Overview of Enterprise Firewall with Application Awareness
The Enterprise Firewall with Application Awareness uses a flexible and easily understood zone-based model for traffic inspection, compared to the older interface-based model.
A firewall policy is a type of localized security policy that allows stateful inspection of TCP, UDP, and ICMP data traffic flows. Traffic flows that originate in a given zone are allowed to proceed to another zone based on the policy between the two zones. A zone is a grouping of one or more VPNs. Grouping VPNs into zones allows you to establish security boundaries in your overlay network so that you can control all data traffic that passes between zones.
Zone configuration consists of the following components:
-
Source zone—A grouping of VPNs where the data traffic flows originate. A VPN can be part of only one zone.
-
Destination zone—A grouping of VPNs where the data traffic flows terminate. A VPN can be part of only one zone.
-
Firewall policy—A security policy, similar to a localized security policy, that defines the conditions that the data traffic flow from the source zone must match to allow the flow to continue to the destination zone. Firewall policies can match IP prefixes, IP ports, the protocols TCP, UDP, and ICMP, and applications. Matching flows for prefixes, ports, and protocols can be accepted or dropped, and the packet headers can be logged. Nonmatching flows are dropped by default. Matching applications are denied.
-
Zone pair—A container that associates a source zone with a destination zone and that applies a firewall policy to the traffic that flows between the two zones.
Matching flows that are accepted can be processed in two different ways:
-
Inspect—The packet's header can be inspected to determine its source address and port. When a session is inspected, you do not need to create a service-policy that matches the return traffic.
-
Pass—Allow the packet to pass to the destination zone without inspecting the packet's header at all. When a flow is passed, no sessions are created. For such a flow, you must create a service-policy that will match and pass the return traffic.
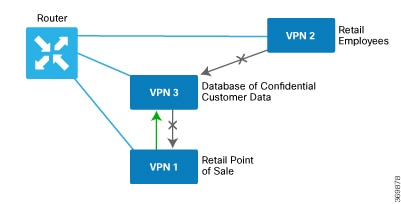
The following figure shows a simple scenario in which three VPNs are configured on a router. One of the VPNs, VPN 3, has shared resources that you want to restrict access to. These resources could be printers or confidential customer data. For the remaining two VPNs in this scenario, only users in one of them, VPN 1, are allowed to access the resources in VPN 3, while users in VPN 2 are denied access to these resources. In this scenario, we want data traffic to flow from VPN 1 to VPN 3, but we do not want traffic to flow in the other direction, from VPN 3 to VPN 1.
 Note |
From Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Release 16.12.2r and onwards, vManage does not show ZBFW statistics for classes that are without any value. If the statistics are "zero" for any of the configured sequences, these are not shown on the device dashboard for zone-based firewall. |
Application Firewall
The Application Firewall blocks traffic based on applications or application-family. This application-aware firewall feature provides the following benefits:
-
Application visibility and granular control
-
Classification of 1400+ layer 7 applications
-
Blocks traffic by application or application-family
You can create lists of individual applications or application families. A sequence that contains a specified application or application family list can be inspected. This inspect action is a Layer 4 action. Matching applications are blocked/denied.
The router provides Application Layer Gateway (ALG) FTP support with Network Address Translation – Direct Internet Access (NAT-DIA), Service NAT, and Enterprise Firewall. Service NAT support is added for FTP ALG on the client and not on the FTP Server.
 Note |
The Application Firewall is valid only for Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN devices. |


 Feedback
Feedback