- About this Manual
- Chapter 1, Shelf and Backplane Hardware
- Chapter 2, Card Reference
- Chapter 3, Card Protection
- Chapter 4, Cisco Transport Controller Operation
- Chapter 5, Security
- Chapter 6, Timing
- Chapter 7, Circuits and Tunnels
- Chapter 8, SDH Topologies and Upgrades
- Chapter 9, Management Network Connectivity
- Chapter 10, Ethernet Operation
- Chapter 11, Alarm Monitoring and Management
- Chapter 12, Performance Monitoring
- Chapter 13, SNMP
- Appendix A, Hardware Specifications
- Appendix B, Administrative and Service States
- Appendix C, Network Element Defaults
- 2.1 Card Overview
- 2.2 TSC Card
- 2.3 SSXC Card
- 2.4 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card
- 2.4.1 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Slots and Connectors
- 2.4.2 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
- 2.4.3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card-Level Indicators
- 2.4.4 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Network-Level Indicators
- 2.4.5 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card OGI Connector Pinout
- 2.5 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card
- 2.5.1 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Slots and Connectors
- 2.5.2 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
- 2.5.3 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card-Level Indicators
- 2.5.4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Network-Level Indicators
- 2.5.5 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card OGI Connector Pinout
- 2.6 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card
- 2.6.1 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Slots and Connectors
- 2.6.2 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
- 2.6.3 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card-Level Indicators
- 2.6.4 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Network-Level Indicators
- 2.6.5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card OGI Connector Pinout
- 2.7 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card
- 2.7.1 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Slots and Connectors
- 2.7.2 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
- 2.7.3 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card-Level Indicators
- 2.7.4 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card Network-Level Indicators
- 2.7.5 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card OGI Connector Pinout
- 2.8 ASAP Card
- 2.8.1 ASAP Connectors
- 2.8.2 ASAP Covers and Plugs
- 2.8.3 ASAP Card Faceplate and Block Diagram with 4PIOs Installed
- 2.8.4 4PIO Module Faceplate
- 2.8.5 1PIO Module Faceplate
- 2.8.6 ASAP Card-Level Indicators
- 2.8.7 ASAP Card Port-Level Indicators
- 2.8.8 ASAP Card Port Numbering (4PIO Installed)
- 2.8.9 ASAP Card Port Numbering (1PIO Installed)
- 2.9 Filler Card
- 2.10 SFP/XFP Modules
Card Reference
This chapter describes Cisco ONS 15600 SDH card features and functions.
Chapter topics include:
•![]() OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card
OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card
•![]() OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card
OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card
•![]() OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card
OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card
•![]() OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card
OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card
2.1 Card Overview

2.1.1 Card Summary
Table 2-1 lists the ONS 15600 SDH cards and provides a short description and cross-reference to each.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
The TSC card performs all system-timing functions for each ONS 15600 SDH. |
See the "TSC Card" section. |
|
|
The SSXC card is the central cross-connect element for ONS 15600 SDH switching. |
See the "SSXC Card" section. |
|
|
The OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 card provides 16 long-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-16 ports per card. |
|
|
|
The OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 card provides 16 short-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-16 ports per card. |
|
|
|
The OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 port 1550 card provides four long-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-64 ports per card. |
|
|
|
The OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 card provides four short-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-64 ports per card. |
|
|
|
The Any-Service Any-Port (ASAP) card provides up to 16 Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-1, STM-4, STM-16, STM-64, or Gigabit Ethernet ports per card, with certain limitations on line rate combinations. |
See the "ASAP Card" section. |
|
|
The filler card is used to fill unused optical (STM-N) traffic card slots in the ONS 15600 SDH shelf. |
See the "Filler Card" section. |
2.1.2 Card Compatibility
Table 2-2 lists Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) software release compatibility for each card. In Table 2-2, "Yes" means the cards are compatible with the listed software versions. Table cells with dashes mean cards are not compatible with the listed software versions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
|
— |
— |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
— |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
— |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
Yes |
|
|
— |
— |
Yes1 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
1 The ASAP card is compatible with the R5.xx maintenance release |
.
2.2 TSC Card

Note ![]() For hardware specifications, see the "A.2.1 TSC Card Specifications" section on page A-5.
For hardware specifications, see the "A.2.1 TSC Card Specifications" section on page A-5.

The TSC card performs all system-timing functions for each ONS 15600 SDH. The TSC card monitors the recovered clocks from each traffic card and two building integrated timing supply (BITS) interfaces for frequency accuracy. The TSC card is provisionable, allowing timing from any optical interface source, a BITS input source, or the internal Stratum 3E as the system-timing reference. You can provision any of the clock inputs as primary or secondary timing sources. If you specify external timing references, your options are BITS1, BITS2, and the internal Stratum 3E sources. If you select line timing, you can specify up to two line ports from which to derive timing, as well as the internal stratum 3E sources. The TSC card also supports BITS OUT. A slow-reference tracking loop allows the TSC to synchronize with the recovered clock and enables holdover if the reference is lost.
The TSC card also provides shelf control related functions. The TSC card has a 100-Mbps Ethernet link to each card on the shelf and monitors the presence of these cards. The TSC provides bulk memory for nonvolatile storage of system software and data and provides EIA-TIA 232 and Ethernet customer interfaces. The TSC card processes and routes RS-DCC and MS-DCC traffic as well as routing the K1, K2, and K3 overhead bytes between traffic (line) cards and SSXC cards. The TSC card controls and monitors the shelf fans and all of the alarm interfaces.
2.2.1 TSC Slots and Connectors
Install TSC cards in Slots 5 and 10 for redundancy. If the active TSC card fails, timing reference and control function switches to the protect TSC card.

Note ![]() All TSC card protection switches conform to the Telcordia protection switching standard of equal to or less than 50 ms.
All TSC card protection switches conform to the Telcordia protection switching standard of equal to or less than 50 ms.
The TSC card has an RJ-45 10/100 Base-T LAN port on the faceplate. Two additional RJ-45 10/100 Base-T LAN ports and two EIA/TIA-232 DB-9 type craft user interfaces are available on the Customer Access Panel (CAP/CAP2) on the backplane.
2.2.2 TSC Faceplate and Block Diagram
Figure 2-1 shows the TSC card faceplate and a block diagram of the card.
Figure 2-1 TSC Card Faceplate and Block Diagram

2.2.3 TSC Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-3 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the TSC card faceplate.
2.2.4 TSC Network-Level Indicators
Table 2-4 describes the functions of the network-level LEDs on the TSC card faceplate.
2.2.5 TSC Push-Button Switches
Table 2-5 describes the functions of the push-button switches on the TSC card faceplate.
2.3 SSXC Card

Note ![]() For hardware specifications, see the "A.2.2 SSXC Specifications" section on page A-6.
For hardware specifications, see the "A.2.2 SSXC Specifications" section on page A-6.
The SSXC is the central element for ONS 15600 SDH switching. The SSXC card establishes connections and performs time division switching (TDS) at VC3 and VC4-Nc levels between ONS 15600 SDH traffic cards.
The SSXC card works with the TSC card to maintain connections and set up cross-connects within the ONS 15600 SDH. You establish cross-connect and provisioning information using CTC or TL1. The TSC card stores the proper internal cross-connect information and relays the setup information to the SSXC card.
2.3.1 SSXC Switch Matrix
The switch matrix on each SSXC card consists of 6,144 bidirectional VC3 ports, with a maximum of 6,144 bidirectional VC3 cross-connections. When creating bidirectional VC3 cross-connects, each bidirectional cross-connect uses two VC3 ports, with the result that the SSXC card supports 3,072 bidirectional VC3 cross-connects. Any VC3 on any port can be connected to any other port, meaning that the STS cross-connections are nonblocking. Nonblocking connections allow network operators to connect any VC3, VC4, VC4-4c, VC4-8c, VC4-16c, or VC4-64c payload that is received on an STM-16 or STM-64 interface (or additionally any VC4-2c and/or VC4-3c payload that is received on an ASAP interface) to any other interface capable of supporting the bandwidth.
The SSXC card has 128 input ports and 128 output ports capable of VC4-16c. A VC3 on any of the input ports can be mapped to an VC3 output port, thus providing full VC3 time slot assignments (TSAs).
2.3.2 SSXC Slots and Connectors
Install an SSXC card in Slot 6 and a second SSXC card in Slot 8 for redundancy. (Slots 7 and 9 are also occupied by the SSXC faceplates.) The SSXC card has no external interfaces. All SSXC card interfaces are provided on the ONS 15600 SDH backplane.
2.3.3 SSXC Faceplate and Block Diagram
Figure 2-2 shows the SSXC card faceplate and a block diagram of the card.
Figure 2-2 SSXC Card Faceplate and Block Diagram

2.3.4 SSXC Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-6 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the SSXC card faceplate.
2.4 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card

Note ![]() For card specifications, see the "A.2.3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Specifications" section on page A-6.
For card specifications, see the "A.2.3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Specifications" section on page A-6.
The OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 card provides 16 long-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-16 ports per card. The ports operate at 2488.320 Mbps over a single-mode fiber span. The OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 card has four physical connector adapters with eight fibers per connector adapter. The card supports VC3 payloads and concatenated payloads at VC4, VC4-4c, VC4-8c, or VC4-16c signal levels.
2.4.1 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Slots and Connectors
You can install OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 cards in Slots 1 through 4 and 11 through 14. The card provides four bidirectional OGI-type connector adapters on the faceplate (angled downward), each carrying eight fiber strands (four transmit and four receive).
2.4.2 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
Figure 2-3 shows the OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 faceplate and a block diagram of the card.
Figure 2-3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram

2.4.3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-7 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 card.
2.4.4 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Network-Level Indicators
Table 2-8 describes the functions of the network-level LEDs on the OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 card.
2.4.5 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card OGI Connector Pinout
Table 2-9 lists the OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 card OGI connector pinouts.
2.5 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card

Note ![]() For card specifications, see the "A.2.4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Specifications" section on page A-8.
For card specifications, see the "A.2.4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Specifications" section on page A-8.
The OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 card provides 16 short-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-16 ports per card. The ports operate at 2488.320 Mbps over a single-mode fiber span. The OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 card has four physical connector adapters with eight fibers per connector adapter. The card supports VC3 payloads and concatenated payloads at VC4, VC4-4c, VC4-8c, or VC4-16c signal levels.
2.5.1 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Slots and Connectors
You can install OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 cards in Slots 1 through 4 and 11 through 14. The card provides four bidirectional OGI-type connector adapters on the faceplate (angled downward), each carrying eight fiber strands (four transmit and four receive).
2.5.2 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
Figure 2-4 shows the OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 faceplate and block diagram.
Figure 2-4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram

2.5.3 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-10 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 card.
2.5.4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Network-Level Indicators
Table 2-11 describes the functions of the network-level LEDs on the OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 card.
2.5.5 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card OGI Connector Pinout
Table 2-12 lists the OC48/STM16 SR/SH card OGI connector pinouts.
2.6 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card

Note ![]() For card specifications, see the "A.2.5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Specifications" section on page A-9.
For card specifications, see the "A.2.5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Specifications" section on page A-9.
The OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 port 1550 card provides four long-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-64 ports per card. The ports operate at 9953.28 Mbps over a single-mode fiber. The OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 port 1550 card has four physical connector adapters with two fibers per connector adapter. The card supports VC3 payloads and concatenated payloads at VC4, VC4-4c, VC4-8c, VC4-16c, or VC4-64c signal levels.
2.6.1 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Slots and Connectors
You can install OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 port 1550 cards in Slots 1 through 4 and 11 through 14. The card provides four bidirectional OGI-type connector adapters on the faceplate (angled downward), carrying two fiber strands (one transmit and one receive). Only one transmit and receive pair is used per connector adapter. On a breakout cable, use port three, fiber 4 (transmit) and fiber 3 (receive).
2.6.2 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
Figure 2-5 shows the OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 faceplate and a block diagram of the card.
Figure 2-5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram

2.6.3 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-13 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 card.
2.6.4 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Network-Level Indicators
Table 2-14 describes the functions of the network-level LEDs on the OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 card.
2.6.5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card OGI Connector Pinout
Table 2-15 lists the OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 card OGI connector pinouts.
2.7 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card

Note ![]() For card specifications, see the "A.2.6 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Specifications" section on page A-10.
For card specifications, see the "A.2.6 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Specifications" section on page A-10.
The OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 card provides four short-range, Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-64 ports per card. The ports operate at 9953.28 Mbps over a single-mode fiber. The OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 port 1310 card has four physical connector adapters with two fibers per connector adapter. The card supports VC3 payloads and concatenated payloads at VC4, VC4-4c, VC4-8c, VC4-16c, or VC4-64c signal levels.
2.7.1 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Slots and Connectors
You can install OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 cards in Slots 1 through 4 and 11 through 14. The card provides four bidirectional OGI-type connector adapters on the faceplate (angled downward), carrying two fiber strands (one transmit and one receive). Only one transmit and receive pair is used per connector adapter. On a breakout cable, use port three, fiber 4 (transmit) and fiber 3 (receive).
2.7.2 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
Figure 2-6 shows the OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 faceplate and block diagram.
Figure 2-6 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram

2.7.3 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-16 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 card.
2.7.4 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card Network-Level Indicators
Table 2-17 describes the functions of the network-level LEDs on the OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 card.
2.7.5 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card OGI Connector Pinout
Table 2-18 lists the OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 card OGI connector pinouts.
2.8 ASAP Card

Note ![]() For card specifications, see the "A.2.7 ASAP Specifications" section on page A-11.
For card specifications, see the "A.2.7 ASAP Specifications" section on page A-11.
The ASAP card provides up to 16 Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-1, STM-4, STM-16, or Gigabit Ethernet ports, or up to 4 Telcordia GR-253-CORE compliant, SDH STM-64 ports, in any combination of line rates. The ASAP card, when used with the 4-Port I/O (4PIO) module, has up to 16 physical connector adapters (known as Small Form-factor Pluggables [SFPs]). The SFP ports operate at up to 2488.320 Mbps over a single-mode fiber. The ASAP card, when used with the 1-Port I/O (1PIO) module, has up to 4 physical connector adapters (known as 10Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggables [XFPs]). The XFP ports operate at up to 9953.280 Mbps over a single-mode fiber. Both XFP and SFP physical connector adapters have two fibers per connector adapter (transmit [Tx] and receive [Rx]). The ASAP card supports VC3 payloads and concatenated payloads at VC4, VC4-2c, VC4-3c, VC4-4c, VC4-8c, VC4-16c and VC4-64c signal levels. The ASAP card is interoperable with ONS 15454 SDH E-Series, G-Series, and ML-Series Ethernet cards.
There are three major components to the ASAP card:
•![]() Carrier card, which can be installed in Slots 1 through 4 and 11 through 14
Carrier card, which can be installed in Slots 1 through 4 and 11 through 14
•![]() 4PIO and 1PIO modules, also called Pluggable Input/Output Module (PIMs), which plug into the ASAP carrier card
4PIO and 1PIO modules, also called Pluggable Input/Output Module (PIMs), which plug into the ASAP carrier card
•![]() SFPs/XFPs, called Pluggable Port Modules (PPMs) in CTC, which plug into the 4PIO or 1PIO (PIM) module and provide the fiber interface using a female LC connector
SFPs/XFPs, called Pluggable Port Modules (PPMs) in CTC, which plug into the 4PIO or 1PIO (PIM) module and provide the fiber interface using a female LC connector
2.8.1 ASAP Connectors
An ASAP carrier card supports any combination of four 4PIOs or 1PIOs. Each 4PIO supports up to four SFPs, while each 1PIO supports one SFP/XFP. The maximum configuration for an ASAP card is 16 SFP or 4 XFP ports, or a mix of both. The ports can each be provisioned as either STM-1, STM-4, STM-16, STM64 (1PIO only), or Gigabit Ethernet.
In addition, the ports can be provisioned with STM-16 dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) SFPs. 32 SFPs, each with separate product IDs (PIDs), allow operation on 32 channels, separated by 100 GHz on the ITU grid. The modules offer operation in the red band from 1546.12 to 1560.61 nm and in the blue band from 1530.33 to 1544.53 nm. These SFPs can be used in Metro, Regional, or Long Haul applications. Eight ASAP cards can be installed in a shelf, and up to four ITU-T SFPs can be plugged into each of the four 4PIO/PIMs (or one XFP in the 1PIO), providing a maximum of 128 ITU-T SFPs in a single shelf.
For detailed information about SFPs/XFPs, see the "SFP/XFP Modules" section. To determine the line rates supported by each SFP/XFP, see the "A.3 SFP/XFP Specifications" section on page A-12.
2.8.2 ASAP Covers and Plugs
The covers and plugs that are shipped with the ASAP carrier card, 4PIOs, 1PIOs, and SFPs/XFPs must be used in configurations where any of the these slots are unoccupied.
2.8.3 ASAP Card Faceplate and Block Diagram with 4PIOs Installed
Figure 2-7 shows the ASAP card faceplate, with four 4PIOs installed, and block diagram.
Figure 2-7 ASAP Card Faceplate and Block Diagram (4PIOs Installed)

2.8.4 4PIO Module Faceplate
Figure 2-8 shows the 4PIO module faceplate.
Figure 2-8 4PIO Module Faceplate

2.8.5 1PIO Module Faceplate
Figure 2-9 shows the 1PIO module faceplate.
Figure 2-9 1PIO Module Faceplate

2.8.6 ASAP Card-Level Indicators
Table 2-19 describes the functions of the card-level LEDs on the ASAP carrier module.
2.8.7 ASAP Card Port-Level Indicators
Table 2-20 describes the functions of the port-level LEDs on the 4PIO and 1PIO modules, depending on whether the port is configured for SDH or Ethernet. (On the 4PIO modules, the port-level LEDs are numbered 1 through 4.)
2.8.8 ASAP Card Port Numbering (4PIO Installed)
Figure 2-10 shows the installed 4PIO modules and corresponding port numbers for each SFP slot.
Figure 2-10 ASAP 4PIO Port Numbering

2.8.9 ASAP Card Port Numbering (1PIO Installed)
Figure 2-11 shows the installed 1PIO modules and corresponding port numbers for each XFP slot.
Figure 2-11 ASAP 1PIO Port Numbering

2.9 Filler Card

Note ![]() For card specifications, see the "A.2.8 Filler Card Specifications" section on page A-12.
For card specifications, see the "A.2.8 Filler Card Specifications" section on page A-12.
The Filler card is used to fill unused optical (STM-N) traffic card slots in the ONS 15600 SDH shelf. In Software Release 1.1 and later, the Filler card has a card presence indicator (CPI) that allows the shelf to report the presence of the filler card to CTC. The Filler card uses dummy backplane connectors and a standard faceplate to secure the card in the empty shelf slot.
Figure 2-12 shows the Filler card body and faceplate.
Figure 2-12 ONS 15600 SDH Filler Card

2.10 SFP/XFP Modules
This section describes the SFPs that provide the fiber interface to the ONS 15600 SDH ASAP card when used with the 4PIO modules. A line rate (STM-1, STM-4, STM-16, or Gigabit Ethernet) must be assigned to each SFP in the CTC software interface or using TL1. In CTC, SFPs are known as pluggable port modules (PPMs). To provision PPMs, refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 SDH Procedure Guide.

Note ![]() For information about XFPs, which allow you to provision an STM-64 line rate when used with the 1PIO module, see the "XFP Description" section.
For information about XFPs, which allow you to provision an STM-64 line rate when used with the 1PIO module, see the "XFP Description" section.
Table 2-21 lists the SFPs (PPMs) that are compatible with the ASAP card.

To determine the line rates supported by each SFP/XFP, see the "A.3 SFP/XFP Specifications" section on page A-12.
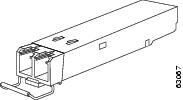
SFPs are integrated fiber optic transceivers that provide high-speed serial links from a port or slot to the network. Various latching mechanisms can be used on the SFP/XFP modules. There is no correlation between the type of latch and the model type (such as SX or LX/LH) or technology type (such as Gigabit Ethernet). See the label on the SFP/XFP for technology type and model. One type of latch available is a Mylar tab as shown in Figure 2-13, a second type of latch available is an actuator/button (Figure 2-14), and a third type of latch is a bail clasp (Figure 2-15).
SFP dimensions are:
•![]() Height 0.03 in. (8.5 mm)
Height 0.03 in. (8.5 mm)
•![]() Width 0.53 in. (13.4 mm)
Width 0.53 in. (13.4 mm)
•![]() Depth 2.22 in. (56.5 mm)
Depth 2.22 in. (56.5 mm)
SFP temperature ranges for are:
•![]() COM—Commercial operating temperature range: 23 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 70 degrees Celsius)
COM—Commercial operating temperature range: 23 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 70 degrees Celsius)
•![]() EXT—Extended operating temperature range: 23 to185 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 85 degrees Celsius)
EXT—Extended operating temperature range: 23 to185 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 85 degrees Celsius)
•![]() IND—Industrial operating temperature range: -40 to 185 degrees Fahrenheit (-40 to 85 degrees Celsius)
IND—Industrial operating temperature range: -40 to 185 degrees Fahrenheit (-40 to 85 degrees Celsius)
Figure 2-13 Mylar Tab SFP
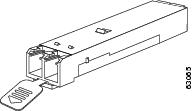
Figure 2-14 Actuator/Button SFP
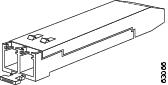
Figure 2-15 Bail Clasp SFP
2.10.1 XFP Description
The 10-Gbps 1310-nm and 1550-nm XFP transceivers are integrated fiber optic transceivers that provide high-speed serial links at the following signaling rates: 9.95 Gbps, 10.31 Gbps, and 10.52 Gbps. The XFP integrates both the receiver and transmit path. The transmit side recovers and retimes the 10-Gbps serial data and passes it to a laser driver. The laser driver biases and modulates single mode (SMF) optical interfaces at 1310-nm or 1550-nm. The modules support all data encodings through an LC connector. The receive side recovers, retimes the 10-Gbps optical data stream from a positive-intrinsic-negative (PIN) photodetector, transimpedance amplifier and passes it to an output driver.

|
|
(Cisco Product ID) |
|
|---|---|---|
ASAP 1PIO only |
ONS-XC-10G-S1 |
10-2112-01 |
The XFP module uses the bail clasp latching mechanism, shown unlatched in Figure 2-16 and latched in Figure 2-17. See the label on the XFP for technology type and model.
Figure 2-16 Bail Clasp XFP (Unlatched)

Figure 2-17 Bail Clasp XFP (Latched)

XFP dimensions are:
•![]() Height 0.33 in. (8.5 mm)
Height 0.33 in. (8.5 mm)
•![]() Width 0.72 in. (18.3 mm)
Width 0.72 in. (18.3 mm)
•![]() Depth 3.1 in. (78 mm)
Depth 3.1 in. (78 mm)
XFP temperature ranges are:
•![]() COM—Commercial operating temperature range: 23 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 70 degrees Celsius)
COM—Commercial operating temperature range: 23 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 70 degrees Celsius)
•![]() EXT—Extended operating temperature range: 23 to185 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 85 degrees Celsius)
EXT—Extended operating temperature range: 23 to185 degrees Fahrenheit (-5 to 85 degrees Celsius)
•![]() IND—Industrial operating temperature range: -40 to 185 degrees Fahrenheit (-40 to 85 degrees Celsius)
IND—Industrial operating temperature range: -40 to 185 degrees Fahrenheit (-40 to 85 degrees Celsius)
2.10.2 PPM Provisioning
SFPs and XFPs are known as pluggable-port modules (PPMs) in the CTC. Multirate PPMs for the ASAP card can be provisioned for different line rates in CTC. For more information about provisioning PPMs, refer to the Cisco ONS 15600 SDH Procedure Guide.
 Feedback
Feedback