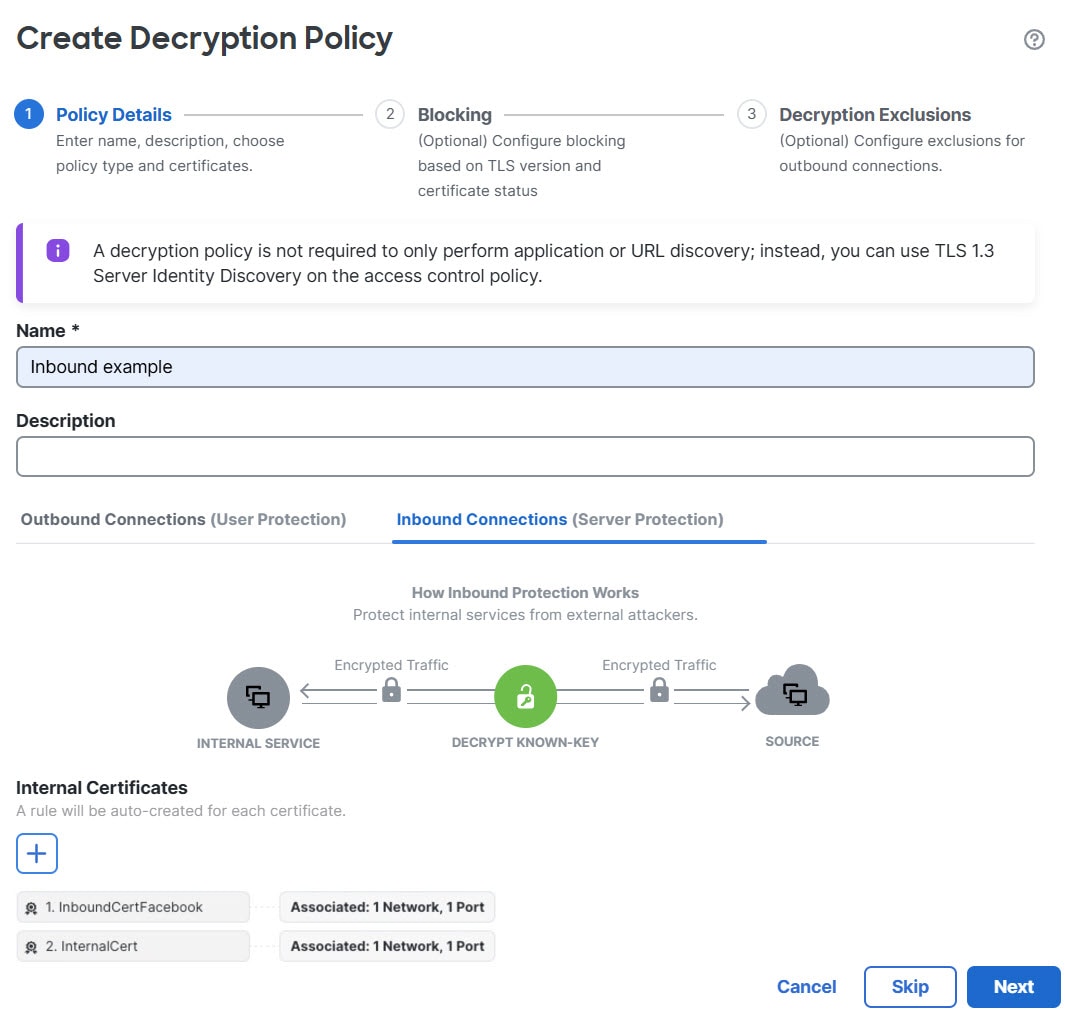
About Decryption Policies
A decryption policy determines how the system handles encrypted traffic on your network. You can configure one or more decryption policies, associate a decryption policy with an access control policy, then deploy the access control policy to a managed device. When the device detects a TCP handshake, the access control policy first handles and inspects the traffic. If it subsequently identifies a TLS/SSL-encrypted session over the TCP connection, the decryption policy takes over, handling and decrypting the encrypted traffic.
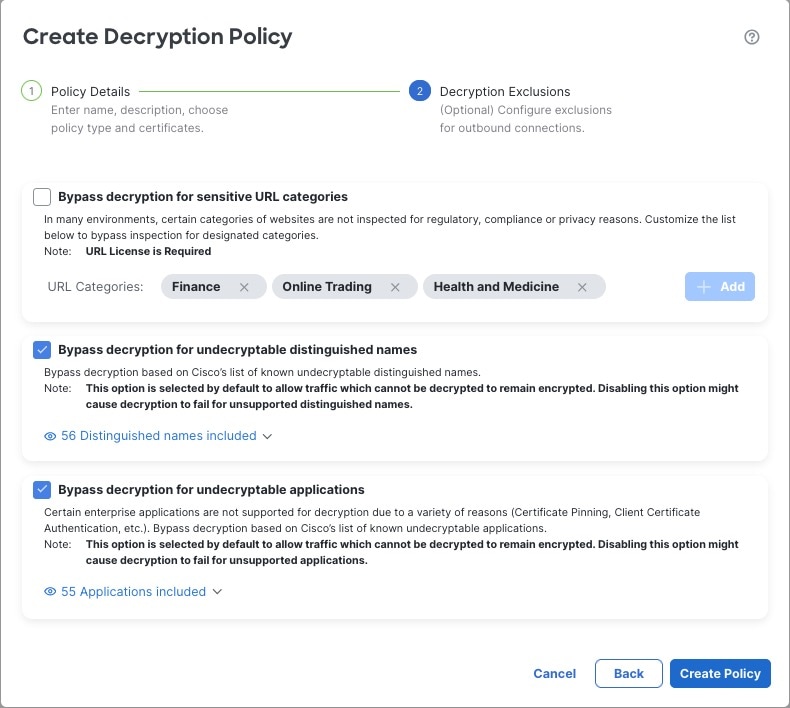
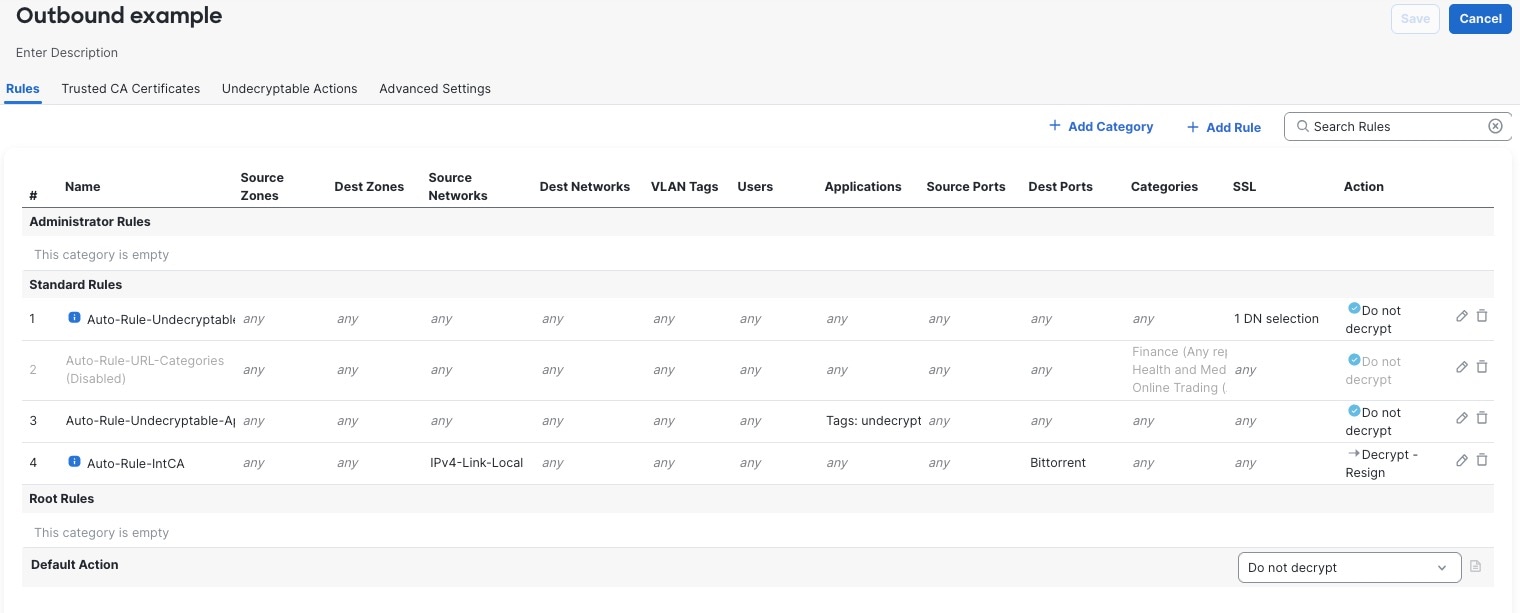
You can create multiple rules at the same time, including rules for decrypting incoming traffic (Decrypt - Known Key rule action) and outgoing traffic (Decrypt - Resign rule action). To create a rule with a Do Not Decrypt or other rule action (such as Block or Monitor), create an empty decryption policy and add the rule afterward.
Do Not Decrypt policy example
Following is an example decryption policy with a Do Not Decrypt rule action:

The simplest decryption policy, as shown in the following diagram, directs the device where it is deployed to handle encrypted traffic with a single default action. You can set the default action to block decryptable traffic without further inspection, or to inspect undecrypted decryptable traffic with access control. The system can then either allow or block the encrypted traffic. If the device detects undecryptable traffic, it either blocks the traffic without further inspection or does not decrypt it, inspecting it with access control.





 Feedback
Feedback