Information About ICMP for IPv6 Redirect
ICMP for IPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) in IPv6 functions the same as ICMP in IPv4. ICMP generates error messages, such as ICMP destination unreachable messages, and informational messages, such as ICMP echo request and reply messages. Additionally, ICMP packets in IPv6 are used in the IPv6 neighbor discovery process, path MTU discovery, and the Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) protocol for IPv6. MLD is used by IPv6 devices to discover multicast listeners (nodes that want to receive multicast packets destined for specific multicast addresses) on directly attached links. MLD is based on version 2 of the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) for IPv4.
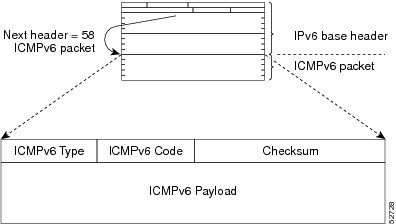
A value of 58 in the Next Header field of the basic IPv6 packet header identifies an IPv6 ICMP packet. ICMP packets in IPv6 are like a transport-layer packet in the sense that the ICMP packet follows all the extension headers and is the last piece of information in the IPv6 packet. Within IPv6 ICMP packets, the ICMPv6 Type and ICMPv6 Code fields identify IPv6 ICMP packet specifics, such as the ICMP message type. The value in the Checksum field is derived (computed by the sender and checked by the receiver) from the fields in the IPv6 ICMP packet and the IPv6 pseudoheader. The ICMPv6 Data field contains error or diagnostic information relevant to IP packet processing. The figure below shows the IPv6 ICMP packet header format.
IPv6 Neighbor Redirect Message
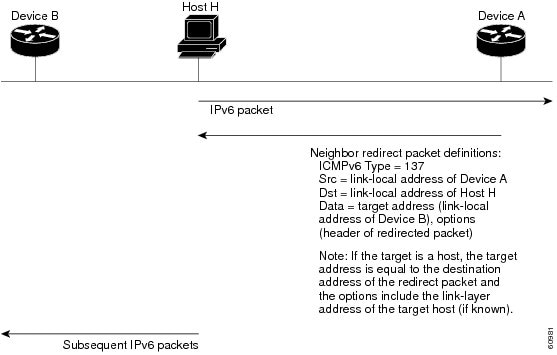
A value of 137 in the type field of the ICMP packet header identifies an IPv6 neighbor redirect message. Devices send neighbor redirect messages to inform hosts of better first-hop nodes on the path to a destination (see the figure below).
 Note |
A device must be able to determine the link-local address for each of its neighboring devices in order to ensure that the target address (the final destination) in a redirect message identifies the neighbor device by its link-local address. For static routing, the address of the next-hop device should be specified using the link-local address of the device; for dynamic routing, all IPv6 routing protocols must exchange the link-local addresses of neighboring devices. |
After forwarding a packet, a device should send a redirect message to the source of the packet under the following circumstances:
-
The destination address of the packet is not a multicast address.
-
The packet was not addressed to the device.
-
The packet is about to be sent out the interface on which it was received.
-
The device determines that a better first-hop node for the packet resides on the same link as the source of the packet.
-
The source address of the packet is a global IPv6 address of a neighbor on the same link, or a link-local address.
Use the ipv6 icmp error-interval command to limit the rate at which the device generates all IPv6 ICMP error messages, including neighbor redirect messages, which ultimately reduces link-layer congestion.
 Note |
A device must not update its routing tables after receiving a neighbor redirect message, and hosts must not originate neighbor redirect messages. |
 Feedback
Feedback