Role and Benefit of the VPN Distinguisher Attribute
Route-target (RT) extended community attributes identify the VPN membership of routes. The RT attributes are placed onto a route at the exporting (egress) provider edge router (PE) and are transported across the iBGP cloud and across autonomous systems. Any Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instances at the remote PE that want to import such routes must have the corresponding RTs set as import RTs for that VRF.
The figure below illustrates two autonomous systems, each containing customer edge routers (CEs) that belong to different VPNs. Each PE tracks which route distinguisher (RD) corresponds to which VPN, thus controlling the traffic that belongs to each VPN.
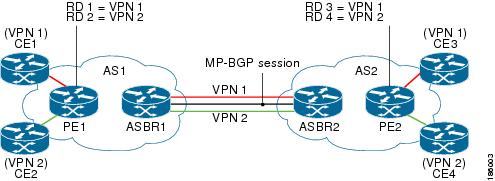
In an Inter-AS Option B scenario like the one in the figure above, these routes are carried across an AS boundary from Autonomous System Border Router 1 (ASBR1) to ASBR2 over an MP-eBGP session, with the routes’ respective RTs as extended community attributes being received by ASBR2.
ASBR2 must maintain complex RT mapping schemes to translate RTs originated by AS1 to RTs recognized by AS2, so that the RTs can be imported by their respective VPN membership CE connections on PE2 for CE3 and CE4.
Some network administrators prefer to hide the RTs they source in AS1 from devices in AS2. In order to do that, the administrator must differentiate routes belonging to each VPN with a certain attribute so that the RTs can be removed on the outbound side of ASBR1 before sending routes to ASBR2, and ASBR2 can then map that attribute to recognizable RTs in AS2. The VPN Distinguisher (VD) extended community attribute serves that purpose.
The benefit of the BGP—VPN Distinguisher Attribute feature is that source RTs can be kept private from devices in destination autonomous systems.
 Feedback
Feedback