protect port:
a. ![]() In the Selected Group area, click the protect port. Next to Switch Commands, click Force.
In the Selected Group area, click the protect port. Next to Switch Commands, click Force.
b. ![]() In the Confirm Force Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm Force Operation dialog box, click Yes.
c. ![]() In the Selected Group area, verify that the following appears:
In the Selected Group area, verify that the following appears:
•![]() Protect port - Protect/Active [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_WORKING], [PORT STATE]
Protect port - Protect/Active [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_WORKING], [PORT STATE]
•![]() Working port - Working/Standby [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_WORKING], [PORT STATE]
Working port - Working/Standby [FORCE_SWITCH_TO_WORKING], [PORT STATE]
Step 10 ![]() Verify that the traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. If a traffic interruption occurs, complete Step a and then refer to your next level of support. If a traffic interruption does not occur, complete Steps a and 12.
Verify that the traffic on the test set connected to the node is still running. If a traffic interruption occurs, complete Step a and then refer to your next level of support. If a traffic interruption does not occur, complete Steps a and 12.
Step 11 ![]() Clear the switch on the protect port:
Clear the switch on the protect port:
a. ![]() Next to Switch Commands, click Clear.
Next to Switch Commands, click Clear.
b. ![]() In the Confirm Clear Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm Clear Operation dialog box, click Yes.
c. ![]() In the Selected Group area, verify the following states:
In the Selected Group area, verify the following states:
•![]() Protect port - Protect/Standby
Protect port - Protect/Standby
•![]() Working port - Working/Active
Working port - Working/Active
Step 12 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A38 Provision a Linear ADM Network
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at an ONS 15454 where you want to provision in a linear ADM network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at an ONS 15454 where you want to provision in a linear ADM network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Figure 6-1 shows three ONS 15454s in a linear ADM configuration. In this example, working traffic flows from Slot 5/Node 1 to Slot 5/Node 2, and from Slot 12/Node 2 to Slot 12/Node 3. Slots 6 and 13 contain the protect OC-N cards. Slots 5 and 6 and Slots 12 and 13 are in 1+1 protection.
Figure 6-1 Linear ADM Configuration

Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs. Verify that 1+1 protection is created for the OC-N cards at the node. If the protection group has not been created, complete the "DLP-A73 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 4-30.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs. Verify that 1+1 protection is created for the OC-N cards at the node. If the protection group has not been created, complete the "DLP-A73 Create a 1+1 Protection Group" task on page 4-30.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for all other nodes that you will include in the linear ADM.
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for all other nodes that you will include in the linear ADM.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the working and protect cards in the 1+1 protection groups correspond to the physical fiber connections between the nodes, that is, working cards are fibered to working cards and protect cards are fibered to protect cards.
Verify that the working and protect cards in the 1+1 protection groups correspond to the physical fiber connections between the nodes, that is, working cards are fibered to working cards and protect cards are fibered to protect cards.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for the working OC-N ports on each linear ADM node.
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for the working OC-N ports on each linear ADM node.

Note ![]() If linear ADM nodes are not connected to a LAN, you will need to create the DCC terminations using a direct (craft) connection to the node. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes without LAN connections have DCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
If linear ADM nodes are not connected to a LAN, you will need to create the DCC terminations using a direct (craft) connection to the node. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes without LAN connections have DCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.

Note ![]() Terminating nodes (Nodes 1 and 3 in Figure 6-1) will have one DCC termination, and intermediate nodes (Node 2 in Figure 6-1) will have two DCC terminations (Slots 5 and 12 in the example).
Terminating nodes (Nodes 1 and 3 in Figure 6-1) will have one DCC termination, and intermediate nodes (Node 2 in Figure 6-1) will have two DCC terminations (Slots 5 and 12 in the example).
Step 6 ![]() Verify that the timing has been set up at each linear node. If not, complete the "NTP-A28 Set Up Timing" procedure on page 4-22. If a node is using line timing, use its working OC-N card as the timing source.
Verify that the timing has been set up at each linear node. If not, complete the "NTP-A28 Set Up Timing" procedure on page 4-22. If a node is using line timing, use its working OC-N card as the timing source.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "A174 Linear ADM Network Acceptance Test" procedure.
Complete the "A174 Linear ADM Network Acceptance Test" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A174 Linear ADM Network Acceptance Test
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on a node in the linear ADM network you are testing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on a node in the linear ADM network you are testing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 5 ![]() On the network map, double-click the linear ADM node you are testing to open it in node view.
On the network map, double-click the linear ADM node you are testing to open it in node view.
Step 6 ![]() Create a test circuit from that node to an adjacent linear ADM node.
Create a test circuit from that node to an adjacent linear ADM node.
•![]() For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
Step 7 ![]() Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
•![]() DS-1 card—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-1 card—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
Step 8 ![]() Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before going to the next step.
Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before going to the next step.
Step 9 ![]() Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the destination port's receive (Rx) connector.
Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the destination port's receive (Rx) connector.
Step 10 ![]() At the circuit source card:
At the circuit source card:
a. ![]() Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
b. ![]() Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Step 11 ![]() Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 6 through 10 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 6 through 10 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Step 12 ![]() Inject BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, indicating a complete end-to-end circuit.
Inject BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, indicating a complete end-to-end circuit.
Step 13 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Step 14 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Step 15 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A88 Optical 1+1 Protection Test" task to test the OC-N port protection group switching.
Complete the "DLP-A88 Optical 1+1 Protection Test" task to test the OC-N port protection group switching.
Step 16 ![]() Set up and complete a BER test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Set up and complete a BER test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Step 17 ![]() Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Step 18 ![]() In network view, click the Alarms tab.
In network view, click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 19 ![]() Delete the test circuit. See the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18.
Delete the test circuit. See the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18.
Step 20 ![]() Repeat Steps 6 through 19 for the next linear ADM node you are testing.
Repeat Steps 6 through 19 for the next linear ADM node you are testing.
Step 21 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
After all tests are successfully completed and no alarms exist in the network, the network is ready for service application.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A40 Provision BLSR Nodes
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A44 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations" task on page 2-37, verifying that the following rules are observed:
Complete the "DLP-A44 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations" task on page 2-37, verifying that the following rules are observed:
•![]() Verify that the east port at one node is connected to the west port on an adjacent node, and this east to west port connection is used at all BLSR nodes, similar to Figure 6-2. In the figure, the OC-N drop card on the left side of the shelf is the west port, and the drop card on the right side of the shelf is considered the east port.
Verify that the east port at one node is connected to the west port on an adjacent node, and this east to west port connection is used at all BLSR nodes, similar to Figure 6-2. In the figure, the OC-N drop card on the left side of the shelf is the west port, and the drop card on the right side of the shelf is considered the east port.
Figure 6-2 Four-Node, Two-Fiber BLSR Fiber Connection Example

•![]() For four-fiber BLSRs, verify that the same east port to west port connection is used for the working and protect fibers, similar to Figure 6-3. Verify that the working and protect card connections are not mixed. The working cards are the cards where you will provision the DCC terminations.
For four-fiber BLSRs, verify that the same east port to west port connection is used for the working and protect fibers, similar to Figure 6-3. Verify that the working and protect card connections are not mixed. The working cards are the cards where you will provision the DCC terminations.
Figure 6-3 Four-Node, Four-Fiber BLSR Fiber Connection Example

Step 2 ![]() Log into an ONS 15454 that you want to configure in a BLSR. See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 3.
Log into an ONS 15454 that you want to configure in a BLSR. See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 3.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task. Provision the two ports/cards that will serve as the BLSR ports at the node. For four-fiber BLSRs, provision the DCC terminations on the OC-N cards that will carry the working traffic, but do not provision DCCs on the protect cards.
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task. Provision the two ports/cards that will serve as the BLSR ports at the node. For four-fiber BLSRs, provision the DCC terminations on the OC-N cards that will carry the working traffic, but do not provision DCCs on the protect cards.

Note ![]() If an ONS 15454 is not connected to a corporate LAN, DCC provisioning must be performed through a direct (craft) connection to the node. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCCs provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
If an ONS 15454 is not connected to a corporate LAN, DCC provisioning must be performed through a direct (craft) connection to the node. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCCs provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
Step 4 ![]() For four-fiber BLSRs, complete the "DLP-A214 Change the Service State for a Port" task to put the protect OC-N cards/ports in service.
For four-fiber BLSRs, complete the "DLP-A214 Change the Service State for a Port" task to put the protect OC-N cards/ports in service.
Step 5 ![]() If a BLSR span passes through third-party equipment that cannot transparently transport the K3 byte, complete the "DLP-A89 Remap the K3 Byte" task. This task is not necessary for most users.
If a BLSR span passes through third-party equipment that cannot transparently transport the K3 byte, complete the "DLP-A89 Remap the K3 Byte" task. This task is not necessary for most users.
Step 6 ![]() Repeat Steps 2 through 4 at each node that will be in the BLSR. Verify that the EOC (DCC Termination Failure) and LOS (Loss of Signal) are cleared after DCCs are provisioned on all nodes in the ring.
Repeat Steps 2 through 4 at each node that will be in the BLSR. Verify that the EOC (DCC Termination Failure) and LOS (Loss of Signal) are cleared after DCCs are provisioned on all nodes in the ring.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "A126 Create a BLSR" procedure.
Complete the "A126 Create a BLSR" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A89 Remap the K3 Byte

Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the OC48AS card that connects to the third-party equipment.
In node view, double-click the OC48AS card that connects to the third-party equipment.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click BLSR Ext Byte and choose the alternate byte: Z2, E2, or F1.
Click BLSR Ext Byte and choose the alternate byte: Z2, E2, or F1.
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() For four-fiber BLSRs only, repeat Steps 2 through 4 for each protect card.
For four-fiber BLSRs only, repeat Steps 2 through 4 for each protect card.
Step 6 ![]() Repeat this task at the node and card on the other end of the BLSR span.
Repeat this task at the node and card on the other end of the BLSR span.

Note ![]() The extension byte chosen in Step 3 should match at both ends of the span.
The extension byte chosen in Step 3 should match at both ends of the span.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A126 Create a BLSR
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at a node on the network where you will create the BLSR.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at a node on the network where you will create the BLSR.
Step 2 ![]() Complete one of the following tasks:
Complete one of the following tasks:
•![]() A328 Create a BLSR Using the BLSR Wizard - Use this task to create the BLSR using the CTC BLSR wizard. The BLSR wizard checks to see that each node is ready for BLSR provisioning, then provisions all the nodes at once. Using the BLSR wizard is recommended.
A328 Create a BLSR Using the BLSR Wizard - Use this task to create the BLSR using the CTC BLSR wizard. The BLSR wizard checks to see that each node is ready for BLSR provisioning, then provisions all the nodes at once. Using the BLSR wizard is recommended.
•![]() A329 Create a BLSR Manually - Use this task to provision the BLSR manually at each node that will be in the BLSR.
A329 Create a BLSR Manually - Use this task to provision the BLSR manually at each node that will be in the BLSR.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test" procedure or the "A176 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test" procedure.
Complete the "A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test" procedure or the "A176 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A328 Create a BLSR Using the BLSR Wizard
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click Create BLSR.
Click Create BLSR.
Step 4 ![]() In the BLSR Creation dialog box, set the BLSR properties:
In the BLSR Creation dialog box, set the BLSR properties:
•![]() Ring Type—Choose the BLSR ring type, either two-fiber or four-fiber.
Ring Type—Choose the BLSR ring type, either two-fiber or four-fiber.
•![]() Speed—Choose the BLSR ring speed: OC-12 (two-fiber BLSR only), OC-48, or OC-192. The speed must match the OC-N speed of the BLSR trunk (span) cards.
Speed—Choose the BLSR ring speed: OC-12 (two-fiber BLSR only), OC-48, or OC-192. The speed must match the OC-N speed of the BLSR trunk (span) cards.

Note ![]() If you are creating an OC-12 BLSR and will eventually upgrade it to OC-48 or OC-192, use the single-port OC-12 cards (OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310, OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310, or OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310). You cannot upgrade a BLSR on a four-port OC-12 (OC12/STM4-4) because OC-48 and OC-192 cards are single-port.
If you are creating an OC-12 BLSR and will eventually upgrade it to OC-48 or OC-192, use the single-port OC-12 cards (OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310, OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310, or OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310). You cannot upgrade a BLSR on a four-port OC-12 (OC12/STM4-4) because OC-48 and OC-192 cards are single-port.
•![]() Ring Name—Assign a ring name. The name can be from 1 to 6 characters in length. Any alphanumeric string is permissible, and upper and lower case letters can be combined. Do not use the character string "All" in either upper or lower case letters, this is a TL1 keyword and will be rejected. Do not choose a name that is already assigned to another BLSR.
Ring Name—Assign a ring name. The name can be from 1 to 6 characters in length. Any alphanumeric string is permissible, and upper and lower case letters can be combined. Do not use the character string "All" in either upper or lower case letters, this is a TL1 keyword and will be rejected. Do not choose a name that is already assigned to another BLSR.
•![]() Reversion time—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path following a ring switch. The default is 5 minutes. Ring reversions can be set to Never.
Reversion time—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path following a ring switch. The default is 5 minutes. Ring reversions can be set to Never.
For four-fiber BLSRs only, complete the following:
•![]() Span Reversion—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path following a span switch. The default is 5 minutes. Span reversions can be set to Never.
Span Reversion—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path following a span switch. The default is 5 minutes. Span reversions can be set to Never.
Step 5 ![]() Click Next. If the network graphic appears, go to Step 6.
Click Next. If the network graphic appears, go to Step 6.
If CTC determines that a BLSR cannot be created, for example, not enough optical cards are installed or it finds circuits with path protection selectors, a "Cannot Create BLSR" message appears. If this occurs, complete the following steps:
a. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
b. ![]() In the Create BLSR window, click Excluded Nodes. Review the information explaining why the BLSR could not be created, then click OK.
In the Create BLSR window, click Excluded Nodes. Review the information explaining why the BLSR could not be created, then click OK.
c. ![]() Depending on the problem, click Back to start over or click Cancel to cancel the operation.
Depending on the problem, click Back to start over or click Cancel to cancel the operation.
d. ![]() Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure, making sure all steps are completed accurately, then start this procedure again.
Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure, making sure all steps are completed accurately, then start this procedure again.
Step 6 ![]() In the network graphic, double-click a BLSR span line. If the span line is DCC connected to other BLSR cards that constitute a complete ring, the lines turn blue and the Finish button appears. If the lines do not form a complete ring, double-click span lines until a complete ring is formed. When the ring is DCC connected, go to Step 7 if you are completing a four-fiber BLSR or go to Step 8 if you are completing a two-fiber BLSR.
In the network graphic, double-click a BLSR span line. If the span line is DCC connected to other BLSR cards that constitute a complete ring, the lines turn blue and the Finish button appears. If the lines do not form a complete ring, double-click span lines until a complete ring is formed. When the ring is DCC connected, go to Step 7 if you are completing a four-fiber BLSR or go to Step 8 if you are completing a two-fiber BLSR.
Step 7 ![]() For four-fiber BLSRs, click Next. For two-fiber BLSRs go to go to Step 8. In the Protect Port Selection section, choose the protect ports from the West Protect and East Protect columns. Go to the next step.
For four-fiber BLSRs, click Next. For two-fiber BLSRs go to go to Step 8. In the Protect Port Selection section, choose the protect ports from the West Protect and East Protect columns. Go to the next step.
Step 8 ![]() Click Finish. If the BLSR window appears with the BLSR you created, go to Step 9. If a "Cannot Create BLSR" or "Error While Creating BLSR" message appears:
Click Finish. If the BLSR window appears with the BLSR you created, go to Step 9. If a "Cannot Create BLSR" or "Error While Creating BLSR" message appears:
a. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
b. ![]() In the Create BLSR window, click Excluded Nodes. Review the information explaining why the BLSR could not be created, then click OK.
In the Create BLSR window, click Excluded Nodes. Review the information explaining why the BLSR could not be created, then click OK.
c. ![]() Depending on the problem, click Back to start over or click Cancel to cancel the operation.
Depending on the problem, click Back to start over or click Cancel to cancel the operation.
d. ![]() Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure, making sure all steps are completed accurately, then start this procedure again.
Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure, making sure all steps are completed accurately, then start this procedure again.

Note ![]() Some or all of the following alarms may briefly appear during BLSR setup: E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, APSDFLTK, or BLSROSYNC.
Some or all of the following alarms may briefly appear during BLSR setup: E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, APSDFLTK, or BLSROSYNC.
Step 9 ![]() Verify the following:
Verify the following:
•![]() On the network view graphic, a green span line appears between all BLSR nodes.
On the network view graphic, a green span line appears between all BLSR nodes.
•![]() All E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, DFLTK, and BLSROSYNC alarms are cleared. See the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide for alarm troubleshooting.
All E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, DFLTK, and BLSROSYNC alarms are cleared. See the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide for alarm troubleshooting.

Note ![]() The numbers in parentheses after the node name are the BLSR node IDs assigned by CTC. Every ONS 15454 in a BLSR is given a unique node ID, 0 through 31. To change it, complete the "DLP-A326 Change a BLSR Node ID" task on page 15-12.
The numbers in parentheses after the node name are the BLSR node IDs assigned by CTC. Every ONS 15454 in a BLSR is given a unique node ID, 0 through 31. To change it, complete the "DLP-A326 Change a BLSR Node ID" task on page 15-12.
Step 10 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A329 Create a BLSR Manually
Step 1 ![]() In node view, click the Provisioning > Ring tabs.
In node view, click the Provisioning > Ring tabs.
Step 2 ![]() Click Create.
Click Create.
Step 3 ![]() In the Suggestion dialog box, click OK.
In the Suggestion dialog box, click OK.
Step 4 ![]() In the Create BLSR dialog box, set the BLSR properties:
In the Create BLSR dialog box, set the BLSR properties:
•![]() Ring Type—Choose the BLSR ring type, either two-fiber or four-fiber.
Ring Type—Choose the BLSR ring type, either two-fiber or four-fiber.
•![]() Ring Name—Assign a ring name. You must use the same ring name for each node in the BLSR. Any alphanumeric character string is permissible, and upper and lower case letters can be combined. Do not use the character string "All" in either upper or lower case letters, this is a TL1 keyword and will be rejected. Do not choose a name that is already assigned to another BLSR.
Ring Name—Assign a ring name. You must use the same ring name for each node in the BLSR. Any alphanumeric character string is permissible, and upper and lower case letters can be combined. Do not use the character string "All" in either upper or lower case letters, this is a TL1 keyword and will be rejected. Do not choose a name that is already assigned to another BLSR.
•![]() Node ID—Choose a Node ID from the pull-down menu (0 through 31). The Node ID identifies the node to the BLSR. Nodes in the same BLSR must have unique Node IDs.
Node ID—Choose a Node ID from the pull-down menu (0 through 31). The Node ID identifies the node to the BLSR. Nodes in the same BLSR must have unique Node IDs.
•![]() Reversion time—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path. The default is 5 minutes. All nodes in a BLSR must have the same reversion time setting.
Reversion time—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path. The default is 5 minutes. All nodes in a BLSR must have the same reversion time setting.
•![]() West Line—Assign the west BLSR port for the node from the pull-down menu.
West Line—Assign the west BLSR port for the node from the pull-down menu.

Note ![]() The east and west ports must match the fiber connections and DCC terminations set up in the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure.
The east and west ports must match the fiber connections and DCC terminations set up in the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure.
•![]() East Line—Assign the east BLSR port for the node from the pull-down menu.
East Line—Assign the east BLSR port for the node from the pull-down menu.
For four-fiber BLSRs, complete the following:
•![]() Span Reversion—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path following a span reversion. The default is 5 minutes. Span reversions can be set to Never. If you set a reversion time, the times must be the same for both ends of the span. That is, if Node A's west fiber is connected to Node B's east port, the Node A west span reversion time must be the same as the Node B east span reversion time. To avoid reversion time mismatches, Cisco recommends that you use the same span reversion time throughout the ring.
Span Reversion—Set the amount of time that will pass before the traffic reverts to the original working path following a span reversion. The default is 5 minutes. Span reversions can be set to Never. If you set a reversion time, the times must be the same for both ends of the span. That is, if Node A's west fiber is connected to Node B's east port, the Node A west span reversion time must be the same as the Node B east span reversion time. To avoid reversion time mismatches, Cisco recommends that you use the same span reversion time throughout the ring.
•![]() West Protect—Assign the west BLSR port that will connect to the west protect fiber from the pull-down menu.
West Protect—Assign the west BLSR port that will connect to the west protect fiber from the pull-down menu.
•![]() East Protect—Assign the east BLSR port that will connect to the east protect fiber from the pull-down menu.
East Protect—Assign the east BLSR port that will connect to the east protect fiber from the pull-down menu.
Step 5 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.

Note ![]() Some or all of the following alarms will appear until all the BLSR nodes are provisioned: E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, APSDFLTK, BLSROSYNC. The alarms will clear after you configure all the nodes in the BLSR.
Some or all of the following alarms will appear until all the BLSR nodes are provisioned: E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, APSDFLTK, BLSROSYNC. The alarms will clear after you configure all the nodes in the BLSR.
Step 6 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Other Node.
From the View menu, choose Go to Other Node.
Step 7 ![]() In the Select Node dialog box, choose the next node that you want to add to the BLSR.
In the Select Node dialog box, choose the next node that you want to add to the BLSR.
Step 8 ![]() Repeat Steps 1 through 7 at each node that you want to add to the BLSR. When all nodes have been added, continue with Step 9.
Repeat Steps 1 through 7 at each node that you want to add to the BLSR. When all nodes have been added, continue with Step 9.
Step 9 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View. After 10 to 15 seconds, verify the following:
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View. After 10 to 15 seconds, verify the following:
•![]() A green span line appears between all BLSR nodes.
A green span line appears between all BLSR nodes.
•![]() All E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, DFLTK, and BLSROSYNC alarms are cleared.
All E-W MISMATCH, RING MISMATCH, APSCIMP, DFLTK, and BLSROSYNC alarms are cleared.
Step 10 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test

Note ![]() This procedure requires that you create test circuits and perform ring switches around the ring. For clarity, "Node 1" refers to the login node where you begin the procedure. "Node 2" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 1, "Node 3" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk card of Node 2, and so on.
This procedure requires that you create test circuits and perform ring switches around the ring. For clarity, "Node 1" refers to the login node where you begin the procedure. "Node 2" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 1, "Node 3" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk card of Node 2, and so on.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at one of the ONS 15454s on the BLSR you are testing. (This node will be called Node 1.). If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at one of the ONS 15454s on the BLSR you are testing. (This node will be called Node 1.). If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 5 ![]() On the network view, double-click Node 1.
On the network view, double-click Node 1.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A217 BLSR Exercise Ring Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A217 BLSR Exercise Ring Test" task.
Step 7 ![]() Create a test circuit from Node 1 to the node connected to the east OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 1. (This node will be called Node 2.)
Create a test circuit from Node 1 to the node connected to the east OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 1. (This node will be called Node 2.)
•![]() For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
Step 8 ![]() Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
•![]() DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS-3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS-3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
Step 9 ![]() Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting the test set transmit (Tx) connector to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before going to the next step.
Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting the test set transmit (Tx) connector to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before going to the next step.
Step 10 ![]() Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Step 11 ![]() At the circuit source card:
At the circuit source card:
a. ![]() Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
b. ![]() Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Step 12 ![]() Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 1 through 7 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 1 through 7 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Step 13 ![]() Inject BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, verifying a complete end-to-end circuit.
Inject BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, verifying a complete end-to-end circuit.
Step 14 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Step 15 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Although a service interruption under 60 ms may occur, the test circuit should continue to work before, during, and after the switches. If the circuit stops working, do not continue. Contact your next level of support.
Step 16 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A91 BLSR Switch Test" task at Node 1.
Complete the "DLP-A91 BLSR Switch Test" task at Node 1.
Step 17 ![]() Set up and complete a BER test on the test circuit. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Set up and complete a BER test on the test circuit. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Step 18 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Step 19 ![]() Repeating Steps 5 through 18 for Nodes 2 and higher, work your way around the BLSR, testing each node and span in the ring. Create test circuits between every two consecutive nodes.
Repeating Steps 5 through 18 for Nodes 2 and higher, work your way around the BLSR, testing each node and span in the ring. Create test circuits between every two consecutive nodes.
Step 20 ![]() After you test the entire ring, remove any loopbacks and test sets from the nodes.
After you test the entire ring, remove any loopbacks and test sets from the nodes.
Step 21 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
After all tests are successfully completed and no alarms exist in the network, the network is ready for service application. Continue with Chapter 8, "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels."
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A217 BLSR Exercise Ring Test
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click the row of the BLSR you will exercise, then click Edit.
Click the row of the BLSR you will exercise, then click Edit.
Step 4 ![]() Exercise the west port:
Exercise the west port:
a. ![]() Right-click the west port of any BLSR node and choose Set West Protection Operation. Figure 6-4 shows an example. (To move a graphic icon, press Ctrl while you drag and drop it to a new location.)
Right-click the west port of any BLSR node and choose Set West Protection Operation. Figure 6-4 shows an example. (To move a graphic icon, press Ctrl while you drag and drop it to a new location.)

Note ![]() For two fiber BLSRs, the squares on the node icons represent the BLSR working and protect channels. You can right-click either channel. For four-fiber BLSRs, the squares represent ports. Right-click either working or protect ports.
For two fiber BLSRs, the squares on the node icons represent the BLSR working and protect channels. You can right-click either channel. For four-fiber BLSRs, the squares represent ports. Right-click either working or protect ports.
Figure 6-4 Protection Operation on a Three-Node BLSR

b. ![]() In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE RING from the drop-down menu.
In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE RING from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
On the network view graphic, an E appears on the working BLSR channel where you invoked the protection switch. The E will appear for 10 to 15 seconds, then disappear.
Step 5 ![]() Exercise the east port:
Exercise the east port:
a. ![]() Right-click the east port of any BLSR node and choose Set East Protection Operation.
Right-click the east port of any BLSR node and choose Set East Protection Operation.

Note ![]() For two fiber BLSRs, the squares on the node icons represent the BLSR working and protect channels. You can right-click either channel. For four-fiber BLSRs, the squares represent ports. Right-click either working or protect ports.
For two fiber BLSRs, the squares on the node icons represent the BLSR working and protect channels. You can right-click either channel. For four-fiber BLSRs, the squares represent ports. Right-click either working or protect ports.
b. ![]() In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE RING from the drop-down menu.
In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE RING from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
On the network view graphic, an E appears on the BLSR channel where you invoked the exercise. The E will appear for 10-15 seconds, then disappear.
Step 6 ![]() In the Cisco Transport Controller window, click the History tab. Verify that an EXERCISE-RING (Exercising Ring Successfully) condition appears for the node where you exercised the ring. Other conditions that appear include EXERCISE-RING-REQ, KB-PASSTHR, and FE-EXERCISING-RING.
In the Cisco Transport Controller window, click the History tab. Verify that an EXERCISE-RING (Exercising Ring Successfully) condition appears for the node where you exercised the ring. Other conditions that appear include EXERCISE-RING-REQ, KB-PASSTHR, and FE-EXERCISING-RING.
If you do not see any BLSR exercise conditions, click the Filter button and verify that filtering is not turned on. Also, check that alarms and conditions are not suppressed for a node or BLSR drop cards. See the "A72 Suppress Alarms or Discontinue Alarm Suppression" procedure for more information.
Step 7 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 8 ![]() From the File menu choose Close to close the BLSR window.
From the File menu choose Close to close the BLSR window.
Step 9 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A91 BLSR Switch Test
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click the row of the BLSR you will switch, then click Edit.
Click the row of the BLSR you will switch, then click Edit.
Step 4 ![]() Initiate a Force Ring switch the west port:
Initiate a Force Ring switch the west port:
a. ![]() Right-click any BLSR node west port and choose Set West Protection Operation. Figure 6-4 shows an example. (To move a graphic icon, click it, then press Ctrl while you drag and drop it to a new location.)
Right-click any BLSR node west port and choose Set West Protection Operation. Figure 6-4 shows an example. (To move a graphic icon, click it, then press Ctrl while you drag and drop it to a new location.)

Note ![]() For two fiber BLSRs, the squares on the node icons represent the BLSR working and protect channels. You can right-click either channel. For four-fiber BLSRs, the squares represent ports. Right-click either working or protect port.
For two fiber BLSRs, the squares on the node icons represent the BLSR working and protect channels. You can right-click either channel. For four-fiber BLSRs, the squares represent ports. Right-click either working or protect port.
b. ![]() In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE RING from the drop-down menu.
In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE RING from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
On the network view graphic, an F appears on the BLSR channel where you invoked the Force Ring switch. The BLSR span lines turn purple where the switch was invoked, and all span lines between other BLSR nodes turn green.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the conditions:
Verify the conditions:
a. ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
b. ![]() Click Retrieve.
Click Retrieve.
c. ![]() Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch on the West port:
Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch on the West port:
FORCE-REQ-RING—A Force Switch Request On Ring condition is reported against the span's working slot on the west side of the node.
RING-SW-EAST—A Ring Switch Active on the east side condition is reported against the working span on the east side of the node.

Note ![]() Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
d. ![]() Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node that is connected to the West line of the node where you performed the switch:
Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node that is connected to the West line of the node where you performed the switch:
FE-FRCDWKSWPR-RING—A Far-End Working Facility Forced to Switch to Protection condition is reported against the working span on the east side of the node.
RING-SW-WEST—A Ring Switch Active on the west side condition is reported against the working span on the west side of the node.
Step 6 ![]() (Optional) If you remapped the K3 byte to run an ONS 15454 BLSR through third-party equipment, check the following condition. Verify a FULLPASSTHR-BI condition reported on other nodes that are not connected to the west side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
(Optional) If you remapped the K3 byte to run an ONS 15454 BLSR through third-party equipment, check the following condition. Verify a FULLPASSTHR-BI condition reported on other nodes that are not connected to the west side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
Step 7 ![]() Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
a. ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
b. ![]() Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
c. ![]() Verify the following:
Verify the following:
•![]() The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the west side of the node and Act/Act on the east side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the west side of the node and Act/Act on the east side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
•![]() The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the east side of the node and Act/Act on the west side of the node that is connected to the west line of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the east side of the node and Act/Act on the west side of the node that is connected to the west line of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
•![]() The line states are shown as Act/Act on both East and west sides of the remaining nodes in the ring.
The line states are shown as Act/Act on both East and west sides of the remaining nodes in the ring.
Step 8 ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu choose Go to Network View.
Step 9 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 10 ![]() Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Ring switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Ring switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Step 11 ![]() Clear the switch on the west port:
Clear the switch on the west port:
a. ![]() Right-click the west port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Ring switch and choose Set West Protection Operation.
Right-click the west port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Ring switch and choose Set West Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
On the network view graphic, the Force Ring switch is removed, the F indicating the switch is removed, and the span lines between BLSR nodes will be purple and green. The span lines may take a few moments to change color.
Step 12 ![]() From network view, click the Conditions tab. Verify that all conditions raised in this procedure are cleared from the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing.
From network view, click the Conditions tab. Verify that all conditions raised in this procedure are cleared from the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing.
Step 13 ![]() Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
a. ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
a. ![]() Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
b. ![]() Verify that the line states are shown as Act/Stby on both the east and west sides of each node in the ring.
Verify that the line states are shown as Act/Stby on both the east and west sides of each node in the ring.
Step 14 ![]() Initiate a Force Ring switch on the east port:
Initiate a Force Ring switch on the east port:
a. ![]() Right-click the east port of BLSR node and choose Set East Protection Operation.
Right-click the east port of BLSR node and choose Set East Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE RING from the drop-down menu.
In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE RING from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
On the network view graphic, an F appears on the working BLSR channel where you invoked the Force Ring switch. The BLSR span lines are purple where the Force Ring switch was invoked, and all span lines between other BLSR nodes are green. The span lines may take a few moments to change color.
Step 15 ![]() Verify the conditions:
Verify the conditions:
a. ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
b. ![]() Click Retrieve.
Click Retrieve.
c. ![]() Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch on the East port:
Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch on the East port:
•![]() FORCE-REQ-RING—A Force Switch Request On Ring condition is reported against the span's working slot on the east side of the node.
FORCE-REQ-RING—A Force Switch Request On Ring condition is reported against the span's working slot on the east side of the node.
•![]() RING-SW-WEST—A Ring Switch Active on the west side condition is reported against the working span on the east side of the node.
RING-SW-WEST—A Ring Switch Active on the west side condition is reported against the working span on the east side of the node.

Note ![]() Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
d. ![]() Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node that is connected to the East line of the node where you performed the switch:
Verify that the following conditions are reported on the node that is connected to the East line of the node where you performed the switch:
•![]() FE-FRCDWKSWPR-RING—A Far-End Working Facility Forced to Switch to Protection condition is reported against the working span on the west side of the node.
FE-FRCDWKSWPR-RING—A Far-End Working Facility Forced to Switch to Protection condition is reported against the working span on the west side of the node.
•![]() RING-SW-EAST—A Ring Switch Active on the east side condition is reported against the working span on the west side of the node.
RING-SW-EAST—A Ring Switch Active on the east side condition is reported against the working span on the west side of the node.
Step 16 ![]() (Optional) If you remapped the K3 byte to run an ONS 15454 BLSR through third-party equipment, verify a FULLPASSTHR-BI condition reported on other nodes that are not connected to the west side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
(Optional) If you remapped the K3 byte to run an ONS 15454 BLSR through third-party equipment, verify a FULLPASSTHR-BI condition reported on other nodes that are not connected to the west side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
Step 17 ![]() Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
a. ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
b. ![]() Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
c. ![]() Verify the following:
Verify the following:
•![]() The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the east side of the node and Act/Act on the west side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the east side of the node and Act/Act on the west side of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
•![]() The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the west side of the node and Act/Act on the east side of the node that is connected to the east line of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
The line states are shown as Stby/Stby on the west side of the node and Act/Act on the east side of the node that is connected to the east line of the node where you invoked the Force Ring switch.
•![]() The line states are shown as Act/Act on both East and West sides of the remaining nodes in the ring.
The line states are shown as Act/Act on both East and West sides of the remaining nodes in the ring.
Step 18 ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu choose Go to Network View.
Step 19 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 20 ![]() Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Ring switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Ring switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Step 21 ![]() Clear the switch on the east port:
Clear the switch on the east port:
a. ![]() Right-click the west port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Ring switch and choose Set East Protection Operation.
Right-click the west port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Ring switch and choose Set East Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
On the network view graphic, the Force Ring switch is removed, the F indicating the switch is removed, and the span lines between BLSR nodes will be purple and green. The span lines may take a few moments to change color.
Step 22 ![]() From network view, click the Conditions tab. Verify that all conditions raised in this procedure are cleared from the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing.
From network view, click the Conditions tab. Verify that all conditions raised in this procedure are cleared from the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing.
Step 23 ![]() Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
Verify the BLSR line status on each node:
a. ![]() From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
From the View menu choose Go to Node View.
b. ![]() Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
Click the Maintenance > BLSR tabs.
c. ![]() Verify that the line states are shown as Act/Stby on both the East and west sides of each node in the ring.
Verify that the line states are shown as Act/Stby on both the East and west sides of each node in the ring.
Step 24 ![]() From the File menu choose Close to close the BLSR window.
From the File menu choose Close to close the BLSR window.
Step 25 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A176 Four-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test


Note ![]() This procedure requires that you create test circuits and perform a ring switch. For clarity, "Node 1" refers to the login node where you begin the procedure. "Node 2" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 1, "Node 3" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk card of Node 2, and so on.
This procedure requires that you create test circuits and perform a ring switch. For clarity, "Node 1" refers to the login node where you begin the procedure. "Node 2" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 1, "Node 3" refers to the node connected to the East OC-N trunk card of Node 2, and so on.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on the BLSR you are testing. (This node will be called Node 1.) If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on the BLSR you are testing. (This node will be called Node 1.) If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 5 ![]() On the network map, double-click Node 1.
On the network map, double-click Node 1.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A92 Four-Fiber BLSR Exercise Span Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A92 Four-Fiber BLSR Exercise Span Test" task.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A217 BLSR Exercise Ring Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A217 BLSR Exercise Ring Test" task.
Step 8 ![]() Create a test circuit between Node 1 and Node 2.
Create a test circuit between Node 1 and Node 2.
•![]() For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
Step 9 ![]() Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
•![]() DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
Step 10 ![]() Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end of the cable to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end of the cable to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before continuing.
Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end of the cable to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end of the cable to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before continuing.
Step 11 ![]() Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card. To do so, attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector; attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Step 12 ![]() At the circuit source card:
At the circuit source card:
a. ![]() Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
b. ![]() Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Step 13 ![]() Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 6 through 12 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 6 through 12 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Step 14 ![]() Inject global BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, verifying a complete end-to-end circuit.
Inject global BIT errors from the test set. Verify that the errors appear at the test set, verifying a complete end-to-end circuit.
Step 15 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Step 16 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Step 17 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A91 BLSR Switch Test" task to test the BLSR protection switching at Node 1.
Complete the "DLP-A91 BLSR Switch Test" task to test the BLSR protection switching at Node 1.
Step 18 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A93 Four-Fiber BLSR Span Switching Test" task at Node 1.
Complete the "DLP-A93 Four-Fiber BLSR Span Switching Test" task at Node 1.
Step 19 ![]() Set up and complete a BER test on the test circuit between Node 1 and 2. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Set up and complete a BER test on the test circuit between Node 1 and 2. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Step 20 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Step 21 ![]() At Node 2, repeat Steps 5 through 20, creating a test circuit between Node 2 and the node connected to the east OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 2 (Node 3). Work your way around the BLSR creating test circuits between every two consecutive nodes.
At Node 2, repeat Steps 5 through 20, creating a test circuit between Node 2 and the node connected to the east OC-N trunk (span) card of Node 2 (Node 3). Work your way around the BLSR creating test circuits between every two consecutive nodes.
Step 22 ![]() After you test the entire ring, remove any loopbacks and test sets from the nodes.
After you test the entire ring, remove any loopbacks and test sets from the nodes.
Step 23 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 24 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 25 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
After all tests are successfully completed and no alarms exist in the network, the network is ready for service application. Continue with Chapter 8, "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels."
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A92 Four-Fiber BLSR Exercise Span Test
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click the BLSR you will exercise, then click Edit.
Click the BLSR you will exercise, then click Edit.
Step 4 ![]() Exercise the west span:
Exercise the west span:
a. ![]() Right-click the west port of the four-fiber BLSR node that you want to exercise and choose Set West Protection Operation. (To move a graphic icon, press Ctrl while you drag and drop it to a new location.)
Right-click the west port of the four-fiber BLSR node that you want to exercise and choose Set West Protection Operation. (To move a graphic icon, press Ctrl while you drag and drop it to a new location.)

Note ![]() The squares on the network map represent ports. Right-click a working port.
The squares on the network map represent ports. Right-click a working port.
b. ![]() In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK. In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
Click OK. In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
On the network view graphic, an E appears on the BLSR channel where you invoked the exercise. The E will appear for 10-15 seconds, then disappear.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the conditions:
Verify the conditions:
a. ![]() Click the Conditions tab, then click Retrieve.
Click the Conditions tab, then click Retrieve.
b. ![]() Verify the following conditions:
Verify the following conditions:
•![]() EXERCISING-SPAN—An Exercise Ring Successful condition is reported on the node where the span was exercised.
EXERCISING-SPAN—An Exercise Ring Successful condition is reported on the node where the span was exercised.
•![]() FE-EX-SPAN—A Far-End Exercise Span Request condition is reported against the East span of the node connected to the west side of the node where you exercised the span.
FE-EX-SPAN—A Far-End Exercise Span Request condition is reported against the East span of the node connected to the west side of the node where you exercised the span.
•![]() KB-PASSTHR—If applicable, a K Byte Pass Though Active condition is reported.
KB-PASSTHR—If applicable, a K Byte Pass Though Active condition is reported.

Note ![]() Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Step 6 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 7 ![]() Exercise the east span:
Exercise the east span:
a. ![]() Right-click the east port of the four-fiber BLSR node that you want to exercise and choose Set East Protection Operation.
Right-click the east port of the four-fiber BLSR node that you want to exercise and choose Set East Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose EXERCISE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box, click Yes.
On the network view graphic, an E appears on the BLSR channel where you invoked the exercise. The E will appear for 10 to 15 seconds, then disappear.
Step 8 ![]() From the File menu, choose Close.
From the File menu, choose Close.
Step 9 ![]() Verify the conditions:
Verify the conditions:
a. ![]() Click the Conditions tab, then click Retrieve.
Click the Conditions tab, then click Retrieve.
b. ![]() Verify the following conditions:
Verify the following conditions:
•![]() EXERCISING-SPAN—An Exercise Ring Successful condition is reported on the node where the span was exercised.
EXERCISING-SPAN—An Exercise Ring Successful condition is reported on the node where the span was exercised.
•![]() FE-EX-SPAN—A Far-End Exercise Span Request condition is reported against the East span of the node connected to the west side of the node where you exercised the span.
FE-EX-SPAN—A Far-End Exercise Span Request condition is reported against the East span of the node connected to the west side of the node where you exercised the span.
•![]() KB-PASSTHR—If applicable, a K Byte Pass Though Active condition is reported.
KB-PASSTHR—If applicable, a K Byte Pass Though Active condition is reported.

Note ![]() Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of the window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Step 10 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 11 ![]() From the File menu choose Close to close the BLSR window.
From the File menu choose Close to close the BLSR window.
Step 12 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A93 Four-Fiber BLSR Span Switching Test
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Click the Provisioning > BLSR tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click Edit. A BLSR window appears containing a graphic of the BLSR.
Click Edit. A BLSR window appears containing a graphic of the BLSR.

Note ![]() If the node icons are stacked on the BLSR graphic, press Ctrl while you drag and drop each one to a new location so you can see the BLSR port information clearly.
If the node icons are stacked on the BLSR graphic, press Ctrl while you drag and drop each one to a new location so you can see the BLSR port information clearly.
Step 4 ![]() Switch the west span:
Switch the west span:
a. ![]() Right-click the west port of the four-fiber BLSR node that you want to exercise and choose Set West Protection Operation. Figure 6-4 shows an example.
Right-click the west port of the four-fiber BLSR node that you want to exercise and choose Set West Protection Operation. Figure 6-4 shows an example.

Note ![]() The squares on the network map represent ports. Right-click a working port.
The squares on the network map represent ports. Right-click a working port.
b. ![]() In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
On the network view graphic, an F appears on the BLSR channel where you invoked the protection switch. The BLSR span lines turn purple where the Force Span switch was invoked, and all span lines between other BLSR nodes turn green.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the conditions:
Verify the conditions:
a. ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
b. ![]() Click Retrieve.
Click Retrieve.
c. ![]() Verify that a SPAN-SW-WEST (Span Switch West) condition is reported on the node where you invoked the Force Span switch, and a SPAN-SW-EAST (Span Switch East) condition is reported on the node connected to the west line of the node where you performed the switch. Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Verify that a SPAN-SW-WEST (Span Switch West) condition is reported on the node where you invoked the Force Span switch, and a SPAN-SW-EAST (Span Switch East) condition is reported on the node connected to the west line of the node where you performed the switch. Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of window is off. Click the Node column to sort conditions by node.
Step 6 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 7 ![]() Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Span switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Span switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Step 8 ![]() Clear the west switch:
Clear the west switch:
a. ![]() Right-click the west port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Span switch and choose Set West Protection Operation.
Right-click the west port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Span switch and choose Set West Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
In the Set West Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
On the network view graphic, the Force Span switch is removed, the F disappears, and the span lines between BLSR nodes will be purple and green. The span lines may take a few moments to change color.
Step 9 ![]() Switch the east span:
Switch the east span:
a. ![]() Right-click the east port of BLSR node and choose Set East Protection Operation.
Right-click the east port of BLSR node and choose Set East Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose FORCE SPAN from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
Click Yes in the two Confirm BLSR Operation dialog boxes that appear.
On the network view graphic, an F appears on the BLSR channel where you invoked the Force Span switch. The BLSR span lines are purple where the Force Span switch was invoked, and all span lines between other BLSR nodes are green. The span lines may take a few moments to change color.
Step 10 ![]() Verify the conditions:
Verify the conditions:
a. ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
b. ![]() Click Retrieve.
Click Retrieve.
c. ![]() Verify that a SPAN-SW-EAST (Span Switch East) condition is reported on the node where you invoked the Force Span switch, and a SPAN-SW-WEST (Span Switch West) condition is reported on the node connected to the west line of the node where you performed the switch. Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of window is off.
Verify that a SPAN-SW-EAST (Span Switch East) condition is reported on the node where you invoked the Force Span switch, and a SPAN-SW-WEST (Span Switch West) condition is reported on the node connected to the west line of the node where you performed the switch. Make sure the Filter button in the lower right corner of window is off.
Step 11 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Step 12 ![]() Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Span switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Display the BLSR window where you invoked the Force Span switch (the window may be hidden by the CTC window).
Step 13 ![]() Clear the east switch:
Clear the east switch:
a. ![]() Right-click the east port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Span switch and choose Set East Protection Operation.
Right-click the east port of the BLSR node where you invoked the Force Span switch and choose Set East Protection Operation.
b. ![]() In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
In the Set East Protection Operation dialog box, choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
d. ![]() Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
Click Yes in the Confirm BLSR Operation dialog box.
On the network view graphic, the Force Span switch is removed, the F indicating the switch is removed, and the span lines between BLSR nodes will be purple and green. The span lines may take a few moments to change color.
Step 14 ![]() From the File menu, choose Close to close the BLSR window.
From the File menu, choose Close to close the BLSR window.
Step 15 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes

Note ![]() The path protection is the default ONS 15454 topology. It is available as soon as you install the path protection OC-N cards, connect the OC-N fibers, and create the DCC terminations. Unlike the BLSRs, ONS 15454 path protection configurations do not require explicit set up.
The path protection is the default ONS 15454 topology. It is available as soon as you install the path protection OC-N cards, connect the OC-N fibers, and create the DCC terminations. Unlike the BLSRs, ONS 15454 path protection configurations do not require explicit set up.
Step 1 ![]() Verify that the fiber is correctly connected to the path protection trunk (span) OC-N cards similar to Figure 6-5. See the "NTP-A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-29.
Verify that the fiber is correctly connected to the path protection trunk (span) OC-N cards similar to Figure 6-5. See the "NTP-A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-29.
Figure 6-5 Path Protection Fiber Connection Example

Step 2 ![]() Log into an ONS 15454 in the path protection you are turning up. See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 3.
Log into an ONS 15454 in the path protection you are turning up. See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 3.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task or "DLP-A355 Provision SONET LDCC Terminations" task for the two cards/ports that will serve as the path protection ports on the node, for example, Slot 5 (OC-48)/Node 1 and Slot 12 (OC-48)/Node 1.
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task or "DLP-A355 Provision SONET LDCC Terminations" task for the two cards/ports that will serve as the path protection ports on the node, for example, Slot 5 (OC-48)/Node 1 and Slot 12 (OC-48)/Node 1.

Note ![]() If an ONS 15454 is not connected to a corporate LAN, DCC or LDCC provisioning must be performed through a direct (craft) connection. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCC or LDCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
If an ONS 15454 is not connected to a corporate LAN, DCC or LDCC provisioning must be performed through a direct (craft) connection. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCC or LDCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
Step 4 ![]() Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for each node in the path protection.
Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for each node in the path protection.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure.
Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test

Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at one of the ONS 15454s on the path protection you are testing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at one of the ONS 15454s on the path protection you are testing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 5 ![]() On the network map, double-click the node that you logged into in Step 1.
On the network map, double-click the node that you logged into in Step 1.
Step 6 ![]() Create a test circuit from that node to the next adjacent path protection node.
Create a test circuit from that node to the next adjacent path protection node.
•![]() For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
Step 7 ![]() Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
•![]() DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
Step 8 ![]() Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before continuing.
Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before continuing.
Step 9 ![]() Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card:
Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card:
a. ![]() Attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector.
Attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector.
b. ![]() Attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Step 10 ![]() At the circuit source card:
At the circuit source card:
a. ![]() Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
b. ![]() Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Step 11 ![]() Verify that the test set has a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 1 through 8 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Verify that the test set has a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 1 through 8 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Step 12 ![]() Inject BIT errors from the test set. To verify that you have a complete end-to-end circuit, verify that the errors appear at the test set.
Inject BIT errors from the test set. To verify that you have a complete end-to-end circuit, verify that the errors appear at the test set.
Step 13 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Step 14 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Step 15 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 16 ![]() Click one of the two spans leaving the circuit source node.
Click one of the two spans leaving the circuit source node.
Step 17 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A94 Path Protection Switching Test" task to test the path protection protection switching function on this span.
Complete the "DLP-A94 Path Protection Switching Test" task to test the path protection protection switching function on this span.
Step 18 ![]() In network view, click the other circuit source span and repeat Step 17.
In network view, click the other circuit source span and repeat Step 17.
Step 19 ![]() Set up and complete a BER Test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for the length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Set up and complete a BER Test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for the length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Step 20 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Step 21 ![]() Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Step 22 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 23 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 24 ![]() Repeat Steps 6 through 20 for each node on the network.
Repeat Steps 6 through 20 for each node on the network.
Step 25 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
After all tests are successfully completed and no alarms exist in the network, the network is ready for service application. Continue with Chapter 8, "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels."
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A94 Path Protection Switching Test

Note ![]() Although a service interruption under 60 ms may occur, the test circuit should continue to work before, during, and after the switches. If the circuit stops working, do not continue. Contact your next level of support.
Although a service interruption under 60 ms may occur, the test circuit should continue to work before, during, and after the switches. If the circuit stops working, do not continue. Contact your next level of support.
Step 1 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to the Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to the Network View.
Step 2 ![]() Right-click a network span and choose Circuits.
Right-click a network span and choose Circuits.
The Circuits on Span dialog box shows the path protection circuits, including circuit names, locations, and a color code showing which circuits are active on the span.
Step 3 ![]() Initiate a Force switch for all circuits on the span:
Initiate a Force switch for all circuits on the span:
a. ![]() Click the Perform UPSR span switching field.
Click the Perform UPSR span switching field.
b. ![]() Choose FORCE SWITCH AWAY from the drop-down menu.
Choose FORCE SWITCH AWAY from the drop-down menu.
c. ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
d. ![]() In the Confirm UPSR Switch dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm UPSR Switch dialog box, click Yes.
e. ![]() In the Protection Switch Result dialog box, click OK.
In the Protection Switch Result dialog box, click OK.
In the Circuits on Span dialog box, the Switch State for all circuits is FORCE. Unprotected circuits will not switch.
Step 4 ![]() Clear the Force switch:
Clear the Force switch:
a. ![]() Click the Perform UPSR span switching field and choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
Click the Perform UPSR span switching field and choose CLEAR from the drop-down menu.
b. ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
c. ![]() In the Confirm UPSR Switch dialog box, click Yes.
In the Confirm UPSR Switch dialog box, click Yes.
d. ![]() In the Protection Switch Result dialog box, click OK.
In the Protection Switch Result dialog box, click OK.
In the Circuits on Span window, the Switch State for all path protection circuits is CLEAR.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A216 Provision a Traditional Path Protection Dual Ring Interconnect

Note ![]() To route circuits on the DRI, you must check the Dual Ring Interconnect check box during circuit creation.
To route circuits on the DRI, you must check the Dual Ring Interconnect check box during circuit creation.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the following steps if you have not provisioned the path protection configurations that you will interconnect in a path protection DRI. If the path protection configurations are created, go to Step 3.
Complete the following steps if you have not provisioned the path protection configurations that you will interconnect in a path protection DRI. If the path protection configurations are created, go to Step 3.
a. ![]() Complete the "A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes" procedure to provision the path protection configurations.
Complete the "A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes" procedure to provision the path protection configurations.
b. ![]() Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure to test the path protection configurations.
Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure to test the path protection configurations.

Note ![]() All path protection configurations that will be interconnected must have the same OC-N rate.
All path protection configurations that will be interconnected must have the same OC-N rate.
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the path protection DRI interconnect nodes have OC-N cards installed and have fiber connections to the other interconnect node:
Verify that the path protection DRI interconnect nodes have OC-N cards installed and have fiber connections to the other interconnect node:
•![]() The OC-N cards that will connect the path protection configurations must be installed at the interconnect nodes. The OC-N cards in the path protection nodes and the interconnect nodes must be the same type.
The OC-N cards that will connect the path protection configurations must be installed at the interconnect nodes. The OC-N cards in the path protection nodes and the interconnect nodes must be the same type.
•![]() The interconnect nodes must have fiber connections. An example is shown in Figure 6-6. This example shows a path protection DRI with two rings, Nodes 1 through 4 and 5 through 8. In the example, an additional OC-N is installed in Slot 13 at Node 4 and connected to an OC-N in Slot 6 at Node 6. Nodes 3 and 5 are interconnected with OC-N cards in Slot 6 (Node 3) and Slot 13 (Node 5).
The interconnect nodes must have fiber connections. An example is shown in Figure 6-6. This example shows a path protection DRI with two rings, Nodes 1 through 4 and 5 through 8. In the example, an additional OC-N is installed in Slot 13 at Node 4 and connected to an OC-N in Slot 6 at Node 6. Nodes 3 and 5 are interconnected with OC-N cards in Slot 6 (Node 3) and Slot 13 (Node 5).
Figure 6-6 Traditional Path Protection DRI Fiber Connection Example

Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A217 Provision an Integrated Path Protection Interconnect
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at a node in the path protection DRI network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at a node in the path protection DRI network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the following steps if you have not provisioned the path protection configurations that you will interconnect in a path protection DRI. If the path protection configurations are created, continue with Step 3.
Complete the following steps if you have not provisioned the path protection configurations that you will interconnect in a path protection DRI. If the path protection configurations are created, continue with Step 3.
a. ![]() Complete the "A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes" procedure to provision the path protection configurations.
Complete the "A44 Provision Path Protection Nodes" procedure to provision the path protection configurations.
b. ![]() Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure to test the path protection configurations.
Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure to test the path protection configurations.

Note ![]() All path protection configurations that will be interconnected must have the same OC-N rate.
All path protection configurations that will be interconnected must have the same OC-N rate.
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the path protection DRI interconnect nodes have OC-N cards installed and have fiber connections to the other interconnect node:
Verify that the path protection DRI interconnect nodes have OC-N cards installed and have fiber connections to the other interconnect node:
•![]() The OC-N cards that will connect the path protection configurations must be installed at the interconnect nodes. The OC-N cards in the path protection nodes and the interconnect nodes must be the same type.
The OC-N cards that will connect the path protection configurations must be installed at the interconnect nodes. The OC-N cards in the path protection nodes and the interconnect nodes must be the same type.
•![]() The interconnect nodes must have the correct fiber connections. An example is shown in Figure 6-7. This example shows a path protection DRI with two rings.
The interconnect nodes must have the correct fiber connections. An example is shown in Figure 6-7. This example shows a path protection DRI with two rings.
Figure 6-7 Integrated Path Protection DRI Example
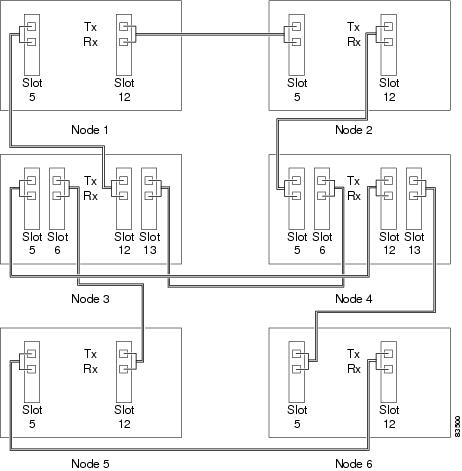
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A224 Provision an Open-Ended Path Protection
Step 1 ![]() Verify that the fiber is correctly connected to the path protection trunk (span) OC-N cards at each open-ended path protection node. Figure 6-8 shows an example. Node 1 is connected to ONS 15454 Nodes 2 and 3 through Slots 12 and 5. Trunk cards at Nodes 2 and 3 are connected to the third-party vendor equipment.
Verify that the fiber is correctly connected to the path protection trunk (span) OC-N cards at each open-ended path protection node. Figure 6-8 shows an example. Node 1 is connected to ONS 15454 Nodes 2 and 3 through Slots 12 and 5. Trunk cards at Nodes 2 and 3 are connected to the third-party vendor equipment.
Figure 6-8 ONS 15454 Open-Ended Path Protection Fiber Connection Example

Step 2 ![]() Verify that the third-party cards or units to which the ONS 15454 trunk cards are connected are the same OC-N rate as the ONS 15454 trunk cards. The third-party time slots must match the ONS 15454 card time slots to which they are connected. For example, if your trunk card is an OC-48, the third-party vendor card or unit must have STSs 1-48 available.
Verify that the third-party cards or units to which the ONS 15454 trunk cards are connected are the same OC-N rate as the ONS 15454 trunk cards. The third-party time slots must match the ONS 15454 card time slots to which they are connected. For example, if your trunk card is an OC-48, the third-party vendor card or unit must have STSs 1-48 available.
Step 3 ![]() Log into an ONS 15454 in the path protection you are turning up. See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 4.
Log into an ONS 15454 in the path protection you are turning up. See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 4.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task or "DLP-A355 Provision SONET LDCC Terminations" task for the ONS 15454 cards/ports that are connected to another ONS 15454. Do not create DCC or LDCC terminations for the card/port that connects to the third-party equipment. For example in Figure 6-8, DCC terminations are created at the following cards/ports:
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task or "DLP-A355 Provision SONET LDCC Terminations" task for the ONS 15454 cards/ports that are connected to another ONS 15454. Do not create DCC or LDCC terminations for the card/port that connects to the third-party equipment. For example in Figure 6-8, DCC terminations are created at the following cards/ports:
•![]() Nodes 1 and 6: Slot 5 and Slot 12
Nodes 1 and 6: Slot 5 and Slot 12
•![]() Node 2 and 5: Slot 12
Node 2 and 5: Slot 12
•![]() Node 3 and 4: Slot 5
Node 3 and 4: Slot 5

Note ![]() If an ONS 15454 is not connected to a corporate LAN, DCC or LDCC provisioning must be performed through a direct (craft) connection. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCC or LDCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
If an ONS 15454 is not connected to a corporate LAN, DCC or LDCC provisioning must be performed through a direct (craft) connection. Remote provisioning is possible only after all nodes in the network have DCC or LDCC terminations provisioned to in-service OC-N ports.
Step 5 ![]() Repeat Steps 3 through 4 for each node in the path protection.
Repeat Steps 3 through 4 for each node in the path protection.
Step 6 ![]() Following the documentation provided by the third-party vendor, provision the optical loop leading from the ONS 15454 connection at one end to the ONS 15454 connection at the other end. In other words, you will create an open-ended path protection using procedures for the third-party equipment.
Following the documentation provided by the third-party vendor, provision the optical loop leading from the ONS 15454 connection at one end to the ONS 15454 connection at the other end. In other words, you will create an open-ended path protection using procedures for the third-party equipment.
Step 7 ![]() Complete the "A225 Open-Ended Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure.
Complete the "A225 Open-Ended Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A225 Open-Ended Path Protection Acceptance Test

Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at the node that will be the source node for traffic traversing the third-party network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at the node that will be the source node for traffic traversing the third-party network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Alarms tab.
Click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Conditions tab.
Click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 5 ![]() On the network map, double-click the node that you logged into in Step 1.
On the network map, double-click the node that you logged into in Step 1.
Step 6 ![]() Create a test circuit from that node to the OC-N trunk (span) cards on the nodes that connect to the third-party network. For example, in Figure 6-8, a circuit is created from Node 1 to the Slot 5 OC-N card at Node 2, and a secondary circuit destination is created on the Slot 12 OC-N card at Node 3. For circuit creation procedures, complete one of the following:
Create a test circuit from that node to the OC-N trunk (span) cards on the nodes that connect to the third-party network. For example, in Figure 6-8, a circuit is created from Node 1 to the Slot 5 OC-N card at Node 2, and a secondary circuit destination is created on the Slot 12 OC-N card at Node 3. For circuit creation procedures, complete one of the following:
•![]() For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-1 circuits, complete the "NTP-A181 Create an Automatically Routed DS-1 Circuit" procedure on page 8-6. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For DS-3 circuits, complete the "NTP-A184 Create an Automatically Routed DS-3 Circuit" procedure on page 8-22. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
•![]() For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
For OC-N circuits, complete the "NTP-A188 Create an Automatically Routed OC-N Circuit" procedure on page 8-42. When you set the circuit state, choose IS and check the Apply to drop ports check box.
Step 7 ![]() Create a circuit within the third-party network from ONS 15454 connection ports to the second set of ONS 15454 connection ports on both path protection spans. Refer to the third-party equipment documentation for circuit creation procedures.
Create a circuit within the third-party network from ONS 15454 connection ports to the second set of ONS 15454 connection ports on both path protection spans. Refer to the third-party equipment documentation for circuit creation procedures.
Step 8 ![]() Repeat Step 6 to create a second circuit at the terminating node on the other side of the third-party network. In Figure 6-8, this is Node 6. However, this circuit will have two sources, one at Node 4/Slot 12, and one at Node 5/Slot 5. The destination will be a drop card on Node 6.
Repeat Step 6 to create a second circuit at the terminating node on the other side of the third-party network. In Figure 6-8, this is Node 6. However, this circuit will have two sources, one at Node 4/Slot 12, and one at Node 5/Slot 5. The destination will be a drop card on Node 6.
Step 9 ![]() Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
Configure the test set for the test circuit type you created:
•![]() DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-1—If you are testing an unmuxed DS-1, you must have a DSX-1 panel or a direct DS-1 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for DS-1. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS-3—If you are testing a clear channel DS-3, you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface into the ONS 15454. Set the test set for clear channel DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
DS3XM-6—If you are testing a DS-1 circuit on a DS3XM-6 card you must have a DSX-3 panel or a direct DS-3 interface to the ONS 15454. Set the test set for a muxed DS3, then choose the DS-1 to test on the muxed DS-3. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
•![]() OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
OC-N—If you are testing an OC-N circuit, set the test set for the applicable circuit size. For information about configuring your test set, consult your test set user guide.
Step 10 ![]() Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before continuing.
Verify the integrity of all patch cables that will be used in this test by connecting one end to the test set transmit (Tx) connector and the other end to the test set receive (Rx) connector. If the test set does not run error-free, check the cable for damage and check the test set to make sure it is set up correctly before continuing.
Step 11 ![]() Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card:
Create a physical loopback at the circuit destination card:
a. ![]() Attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector.
Attach one end of a patch cable to the destination port's transmit (Tx) connector.
b. ![]() Attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Attach the other end to the port's receive (Rx) connector.
Step 12 ![]() At the circuit source card:
At the circuit source card:
a. ![]() Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
Connect the transmit (Tx) connector of the test set to the circuit receive (Rx) connector.
b. ![]() Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Connect the test set receive (Rx) connector to the circuit transmit (Tx) connector.
Step 13 ![]() Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 1 through 8 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Verify that the test set shows a clean signal. If a clean signal does not appear, repeat Steps 1 through 8 to make sure the test set and cabling are configured correctly.
Step 14 ![]() Inject BIT errors from the test set. To verify that you have a complete end-to-end circuit, verify that the errors appear at the test set.
Inject BIT errors from the test set. To verify that you have a complete end-to-end circuit, verify that the errors appear at the test set.
Step 15 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A356 TCC2 Active/Standby Switch Test" task.
Step 16 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Complete the "DLP-A255 Cross-Connect Card Side Switch Test" task.
Although a service interruption under 60 ms may occur, the test circuit should continue to work before, during, and after the switches. If the circuit stops working, do not continue. Contact your next level of support.
Step 17 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 18 ![]() Click one of the two spans leaving the circuit source node.
Click one of the two spans leaving the circuit source node.
Step 19 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A94 Path Protection Switching Test" task to test the path protection switching function on this span.
Complete the "DLP-A94 Path Protection Switching Test" task to test the path protection switching function on this span.
Step 20 ![]() In network view, click the other circuit source span and repeat Step 19.
In network view, click the other circuit source span and repeat Step 19.
Step 21 ![]() Set up and complete a BER Test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for the length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Set up and complete a BER Test. Use the existing configuration and follow your site requirements for the length of time. Record the test results and configuration.
Step 22 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Complete the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18 for the test circuit.
Step 23 ![]() Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Remove any loopbacks, switches, or test sets from the nodes after all testing is complete.
Step 24 ![]() In network view, click the Alarms tab.
In network view, click the Alarms tab.
a. ![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not on. See the "DLP-A227 Disable Alarm Filtering" task as necessary.
b. ![]() Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained alarms appear on the network. If unexplained alarms appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
c. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the alarm information.
Step 25 ![]() In network view, click the Conditions tab.
In network view, click the Conditions tab.
a. ![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear on the network. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide if necessary.
b. ![]() Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Complete the "DLP-A516 Export CTC Data" task to export the conditions information.
Step 26 ![]() Repeat Steps 6 through 25 for each node that will be a source or destination for circuits traversing the third-party network.
Repeat Steps 6 through 25 for each node that will be a source or destination for circuits traversing the third-party network.
Step 27 ![]() If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
If a node fails any test, repeat the test while verifying correct setup and configuration. If the test fails again, refer to the next level of support.
After all tests are successfully completed and no alarms exist in the network, the network is ready for service application. Continue with Chapter 8, "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels."
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A46 Subtend a Path Protection from a BLSR
Purpose |
This procedure subtends a path protection from an existing BLSR. |
Tools/Equipment |
One BLSR node must have OC-N cards and fibers to carry the path protection. |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A175 Two-Fiber BLSR Acceptance Test or |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |

Note ![]() The path protection is the default ONS 15454 topology. It is available as soon as you install the path protection OC-N cards, connect the OC-N fibers, and create the DCC terminations. Unlike the BLSRs, ONS 15454 path protection configurations do not require explicit set up.
The path protection is the default ONS 15454 topology. It is available as soon as you install the path protection OC-N cards, connect the OC-N fibers, and create the DCC terminations. Unlike the BLSRs, ONS 15454 path protection configurations do not require explicit set up.
Step 1 ![]() In the node that will subtend the path protection (Node 3 in Figure 6-9), install the two OC-N cards that will serve as the path protection trunk (span) cards (Node 3, Slots 6 and 13). See the "NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-12. If they are already installed, continue with Step 2.
In the node that will subtend the path protection (Node 3 in Figure 6-9), install the two OC-N cards that will serve as the path protection trunk (span) cards (Node 3, Slots 6 and 13). See the "NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-12. If they are already installed, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Attach fibers from these cards to the path protection trunk cards on the neighbor path protection node or nodes. In Figure 6-9, Node 3/Slot 6 connects to Node 4/Slot 13, and Node 3/Slot 13 connects to Node 4/Slot 6.
Attach fibers from these cards to the path protection trunk cards on the neighbor path protection node or nodes. In Figure 6-9, Node 3/Slot 6 connects to Node 4/Slot 13, and Node 3/Slot 13 connects to Node 4/Slot 6.
Figure 6-9 Path Protection Subtended from a BLSR

Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at the ONS 15454 that will subtend the path protection (Node 3 in the example).
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at the ONS 15454 that will subtend the path protection (Node 3 in the example).
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for each OC-N card that will carry the path protection.
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for each OC-N card that will carry the path protection.
Step 5 ![]() Log into a path protection node that connects to the node in Step 3. (In Figure 6-9, Node 4 is the only other node in the path protection.)
Log into a path protection node that connects to the node in Step 3. (In Figure 6-9, Node 4 is the only other node in the path protection.)
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for each OC-N card that will carry the path protection.
Complete the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task for each OC-N card that will carry the path protection.
Step 7 ![]() Repeat Step 6 for each node in the path protection.
Repeat Step 6 for each node in the path protection.
Step 8 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go To Network View to view the subtending rings.
From the View menu, choose Go To Network View to view the subtending rings.
Step 9 ![]() Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure.
Complete the "A177 Path Protection Acceptance Test" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A47 Subtend a BLSR from a Path Protection
Step 1 ![]() In the path protection node that will subtend the BLSR, install the two OC-N cards that will serve as the BLSR trunk (span) cards (in Figure 6-9, Node 3, Slots 5 and 12). See the "NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-12.
In the path protection node that will subtend the BLSR, install the two OC-N cards that will serve as the BLSR trunk (span) cards (in Figure 6-9, Node 3, Slots 5 and 12). See the "NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-12.
Step 2 ![]() Attach fibers from the cards in Step 1 to the BLSR trunk cards on another BLSR node or nodes. In Figure 6-9, Slot 5/Node 3 connects to Slot 12/Node 2, and Slot 12/Node 3 connects to Slot 5/Node 1.
Attach fibers from the cards in Step 1 to the BLSR trunk cards on another BLSR node or nodes. In Figure 6-9, Slot 5/Node 3 connects to Slot 12/Node 2, and Slot 12/Node 3 connects to Slot 5/Node 1.
Step 3 ![]() Log into the ONS 15454 that will subtend the BLSR (the node in Step 1). See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 4.
Log into the ONS 15454 that will subtend the BLSR (the node in Step 1). See the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 4.
Step 4 ![]() Create the DCCs on both OC-N trunk cards (east and west) that will carry the BLSR. See the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task.
Create the DCCs on both OC-N trunk cards (east and west) that will carry the BLSR. See the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task.
Step 5 ![]() Create the subtending BLSR:
Create the subtending BLSR:
a. ![]() Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure for each node that will be in the BLSR. If you have already provisioned the BLSR, perform this procedure for the subtending node only.
Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure for each node that will be in the BLSR. If you have already provisioned the BLSR, perform this procedure for the subtending node only.
b. ![]() Complete the "A126 Create a BLSR" procedure. Include the node in Step 3 (the node that will subtend the BLSR) in the BLSR.
Complete the "A126 Create a BLSR" procedure. Include the node in Step 3 (the node that will subtend the BLSR) in the BLSR.
Step 6 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to the Network View to see the subtending ring.
From the View menu, choose Go to the Network View to see the subtending ring.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A48 Subtend a BLSR from a BLSR

Note ![]() This procedure assumes that all nodes are configured for the BLSR. If you need to add a node to a BLSR, see the "A212 Add a BLSR Node" procedure.
This procedure assumes that all nodes are configured for the BLSR. If you need to add a node to a BLSR, see the "A212 Add a BLSR Node" procedure.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at the node that will subtend the BLSR (Node 4 in Figure 6-10). If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 at the node that will subtend the BLSR (Node 4 in Figure 6-10). If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Install the OC-N cards that will serve as the BLSR trunk (span) cards if they are not already installed. See the "NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-12.
Install the OC-N cards that will serve as the BLSR trunk (span) cards if they are not already installed. See the "NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure on page 2-12.
Figure 6-10 shows two BLSRs shared by one ONS 15454. Ring 1 runs on Nodes 1, 2, 3, and 4. Ring 2 runs on Nodes 4, 5, 6, and 7 and represents the subtending ring added by this procedure. Two BLSR rings, Ring 1 and Ring 2, are provisioned on Node 4. Ring 1 uses cards in Slots 5 and 12, and Ring 2 uses cards in Slots 6 and 13.
Figure 6-10 BLSR Subtended from a BLSR

Step 3 ![]() Attach fibers from the trunk cards in the subtending node to the BLSR trunk cards on its two neighboring BLSR nodes. In Figure 6-10, Node 4/Slot 6 connects to Node 7/Slot 13, and Node 4/Slot 13 connects to Node 5/Slot 6.
Attach fibers from the trunk cards in the subtending node to the BLSR trunk cards on its two neighboring BLSR nodes. In Figure 6-10, Node 4/Slot 6 connects to Node 7/Slot 13, and Node 4/Slot 13 connects to Node 5/Slot 6.
Step 4 ![]() Create the DCCs on the first OC-N card that will carry the BLSR. See the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task.
Create the DCCs on the first OC-N card that will carry the BLSR. See the "DLP-A354 Provision SONET DCC Terminations" task.
Step 5 ![]() Repeat Step 4 for the second OC-N trunk card that will carry the BLSR.
Repeat Step 4 for the second OC-N trunk card that will carry the BLSR.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure for each node that will be in the BLSR. If you have already provisioned the BLSR, perform this procedure for the subtending node only.
Complete the "A40 Provision BLSR Nodes" procedure for each node that will be in the BLSR. If you have already provisioned the BLSR, perform this procedure for the subtending node only.
Step 7 ![]() If the subtending BLSR is not already created, complete the "A126 Create a BLSR" procedure to provision the new BLSR. The subtending BLSR must have a ring name that differs from the ring name of the first BLSR.
If the subtending BLSR is not already created, complete the "A126 Create a BLSR" procedure to provision the new BLSR. The subtending BLSR must have a ring name that differs from the ring name of the first BLSR.

Note ![]() The subtending node can have one Node ID that is used in both BLSRs, or a different Node ID for each BLSR. For example, the same node can be Node 4 in BLSR 1 and Node 2 in BLSR 2.
The subtending node can have one Node ID that is used in both BLSRs, or a different Node ID for each BLSR. For example, the same node can be Node 4 in BLSR 1 and Node 2 in BLSR 2.
Step 8 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View to see the subtending ring.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View to see the subtending ring.
Figure 6-11 shows an example of two subtending BLSRs.
Figure 6-11 Subtended BLSRs on the Network Map

Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A172 Create a Logical Network Map
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on an ONS 15454 on the network where you want to create the network map. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task on page 3-24 on an ONS 15454 on the network where you want to create the network map. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3 ![]() Change the position of the nodes in the network view according to your site plan.
Change the position of the nodes in the network view according to your site plan.
a. ![]() Click a node to select it, then press the Ctrl key while you drag and drop a node icon to a new location.
Click a node to select it, then press the Ctrl key while you drag and drop a node icon to a new location.
b. ![]() Deselect the previously selected node by clicking on any blank part of the network map area.
Deselect the previously selected node by clicking on any blank part of the network map area.
c. ![]() Repeat Step a for each node you need to position.
Repeat Step a for each node you need to position.
Step 4 ![]() On the network view map, right-click and choose Save Node Position.
On the network view map, right-click and choose Save Node Position.
Step 5 ![]() Click Yes in the Save Node Position dialog box.
Click Yes in the Save Node Position dialog box.
CTC displays a progress bar and saves the new node positions.

Note ![]() Retrieve, Provisioning, and Maintenance users can move nodes on the network map, but only Superusers can save new network map configurations. To restore the view to a previously saved version of the network map, right-click on the network view map and choose Reset Node Position.
Retrieve, Provisioning, and Maintenance users can move nodes on the network map, but only Superusers can save new network map configurations. To restore the view to a previously saved version of the network map, right-click on the network view map and choose Reset Node Position.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
 Feedback
Feedback