- About this Guide
- Chapter 1, Install Shelf and Backplane Hardware
- Chapter 2, Install Cards and Fiber-Optic Cable
- Chapter 3, Set Up PC and Log Into the GUI
- Chapter 4, Turn Up Node
- Chapter 5, Turn Up DWDM Node
- Chapter 6, Turn Up Network
- Chapter 7, Turn Up DWDM Network
- Chapter 8, Create Circuits and VT Tunnels
- Chapter 9, Manage Alarms
- Chapter 10, Monitor Performance
- Chapter 11, Manage Circuits
- Chapter 12, Change Node Settings
- Chapter 13, Change Card Settings
- Chapter 14, Upgrade Cards and Spans
- Chapter 15, Convert Network Configurations
- Chapter 16, Add and Remove Nodes
- Chapter 17, Maintain the Node
- Chapter 18, Power Down Node
- Appendix A, CTC Information and Shortcuts
- Appendix B, Specifications
- Before You Begin
- NTP-A15 Install the Common Control Cards
- NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards
- NTP-A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards
- NTP-A17 Install the Electrical Cards
- NTP-A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors
- NTP-A274 Install the FC_MR-4 Cards
- NTP-A242 Install the DWDM Cards
- NTP-A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards
- NTP-A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards
- NTP-A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards
- DLP-A423 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Termination on All DWDM Nodes
- DLP-A424 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node
- DLP-A425 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node
- DLP-A426 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node
- DLP-A427 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node
- NTP-A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables
- NTP-A116 Remove and Replace a Card
- NTP-A20 Replace the Front Door
Install Cards and Fiber-Optic Cable

Note ![]() The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration. Rather, these terms, as well as "Path Protected Mesh Network" and "PPMN," refer generally to Cisco's path protection feature, which may be used in any topological network configuration. Cisco does not recommend using its path protection feature in any particular topological network configuration.
The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration. Rather, these terms, as well as "Path Protected Mesh Network" and "PPMN," refer generally to Cisco's path protection feature, which may be used in any topological network configuration. Cisco does not recommend using its path protection feature in any particular topological network configuration.
This chapter explains how to install the Cisco ONS 15454 cards and fiber-optic cable (fiber).
Before You Begin
This section lists the chapter procedures (NTPs). Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
1. ![]() A15 Install the Common Control Cards—Complete this procedure first before installing any other cards.
A15 Install the Common Control Cards—Complete this procedure first before installing any other cards.
2. ![]() A16 Install the OC-N Cards—Complete as needed.
A16 Install the OC-N Cards—Complete as needed.
3. ![]() A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards—Complete as needed.
A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards—Complete as needed.
4. ![]() A17 Install the Electrical Cards—Complete as needed.
A17 Install the Electrical Cards—Complete as needed.
5. ![]() A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors—Complete as needed.
A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors—Complete as needed.
6. ![]() A274 Install the FC_MR-4 Cards—Complete as needed.
A274 Install the FC_MR-4 Cards—Complete as needed.
7. ![]() A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards—Complete this procedure to install fiber on OC-N cards, Ethernet Gigabit Interface Converters (GBICs), or small form-factor pluggables (SFPs).
A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards—Complete this procedure to install fiber on OC-N cards, Ethernet Gigabit Interface Converters (GBICs), or small form-factor pluggables (SFPs).
8. ![]() A242 Install the DWDM Cards—Complete as needed.
A242 Install the DWDM Cards—Complete as needed.
9. ![]() A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards—Complete as needed.
A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards—Complete as needed.
10. ![]() A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards—Complete as needed.
A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards—Complete as needed.
11. ![]() A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables—Complete as needed.
A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables—Complete as needed.
12. ![]() A116 Remove and Replace a Card—Complete this procedure as needed to remove and replace a card, including deleting the card from Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) and changing an OC-N card without losing the card's provisioning.
A116 Remove and Replace a Card—Complete this procedure as needed to remove and replace a card, including deleting the card from Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) and changing an OC-N card without losing the card's provisioning.
13. ![]() A20 Replace the Front Door—If the front door was removed, complete this procedure to replace the front door and ground strap after installing cards and fiber.
A20 Replace the Front Door—If the front door was removed, complete this procedure to replace the front door and ground strap after installing cards and fiber.

Warning ![]() Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.

NTP-A15 Install the Common Control Cards
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to install the common control cards. |
Tools/Equipment |
Redundant TCC2 cards Redundant XC, XCVT, or XC10G (cross-connect) cards AIC/AIC-I card (optional) |
Prerequisite Procedures |
NTP-A13 Perform the Shelf Installation Acceptance Test, page 1-67 |
Required/As Needed |
Required |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
Step 1 ![]() If you plan to install XC/XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you plan to install XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
If you plan to install XC/XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you plan to install XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A36 Install the TCC2 Cards" task.
Complete the "DLP-A36 Install the TCC2 Cards" task.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A37 Install the XC, XCVT, or XC10G Cards" task unless you are provisioning a DWDM-only node.
Complete the "DLP-A37 Install the XC, XCVT, or XC10G Cards" task unless you are provisioning a DWDM-only node.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A38 Install the Alarm Interface Controller or Alarm Interface Controller-International Card" task, as needed.
Complete the "DLP-A38 Install the Alarm Interface Controller or Alarm Interface Controller-International Card" task, as needed.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, see the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, see the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
Step 5 ![]() Continue with one of the following:
Continue with one of the following:
•![]() If the node you are provisioning is TDM-only (no DWDM cards installed), install the traffic cards. To determine the appropriate procedure, see the NTP list in the "Before You Begin" section.
If the node you are provisioning is TDM-only (no DWDM cards installed), install the traffic cards. To determine the appropriate procedure, see the NTP list in the "Before You Begin" section.
•![]() If the node you are provisioning is DWDM-only or a hybrid, continue with "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI."
If the node you are provisioning is DWDM-only or a hybrid, continue with "Connect the PC and Log into the GUI."
In Table 2-1, X indicates that a card is supported in the slot.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TCC2 |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||||
XC/XCVT |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||||
AIC |
X |
||||||||||||||||
AIC-I |
X |
||||||||||||||||
DS1-14 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
DS1N-14 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X4 |
X4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
DS3-12E |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X4 |
X4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
DS3N-12 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3,4 |
X3,4 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3N-12E |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3,4 |
X3,4 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3I-N-125 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3, |
X3, |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3XM-6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X4 |
X4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
EC1-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X6 |
X6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
E100T-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
E1000-2 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
E100T-G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
E1000-2-G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
G1000-4 |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
G1K-4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
ML100-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
ML1000-2 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC3IR/STM1SH 1310-8 |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
OC12 IR STM4 SH 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310-4 |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
OC48 IR 13107 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 LR 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 IR/STM16 SH AS 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 LR/STM16 LH AS 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48-ELR/STM16 EH 100 GHz |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 ELR 200 GHz |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC192 SR/STM64 IO 1310 |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
OC192 IR/STM64 SH 1550 |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
OC192 LR/STM64 LH ITU 15xx.xx |
Not supported with XC/XCVT cards. Requires XC10G cards. |
||||||||||||||||
TXP_MR_2.5G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
TXPP_MR_2.5G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
TXP_MR_10G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
FC_MR-4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
MXP_2.5G_10G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
1 MS identifies slots 1 to 4 and 14 to 17 ("multispeed" slot). 2 HS identifies slots 5, 6, 12, and 13 ("high-speed" slot). 3 This identifies 1:N cards that operate as normal DS1 or DS3 cards when installed in certain slots. 4 This DS3 card cannot be used in this slot if used with a high-density EIA or in a 1:N configuration. 5 This card can only be use with the XCVT card, not the XC card. 6 EC1 cards cannot be used in this slot if used with a high-density EIA. 7 The OC48AS will operate in the high speed slots with the XC/XCVT in R3.4 and later. In Release R3.3, OC48AS with XC/XCVT is not supported. |
In Table 2-2, X indicates that a card is supported in the slot. The XC10G card requires the ANSI shelf (5454-SA-ANSI) or the high-density shelf (15454-SA-HD).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TCC2 |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||||
XC10G |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||||
AIC |
X |
||||||||||||||||
AIC-I |
X |
||||||||||||||||
DS1-14 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
DS1N-14 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X4 |
X4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
DS3-12E |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X4 |
X4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
DS3N-12 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3,4 |
X3,4 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3N-12E |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
X3,4 |
X3,4 |
X3 |
X3 |
X |
X3 |
X3 |
|||||
DS3XM-6 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X4 |
X4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
EC1-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X5 |
X5 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
E100T-12 |
Not supported with the XC10G card. |
||||||||||||||||
E1000-2 |
Not supported with the XC10G card. |
||||||||||||||||
E100T-G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
E1000-2-G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
G1000-4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
G1K-4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
ML100-12 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
ML1000-2 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC3IR/STM1SH 1310-8 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||
OC12 IR STM4 SH 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310-4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||
OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC48 IR 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 LR 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 IR/STM16 SH AS 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC48 LR/STM16 LH AS 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
OC48-ELR/STM16 EH 100 GHz |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC48 ELR 200 GHz |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC192 SR/STM64 IO 1310 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC192 IR/STM64 SH 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
OC192 LR/STM64 LH ITU 15xx.xx |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||||||||||
TXP_MR_2.5G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
TXPP_MR_2.5G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
TXP_MR_10G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
MXP_2.5G_10G |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
FC_MR-4 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|||||
1 MS identifies slots 1 to 4 and 14 to 17 ("multispeed" slot). 2 HS identifies slots 5, 6, 12, and 13 ("high-speed" slot). 3 This identifies 1:N cards that operate as normal DS1 or DS3 cards when installed in certain slots. 4 This DS3 card cannot be used in this slot if used with a high-density EIA or in a 1:N configuration. 5 EC1 cards cannot be used in this slot if used with a high-density EIA. |
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A36 Install the TCC2 Cards

Note ![]() When installing cards, allow each card to boot completely before installing the next card.
When installing cards, allow each card to boot completely before installing the next card.
Step 1 ![]() Open the latches/ejectors of the first TCC2 card that you will install.
Open the latches/ejectors of the first TCC2 card that you will install.
Step 2 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 7 or 11).
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 7 or 11).
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
Step 4 ![]() Verify the LED activity of the TCC2 card:
Verify the LED activity of the TCC2 card:
•![]() All LEDs turn on briefly.
All LEDs turn on briefly.
•![]() The red FAIL LED, the yellow ACT/STBY LED, the red REM LED, the green SYNC LED, and the green ACO LED turn on and remain on for about 10 seconds.
The red FAIL LED, the yellow ACT/STBY LED, the red REM LED, the green SYNC LED, and the green ACO LED turn on and remain on for about 10 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED and the green ACT/STBY LED turn on and remain on for about 40 seconds.
The red FAIL LED and the green ACT/STBY LED turn on and remain on for about 40 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for about 10 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for about 10 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for about 5 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for about 5 seconds.
•![]() Both green PWR LEDs turn on for 5 seconds. The PWR LEDs then turn red for 2 to 3 minutes before going to steady green.
Both green PWR LEDs turn on for 5 seconds. The PWR LEDs then turn red for 2 to 3 minutes before going to steady green.
•![]() All LEDs (including the CRIT, MAJ, MIN, REM, SYNC, and ACO LEDs) blink once and turn off for about 10 seconds.
All LEDs (including the CRIT, MAJ, MIN, REM, SYNC, and ACO LEDs) blink once and turn off for about 10 seconds.
•![]() The ACT/STBY LED turns on. (The ACT/STBY LED might take several minutes to turn on while the DCC processor boots.)
The ACT/STBY LED turns on. (The ACT/STBY LED might take several minutes to turn on while the DCC processor boots.)

Note ![]() It may take up to 3 minutes for the A and B power alarms to clear.
It may take up to 3 minutes for the A and B power alarms to clear.

Note ![]() If the FAIL LED is on continuously, see the tip below about the TCC2 card automatic upload.
If the FAIL LED is on continuously, see the tip below about the TCC2 card automatic upload.

Note ![]() Alarm LEDs might be on; disregard alarm LEDs until you are logged into CTC and can view the Alarms tab.
Alarm LEDs might be on; disregard alarm LEDs until you are logged into CTC and can view the Alarms tab.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is green for active. The IP address, temperature of the node, and time of day appear on the LCD. The default time and date is 12:00 AM, January 1, 1970.
Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is green for active. The IP address, temperature of the node, and time of day appear on the LCD. The default time and date is 12:00 AM, January 1, 1970.
Step 6 ![]() The LCD cycles through the IP address, node name, and software version. Verify that the correct software version displays on the LCD.
The LCD cycles through the IP address, node name, and software version. Verify that the correct software version displays on the LCD.
Step 7 ![]() If the LCD shows the correct software version, continue with Step 8. If the LCD does not show the correct software version, upgrade the software or remove the TCC2 card and install a replacement card.
If the LCD shows the correct software version, continue with Step 8. If the LCD does not show the correct software version, upgrade the software or remove the TCC2 card and install a replacement card.
Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Software Upgrade Guide to replace the software. To exchange the TCC2 card, see the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 8 ![]() Open the latches/ejectors of the redundant TCC2 card.
Open the latches/ejectors of the redundant TCC2 card.
Step 9 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 7 or 11).
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 7 or 11).
Step 10 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 11 ![]() Verify the LED activity of the redundant TCC2 card:
Verify the LED activity of the redundant TCC2 card:
•![]() All LEDs turn on briefly.
All LEDs turn on briefly.
•![]() The red FAIL LED, the yellow ACT/STBY LED, the red REM LED, the green SYNC LED, and the green ACO LED turn on for about 10 seconds.
The red FAIL LED, the yellow ACT/STBY LED, the red REM LED, the green SYNC LED, and the green ACO LED turn on for about 10 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED and the green ACT/STBY LED turn on for about 40 seconds.
The red FAIL LED and the green ACT/STBY LED turn on for about 40 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for about 10 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for about 10 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for about 5 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for about 5 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs (including the CRIT, MAJ, MIN, REM, SYNC, and ACO LEDs) blink once and turn off for about 10 seconds.
All LEDs (including the CRIT, MAJ, MIN, REM, SYNC, and ACO LEDs) blink once and turn off for about 10 seconds.
•![]() The ACT/STBY LED turns on. (The ACT/STBY LED might take several minutes to turn on while the DCC processor boots.)
The ACT/STBY LED turns on. (The ACT/STBY LED might take several minutes to turn on while the DCC processor boots.)

Tip ![]() If you install a standby TCC2 card that has a different software version than the active TCC card, the newly installed standby TCC2 card automatically copies the software version from the active TCC2 card. You do not need to do anything in this situation. However, the loading TCC2 card does not boot up in the normal manner. When the standby card is first inserted, the LEDs follow most of the sequence listed in Step 11. After the red FAIL LED turns on for about 5 seconds, the FAIL LED and the ACT/STBY LED begin to flash alternately for up to 30 minutes while the new software loads onto the active TCC2 card. After loading the new software the upgraded TCC2 card's LEDs repeat the sequence from Step 11, and the amber ACT/STBY LED turns on.
If you install a standby TCC2 card that has a different software version than the active TCC card, the newly installed standby TCC2 card automatically copies the software version from the active TCC2 card. You do not need to do anything in this situation. However, the loading TCC2 card does not boot up in the normal manner. When the standby card is first inserted, the LEDs follow most of the sequence listed in Step 11. After the red FAIL LED turns on for about 5 seconds, the FAIL LED and the ACT/STBY LED begin to flash alternately for up to 30 minutes while the new software loads onto the active TCC2 card. After loading the new software the upgraded TCC2 card's LEDs repeat the sequence from Step 11, and the amber ACT/STBY LED turns on.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.

Note ![]() Alarm LEDs might be on; disregard alarm LEDs until you are logged into CTC and can view the Alarms tab.
Alarm LEDs might be on; disregard alarm LEDs until you are logged into CTC and can view the Alarms tab.
Step 12 ![]() Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is amber for standby.
Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is amber for standby.
Step 13 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A37 Install the XC, XCVT, or XC10G Cards

Note ![]() Do not use this procedure to upgrade cross-connect cards. If you are upgrading an XC card to an XCVT, or an XCVT card to a XC10G, see Chapter 14, "Upgrade Cards and Spans."
Do not use this procedure to upgrade cross-connect cards. If you are upgrading an XC card to an XCVT, or an XCVT card to a XC10G, see Chapter 14, "Upgrade Cards and Spans."

Note ![]() When installing cards, let each card boot completely before installing the next card.
When installing cards, let each card boot completely before installing the next card.
Step 1 ![]() Open the latches/ejectors of the first XC, XCVT, or XC10G card that you will install.
Open the latches/ejectors of the first XC, XCVT, or XC10G card that you will install.
Step 2 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 8 or 10).
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 8 or 10).
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 4 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
The red LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
•![]() The red LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
The red LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
•![]() The red LED turns on for 5 to 10 seconds.
The red LED turns on for 5 to 10 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn on.
All LEDs blink once and turn on.
•![]() The ACT/STBY LED turns on.
The ACT/STBY LED turns on.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs act erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 1 to 4.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs act erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 1 to 4.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is green for active.
Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is green for active.
Step 6 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the second cross-connect card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 8 or 10).
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the second cross-connect card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 8 or 10).
Step 7 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 8 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
The red LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
•![]() The red LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
The red LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
•![]() The red LED turns on for 5 to 10 seconds.
The red LED turns on for 5 to 10 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn on.
All LEDs blink once and turn on.
•![]() The ACT/STBY LED turns on.
The ACT/STBY LED turns on.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED is turned on continuously or the LEDs act erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 6 through 8.
If the red FAIL LED is turned on continuously or the LEDs act erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 6 through 8.
Step 9 ![]() Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is amber for standby.
Verify that the ACT/STBY LED is amber for standby.
Step 10 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A38 Install the Alarm Interface Controller or Alarm Interface Controller-International Card
Purpose |
This task installs the AIC or AIC-I card. The AIC or AIC-I card provides connections for external alarms and controls (environmental alarms). |
Tools/Equipment |
AIC or AIC-I card |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A37 Install the XC, XCVT, or XC10G Cards for TDM and hybrid nodes |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() When installing cards, allow each card to boot completely before installing the next card.
When installing cards, allow each card to boot completely before installing the next card.
Step 1 ![]() Open the latches/ejectors on the card.
Open the latches/ejectors on the card.
Step 2 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 9).
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot (Slot 9).
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 4 ![]() If you have installed the AIC card, verify the following:
If you have installed the AIC card, verify the following:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 1 second, then blinks for 1 to 5 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 1 second, then blinks for 1 to 5 seconds.
•![]() After 1 to 5 seconds, all LEDs blink once and turn off.
After 1 to 5 seconds, all LEDs blink once and turn off.
•![]() The ACT LED turns on.
The ACT LED turns on.
Step 5 ![]() If you have installed the AIC-I card, verify the following:
If you have installed the AIC-I card, verify the following:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 1 second, then blinks for 1 to 5 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 1 second, then blinks for 1 to 5 seconds.
•![]() The PWR A and PWR B LEDs become red and the two INPUT/OUTPUT LEDs become green for approximately 3 seconds.
The PWR A and PWR B LEDs become red and the two INPUT/OUTPUT LEDs become green for approximately 3 seconds.
•![]() The PWR A LED turns green, the INPUT/OUTPUT LEDs turn off, and the ACT LED turns on.
The PWR A LED turns green, the INPUT/OUTPUT LEDs turn off, and the ACT LED turns on.

Note ![]() It may take up to 3 minutes for the PWR A and PWR B LEDs to update.
It may take up to 3 minutes for the PWR A and PWR B LEDs to update.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, no LEDs turn on.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, no LEDs turn on.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs act erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 1 to 5.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs act erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 1 to 5.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A16 Install the OC-N Cards

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.
Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.

Warning ![]() On all OC-N cards except the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is on even when the optical port is not in service. On the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is active when the card is booted and the safety key is in the on position (labeled 1). The laser is off when the safety key is off (labeled 0).
On all OC-N cards except the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is on even when the optical port is not in service. On the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is active when the card is booted and the safety key is in the on position (labeled 1). The laser is off when the safety key is off (labeled 0).


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() To simplify path protection to bidirectional line switch ring (BLSR) conversion and node addition, install OC-N cards according to a high-speed east (Slots 12 and 13) and west (Slots 5 and 6) configuration. This configuration is not mandatory.
To simplify path protection to bidirectional line switch ring (BLSR) conversion and node addition, install OC-N cards according to a high-speed east (Slots 12 and 13) and west (Slots 5 and 6) configuration. This configuration is not mandatory.

Note ![]() If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.

Note ![]() During the boot process an out-of-service (OOS) OC-N port will output AIS-L to any in-service (IS) far-end receivers . See the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide for further information about the AIS-L condition.
During the boot process an out-of-service (OOS) OC-N port will output AIS-L to any in-service (IS) far-end receivers . See the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide for further information about the AIS-L condition.
Step 1 ![]() If you installed XC or XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
If you installed XC or XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
Install higher-capacity cards first; for example, install an OC-192 card before installing an OC-48 card. Let each card completely boot before installing the next card.
Step 2 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.

Warning ![]() Before installing an OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, make sure the safety key on the faceplate is in off position (labeled 0). When in the on position (labeled 1), the laser is activated.
Before installing an OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, make sure the safety key on the faceplate is in off position (labeled 0). When in the on position (labeled 1), the laser is activated.
Step 3 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the OC-N card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the OC-N card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn off for 5 to 10 seconds.
All LEDs blink once and turn off for 5 to 10 seconds.
•![]() The ACT or ACT/STBY LED becomes amber. The signal fail (SF) LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.
The ACT or ACT/STBY LED becomes amber. The signal fail (SF) LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.
Step 6 ![]() If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 5, check the following:
If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 5, check the following:
•![]() When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If an OC-N card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming the card is faulty.
When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If an OC-N card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming the card is faulty.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 5.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 5.
Step 7 ![]() Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure.
Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Class 1 Laser Product.
Class 1 Laser Product.

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.

Note ![]() Cisco recommends that you install transponder and muxponder cards after you install OC-N cards, as applicable.
Cisco recommends that you install transponder and muxponder cards after you install OC-N cards, as applicable.
Step 1 ![]() If you installed XC or XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
If you installed XC or XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
Step 2 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 3 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the transponder or muxponder card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the transponder or muxponder card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn off for 5 to 10 seconds.
All LEDs blink once and turn off for 5 to 10 seconds.
•![]() The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The signal fail (SF) LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.
The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The signal fail (SF) LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.
Step 6 ![]() If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mirror Step 5, check the following:
If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mirror Step 5, check the following:
•![]() When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a transponder or muxponder card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming the card is faulty.
When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a transponder or muxponder card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming the card is faulty.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 5.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 5.
Step 7 ![]() If you installed an MXP_2.5G_10G, TXP_MR_2.5G, or TXPP_MR_2.5G card, complete the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
If you installed an MXP_2.5G_10G, TXP_MR_2.5G, or TXPP_MR_2.5G card, complete the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
Step 8 ![]() Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure.
Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A17 Install the Electrical Cards

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() Install higher-capacity cards first; for example, install a DS-3 card before installing a DS-1 card. Let each card boot completely before installing the next card.
Install higher-capacity cards first; for example, install a DS-3 card before installing a DS-1 card. Let each card boot completely before installing the next card.

Note ![]() If you are installing OC-N, TXP, or MXP cards Cisco recommends that you install these before you install electrical cards, as applicable.
If you are installing OC-N, TXP, or MXP cards Cisco recommends that you install these before you install electrical cards, as applicable.
Step 1 ![]() If you installed XC or XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
If you installed XC or XCVT cards, review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
Step 2 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 3 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 10 to 15 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 10 to 15 seconds.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for 30 to 40 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for 30 to 40 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
All LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
•![]() The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.
The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 5.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 5.
Step 6 ![]() Continue with the "A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors" procedure if necessary.
Continue with the "A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors" procedure if necessary.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.
Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If you are installing OC-N, TXP, or MXP cards Cisco recommends that you install these before you install Ethernet cards
If you are installing OC-N, TXP, or MXP cards Cisco recommends that you install these before you install Ethernet cards
Step 1 ![]() If you installed XC or XCVT cards review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
If you installed XC or XCVT cards review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A39 Install Ethernet Cards" task. Allow each card to boot completely before installing the next card.
Complete the "DLP-A39 Install Ethernet Cards" task. Allow each card to boot completely before installing the next card.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task if you are using E1000-2, E1000-2-G, G1000-4, or ML1000-2 cards.
Complete the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task if you are using E1000-2, E1000-2-G, G1000-4, or ML1000-2 cards.

Note ![]() If you need to remove a GBIC or SFP, complete the "DLP-A470 Remove GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
If you need to remove a GBIC or SFP, complete the "DLP-A470 Remove GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
Step 4 ![]() Continue with the "A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Continue with the "A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A39 Install Ethernet Cards
Purpose |
This task installs the Ethernet cards. |
Tools/Equipment |
Ethernet cards |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |
Step 1 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 2 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Step 3 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 4 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
The red FAIL LED blinks for 35 to 45 seconds.
•![]() All LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
All LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
•![]() The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.
The ACT or ACT/STBY LED turns on. The SF LED can persist until all card ports connect to their far end counterparts and a signal is present.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors
Purpose |
This task installs gigabit interface converters (required for E-Series Ethenet, G-Series Ethernet, and FC_MR-4 cards) and small-form factor pluggables (SFPs) (required for ML1000-2 and MXP cards) and attaches fiber to the connectors. |
Tools/Equipment |
For E1000-2-G use: • • For the G1000-4 or G1K-4 card use: • • • • For the ML1000-2 card use: • • For the MXP card use: • • For the FC_MR-4 card use: • • |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() G-Series cards manufactured before August 2003 do not support DWDM GBICs. G1000-4 cards compatible with DWDM GBICs have a CLEI code of SNP8KW0KAB. Compatible G1K-4 cards have a CLEI code of WM5IRWPCAA.
G-Series cards manufactured before August 2003 do not support DWDM GBICs. G1000-4 cards compatible with DWDM GBICs have a CLEI code of SNP8KW0KAB. Compatible G1K-4 cards have a CLEI code of WM5IRWPCAA.

Note ![]() All versions of G1000-4 and G1K-4 cards support CWDM GBICs.
All versions of G1000-4 and G1K-4 cards support CWDM GBICs.

Note ![]() GBICs and SFPs are hot-swappable and can therefore be installed/removed while the card/shelf assembly is powered and running.
GBICs and SFPs are hot-swappable and can therefore be installed/removed while the card/shelf assembly is powered and running.
Step 1 ![]() Remove the GBIC or SFP from its protective packaging.
Remove the GBIC or SFP from its protective packaging.
Step 2 ![]() Check the label to verify that the GBIC or SFP is the correct type for your network.
Check the label to verify that the GBIC or SFP is the correct type for your network.
Table 2-3 shows the available GBICs.

Note ![]() The GBICs are very similar in appearance. Check the GBIC label carefully before installing it.
The GBICs are very similar in appearance. Check the GBIC label carefully before installing it.
Table 2-4 shows the available SFPs.
Step 3 ![]() Verify the type of GBIC or SFP you are using:
Verify the type of GBIC or SFP you are using:
•![]() If you are using a GBIC with clips, go to Step 4.
If you are using a GBIC with clips, go to Step 4.
•![]() If you are using a GBIC with a handle, go to Step 5.
If you are using a GBIC with a handle, go to Step 5.
•![]() If you are using an SFP, go to Step 6.
If you are using an SFP, go to Step 6.
Step 4 ![]() For GBICs with clips:
For GBICs with clips:
a. ![]() Grip the sides of the GBIC with your thumb and forefinger and insert the GBIC into the slot on the card.
Grip the sides of the GBIC with your thumb and forefinger and insert the GBIC into the slot on the card.

Note ![]() GBICs are keyed to prevent incorrect installation.
GBICs are keyed to prevent incorrect installation.
b. ![]() Slide the GBIC through the flap that covers the opening until you hear a click. The click indicates the GBIC is locked into the slot.
Slide the GBIC through the flap that covers the opening until you hear a click. The click indicates the GBIC is locked into the slot.
c. ![]() When you are ready to attach the network fiber-optic cable, remove the protective plug from the GBIC and save the plug for future use.
When you are ready to attach the network fiber-optic cable, remove the protective plug from the GBIC and save the plug for future use.
d. ![]() Continue with Step 7.
Continue with Step 7.
Step 5 ![]() For GBICs with a handle:
For GBICs with a handle:
a. ![]() Remove the protective plug from the SC-type connector.
Remove the protective plug from the SC-type connector.
b. ![]() Grip the sides of the GBIC with your thumb and forefinger and insert the GBIC into the slot on the card.
Grip the sides of the GBIC with your thumb and forefinger and insert the GBIC into the slot on the card.
c. ![]() Lock the GBIC into place by closing the handle down. The handle is in the correct closed position when it does not obstruct access to an SC-type connector.
Lock the GBIC into place by closing the handle down. The handle is in the correct closed position when it does not obstruct access to an SC-type connector.
d. ![]() Slide the GBIC through the cover flap until you hear a click.
Slide the GBIC through the cover flap until you hear a click.
The click indicates that the GBIC is locked into the slot.
e. ![]() Continue with Step 7.
Continue with Step 7.

Warning ![]() GBICs are Class I laser products. These products have been tested and comply with Class I limits.
GBICs are Class I laser products. These products have been tested and comply with Class I limits.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture ports of the single-mode fiber optic modules when no cable is connected. Avoid exposure and do not stare into open apertures.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture ports of the single-mode fiber optic modules when no cable is connected. Avoid exposure and do not stare into open apertures.
Step 6 ![]() For SFPs:
For SFPs:
a. ![]() Plug the LC duplex connector of the fiber into a Cisco-supported SFP connector.
Plug the LC duplex connector of the fiber into a Cisco-supported SFP connector.
b. ![]() If the new SFP connector has a latch, close the latch over the cable to secure it.
If the new SFP connector has a latch, close the latch over the cable to secure it.
c. ![]() Plug the cabled SFP connector into the card port until it clicks.
Plug the cabled SFP connector into the card port until it clicks.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A470 Remove GBIC or SFP Connectors

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments.
Step 1 ![]() Disconnect the network fiber cable from the GBIC SC connector or SFP LC duplex connector. If the SFP connector has a latch securing the fiber cable, pull it upward to release the cable.
Disconnect the network fiber cable from the GBIC SC connector or SFP LC duplex connector. If the SFP connector has a latch securing the fiber cable, pull it upward to release the cable.
Step 2 ![]() If you are using a GBIC with clips:
If you are using a GBIC with clips:
a. ![]() Release the GBIC from the slot by squeezing the two plastic tabs on each side of the GBIC.
Release the GBIC from the slot by squeezing the two plastic tabs on each side of the GBIC.
b. ![]() Slide the GBIC out of the Gigabit Ethernet module slot. A flap closes over the GBIC or SFP slot to protect the connector on the Gigabit Ethernet card.
Slide the GBIC out of the Gigabit Ethernet module slot. A flap closes over the GBIC or SFP slot to protect the connector on the Gigabit Ethernet card.
Step 3 ![]() If you are using a GBIC with a handle:
If you are using a GBIC with a handle:
a. ![]() Release the GBIC by opening the handle.
Release the GBIC by opening the handle.
b. ![]() Pull the handle of the GBIC.
Pull the handle of the GBIC.
c. ![]() Slide the GBIC out of the Gigabit Ethernet card slot. A flap closes over the GBIC slot to protect the connector on the Gigabit Ethernet card.
Slide the GBIC out of the Gigabit Ethernet card slot. A flap closes over the GBIC slot to protect the connector on the Gigabit Ethernet card.
Step 4 ![]() If you are using an SFP:
If you are using an SFP:
a. ![]() If the SFP connector has a latch securing the fiber cable, pull it upward to release the cable.
If the SFP connector has a latch securing the fiber cable, pull it upward to release the cable.
b. ![]() Pull the fiber cable straight out of the connector.
Pull the fiber cable straight out of the connector.
c. ![]() Unplug the SFP connector and fiber from the card.
Unplug the SFP connector and fiber from the card.
d. ![]() Slide the SFP out of the Gigabit Ethernet card slot.
Slide the SFP out of the Gigabit Ethernet card slot.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A274 Install the FC_MR-4 Cards
Purpose |
This procedure installs the Fibre Channel (FC_MR-4) card. |
Tools/Equipment |
FC_MR-4 card(s) |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.
Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.


Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
Step 1 ![]() If you installed XC or XCVT cards review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
If you installed XC or XCVT cards review Table 2-1 to determine card/slot compatibility. If you installed XC10G cards, review Table 2-2 to determine card/slot compatibility.
Step 2 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 3 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure and install the correct card.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure and install the correct card.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 5 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds. The ACT LED is amber for 3 to 5 seconds.
The red FAIL LED turns on for 20 to 30 seconds. The ACT LED is amber for 3 to 5 seconds.
•![]() The red FAIL LED blinks for up to 2 minutes.
The red FAIL LED blinks for up to 2 minutes.

Note ![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() The FAIL and ACT LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
The FAIL and ACT LEDs blink once and turn off for 1 to 5 seconds.
•![]() The ACT LED turns on green to indicate the card is operational.
The ACT LED turns on green to indicate the card is operational.

Note ![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDs turn off.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task to install GBICs on the FC_MR-4 card.
Complete the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task to install GBICs on the FC_MR-4 card.

Note ![]() If you need to remove a GBIC or SFP, complete the "DLP-A470 Remove GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
If you need to remove a GBIC or SFP, complete the "DLP-A470 Remove GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
Step 7 ![]() Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure.
Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A242 Install the DWDM Cards
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to install DWDM cards (OPT-PRE, OPT-BST, 32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, 4MD-xx.x, AD-1C-xx.x, AD-2C-xx.x, AD-4C-xx.x, AD-1B-xx.x, AD-4B-xx.x, OSCM, or OSC-CSM). Complete this procedure when instructed to do so in Chapter 5, "Turn Up a DWDM Node." |
Tools/Equipment |
OPT-PRE, OPT-BST, 32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, 4MD-xx.x, AD-1C-xx.x, AD-2C-xx.x, AD-4C-xx.x, AD-1B-xx.x, AD-4B-xx.x, OSCM, or OSC-CSM cards (as applicable) |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Class 1M Laser Product.
Class 1M Laser Product.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.



Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.
If you install a card incorrectly, the FAIL LED flashes continuously.

Note ![]() The automatic node setup (ANS) of the ONS 15454 DWDM system begins to determine what kind of site you are installing as soon as you install cards. The automatic power control (APC) is enabled after ANS initializes and after a channel has been provisioned. To provision a DWDM channel, see the "A227 Provision a DWDM Optical Channel Network Connection" procedure. For more information about amplifier power control, see the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
The automatic node setup (ANS) of the ONS 15454 DWDM system begins to determine what kind of site you are installing as soon as you install cards. The automatic power control (APC) is enabled after ANS initializes and after a channel has been provisioned. To provision a DWDM channel, see the "A227 Provision a DWDM Optical Channel Network Connection" procedure. For more information about amplifier power control, see the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 1 ![]() Plan your node installation or consult the site plan. As soon as you begin installing cards, ANS determines what kind of site to set up based on the following parameters:
Plan your node installation or consult the site plan. As soon as you begin installing cards, ANS determines what kind of site to set up based on the following parameters:
•![]() Hub site—Two 32DMX-O and two 32MUX-O cards are provisioned but no AD-xC or AD-xB cards are provisioned
Hub site—Two 32DMX-O and two 32MUX-O cards are provisioned but no AD-xC or AD-xB cards are provisioned
•![]() Terminal—One 32DMX-O and one 32MUX-O card are provisioned, and no AD-xC or AD-xB cards are provisioned
Terminal—One 32DMX-O and one 32MUX-O card are provisioned, and no AD-xC or AD-xB cards are provisioned
•![]() Line site—Only one OPT-PRE or OPT-BST is provisioned per line direction. (Up to two OPT-PRE and/or two OPT-BST cards can be provisioned in the same shelf.)
Line site—Only one OPT-PRE or OPT-BST is provisioned per line direction. (Up to two OPT-PRE and/or two OPT-BST cards can be provisioned in the same shelf.)
•![]() OADM site—At least 1 AD-xC or AD-xB is provisioned and no 32DMX-O or 32MUX-O cards are provisioned
OADM site—At least 1 AD-xC or AD-xB is provisioned and no 32DMX-O or 32MUX-O cards are provisioned
•![]() Unknown—Provisioned cards do not follow any of the previously listed categories
Unknown—Provisioned cards do not follow any of the previously listed categories
Step 2 ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
Step 3 ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the DWDM card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.
Use the latches/ejectors to firmly slide the DWDM card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the slot.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure and install the correct card.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure and install the correct card.
Step 4 ![]() Use the following card placement guidelines. For specific information about each card, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Use the following card placement guidelines. For specific information about each card, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
•![]() OPT-BST cards can be installed in any open east and west pair of slots but are often installed in Slots 1 and 17.
OPT-BST cards can be installed in any open east and west pair of slots but are often installed in Slots 1 and 17.
•![]() OPT-PRE cards can be installed in any open east and west pair of slots but are often installed in Slots 2 and 16.
OPT-PRE cards can be installed in any open east and west pair of slots but are often installed in Slots 2 and 16.
•![]() OSCM cards, if used, are installed in Slots 8 and 10.
OSCM cards, if used, are installed in Slots 8 and 10.
•![]() OSC-CSM cards, if used (when there is no OPT-BST), can be installed in any open east and west pair of slots.
OSC-CSM cards, if used (when there is no OPT-BST), can be installed in any open east and west pair of slots.
•![]() 32MUX-O cards are double-slot cards and are often installed in Slots 3 and 4 and Slots 14 and 15.
32MUX-O cards are double-slot cards and are often installed in Slots 3 and 4 and Slots 14 and 15.
•![]() 32DMX-O cards are double-slot and are often installed in Slots 5 and 6 and Slots 12 and 13.
32DMX-O cards are double-slot and are often installed in Slots 5 and 6 and Slots 12 and 13.
•![]() AD cards (channel or band) and 4MD-xx.x combiner cards are installed in any open slots.
AD cards (channel or band) and 4MD-xx.x combiner cards are installed in any open slots.

Note ![]() Refer to Figures 2-8, 2-9, 2-10, and 2-11 to see typical site shelf diagrams that contain cards and show cabling schemes.
Refer to Figures 2-8, 2-9, 2-10, and 2-11 to see typical site shelf diagrams that contain cards and show cabling schemes.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.
Verify that the card is inserted correctly and close the latches/ejectors on the card.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latches/ejectors when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 6 ![]() Verify the LED activity:
Verify the LED activity:
•![]() The FAIL LED turns on for approximately 35 seconds
The FAIL LED turns on for approximately 35 seconds
•![]() The FAIL LED blinks for approximately 40 seconds
The FAIL LED blinks for approximately 40 seconds
•![]() All LEDs turn on and then turn off within 5 seconds
All LEDs turn on and then turn off within 5 seconds
•![]() If new software is being downloaded to the card, the ACT and SF LEDs blink for 20 seconds to 3.5 minutes, depending on the card type
If new software is being downloaded to the card, the ACT and SF LEDs blink for 20 seconds to 3.5 minutes, depending on the card type
•![]() The ACT LED turns on
The ACT LED turns on
•![]() The signal fail (SF) LED stays on until all card ports connect to their far-end counterparts and a signal is present
The signal fail (SF) LED stays on until all card ports connect to their far-end counterparts and a signal is present
Step 7 ![]() If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 5, check the following:
If the card does not boot up properly, or the LED activity does not mimic Step 5, check the following:
•![]() When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a DWDM card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming the card is faulty.
When a physical card type does not match the type of card provisioned for that slot in CTC, the card might not boot. If a DWDM card does not boot, open CTC and ensure that the slot is not provisioned for a different card type before assuming the card is faulty.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
If the red FAIL LED does not turn on, check the power.
•![]() If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
If you insert a card into a slot provisioned for a different card, all LEDS turn off.
•![]() If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 6.
If the red FAIL LED is on continuously or the LEDs behave erratically, the card is not installed properly. Remove the card and repeat Steps 2 to 6.
Step 8 ![]() If you installed OPT-PRE cards, complete the "A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards" procedure.
If you installed OPT-PRE cards, complete the "A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards" procedure.
Step 9 ![]() Complete the "A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards" procedure.
Complete the "A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to install the dispersion compensating cards (DCU-xx.x) for DWDM shelves and is required if OPT-PRE cards are installed. Required if the span is very long. If Metroplanner is used to generate the bill of materials, the need for DCUs will be indicated. Complete this procedure when instructed to do so in Chapter 5, "Turn Up a DWDM Node." |
Tools/Equipment |
DCU-xx.x cards |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A15 Install the Common Control Cards |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |

Warning ![]() During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool due to electrical hazard.

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Class 1M laser product.
Class 1M laser product.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.



Note ![]() If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.
If protective clips are installed on the backplane connectors of the cards, remove the clips before installing the cards.

Note ![]() If a DCU is not required, a 4 dB optical attenuated patch cord must be placed between the OPT-PRE DCC Tx and Tx ports.
If a DCU is not required, a 4 dB optical attenuated patch cord must be placed between the OPT-PRE DCC Tx and Tx ports.
Step 1 ![]() Pull the card latch inward with your finger.
Pull the card latch inward with your finger.
Step 2 ![]() Firmly slide the DCU card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the horizontal dispersion compensating card slots at the top of the shelf.
Firmly slide the DCU card along the guide rails until the card plugs into the receptacle at the back of the horizontal dispersion compensating card slots at the top of the shelf.

Note ![]() The West dispersion compensating card is commonly installed on the left side and the East card is commonly installed on the right.
The West dispersion compensating card is commonly installed on the left side and the East card is commonly installed on the right.

Note ![]() If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure and install the correct card.
If you install the wrong card in a slot, complete the "A116 Remove and Replace a Card" procedure and install the correct card.
Step 3 ![]() Release the finger latch.
Release the finger latch.

Note ![]() It is possible to close the latch when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
It is possible to close the latch when the card is not completely plugged into the backplane. Ensure that you cannot insert the card any further.
Step 4 ![]() Verify that the card is engaged with the backplane by grasping and gently pulling the card handle. If the card does not move, it is fully installed. If it moves, repeat Step 2.
Verify that the card is engaged with the backplane by grasping and gently pulling the card handle. If the card does not move, it is fully installed. If it moves, repeat Step 2.
Step 5 ![]() Continue with the "A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards" procedure.
Continue with the "A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to install fiber-optic cables on OC-N cards or GBICs according to topology. |
Tools/Equipment |
Fiber-optic cables Fiber boot |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards (if applicable) |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Warning ![]() Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.
Class I (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.

Warning ![]() Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not stare into the beam or view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example, eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified may result in hazardous radiation exposure.

Warning ![]() On all OC-N cards except the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is on even when the optical port is not in service. On the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is active when the card is booted and the safety key is in the on position (labeled 1). The laser is off when the safety key is off (labeled 0).
On all OC-N cards except the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is on even when the optical port is not in service. On the OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 card, the laser is active when the card is booted and the safety key is in the on position (labeled 1). The laser is off when the safety key is off (labeled 0).

Warning ![]() Follow all directions and warning labels when working with optical fibers. To prevent eye damage, never look directly into a fiber or connector.
Follow all directions and warning labels when working with optical fibers. To prevent eye damage, never look directly into a fiber or connector.




Note ![]() Fiber boots are not recommended for OC192 cards or OC48AS cards because of the downward angle of the optical ports.
Fiber boots are not recommended for OC192 cards or OC48AS cards because of the downward angle of the optical ports.

Note ![]() You can install the fiber immediately after installing the cards, or wait until you are ready to turn up the network. See "Turn Up Network."
You can install the fiber immediately after installing the cards, or wait until you are ready to turn up the network. See "Turn Up Network."
Step 1 ![]() Test the optical receive levels for the cards installed and attenuate accordingly. See Table 2-5 for the minimum and maximum levels.
Test the optical receive levels for the cards installed and attenuate accordingly. See Table 2-5 for the minimum and maximum levels.
|
|
|
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 |
-15 dBm |
-8 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC3IR/STM1SH 1310-8 |
-15 dBm |
-8 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310 |
-15 dBm |
-8 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1310 |
-3 dBm |
+2 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1550 |
-3 dBm |
+2 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310-4 |
-15 dBm |
-8 dBm |
-30 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC48 IR 1310 |
-5 dBm |
0 dBm |
-18 dBm |
0 dBm |
OC48 LR 1550 |
-2 dBm |
+3 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC48 IR/STM16 SH AS 1310 |
-5 dBm |
0 dBm |
-18 dBm |
0 dBm |
OC48 LR/STM16 LH AS 1550 |
-2 dBm |
+3 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC48 ELR/STM16 EH 100 GHz |
-2 dBm |
0 dBm |
-27 dBm at 1E-12 BER |
-9 dBm |
OC48 ELR/STM16 EH 200 GHz |
-2 dBm |
0 dBm |
-28 dBm |
-8 dBm |
OC192 SR/STM64 IO 1310 |
-6 dBm |
-1 dBm |
-11 dBm |
-1 dBm |
OC192 IR/STM64 SH 1550 |
-1 dBm |
+2 dBm |
-14 dBm |
-1 dBm |
OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 |
+7 dBm |
+10 dBm |
-19 dBm |
-10 dBm |
OC192 LR/STM64 LH ITU 15xx.xx |
+3 dBm |
+6 dBm |
-22 dBm |
-9 dBm |
TXP_MR_10G (trunk side) |
-16 dBm1 |
+3 dBm1 |
-24 dBm |
-8 dBm |
TXP_MR_10G (client side) |
-6 dBm |
-1 dBm |
-14 dBm |
-1 dBm |
MXP_2.5G_10G (trunk side) |
-16 dBm1 |
+3 dBm1 |
-24 dBm |
-8 dBm |
MXP_2.5G_10G (client side) |
-5 dBm |
0 dBm |
depends on SFP |
depends on SFP |
TXP_MR_2.5G (trunk side) TXPP_MR_2.5G (trunk side) |
-16 dBm |
+3 dBm |
depends on forward error correction (FEC) |
depends on FEC |
TXP_MR_2.5G (client side) TXPP_MR_2.5G (client side) |
-6 dBm |
-1 dBm |
-14 dBm at 1E-12 BER |
-1 dBm at 1E-12 BER |
1 On transponder and muxponder cards, the optical output power on the trunk side can be configured from -16 to +3 dBm with an accuracy of +/-0.5 dB. |
Step 2 ![]() Inspect and clean all fiber connectors thoroughly. See the "NTP-A112 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 17-21 for instructions. Dust particles can degrade performance. Put caps on any fiber connectors that are not used.
Inspect and clean all fiber connectors thoroughly. See the "NTP-A112 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 17-21 for instructions. Dust particles can degrade performance. Put caps on any fiber connectors that are not used.
Step 3 ![]() As needed, complete the "DLP-A207 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on the LGX Interface" task.
As needed, complete the "DLP-A207 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on the LGX Interface" task.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A428 Install Fiber-Optic Cables in a 1+1 Configuration" task.
Complete the "DLP-A428 Install Fiber-Optic Cables in a 1+1 Configuration" task.

Note ![]() To install fiber-optic cables on Ethernet cards, FC_MR-4 cards, or transponder/muxponder cards, see the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
To install fiber-optic cables on Ethernet cards, FC_MR-4 cards, or transponder/muxponder cards, see the "DLP-A469 Install GBIC or SFP Connectors" task.
Step 5 ![]() As needed, complete the "DLP-A43 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for Path Protection Configurations" task.
As needed, complete the "DLP-A43 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for Path Protection Configurations" task.
Step 6 ![]() As needed, complete the "DLP-A44 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations" task.
As needed, complete the "DLP-A44 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations" task.
Step 7 ![]() As needed, complete the "DLP-A45 Install the Fiber Boot" task.
As needed, complete the "DLP-A45 Install the Fiber Boot" task.
Step 8 ![]() Continue with the "A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Continue with the "A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A207 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on the LGX Interface
Step 1 ![]() Align the keyed ridge of the cable connector with the receiving SC connector on the LGX faceplate connection point. Each module supports at least one transmit and one receive connector to create an optical carrier port.
Align the keyed ridge of the cable connector with the receiving SC connector on the LGX faceplate connection point. Each module supports at least one transmit and one receive connector to create an optical carrier port.
Step 2 ![]() Gently insert the cable connector into the faceplate connection point until the connector snaps into place.
Gently insert the cable connector into the faceplate connection point until the connector snaps into place.
Step 3 ![]() Connect the fiber optic cable to the OC-N card. Figure 2-1 shows the cable location.
Connect the fiber optic cable to the OC-N card. Figure 2-1 shows the cable location.
Figure 2-1 Installing Fiber-Optic Cables

Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A428 Install Fiber-Optic Cables in a 1+1 Configuration

Note ![]() The Cisco OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC-12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH interface optics, all working at 1310 nm, are optimized for the most widely used SMF-28 fiber, available from many suppliers.
The Cisco OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC-12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH interface optics, all working at 1310 nm, are optimized for the most widely used SMF-28 fiber, available from many suppliers.

Note ![]() Corning MetroCor fiber is optimized for optical interfaces that transmit at 1550 nm or in the C and L DWDM windows. This fiber targets interfaces with higher dispersion tolerances than those found in OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC-12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH interface optics. If you are using Corning MetroCor fiber, OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC- 12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH interface optics will become dispersion limited before they will become attenuation limited. In this case, consider using OC-3 LR/STM-1 LH, OC-12 LR/STM-4 LH, and OC-48 LR/STM-16 LH cards instead of OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC-12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH cards.
Corning MetroCor fiber is optimized for optical interfaces that transmit at 1550 nm or in the C and L DWDM windows. This fiber targets interfaces with higher dispersion tolerances than those found in OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC-12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH interface optics. If you are using Corning MetroCor fiber, OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC- 12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH interface optics will become dispersion limited before they will become attenuation limited. In this case, consider using OC-3 LR/STM-1 LH, OC-12 LR/STM-4 LH, and OC-48 LR/STM-16 LH cards instead of OC-3 IR/STM-1 SH, OC-12 IR/STM-4 SH, and OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH cards.

Note ![]() With all fiber types, network planners/engineers should review the relative fiber type and optics specifications to determine attenuation, dispersion, and other characteristics to ensure appropriate deployment.
With all fiber types, network planners/engineers should review the relative fiber type and optics specifications to determine attenuation, dispersion, and other characteristics to ensure appropriate deployment.
Step 1 ![]() Plan your fiber connections. Use the same plan for all 1+1 nodes.
Plan your fiber connections. Use the same plan for all 1+1 nodes.
Step 2 ![]() Align the keyed ridge of the cable connector with the transmit (Tx) connector of a working OC-N card at one node and plug the other end of the fiber into the receive (Rx) connector of a working OC-N card at the adjacent node. The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports). Figure 2-1 shows the cable location.
Align the keyed ridge of the cable connector with the transmit (Tx) connector of a working OC-N card at one node and plug the other end of the fiber into the receive (Rx) connector of a working OC-N card at the adjacent node. The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports). Figure 2-1 shows the cable location.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for the corresponding protect ports on the two nodes and all other working/protect port pairs you want to place in a 1+1 configuration.
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for the corresponding protect ports on the two nodes and all other working/protect port pairs you want to place in a 1+1 configuration.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A43 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for Path Protection Configurations
Purpose |
This task connects the fiber-optic cables to the east and west path protection ports at each node. See "Turn Up Network" to provision and test path protection configurations. |
Tools/Equipment |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.

Step 1 ![]() Plan your fiber connections. Use the same plan for all path protection nodes.
Plan your fiber connections. Use the same plan for all path protection nodes.
Step 2 ![]() Plug the fiber into the transmit (Tx) connector of an OC-N card at one node and plug the other end of the fiber into the receive (Rx) connector of an OC-N card at the adjacent node. The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Plug the fiber into the transmit (Tx) connector of an OC-N card at one node and plug the other end of the fiber into the receive (Rx) connector of an OC-N card at the adjacent node. The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have configured the ring.
Repeat Step 2 until you have configured the ring.
Figure 2-2 shows fiber connections for a four-node path protection with trunk (span) cards in Slot 5 (west) and Slot 12 (east).
Figure 2-2 Connecting Fiber to a Four-Node path protection

Figure 2-3 shows a traditional path protection dual ring interconnect example.
Figure 2-3 Connecting Fiber to an Eight-Node Traditional Path Protection Interconnect

Figure 2-4 shows an integrated dual ring interconnect example.
Figure 2-4 Connecting Fiber to a Six-Node Integrated Path Protection Interconnect
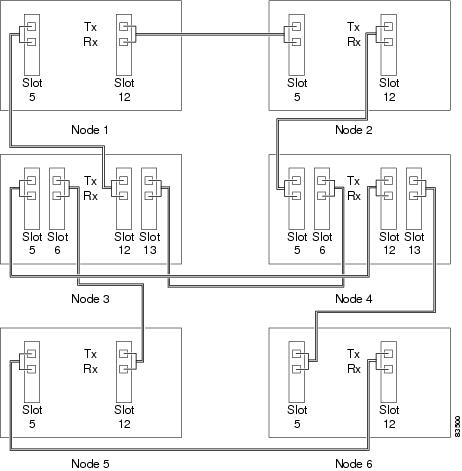
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A44 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for BLSR Configurations
Purpose |
This task installs the fiber-optics to the east and west BLSR ports at each node. See "Turn Up Network" to provision and test BLSR configurations. |
Tools/Equipment |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.

Step 1 ![]() Plan your fiber connections. Use the same plan for all BLSR nodes.
Plan your fiber connections. Use the same plan for all BLSR nodes.
Step 2 ![]() Plug the fiber into the transmit (Tx) connector of an OC-N card at one node and plug the other end into the receive (Rx) connector of an OC-N card at the adjacent node. The card displays a SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched.
Plug the fiber into the transmit (Tx) connector of an OC-N card at one node and plug the other end into the receive (Rx) connector of an OC-N card at the adjacent node. The card displays a SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched.

Note ![]() Do not mix working and protect card connections when connecting a four-fiber BLSR. The BLSR does not function if working and protect cards are interconnected. See Figure 2-6 for an example of correct four-fiber BLSR cabling.
Do not mix working and protect card connections when connecting a four-fiber BLSR. The BLSR does not function if working and protect cards are interconnected. See Figure 2-6 for an example of correct four-fiber BLSR cabling.
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have configured the ring.
Repeat Step 2 until you have configured the ring.
Figure 2-5 shows fiber connections for a two-fiber BLSR with trunk (span) cards in Slot 5 (west) and Slot 12 (east).
Figure 2-5 Connecting Fiber to a Four-Node, Two-Fiber BLSR

Figure 2-6 shows fiber connections for a four-fiber BLSR. Slot 5 (west) and Slot 12 (east) carry the working traffic. Slot 6 (west) and Slot 13 (east) carry the protect traffic.
Figure 2-6 Connecting Fiber to a Four-Node, Four-Fiber BLSR

Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A45 Install the Fiber Boot

Note ![]() You can install the fiber boots on the fiber-optic cables before or after the fibers are attached to the OC-N card.
You can install the fiber boots on the fiber-optic cables before or after the fibers are attached to the OC-N card.

Note ![]() The fiber boot does not support the OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH AS 1310, OC-48 LR/STM-16 LH AS 1550, and OC-192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 cards. The boots are not necessary for these cards because of the angled SC connectors on the cards.
The fiber boot does not support the OC-48 IR/STM-16 SH AS 1310, OC-48 LR/STM-16 LH AS 1550, and OC-192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 cards. The boots are not necessary for these cards because of the angled SC connectors on the cards.

Note ![]() If you are installing an OC3IR/STM1SH 1310-8 card, you must use a fiber clip instead of a fiber boot on the port 8 Rx fiber connector.
If you are installing an OC3IR/STM1SH 1310-8 card, you must use a fiber clip instead of a fiber boot on the port 8 Rx fiber connector.
Step 1 ![]() Position the open slot of the fiber boot underneath the fiber cable.
Position the open slot of the fiber boot underneath the fiber cable.
Step 2 ![]() Push the fiber cable down into the fiber boot. Figure 2-7 shows the fiber boot attachment.
Push the fiber cable down into the fiber boot. Figure 2-7 shows the fiber boot attachment.
Figure 2-7 Attaching a Fiber Boot

Step 3 ![]() Twist the fiber boot to lock the fiber cable into the tail end of the fiber boot.
Twist the fiber boot to lock the fiber cable into the tail end of the fiber boot.
Step 4 ![]() Slide the fiber boot forward along the fiber cable until the fiber boot fits snugly onto the end of the SC cable connector.
Slide the fiber boot forward along the fiber cable until the fiber boot fits snugly onto the end of the SC cable connector.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards
Purpose |
This procedure installs the fiber-optic cables to DWDM cards and dispersion compensating cards. The CTC automatic node setup (ANS) feature calculates and provisions the power settings between cards and nodes. This application depends on the presence of correct cabling. See "Turn Up DWDM Network" to provision and test DWDM configurations. |
Tools/Equipment |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards (as applicable) |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Warning ![]() Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.

Warning ![]() Class 1M laser product.
Class 1M laser product.

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Check the optical receive levels for the cards installed and attenuate accordingly. See Table 2-6 for DWDM card minimum and maximum transmit and receive levels. Power levels must be within the acceptable range for that card.
Check the optical receive levels for the cards installed and attenuate accordingly. See Table 2-6 for DWDM card minimum and maximum transmit and receive levels. Power levels must be within the acceptable range for that card.
Step 2 ![]() Inspect and clean all fiber connectors thoroughly. See the "NTP-A112 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 17-21 for instructions. Dust particles can degrade performance. Put caps on any fiber connectors that are not used.
Inspect and clean all fiber connectors thoroughly. See the "NTP-A112 Clean Fiber Connectors" procedure on page 17-21 for instructions. Dust particles can degrade performance. Put caps on any fiber connectors that are not used.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A423 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Termination on All DWDM Nodes" task.
Complete the "DLP-A423 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Termination on All DWDM Nodes" task.
Step 4 ![]() As required, complete the "DLP-A424 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node" task.
As required, complete the "DLP-A424 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node" task.
Step 5 ![]() As required, complete the"DLP-A425 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node" task.
As required, complete the"DLP-A425 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node" task.
Step 6 ![]() As required, complete the "DLP-A426 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node" task.
As required, complete the "DLP-A426 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node" task.
Step 7 ![]() As required, complete the "DLP-A427 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node" task.
As required, complete the "DLP-A427 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node" task.
Step 8 ![]() Continue with the "A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Continue with the "A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A423 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for OSC Link Termination on All DWDM Nodes

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber optic cabling for the OSC by consulting the following rules:
Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber optic cabling for the OSC by consulting the following rules:
•![]() The OPT-BST and the OSC-CSM are the only cards that directly interface with the line (span) fiber.
The OPT-BST and the OSC-CSM are the only cards that directly interface with the line (span) fiber.
•![]() The OSCM only carries supervision channels, not DWDM channels.
The OSCM only carries supervision channels, not DWDM channels.
•![]() The OSCM and the OSC-CSM cannot both be used on the same side of the NE (such as both being on the west side). You can have different cards on each side, for example an OSCM on the west side and an OSC-CSM on the east side.
The OSCM and the OSC-CSM cannot both be used on the same side of the NE (such as both being on the west side). You can have different cards on each side, for example an OSCM on the west side and an OSC-CSM on the east side.
•![]() When an OPT-BST and an OSC-CSM are both used on the same side of an NE, the OPT-BST combines the supervision channel with the DWDM channels and the OSC-CSM acts as an OSCM; it does not carry DWDM traffic.
When an OPT-BST and an OSC-CSM are both used on the same side of an NE, the OPT-BST combines the supervision channel with the DWDM channels and the OSC-CSM acts as an OSCM; it does not carry DWDM traffic.
•![]() When an OPT-BST and an OSC-CSM are used on opposite sides of the NE, the supervision channel does not require any additional connection.
When an OPT-BST and an OSC-CSM are used on opposite sides of the NE, the supervision channel does not require any additional connection.
•![]() The East OPT-BST OSC Rx port is connected to the East OSCM Tx port.
The East OPT-BST OSC Rx port is connected to the East OSCM Tx port.
•![]() The East OPT-BST OSC Tx port is connected to the East OSCM Rx port.
The East OPT-BST OSC Tx port is connected to the East OSCM Rx port.
•![]() The East OPT-BST OSC Rx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM Line Tx port.
The East OPT-BST OSC Rx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM Line Tx port.
•![]() The East OPT-BST OSC Tx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM Line Rx port.
The East OPT-BST OSC Tx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM Line Rx port.
•![]() The West OPT-BST OSC Tx port is connected to the West OSCM Rx port.
The West OPT-BST OSC Tx port is connected to the West OSCM Rx port.
•![]() The West OPT-BST OSC Rx port is connected to the West OSCM Tx port.
The West OPT-BST OSC Rx port is connected to the West OSCM Tx port.
•![]() The West OPT-BST OSC-Tx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM Line Rx port.
The West OPT-BST OSC-Tx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM Line Rx port.
•![]() The West OPT-BST OSC-Rx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM Line Tx port.
The West OPT-BST OSC-Rx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM Line Tx port.
Step 2 ![]() Plug the fiber into the West Line transmit (Rx) connector of an OPT-BST (or OSC-CSM) card and into the adjacent node East OPT-BST or OSC-CSM Line Tx connector. Repeat in the other direction (east to west, Rx to Tx). Ensure that you are connecting the West Line ports to the adjacent node East Line ports.
Plug the fiber into the West Line transmit (Rx) connector of an OPT-BST (or OSC-CSM) card and into the adjacent node East OPT-BST or OSC-CSM Line Tx connector. Repeat in the other direction (east to west, Rx to Tx). Ensure that you are connecting the West Line ports to the adjacent node East Line ports.

Note ![]() The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() At the West side of the first node, plug one end of a fiber cable into the West OPT-BST OSC Rx connector and the other end into West OSCM Tx connector. Repeat the cabling from the West OSCM Rx to the OPT-BST OSC Tx.
At the West side of the first node, plug one end of a fiber cable into the West OPT-BST OSC Rx connector and the other end into West OSCM Tx connector. Repeat the cabling from the West OSCM Rx to the OPT-BST OSC Tx.

Note ![]() An OSC-CSM card takes the place of an OPT-BST and OSCM card for that side of the node and does not require OSC cabling.
An OSC-CSM card takes the place of an OPT-BST and OSCM card for that side of the node and does not require OSC cabling.
Step 5 ![]() At the East side of the first node, plug one end of a fiber cable into the East OPT-BST OSC Rx connector and the other end into East OSCM Tx connector. Repeat the cabling from the East OSCM Rx to the OPT-BST OSC Tx.
At the East side of the first node, plug one end of a fiber cable into the East OPT-BST OSC Rx connector and the other end into East OSCM Tx connector. Repeat the cabling from the East OSCM Rx to the OPT-BST OSC Tx.
Step 6 ![]() Repeat Steps 4 and 5 at each node.
Repeat Steps 4 and 5 at each node.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A424 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Terminal Node
Purpose |
This task installs fiber-optic cables on a terminal node DWDM shelf. See "Turn Up DWDM Network" to provision and test DWDM configurations. |
Tools |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber-optic cabling for the terminal site by consulting the following rules:
Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber-optic cabling for the terminal site by consulting the following rules:
•![]() A terminal site has only one side (as compared to a hub node, which has two sides).
A terminal site has only one side (as compared to a hub node, which has two sides).
•![]() The port line direction is not significant.
The port line direction is not significant.
•![]() The OPT-BST and OPT-PRE cards are not mandatory.
The OPT-BST and OPT-PRE cards are not mandatory.
•![]() The OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the OPT-PRE COM Rx port or the 32 DMX-O COM Rx port.
The OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the OPT-PRE COM Rx port or the 32 DMX-O COM Rx port.
•![]() The OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
The OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
•![]() The 32MUX-O Tx port is connected to the OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
The 32MUX-O Tx port is connected to the OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
Step 2 ![]() Plug one fiber cable end into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.
Plug one fiber cable end into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.

Note ![]() The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A425 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Hub Node
Purpose |
This task installs fiber-optic cables on a hub node DWDM shelf. See "Turn Up DWDM Network" to provision and test DWDM configurations. |
Tools |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber optic cabling for the hub node by consulting the following rules:
Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber optic cabling for the hub node by consulting the following rules:
•![]() The West OPT-BST or OSC-CSM card common (COM) Tx port is connected to the West OPT-PRE COM Rx port or West 32 DMX-O COM Rx port.
The West OPT-BST or OSC-CSM card common (COM) Tx port is connected to the West OPT-PRE COM Rx port or West 32 DMX-O COM Rx port.
•![]() The West OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the West 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
The West OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the West 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
•![]() West 32MUX-O COM Tx port is connected to the West OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Rx port.
West 32MUX-O COM Tx port is connected to the West OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Rx port.
•![]() The East 32MUX-O COM Tx port is connected to the East OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Rx port.
The East 32MUX-O COM Tx port is connected to the East OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Rx port.
•![]() The East OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Tx port is connected to the East OPT-PRE COM Rx port or East 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
The East OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Tx port is connected to the East OPT-PRE COM Rx port or East 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
•![]() The East OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
The East OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the 32DMX-O COM Rx port.
Figure 2-8 shows an example of a hub node with cabling.
Figure 2-8 Fibering a Hub Node

Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.

Note ![]() The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A426 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for a Line Amplifier Node
Purpose |
This task installs fiber-optic cables on a line amplifier node in a DWDM shelf. See "Turn Up DWDM Network" to provision and test DWDM configurations. |
Tools |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber-optic cabling for the line amplifier node by consulting the following rules:
Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber-optic cabling for the line amplifier node by consulting the following rules:
•![]() Line amplifier node layout allows all combinations of OPT-PRE and OPT-BST and allows you to use asymmetrical card choices in west-to-east and east-to-west configurations. For a given line direction, you can configure the four following possibilities:
Line amplifier node layout allows all combinations of OPT-PRE and OPT-BST and allows you to use asymmetrical card choices in west-to-east and east-to-west configurations. For a given line direction, you can configure the four following possibilities:
–![]() Only preamplification
Only preamplification
–![]() Only booster amplification
Only booster amplification
–![]() Both pre- and booster amplification (where a line amplifier node has amplification in at least one direction)
Both pre- and booster amplification (where a line amplifier node has amplification in at least one direction)
–![]() Neither pre- nor booster amplification
Neither pre- nor booster amplification
•![]() If an OPT-PRE card is present west-to-east:
If an OPT-PRE card is present west-to-east:
–![]() The West OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx is connected to the West OPT-PRE COM Rx port
The West OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx is connected to the West OPT-PRE COM Rx port
–![]() The West OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port
The West OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port
•![]() If an OPT-PRE card is not present west-to-east, the West OSC-CSM or the OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
If an OPT-PRE card is not present west-to-east, the West OSC-CSM or the OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
•![]() If an OPT-PRE card is present east-to-west:
If an OPT-PRE card is present east-to-west:
–![]() The East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the East OPT-PRE COM Rx port.
The East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the East OPT-PRE COM Rx port.
–![]() The East OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
The East OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
•![]() If an OPT-PRE card is not present east-to-west, the East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
If an OPT-PRE card is not present east-to-west, the East OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Tx port is connected to the West OSC-CSM or OPT-BST COM Rx port.
Figure 2-9 shows a sample line amplifier node with cabling.
Figure 2-9 Fibering a Line Amplifier Node

Step 2 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.

Note ![]() The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Step 3 ![]() Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 2 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A427 Install Fiber-Optic Cables for an Amplified or Passive OADM Node
Purpose |
This task gives instructions, rules, and examples to install fiber-optic cables on an amplified or passive optical add/drop multiplexing (OADM) node in a DWDM shelf. See "Turn Up DWDM Network" to provision and test DWDM configurations. |
Tools |
Fiber-optic cables |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |

Note ![]() Amplified OADM nodes contain OPT-PRE cards and/or OPT-BST cards. Passive OADM nodes do not. Both contain add/drop channel or band cards or 32MUX-O and 32DMX-O cards.
Amplified OADM nodes contain OPT-PRE cards and/or OPT-BST cards. Passive OADM nodes do not. Both contain add/drop channel or band cards or 32MUX-O and 32DMX-O cards.

Note ![]() To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
To avoid error, connect fiber-optic cable so that the farthest slot to the right represents the east port, and the farthest slot to the left represents the west port. Fiber connected to an east port at one node must plug into the west port on an adjacent node.
Step 1 ![]() Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber-optic cabling for amplified or passive OADM nodes by consulting the following rules:
Refer to your site plan when cabling the node. Connect fiber-optic cabling for amplified or passive OADM nodes by consulting the following rules:
•![]() The two sides of the OADM node do not need to be symmetrical. On each side, you can create one of the following four configurations:
The two sides of the OADM node do not need to be symmetrical. On each side, you can create one of the following four configurations:
–![]() OPT-BST and OPT-PRE
OPT-BST and OPT-PRE
–![]() OSC-CSM and OPT-PRE
OSC-CSM and OPT-PRE
–![]() Only OSC-CSM
Only OSC-CSM
–![]() Only OPT-BST
Only OPT-BST
•![]() Regardless of direction, the TCC2 card supervision always assumes the AD-xC or AD-xB COM Rx port and COM Tx ports are connected.
Regardless of direction, the TCC2 card supervision always assumes the AD-xC or AD-xB COM Rx port and COM Tx ports are connected.
Step 2 ![]() Consult the following rules for OADM node express path cabled connections:
Consult the following rules for OADM node express path cabled connections:
•![]() The TCC2 card checks and guarantees that the AD-xB or AD-xC port sequence on the west line side is the same as the AD-xC or AD-xB port sequence on the East side.
The TCC2 card checks and guarantees that the AD-xB or AD-xC port sequence on the west line side is the same as the AD-xC or AD-xB port sequence on the East side.
•![]() Regardless of direction, the TCC2 card supervision always assumes that the AD-xC or AD-xB EXP-Rx and EXP-Tx port are connected.
Regardless of direction, the TCC2 card supervision always assumes that the AD-xC or AD-xB EXP-Rx and EXP-Tx port are connected.
•![]() When you set a connection between an AD-xC or AD-xB 1 EXP Tx port and an AD-xC or AD-xB 2 COM Rx port, the TCC2 card automatically assumes the same connection between the other AD-xC or AD-xB 1 EXP Rx port and AD-xC or AD-xC 2 COM Tx port.
When you set a connection between an AD-xC or AD-xB 1 EXP Tx port and an AD-xC or AD-xB 2 COM Rx port, the TCC2 card automatically assumes the same connection between the other AD-xC or AD-xB 1 EXP Rx port and AD-xC or AD-xC 2 COM Tx port.
•![]() Tx ports should only be connected to Rx ports.
Tx ports should only be connected to Rx ports.
•![]() EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that all belong to the east side (that is, they are daisy-chained).
EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that all belong to the east side (that is, they are daisy-chained).
•![]() EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that belong to the West side.
EXP ports are connected only to COM ports in between AD-xC or AD-xB cards that belong to the West side.
•![]() The EXP port of the last AD-xC or AD-xB card in the west side is connected to the EXP port of the first AD-xC or AD-xB card in the east side.
The EXP port of the last AD-xC or AD-xB card in the west side is connected to the EXP port of the first AD-xC or AD-xB card in the east side.
•![]() The OPT-BST COM Rx port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM Tx port.
The OPT-BST COM Rx port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM Tx port.
•![]() The OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM Rx port.
The OPT-PRE COM Tx port is connected to the nearest (in slot position) AD-xC or AD-xB COM Rx port.
•![]() If OADM cards are located in adjacent slots, the TCC2 card assumes they are connected in a daisy-chain between the EXP ports and COM ports as noted above.
If OADM cards are located in adjacent slots, the TCC2 card assumes they are connected in a daisy-chain between the EXP ports and COM ports as noted above.
•![]() The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM Rx port is connected to the west OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM Tx port.
The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM Rx port is connected to the west OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM Tx port.
•![]() The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM Tx port is connected to the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Rx port.
The first west AD-xC or AD-xB card COM Tx port is connected to the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Rx port.
•![]() The first east AD-xC or AD-xB card COM Rx port is connected to the east OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM Tx port.
The first east AD-xC or AD-xB card COM Rx port is connected to the east OPT-PRE or OSC-CSM COM Tx port.
•![]() The first east AD-xC or AD-xB COM Tx port is connected to the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM Rx port.
The first east AD-xC or AD-xB COM Tx port is connected to the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM Rx port.
•![]() If a west OPT-PRE is present, the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Tx port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM Rx port.
If a west OPT-PRE is present, the west OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Tx port is connected to the west OPT-PRE COM Rx port.
•![]() If an east OPT-PRE is present, the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Tx port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM Rx port.
If an east OPT-PRE is present, the east OPT-BST or OSC-CSM COM Tx port is connected to the east OPT-PRE COM Rx port.
Step 3 ![]() Consult the following rules for OADM node add/drop path cabled connections:
Consult the following rules for OADM node add/drop path cabled connections:
•![]() AD-xB add/drop (Rx or Tx) ports are only connected to the following ports:
AD-xB add/drop (Rx or Tx) ports are only connected to the following ports:
–![]() 4MD COM Tx or 4MD COM Rx ports
4MD COM Tx or 4MD COM Rx ports
–![]() another AD-xB add/drop port (a pass-through configuration)
another AD-xB add/drop port (a pass-through configuration)
•![]() An AD-xB add/drop band port is only connected to a 4MD card belonging to the same band.
An AD-xB add/drop band port is only connected to a 4MD card belonging to the same band.
•![]() For each specific AD-xB, the add and drop ports for that band card are connected to the COM Tx and COM Rx ports of the same 4MD card.
For each specific AD-xB, the add and drop ports for that band card are connected to the COM Tx and COM Rx ports of the same 4MD card.
•![]() The AD-xB and 4MD card are located in the same direction side (the connected ports will all have the same line direction).
The AD-xB and 4MD card are located in the same direction side (the connected ports will all have the same line direction).
Step 4 ![]() Consult the following rules for OADM node pass-through path cabled connections:
Consult the following rules for OADM node pass-through path cabled connections:
•![]() Pass-through connections are only established between add and drop ports on the same band or channel and same line direction.
Pass-through connections are only established between add and drop ports on the same band or channel and same line direction.
•![]() Only connect AD-xC or AD-xB channel add/drop ports to other AD-xC or AD-xB add/drop ports (as pass-through configurations).
Only connect AD-xC or AD-xB channel add/drop ports to other AD-xC or AD-xB add/drop ports (as pass-through configurations).
•![]() An add (Rx) port is only connected to a drop (Tx) port.
An add (Rx) port is only connected to a drop (Tx) port.
•![]() Only connect 4MD client input/output ports to other 4MD client input/output ports.
Only connect 4MD client input/output ports to other 4MD client input/output ports.
•![]() Only connect a 32DMX-O output port to a 32MUX-O input port.
Only connect a 32DMX-O output port to a 32MUX-O input port.
•![]() A West AD-xB drop (Tx) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM Rx port.
A West AD-xB drop (Tx) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM Rx port.
•![]() A West AD-xB add (Rx) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM Tx port.
A West AD-xB add (Rx) port is connected to the corresponding west 4MD COM Tx port.
•![]() An East AD-xB drop (Tx) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM Rx port.
An East AD-xB drop (Tx) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM Rx port.
•![]() An East AD-xB add (Rx) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM Tx port.
An East AD-xB add (Rx) port is connected to the corresponding east 4MD COM Tx port.
Figure 2-10 shows a sample amplified OADM node with cabling.
Figure 2-10 Fibering an Amplified OADM Node

Figure 2-11 shows an example of a passive OADM node.
Figure 2-11 Fibering a Passive OADM Node

Step 5 ![]() Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.
Plug one end of the fiber cable into the desired Rx port and other end into the desired Tx port.

Note ![]() The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
The card displays an SF LED if the transmit and receive fibers are mismatched (one fiber connects a receive port on one card to a receive port on another card, or the same situation with transmit ports).
Step 6 ![]() Repeat Step 5 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Repeat Step 5 until you have connected the nodes according to the site plan.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A245 Route Fiber-Optic Cables
Purpose |
This procedure describes how to route fiber-optic cables. This procedure can be used for TDM, DWDM, and hybrid nodes. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Any of the following: A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
None |
Step 1 ![]() Open the fold-down front door on the cable-management tray.
Open the fold-down front door on the cable-management tray.
Step 2 ![]() Route the fiber cable on the card faceplate through the fiber clip on the faceplate, if provided. Fiber clips are factory-attached to the faceplate of OC-N card and to some DWDM cards (32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, OSCM, OPT-PRE, and OPT-BST).
Route the fiber cable on the card faceplate through the fiber clip on the faceplate, if provided. Fiber clips are factory-attached to the faceplate of OC-N card and to some DWDM cards (32MUX-O, 32DMX-O, OSCM, OPT-PRE, and OPT-BST).
GBICs do not have fiber clips; therefore, if you are routing fiber from an E1000-2-G, E1000-2, G1000-2-G, G10002, or FC_MR-4 card, skip to Step 3.
Step 3 ![]() Route the fiber cables into the cable-management tray.
Route the fiber cables into the cable-management tray.
Step 4 ![]() Route the fiber cables out either side of the cable-management tray through the cutouts on each side of the shelf assembly. Use the reversible fiber guides to route cables out the desired side.
Route the fiber cables out either side of the cable-management tray through the cutouts on each side of the shelf assembly. Use the reversible fiber guides to route cables out the desired side.
Step 5 ![]() Close the fold-down front door when all fiber cables in the front compartment are properly routed.
Close the fold-down front door when all fiber cables in the front compartment are properly routed.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A116 Remove and Replace a Card
Step 1 ![]() If you are not logged into CTC and you need to remove a card, remove the card as described in Step 3. When you log into CTC, troubleshoot the mismatched equipment alarm (MEA) with the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide.
If you are not logged into CTC and you need to remove a card, remove the card as described in Step 3. When you log into CTC, troubleshoot the mismatched equipment alarm (MEA) with the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 2 ![]() If you are logged into CTC, complete one of the following:
If you are logged into CTC, complete one of the following:
•![]() Complete the "DLP-A191 Delete a Card" task and continue with Step 3.
Complete the "DLP-A191 Delete a Card" task and continue with Step 3.
•![]() Complete the "DLP-A247 Change an OC-N Card" task to delete a card and replace it with a different OC-N card while maintaining existing provisioning.
Complete the "DLP-A247 Change an OC-N Card" task to delete a card and replace it with a different OC-N card while maintaining existing provisioning.
Step 3 ![]() Physically remove the card:
Physically remove the card:
a. ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
b. ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to pull the card forward and away from the shelf.
Use the latches/ejectors to pull the card forward and away from the shelf.
Step 4 ![]() Insert the new card using one of the following procedures as applicable:
Insert the new card using one of the following procedures as applicable:
•![]() A15 Install the Common Control Cards
A15 Install the Common Control Cards
•![]() A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards
A249 Install the Transponder and Muxponder Cards
•![]() A17 Install the Electrical Cards
A17 Install the Electrical Cards
•![]() A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors
A246 Install Ethernet Cards and Connectors
•![]() A274 Install the FC_MR-4 Cards
A274 Install the FC_MR-4 Cards
•![]() A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards
A243 Install the DWDM Dispersion Compensating Cards
Step 5 ![]() Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure or the "A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards" procedure
Continue with the "A247 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on OC-N Cards" procedure or the "A244 Install Fiber-Optic Cables on DWDM Cards" procedure
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A191 Delete a Card
Purpose |
This task deletes a card from CTC. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
|
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() On the shelf graphic in CTC, right-click the card that you want to remove and choose Delete Card.
On the shelf graphic in CTC, right-click the card that you want to remove and choose Delete Card.
You cannot delete a card if any of the following conditions apply:
•![]() The card is a TCC2 card. To replace a TCC2 card, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide.
The card is a TCC2 card. To replace a TCC2 card, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide.
•![]() The card is part of a protection group; see the "DLP-A155 Delete a Protection Group" task on page 12-20.
The card is part of a protection group; see the "DLP-A155 Delete a Protection Group" task on page 12-20.
•![]() The card has circuits; see the "NTP-A278 Modify and Delete Overhead Circuits" procedure on page 11-19 and the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18.
The card has circuits; see the "NTP-A278 Modify and Delete Overhead Circuits" procedure on page 11-19 and the "DLP-A333 Delete Circuits and DWDM Optical Channel Network Connections" task on page 11-18.
•![]() The card is part of a BLSR; see the "A213 Remove a BLSR Node" procedure.
The card is part of a BLSR; see the "A213 Remove a BLSR Node" procedure.
•![]() The card is being used for timing; see the "DLP-A157 Change the Node Timing Source" task on page 12-23.
The card is being used for timing; see the "DLP-A157 Change the Node Timing Source" task on page 12-23.
•![]() The card has a non-DWDM DCC/GCC termination; see the "NTP-A255 Delete Communications Channel Terminations" procedure on page 12-20.
The card has a non-DWDM DCC/GCC termination; see the "NTP-A255 Delete Communications Channel Terminations" procedure on page 12-20.

Note ![]() If you delete a card in CTC but do not remove it from the shelf, it will reboot and reappear in CTC.
If you delete a card in CTC but do not remove it from the shelf, it will reboot and reappear in CTC.
Step 2 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A247 Change an OC-N Card


Note ![]() You cannot change a multiport card to a card with a smaller number of ports.
You cannot change a multiport card to a card with a smaller number of ports.
Step 1 ![]() If the card the active card in a 1+1 protection group, switch traffic away from the card:
If the card the active card in a 1+1 protection group, switch traffic away from the card:
a. ![]() Log into a node on the network. If you are already logged in, go to Step b.
Log into a node on the network. If you are already logged in, go to Step b.
b. ![]() Display the CTC node (login) view.
Display the CTC node (login) view.
c. ![]() Click the Maintenance > Protection tabs.
Click the Maintenance > Protection tabs.
d. ![]() Double-click the protection group that contains the reporting card.
Double-click the protection group that contains the reporting card.
e. ![]() Click the active card of the selected group.
Click the active card of the selected group.
f. ![]() Click Switch and Yes in the Confirmation dialog box.
Click Switch and Yes in the Confirmation dialog box.
Step 2 ![]() In CTC, right-click the card that you want to remove and choose Change Card.
In CTC, right-click the card that you want to remove and choose Change Card.
Step 3 ![]() From the Change Card drop-down menu, choose the desired card type and click OK. An MEA alarm appears until you replace the card.
From the Change Card drop-down menu, choose the desired card type and click OK. An MEA alarm appears until you replace the card.
Step 4 ![]() Physically remove the card:
Physically remove the card:
a. ![]() Disconnect any fiber connections to the front of the card.
Disconnect any fiber connections to the front of the card.
b. ![]() Open the card latches/ejectors.
Open the card latches/ejectors.
c. ![]() Use the latches/ejectors to pull the card forward and away from the shelf.
Use the latches/ejectors to pull the card forward and away from the shelf.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure.
Complete the "A16 Install the OC-N Cards" procedure.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A20 Replace the Front Door

Note ![]() Be careful not to crimp any fiber cables that are connected to the OC-N cards or DWDM cards. Some might not have the fiber boot attached.
Be careful not to crimp any fiber cables that are connected to the OC-N cards or DWDM cards. Some might not have the fiber boot attached.
Step 1 ![]() Insert the front door into the hinges on the shelf assembly.
Insert the front door into the hinges on the shelf assembly.
Step 2 ![]() Attach one end of the ground strap terminal lug (72-3622-01) to the male stud on the inside of the door. Attach and tighten the #6 Kepnut (49-0600-01) using the open-end wrench (Figure 2-12).
Attach one end of the ground strap terminal lug (72-3622-01) to the male stud on the inside of the door. Attach and tighten the #6 Kepnut (49-0600-01) using the open-end wrench (Figure 2-12).
Figure 2-12 Installing the Door Ground Strap Retrofit Kit

Step 3 ![]() Attach the other end of the ground strap to the longer screw on the fiber guide.
Attach the other end of the ground strap to the longer screw on the fiber guide.
a. ![]() Attach the lock washer.
Attach the lock washer.
b. ![]() Attach the terminal lug.
Attach the terminal lug.
c. ![]() Using the open-end wrench, attach and tighten the #4 Kepnut (49-0337-01) on the terminal lug.
Using the open-end wrench, attach and tighten the #4 Kepnut (49-0337-01) on the terminal lug.

Note ![]() To avoid interference with the traffic (line) card, make sure the ground strap is in a flat position when the door is open. To move the ground strap into a flat position, rotate the terminal lug counterclockwise before tightening the Kepnut.
To avoid interference with the traffic (line) card, make sure the ground strap is in a flat position when the door is open. To move the ground strap into a flat position, rotate the terminal lug counterclockwise before tightening the Kepnut.
Step 4 ![]() Replace the left cable-routing channel.
Replace the left cable-routing channel.
Step 5 ![]() Using a Phillips screwdriver, insert and tighten the screws for the cable-routing channel.
Using a Phillips screwdriver, insert and tighten the screws for the cable-routing channel.
Figure 2-13 shows the shelf assembly with the front door and ground strap installed.
Figure 2-13 Shelf Assembly with Door Ground Strap Retrofit Kit Installed

Step 6 ![]() Swing the door closed.
Swing the door closed.

Note ![]() The ONS 15454 comes with a pinned hex key tool for locking and unlocking the front door. Turn the key counterclockwise to unlock the door and clockwise to lock it.
The ONS 15454 comes with a pinned hex key tool for locking and unlocking the front door. Turn the key counterclockwise to unlock the door and clockwise to lock it.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
 Feedback
Feedback