- About this Guide
- Chapter 1, Install Shelf and Backplane Hardware
- Chapter 2, Install Cards and Fiber-Optic Cable
- Chapter 3, Set Up PC and Log Into the GUI
- Chapter 4, Turn Up Node
- Chapter 5, Turn Up DWDM Node
- Chapter 6, Turn Up Network
- Chapter 7, Turn Up DWDM Network
- Chapter 8, Create Circuits and VT Tunnels
- Chapter 9, Manage Alarms
- Chapter 10, Monitor Performance
- Chapter 11, Manage Circuits
- Chapter 12, Change Node Settings
- Chapter 13, Change Card Settings
- Chapter 14, Upgrade Cards and Spans
- Chapter 15, Convert Network Configurations
- Chapter 16, Add and Remove Nodes
- Chapter 17, Maintain the Node
- Chapter 18, Power Down Node
- Appendix A, CTC Information and Shortcuts
- Appendix B, Specifications
- Before You Begin
- NTP-A253 Change the PM Display
- DLP-A124 Refresh PM Counts at 15-Minute Intervals
- DLP-A125 Refresh PM Counts at One-Day Intervals
- DLP-A347 Refresh E-Series and G-Series Ethernet PM Counts
- DLP-A126 View Near-End PM Counts
- DLP-A127 View Far-End PM Counts
- DLP-A348 Monitor PM Counts for a Selected Signal
- DLP-A129 Reset Current PM Counts
- DLP-A349 Clear Selected PM Counts
- DLP-A260 Set Auto-Refresh Interval for Displayed PM Counts
- DLP-A261 Refresh PM Counts for a Different Port
- NTP-A195 Monitor Electrical Performance
- NTP-A198 Monitor Ethernet Performance
- DLP-A256 View Ethernet Statistics PM Parameters
- DLP-A257 View Ethernet Utilization PM Parameters
- DLP-A258 View Ethernet History PM Parameters
- DLP-A320 View ML-Series Ether Ports PM Parameters
- DLP-A321 View ML-Series POS Ports PM Parameters
- DLP-A259 Refresh Ethernet PM Counts at a Different Time Interval
- NTP-A279 Create or Delete Ethernet RMON Thresholds
- NTP-A250 Monitor OC-N Performance
- NTP-A251 Monitor Multirate Transport Performance
- NTP-A252 Monitor DWDM Performance
- DLP-A502 View Optical Service Channel PM Parameters
- DLP-A503 View Optical Amplifier PM Parameters
- DLP-A504 View Optical Multiplexer and Demultiplexer PM Parameters
- DLP-A505 View Channel Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters
- DLP-A506 View Band Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters
- NTP-A285 Monitor FC_MR-4 Performance
- NTP-A289 Create or Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Thresholds
Monitor Performance
This chapter explains how to enable and view performance monitoring statistics for the Cisco ONS 15454. Performance monitoring (PM) parameters are used by service providers to gather, store, and set thresholds and report performance data for early detection of problems. For more PM information, details, and definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Before You Begin
Before performing any of the following procedures, investigate all alarms and clear any trouble conditions. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide as necessary.
This section lists the chapter procedures (NTPs). Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
1. ![]() A253 Change the PM Display—Complete as needed to change the displayed PM counts.
A253 Change the PM Display—Complete as needed to change the displayed PM counts.
2. ![]() A195 Monitor Electrical Performance—Complete as needed to monitor electrical performance.
A195 Monitor Electrical Performance—Complete as needed to monitor electrical performance.
3. ![]() A198 Monitor Ethernet Performance—Complete as needed to monitor Ethernet performance.
A198 Monitor Ethernet Performance—Complete as needed to monitor Ethernet performance.
4. ![]() A279 Create or Delete Ethernet RMON Thresholds—Complete as needed to monitor Ethernet performance.
A279 Create or Delete Ethernet RMON Thresholds—Complete as needed to monitor Ethernet performance.
5. ![]() A250 Monitor OC-N Performance—Complete as needed to monitor optical (OC-N) performance.
A250 Monitor OC-N Performance—Complete as needed to monitor optical (OC-N) performance.
6. ![]() A251 Monitor Multirate Transport Performance—Complete as needed to monitor multirate transport performance.
A251 Monitor Multirate Transport Performance—Complete as needed to monitor multirate transport performance.
7. ![]() A252 Monitor DWDM Performance—Complete as needed to monitor DWDM performance.
A252 Monitor DWDM Performance—Complete as needed to monitor DWDM performance.
8. ![]() A285 Monitor FC_MR-4 Performance—Complete as needed to monitor FC_MR-4 performance.
A285 Monitor FC_MR-4 Performance—Complete as needed to monitor FC_MR-4 performance.
9. ![]() A289 Create or Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Thresholds—Complete as needed to monitor FC_MR-4 performance.
A289 Create or Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Thresholds—Complete as needed to monitor FC_MR-4 performance.

Note ![]() For additional information regarding PM parameters, refer to the Digital transmission surveillance section in Telcordia's GR-1230-CORE, GR-820-CORE, GR-499-CORE, and GR-253-CORE documents, and in the ANSI document entitled Digital Hierarchy - Layer 1 In-Service Digital Transmission Performance Monitoring.
For additional information regarding PM parameters, refer to the Digital transmission surveillance section in Telcordia's GR-1230-CORE, GR-820-CORE, GR-499-CORE, and GR-253-CORE documents, and in the ANSI document entitled Digital Hierarchy - Layer 1 In-Service Digital Transmission Performance Monitoring.
NTP-A253 Change the PM Display
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to change the display of PM counts by selecting drop-down menu or radio button options in the Performance window. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2
Step 2 ![]() In node view, double-click the electrical, Ethernet, optical (OC-N), multirate transport, or DWDM cards where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the electrical, Ethernet, optical (OC-N), multirate transport, or DWDM cards where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 3 ![]() As needed, use the following tasks to change the display of PM counts:
As needed, use the following tasks to change the display of PM counts:
•![]() A124 Refresh PM Counts at 15-Minute Intervals
A124 Refresh PM Counts at 15-Minute Intervals
•![]() A125 Refresh PM Counts at One-Day Intervals
A125 Refresh PM Counts at One-Day Intervals
•![]() A347 Refresh E-Series and G-Series Ethernet PM Counts
A347 Refresh E-Series and G-Series Ethernet PM Counts
•![]() A348 Monitor PM Counts for a Selected Signal
A348 Monitor PM Counts for a Selected Signal
•![]() A349 Clear Selected PM Counts
A349 Clear Selected PM Counts
•![]() A260 Set Auto-Refresh Interval for Displayed PM Counts
A260 Set Auto-Refresh Interval for Displayed PM Counts
•![]() A261 Refresh PM Counts for a Different Port
A261 Refresh PM Counts for a Different Port
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A124 Refresh PM Counts at 15-Minute Intervals
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the 15 min radio button.
Click the 15 min radio button.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring parameters appear in 15-minute intervals synchronized with the time of day.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring parameters appear in 15-minute intervals synchronized with the time of day.
Step 5 ![]() View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current 15-minute interval.
View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current 15-minute interval.
Each monitored performance parameter has corresponding threshold values for the current time period. If the value of the counter exceeds the threshold value for a particular 15-minute interval, a threshold crossing alert (TCA) is raised. The number represents the counter value for each specific performance monitoring parameter.
Step 6 ![]() View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous 15-minute intervals.
View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous 15-minute intervals.

Note ![]() If a complete 15-minute interval count is not possible, the value appears with a yellow background. An incomplete or incorrect count can be caused by monitoring for less than 15 minutes after the counter started, changing node timing settings, changing the time zone settings, replacing a card, resetting a card, or changing port states. When the problem is corrected, the subsequent 15-minute interval appears with a white background.
If a complete 15-minute interval count is not possible, the value appears with a yellow background. An incomplete or incorrect count can be caused by monitoring for less than 15 minutes after the counter started, changing node timing settings, changing the time zone settings, replacing a card, resetting a card, or changing port states. When the problem is corrected, the subsequent 15-minute interval appears with a white background.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A125 Refresh PM Counts at One-Day Intervals
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the 1 day radio button.
Click the 1 day radio button.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring appears in 1-day intervals synchronized with the time of day.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring appears in 1-day intervals synchronized with the time of day.
Step 5 ![]() View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current 1-day interval.
View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current 1-day interval.
Each monitored performance parameter has corresponding threshold values for the current time period. If the value of the counter exceeds the threshold value for a particular 1-day interval, a threshold crossing alert (TCA) is raised. The number represents the counter value for each specific performance monitoring parameter.
Step 6 ![]() View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous 1-day intervals.
View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous 1-day intervals.

Note ![]() If a complete count over a 1-day interval is not possible, the value appears with a yellow background. An incomplete or incorrect count can be caused by monitoring for less than 24 hours after the counter started, changing node timing settings, changing the time zone settings, replacing a card, resetting a card, or changing port states. When the problem is corrected, the subsequent 1-day interval appears with a white background.
If a complete count over a 1-day interval is not possible, the value appears with a yellow background. An incomplete or incorrect count can be caused by monitoring for less than 24 hours after the counter started, changing node timing settings, changing the time zone settings, replacing a card, resetting a card, or changing port states. When the problem is corrected, the subsequent 1-day interval appears with a white background.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A347 Refresh E-Series and G-Series Ethernet PM Counts
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > History tabs.
Click the Performance > History tabs.
Step 3 ![]() From the Interval drop-down menu click one of the following:
From the Interval drop-down menu click one of the following:
•![]() 1 min
1 min
•![]() 15 min
15 min
•![]() 1 hour
1 hour
•![]() 1 day
1 day
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring appears in the interval selected synchronized with the time of day.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring appears in the interval selected synchronized with the time of day.
Step 5 ![]() View the Prev column to find PM counts for the latest selected interval.
View the Prev column to find PM counts for the latest selected interval.
Each monitored performance parameter has corresponding threshold values for the latest time period. If the value of the counter exceeds the threshold value for a particular selected interval, a threshold crossing alert (TCA) is raised. The number represents the counter value for each specific performance monitoring parameter.
Step 6 ![]() View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous intervals.
View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous intervals.

Note ![]() If a complete count over the selected interval is not possible, the value appears with a yellow background. For example, if you selected the 1-day interval, an incomplete or incorrect count can be caused by monitoring for less than 24 hours after the counter started, changing node timing settings, changing the time zone settings, replacing a card, resetting a card, or changing port states. When the problem is corrected, the subsequent 1-day interval appears with a white background.
If a complete count over the selected interval is not possible, the value appears with a yellow background. For example, if you selected the 1-day interval, an incomplete or incorrect count can be caused by monitoring for less than 24 hours after the counter started, changing node timing settings, changing the time zone settings, replacing a card, resetting a card, or changing port states. When the problem is corrected, the subsequent 1-day interval appears with a white background.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A126 View Near-End PM Counts
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Near End radio button.
Click the Near End radio button.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. All PM parameters occurring for the selected card on the incoming signal appear. For PM parameter definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click Refresh. All PM parameters occurring for the selected card on the incoming signal appear. For PM parameter definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 5 ![]() View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current time interval.
View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current time interval.
Step 6 ![]() View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous time intervals.
View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous time intervals.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A127 View Far-End PM Counts
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Far End radio button.
Click the Far End radio button.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. All PM parameters recorded by the far-end node for the selected card on the outgoing signal appear. For PM parameter definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click Refresh. All PM parameters recorded by the far-end node for the selected card on the outgoing signal appear. For PM parameter definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 5 ![]() View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current time interval.
View the Curr column to find PM counts for the current time interval.
Step 6 ![]() View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous time intervals.
View the Prev-n columns to find PM counts for the previous time intervals.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A348 Monitor PM Counts for a Selected Signal
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.

Note ![]() Different port and signal-type menus appear depending on the card type and the circuit type. The appropriate types (DS1, DS3, VT path, STS path) appear based on the card. For example, the DS3XM card lists DS3, DS1, VT path, and STS path PM parameters as signal-types. This enables you to select both the DS-3 port and the DS-1 within the specified DS-3.
Different port and signal-type menus appear depending on the card type and the circuit type. The appropriate types (DS1, DS3, VT path, STS path) appear based on the card. For example, the DS3XM card lists DS3, DS1, VT path, and STS path PM parameters as signal-types. This enables you to select both the DS-3 port and the DS-1 within the specified DS-3.
Step 3 ![]() In the signal type drop-down menus, click the following options as appropriate:
In the signal type drop-down menus, click the following options as appropriate:
•![]() DS: n or Port: n (card port number)
DS: n or Port: n (card port number)
•![]() VT: n (VT path number)
VT: n (VT path number)
•![]() STS: n (STS number within the VT path)
STS: n (STS number within the VT path)
Figure 10-1 shows the Port and Signal-type menus on the Performance window for a DS3XM-6 card.
Figure 10-1 Signal-Type Menus for a DS3XM-6 Card
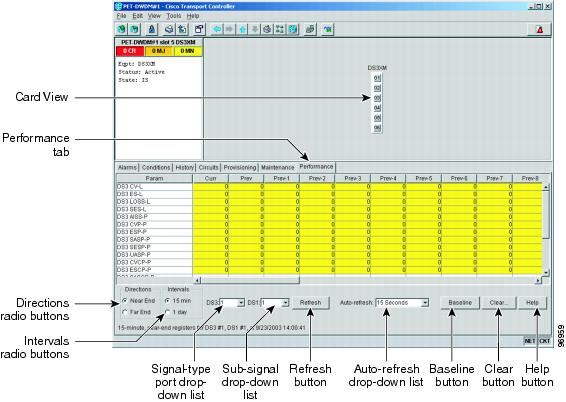
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. All PM counts recorded by the near-end or far-end node for the specified outgoing signal type on the selected card and port appear. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click Refresh. All PM counts recorded by the near-end or far-end node for the specified outgoing signal type on the selected card and port appear. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 5 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A129 Reset Current PM Counts
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click Baseline.
Click Baseline.

Note ![]() The Baseline button clears the PM counts displayed in the current time interval but does not clear the PM counts on the card. When the current time interval expires or the window view changes, the total number of PM counts on the card and on the window appear in the appropriate column. The baseline values are discarded if you change views to a different window and then return to the Performance window.
The Baseline button clears the PM counts displayed in the current time interval but does not clear the PM counts on the card. When the current time interval expires or the window view changes, the total number of PM counts on the card and on the window appear in the appropriate column. The baseline values are discarded if you change views to a different window and then return to the Performance window.
Step 4 ![]() View the current statistics columns to observe changes to PM counts for the current time interval.
View the current statistics columns to observe changes to PM counts for the current time interval.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A349 Clear Selected PM Counts

Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click Clear.
Click Clear.
Step 4 ![]() From the Clear Statistics menu, choose one of three options:
From the Clear Statistics menu, choose one of three options:
•![]() Displayed statistics: Clearing displayed statistics erases from the card and the window all PM counts associated with the current combination of statistics on the selected port. This means the selected time interval, direction, and signal type counts are erased from the card and the window.
Displayed statistics: Clearing displayed statistics erases from the card and the window all PM counts associated with the current combination of statistics on the selected port. This means the selected time interval, direction, and signal type counts are erased from the card and the window.
•![]() All statistics for port x: Clearing all statistics for port x erases from the card and the window all PM counts associated with all combinations of the statistics on the selected port. This means all time intervals, directions, and signal type counts are erased from the card and the window.
All statistics for port x: Clearing all statistics for port x erases from the card and the window all PM counts associated with all combinations of the statistics on the selected port. This means all time intervals, directions, and signal type counts are erased from the card and the window.
•![]() All statistics for card: Clearing all statistics for card erases from the card and the window all PM counts for all ports.
All statistics for card: Clearing all statistics for card erases from the card and the window all PM counts for all ports.
Step 5 ![]() From the Clear Statistics menu, choose OK to clear the selected statistics.
From the Clear Statistics menu, choose OK to clear the selected statistics.
Step 6 ![]() Verify that the selected PM counts have been cleared.
Verify that the selected PM counts have been cleared.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A260 Set Auto-Refresh Interval for Displayed PM Counts
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() From the Auto-refresh drop-down menu, choose one of six options:
From the Auto-refresh drop-down menu, choose one of six options:
•![]() None: This option disables the auto-refresh feature.
None: This option disables the auto-refresh feature.
•![]() 15 Seconds: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 15-second time intervals.
15 Seconds: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 15-second time intervals.
•![]() 30 Seconds: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 30-second time intervals.
30 Seconds: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 30-second time intervals.
•![]() 1 Minute: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 1-minute time intervals.
1 Minute: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 1-minute time intervals.
•![]() 3 Minutes: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 3-minute time intervals.
3 Minutes: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 3-minute time intervals.
•![]() 5 Minutes: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 5-minute time intervals.
5 Minutes: This option sets the window auto-refresh to 5-minute time intervals.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. The PM counts for the newly-selected auto-refresh time interval appear.
Click Refresh. The PM counts for the newly-selected auto-refresh time interval appear.
Depending on the selected auto-refresh interval, the displayed PM counts automatically update when each refresh interval completes. If the auto-refresh interval is set to None, the PM counts that appear are not updated unless you click Refresh.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A261 Refresh PM Counts for a Different Port
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() In the Port drop-down menu, choose a port.
In the Port drop-down menu, choose a port.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh. The PM counts for the newly-selected port appear.
Click Refresh. The PM counts for the newly-selected port appear.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A195 Monitor Electrical Performance
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to view node near-end or far-end performance during selected time intervals on an electrical card and port to detect possible performance problems. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() In node view, double-click the electrical card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the electrical card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Performance tab (Figure 10-2).
Click the Performance tab (Figure 10-2).
Figure 10-2 Viewing Electrical Card Performance Monitoring Information

Step 4 ![]() In the signal type drop-down menus, click one of the following options:
In the signal type drop-down menus, click one of the following options:
•![]() DSn (card port)
DSn (card port)
•![]() VTn (VT path)
VTn (VT path)
•![]() STSn (STS within the VT path)
STSn (STS within the VT path)
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh.
Click Refresh.
Step 6 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-A198 Monitor Ethernet Performance
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to view node transmit and receive performance during selected time intervals on an Ethernet card and port to detect possible performance problems. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A256 View Ethernet Statistics PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A256 View Ethernet Statistics PM Parameters" task.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A257 View Ethernet Utilization PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A257 View Ethernet Utilization PM Parameters" task.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A258 View Ethernet History PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A258 View Ethernet History PM Parameters" task.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A320 View ML-Series Ether Ports PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A320 View ML-Series Ether Ports PM Parameters" task.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A321 View ML-Series POS Ports PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A321 View ML-Series POS Ports PM Parameters" task.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A256 View Ethernet Statistics PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the E-Series or G-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the E-Series or G-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Statistics tabs (Figure 10-3).
Click the Performance > Statistics tabs (Figure 10-3).
Figure 10-3 G-Series Statistics on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the PM parameter names appear in the Param column. The current PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names appear in the Param column. The current PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A257 View Ethernet Utilization PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the E-Series or G-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the E-Series or G-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Utilization tabs (Figure 10-4).
Click the Performance > Utilization tabs (Figure 10-4).
Figure 10-4 G-Series Utilization on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring utilization values for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring utilization values for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the Port # column to find the port you want to monitor.
View the Port # column to find the port you want to monitor.
Step 5 ![]() The transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) bandwidth utilization values for the previous time intervals appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
The transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) bandwidth utilization values for the previous time intervals appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A258 View Ethernet History PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the E-Series or G-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the E-Series or G-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > History tabs (Figure 10-5).
Click the Performance > History tabs (Figure 10-5).
Figure 10-5 Ethernet History on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A320 View ML-Series Ether Ports PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the ML-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the ML-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Ether Ports tabs (Figure 10-6).
Click the Performance > Ether Ports tabs (Figure 10-6).
Figure 10-6 Ether Ports on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A321 View ML-Series POS Ports PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the ML-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the ML-Series Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > POS Ports tabs (Figure 10-7).
Click the Performance > POS Ports tabs (Figure 10-7).
Figure 10-7 POS Ports on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A259 Refresh Ethernet PM Counts at a Different Time Interval
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the Ethernet card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Utilization tab or the History tab.
Click the Utilization tab or the History tab.
Step 4 ![]() From the Interval drop-down menu, choose one of four options:
From the Interval drop-down menu, choose one of four options:
•![]() 1 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-minute time intervals.
1 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-minute time intervals.
•![]() 15 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in 15-minute time intervals.
15 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in 15-minute time intervals.
•![]() 1 hour: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-hour time intervals.
1 hour: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-hour time intervals.
•![]() 1 day: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-day (24 hours) time intervals.
1 day: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-day (24 hours) time intervals.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. The PM counts refresh with values based on the selected time interval.
Click Refresh. The PM counts refresh with values based on the selected time interval.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A279 Create or Delete Ethernet RMON Thresholds

Note ![]() The ONS 15454 ML-Series card uses the Cisco IOS CLI for managing RMON.
The ONS 15454 ML-Series card uses the Cisco IOS CLI for managing RMON.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
•![]() A533 Create Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds
A533 Create Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds
•![]() A529 Delete Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds
A529 Delete Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A533 Create Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds

Note ![]() The ONS 15454 ML-Series card uses the Cisco IOS CLI for managing RMON.
The ONS 15454 ML-Series card uses the Cisco IOS CLI for managing RMON.
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node where you want to set up RMON. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node where you want to set up RMON. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Double-click the Ethernet card where you want to create the RMON alarm thresholds.
Double-click the Ethernet card where you want to create the RMON alarm thresholds.
Step 3 ![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Ether Thresholds tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Ether Thresholds tabs.
Step 4 ![]() Click Create.
Click Create.
The Create Ether Threshold dialog box appears (Figure 10-8).
Figure 10-8 Creating RMON Thresholds
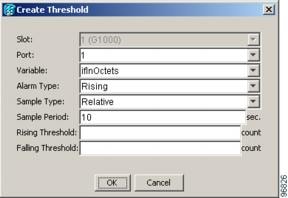
Step 5 ![]() From the Slot menu, choose the appropriate Ethernet card.
From the Slot menu, choose the appropriate Ethernet card.
Step 6 ![]() From the Port drop-down menu, choose the applicable port on the Ethernet card you selected.
From the Port drop-down menu, choose the applicable port on the Ethernet card you selected.
Step 7 ![]() From the Variable drop-down menu, choose the variable. See Table 10-1 for a list of the Ethernet threshold variables available in this field.
From the Variable drop-down menu, choose the variable. See Table 10-1 for a list of the Ethernet threshold variables available in this field.
Step 8 ![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down menu, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down menu, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 9 ![]() From the Sample Type drop-down menu, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down menu, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 10 ![]() Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 11 ![]() Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.

Note ![]() For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a falling threshold of 400 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a falling threshold of 400 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 12 ![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 minutes subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 minutes, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15 minute period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).
Step 13 ![]() Click OK to complete the procedure.
Click OK to complete the procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A529 Delete Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds
Purpose |
This task deletes remote monitoring (RMON) threshold crossing alarms for Ethernet ports. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A533 Create Ethernet RMON Alarm Thresholds |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |

Note ![]() The ONS 15454 ML-Series card uses the Cisco IOS CLI for managing RMON.
The ONS 15454 ML-Series card uses the Cisco IOS CLI for managing RMON.
Step 1 ![]() Double-click the Ethernet card where you want to delete the RMON alarm thresholds.
Double-click the Ethernet card where you want to delete the RMON alarm thresholds.
Step 2 ![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Ether Thresholds tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Ether Thresholds tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click the RMON alarm threshold you want to delete.
Click the RMON alarm threshold you want to delete.
Step 4 ![]() Click Delete. The Delete Threshold dialog box opens.
Click Delete. The Delete Threshold dialog box opens.
Step 5 ![]() Click Yes to delete that threshold.
Click Yes to delete that threshold.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A250 Monitor OC-N Performance
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to view node near-end or far-end performance during selected time intervals on an OC-N card and port to detect possible performance problems. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A121 Enable/Disable Pointer Justification Count Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable clock synchronization monitoring.
Complete the "DLP-A121 Enable/Disable Pointer Justification Count Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable clock synchronization monitoring.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A122 Enable/Disable Intermediate Path Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable monitoring of STS traffic through intermediate nodes.
Complete the "DLP-A122 Enable/Disable Intermediate Path Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable monitoring of STS traffic through intermediate nodes.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A507 View OC-N PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A507 View OC-N PM Parameters" task.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A121 Enable/Disable Pointer Justification Count Performance Monitoring
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
See Table 10-2 for a list of LTE cards.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
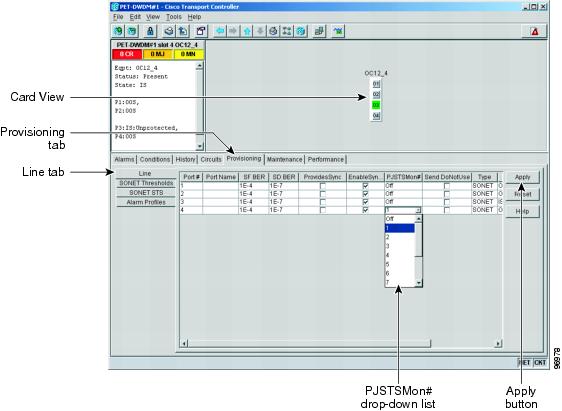
Step 3 ![]() From the PJSTSMon# drop-down menu, make a selection based on the following rules (Figure 10-9):
From the PJSTSMon# drop-down menu, make a selection based on the following rules (Figure 10-9):
•![]() Off means pointer justification monitoring is disabled (default).
Off means pointer justification monitoring is disabled (default).
•![]() 1 to n are the number of STSs on the port. One STS per port can be enabled from the PJSTSMon# card menu.
1 to n are the number of STSs on the port. One STS per port can be enabled from the PJSTSMon# card menu.
Figure 10-9 Enabling or Disabling Pointer Justification Count Parameters
Step 4 ![]() In the State field, confirm that the port is in service (IS).
In the State field, confirm that the port is in service (IS).
Step 5 ![]() If the port is IS, click Apply. If the port is out of service (OOS, OOS_MT, OOS_AINS), select IS in the State field and click Apply.
If the port is IS, click Apply. If the port is out of service (OOS, OOS_MT, OOS_AINS), select IS in the State field and click Apply.
Step 6 ![]() Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() The count fields for PPJC and NPJC PM parameters appear white and blank unless pointer justification count performance monitoring is enabled.
The count fields for PPJC and NPJC PM parameters appear white and blank unless pointer justification count performance monitoring is enabled.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A122 Enable/Disable Intermediate Path Performance Monitoring

Note ![]() The monitored IPPM parameters are STS CV-P, STS ES-P, STS SES-P, STS UAS-P, and STS FC-P. Far-end path monitoring can be performed on the OC3-4 and EC1 cards. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
The monitored IPPM parameters are STS CV-P, STS ES-P, STS SES-P, STS UAS-P, and STS FC-P. Far-end path monitoring can be performed on the OC3-4 and EC1 cards. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() An OC-48 IR card used in a BLSR does not support IPPM during a protection switch.
An OC-48 IR card used in a BLSR does not support IPPM during a protection switch.
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the OC-N card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the OC-N card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
See Table 10-2 for a list of OC-N LTE cards.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > SONET STS tabs (Figure 10-10).
Click the Provisioning > SONET STS tabs (Figure 10-10).
Figure 10-10 SONET STS Tab for Enabling or Disabling IPPM

Step 3 ![]() Click the check box in the Enable IPPM column and make a selection based on the following rules:
Click the check box in the Enable IPPM column and make a selection based on the following rules:
•![]() Unchecked means IPPM is disabled for that STS (default)
Unchecked means IPPM is disabled for that STS (default)
•![]() Checked means IPPM is enabled for that STS
Checked means IPPM is enabled for that STS
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For IPPM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For IPPM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A507 View OC-N PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the OC-N card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the OC-N card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab (Figure 10-11).
Click the Performance tab (Figure 10-11).
Figure 10-11 Viewing OC-N Card Performance Monitoring Information

Step 3 ![]() In the Port drop-down menu, click the port you want to monitor.
In the Port drop-down menu, click the port you want to monitor.
Step 4 ![]() Click Refresh.
Click Refresh.
Step 5 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current), and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current), and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() To monitor another port on a multiport card, choose another port from the Port drop-down menu and click Refresh.
To monitor another port on a multiport card, choose another port from the Port drop-down menu and click Refresh.
Step 7 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A251 Monitor Multirate Transport Performance
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to view node near-end or far-end performance during selected time intervals on a transponder (TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_2.5G, TXPP_MR_2.5G), or muxponder (MXP_2.5G_10G) card and port to detect possible performance problems. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A500 Enable/Disable OTN G.709 Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable optical transport network (OTN) G.709 monitoring.
Complete the "DLP-A500 Enable/Disable OTN G.709 Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable optical transport network (OTN) G.709 monitoring.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A501 Enable/Disable OTN FEC Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable optical transport network (OTN) forward error correction (FEC) monitoring.
Complete the "DLP-A501 Enable/Disable OTN FEC Performance Monitoring" task as needed to enable or disable optical transport network (OTN) forward error correction (FEC) monitoring.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A317 View Optics PM Parameters" task as needed.
Complete the "DLP-A317 View Optics PM Parameters" task as needed.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A318 View Payload PM Parameters" task as needed.
Complete the "DLP-A318 View Payload PM Parameters" task as needed.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A319 View Optical Transport Network PM Parameters" task as needed.
Complete the "DLP-A319 View Optical Transport Network PM Parameters" task as needed.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A500 Enable/Disable OTN G.709 Performance Monitoring
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs (Figure 10-12).
Click the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs (Figure 10-12).
Figure 10-12 OTN Lines Tab for Enabling/Disabling OTN G.709 Performance Monitoring

Step 3 ![]() Make a G.709 selection based on the following rules:
Make a G.709 selection based on the following rules:
•![]() Unchecked disables G.709 for that port (default)
Unchecked disables G.709 for that port (default)
•![]() Checked enables G.709 for that port
Checked enables G.709 for that port
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A501 Enable/Disable OTN FEC Performance Monitoring
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the card you want to monitor. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs (Figure 10-13).
Click the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs (Figure 10-13).
Figure 10-13 OTN Lines Tab for Enabling/Disabling OTN FEC Performance Monitoring

Step 3 ![]() Make an FEC selection based on the following rules:
Make an FEC selection based on the following rules:
•![]() Unchecked disables FEC for that port (default)
Unchecked disables FEC for that port (default)
•![]() Checked enables FEC for that port
Checked enables FEC for that port
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 5 ![]() Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Click the Performance tab to view PM parameters. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A317 View Optics PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the transponder or muxponder card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the transponder or muxponder card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Optics PM tabs (Figure 10-14).
Click the Performance > Optics PM tabs (Figure 10-14).
Figure 10-14 Viewing Optics Performance Monitoring Information

Step 3 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A318 View Payload PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the transponder or muxponder card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the transponder or muxponder card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Payload PM tabs (Figure 10-15).
Click the Performance > Payload PM tabs (Figure 10-15).
Figure 10-15 Viewing Payload Performance Monitoring Information
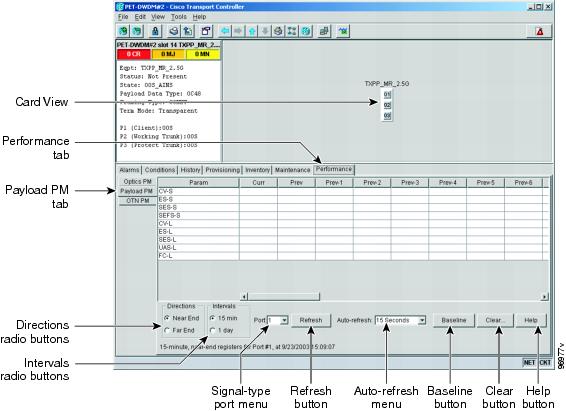
Step 3 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current), and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current), and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.

Note ![]() The PM parameters that appear depend on the data payload and framing type provisioned on the port. Unframed data payloads such as ESCON, DV6000, DSI/D1 video, and HDTV do not provide payload performance monitoring information.
The PM parameters that appear depend on the data payload and framing type provisioned on the port. Unframed data payloads such as ESCON, DV6000, DSI/D1 video, and HDTV do not provide payload performance monitoring information.
Step 4 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A319 View Optical Transport Network PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the transponder or muxponder card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the transponder or muxponder card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > OTN PM > G.709 tabs (Figure 10-16).
Click the Performance > OTN PM > G.709 tabs (Figure 10-16).
Figure 10-16 Viewing OTN G.709 Performance Monitoring Information

Step 3 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 4 ![]() Click the FEC PM tab (Figure 10-17).
Click the FEC PM tab (Figure 10-17).
Figure 10-17 Viewing OTN FEC Performance Monitoring Information

Step 5 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Curr (current) and Prev-n (previous) columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A252 Monitor DWDM Performance
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to view transmit and receive performance during selected time intervals on a DWDM card and port to detect possible performance problems. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A502 View Optical Service Channel PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A502 View Optical Service Channel PM Parameters" task.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A503 View Optical Amplifier PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A503 View Optical Amplifier PM Parameters" task.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A504 View Optical Multiplexer and Demultiplexer PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A504 View Optical Multiplexer and Demultiplexer PM Parameters" task.
Step 5 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A505 View Channel Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A505 View Channel Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters" task.
Step 6 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A506 View Band Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A506 View Band Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters" task.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the "A253 Change the PM Display" procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A502 View Optical Service Channel PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the OSCM or OSC-CSM card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the OSCM or OSC-CSM card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > OC3 Line tabs (Figure 10-18).
Click the Performance > OC3 Line tabs (Figure 10-18).
Figure 10-18 OC3 Line Tab in the Optical Service Channel Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. OC3 line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. OC3 line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Optical Line tab.
Click the Optical Line tab.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A503 View Optical Amplifier PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the optical amplifier card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the optical amplifier card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Optical Line tabs (Figure 10-19).
Click the Performance > Optical Line tabs (Figure 10-19).
Figure 10-19 Optical Line Tab in the Optical Amplifier Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Opt. Ampli. Line tab.
Click the Opt. Ampli. Line tab.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical amplifier line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical amplifier line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A504 View Optical Multiplexer and Demultiplexer PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the 32MUX or 32DMX card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the 32MUX or 32DMX card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Optical Chn tabs (Figure 10-20).
Click the Performance > Optical Chn tabs (Figure 10-20).
Figure 10-20 Optical Channel Tab in the Mux/Demux Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical channel performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical channel performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Optical Line tab.
Click the Optical Line tab.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A505 View Channel Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the optical add/drop channel multiplexer card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the optical add/drop channel multiplexer card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Optical Line tabs (Figure 10-21).
Click the Performance > Optical Line tabs (Figure 10-21).
Figure 10-21 Optical Line Tab in the Channel Filter OADM Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical line performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Optical Chn tab.
Click the Optical Chn tab.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical channel performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical channel performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A506 View Band Filter Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the optical add/drop band multiplexer card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the optical add/drop band multiplexer card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Optical Chn tabs (Figure 10-22).
Click the Performance > Optical Chn tabs (Figure 10-22).
Figure 10-22 Optical Channel Tab in the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical channel performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical channel performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Optical Band tab.
Click the Optical Band tab.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. Optical band performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Click Refresh. Optical band performance monitoring statistics for the selected port appear.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A285 Monitor FC_MR-4 Performance
Purpose |
This procedure enables you to view node transmit and receive performance during selected time intervals on a FC_MR-4 card and port to detect possible performance problems. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
Before you monitor performance, be sure you have created the appropriate circuits and provisioned the card according to your specifications. For more information, see "Create Circuits and VT Tunnels" and "Change Card Settings." |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite |
Security Level |
Retrieve or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node that you want to monitor. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A350 View FC_MR-4 Statistics PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A350 View FC_MR-4 Statistics PM Parameters" task.
Step 3 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A351 View FC_MR-4 Utilization PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A351 View FC_MR-4 Utilization PM Parameters" task.
Step 4 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A352 View FC_MR-4 History PM Parameters" task.
Complete the "DLP-A352 View FC_MR-4 History PM Parameters" task.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A350 View FC_MR-4 Statistics PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Statistics tabs.
Click the Performance > Statistics tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the PM parameter names appear in the Param column. The current PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names appear in the Param column. The current PM parameter values appear in the Port # columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A351 View FC_MR-4 Utilization PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > Utilization tabs (Figure 10-23).
Click the Performance > Utilization tabs (Figure 10-23).
Figure 10-23 FC_MR-4 Utilization on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring utilization values for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring utilization values for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the Port # column to find the port you want to monitor.
View the Port # column to find the port you want to monitor.
Step 5 ![]() The transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) bandwidth utilization values for the previous time intervals appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
The transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) bandwidth utilization values for the previous time intervals appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A352 View FC_MR-4 History PM Parameters
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance > History tabs (Figure 10-24).
Click the Performance > History tabs (Figure 10-24).
Figure 10-24 FC_MR-4 History on the Card View Performance Window

Step 3 ![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each port on the card appear.
Step 4 ![]() View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Prev-n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual.
Step 5 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A353 Refresh FC_MR-4 PM Counts at a Different Time Interval
Step 1 ![]() In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to view PM counts. The card view appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Performance tab.
Click the Performance tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Utilization or the History tab.
Click the Utilization or the History tab.
Step 4 ![]() From the Interval drop-down menu, choose one of four options:
From the Interval drop-down menu, choose one of four options:
•![]() 1 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-minute time intervals.
1 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-minute time intervals.
•![]() 15 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in 15-minute time intervals.
15 min: This option appears the specified PM counts in 15-minute time intervals.
•![]() 1 hour: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-hour time intervals.
1 hour: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-hour time intervals.
•![]() 1 day: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-day (24 hours) time intervals.
1 day: This option appears the specified PM counts in one-day (24 hours) time intervals.
Step 5 ![]() Click Refresh. The PM counts refresh with values based on the selected time interval.
Click Refresh. The PM counts refresh with values based on the selected time interval.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-A289 Create or Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Thresholds
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
•![]() A357 Create FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds
A357 Create FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds
•![]() A358 Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds
A358 Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-A357 Create FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds
Step 1 ![]() Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node where you want to set up RMON. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the "DLP-A60 Log into CTC" task at the node where you want to set up RMON. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2 ![]() Double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to create the RMON alarm thresholds.
Double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to create the RMON alarm thresholds.
Step 3 ![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
Step 4 ![]() Click Create. The Create FCMR Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create FCMR Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 5 ![]() From the Slot menu, choose the appropriate FC_MR-4 card.
From the Slot menu, choose the appropriate FC_MR-4 card.
Step 6 ![]() From the Port drop-down menu, choose the applicable port on the FC_MR-4 card you selected.
From the Port drop-down menu, choose the applicable port on the FC_MR-4 card you selected.
Step 7 ![]() From the Variable drop-down menu, choose the variable. See Table 10-3 for a list of the FC_MR-4 threshold variables available in this field.
From the Variable drop-down menu, choose the variable. See Table 10-3 for a list of the FC_MR-4 threshold variables available in this field.
Step 8 ![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down menu, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down menu, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 9 ![]() From the Sample Type drop-down menu, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down menu, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 10 ![]() Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 11 ![]() Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.

Note ![]() For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a falling threshold of 400 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a falling threshold of 400 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 12 ![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 minutes subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 minutes, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15 minute period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).
Step 13 ![]() Click OK to complete the procedure.
Click OK to complete the procedure.
Step 14 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-A358 Delete FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds
Purpose |
This task deletes remote monitoring (RMON) threshold crossing alarms for FC_MR-4 ports. |
Tools/Equipment |
None |
Prerequisite Procedures |
A357 Create FC_MR-4 RMON Alarm Thresholds |
Required/As Needed |
As needed |
Onsite/Remote |
Onsite or remote |
Security Level |
Provisioning or higher |
Step 1 ![]() Double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to delete the RMON alarm thresholds.
Double-click the FC_MR-4 card where you want to delete the RMON alarm thresholds.
Step 2 ![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
Step 3 ![]() Click the RMON alarm threshold you want to delete.
Click the RMON alarm threshold you want to delete.
Step 4 ![]() Click Delete. The Delete Threshold dialog box opens.
Click Delete. The Delete Threshold dialog box opens.
Step 5 ![]() Click Yes to delete that threshold.
Click Yes to delete that threshold.
Step 6 ![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
 Feedback
Feedback