About Cisco vWAAS
Cisco vWAAS is a virtual appliance, for both enterprises and service providers, which accelerates business applications delivered from private and virtual private cloud infrastructure. Cisco vWAAS enables you to rapidly create WAN optimization services with minimal network configuration or disruption. Cisco vWAAS can be deployed in the physical data center and in private clouds and virtual private clouds offered by service providers.
Cisco vWAAS service is associated with application server virtual machines as they are instantiated or moved. This approach helps enable cloud providers to offer rapid delivery of WAN optimization services with little network configuration or disruption in cloud-based environments
Cisco vWAAS enables migration of business applications to the cloud, reducing the negative effect on the performance of cloud-based application delivery to end users. It enables service providers to offer an excellent application experience over the WAN as a value-added service in their catalogs of cloud services.
Cisco Integrated Services Router-Cisco Wide Area Application Services (Cisco ISR-Cisco WAAS) is the specific implementation of vWAAS running in a Cisco IOS-XE software container on a Cisco ISR 4000 Series router (ISR-4321, ISR-4331, ISR-4351, ISR-4431, ISR-4451, or ISR-4461). In this context, container refers to the hypervisor that runs virtualized applications on a Cisco ISR 4000 Series router.
 Note |
Cisco ISR-4461 is supported for Cisco vWAAS in Cisco WAAS 6.4.1b and later. |
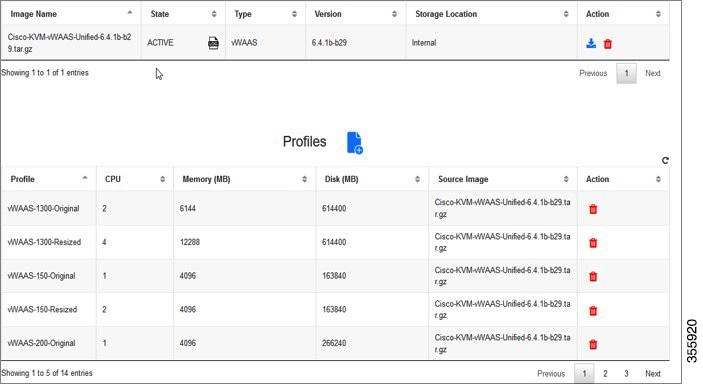
The following table shows the hypervisors supported for Cisco vWAAS. For more information on each of these hypervisors, see Hypervisors Supported for Cisco vWAAS and vCM in this chapter, and in the chapters listed in the following table.
|
Hypervisor |
For More Information: |
|---|---|
|
Cisco ISR-WAAS |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS on Cisco ISR-WAAS." |
|
VMware vSphere ESXi |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS on VMware ESXi." |
|
Microsoft HyperV |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS on Microsoft Hyper-V." |
|
RHEL KVM |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM, KVM on CentOS, and KVM in SUSE Linux." |
|
KVM on CentOS |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM, KVM on CentOS, and KVM in SUSE Linux." |
|
KVM in SUSE Linux |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS on RHEL KVM, KVM on CentOS, and KVM in SUSE Linux." |
|
Cisco Enterprise NFVIS |
See the chapter "Cisco vWAAS with Cisco Enterprise NFVIS." |
Cisco vWAAS supports WAN optimization in a cloud environment where Cisco physical WAN Automation Engine (Cisco WAE) devices cannot usually be deployed. Virtualization also provides various benefits such as elasticity, ease of maintenance, and a reduction of branch office and data center footprint.
The following hardware and cloud platforms are supported for Cisco vWAAS. For more information on each of these supported platforms, see Cisco Hardware Platforms Supported for Cisco vWAAS.
-
Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS)
-
Cisco UCS E-Series Servers
-
Cisco UCS E-Series Network Compute Engines (NCEs)
-
Cisco ISR-4000 Series
-
Cisco ENCS 5400 Series
-
Microsoft Azure Cloud
For details on the interoperability of the hypervisors and platforms supported for vWAAS, see Platforms Supported for vWAAS, by Hypervisor Type.
As shown in the following figure, you can enable vWAAS at the branch and/or the data center:
-
At the branch: With Cisco ENCS 5400-W Series, Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) E-Series servers and E-Series Network Compute Engines (NCEs), on either the Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) or Cisco ISR G2 branch router.
-
At the data center: With a Cisco UCS server.
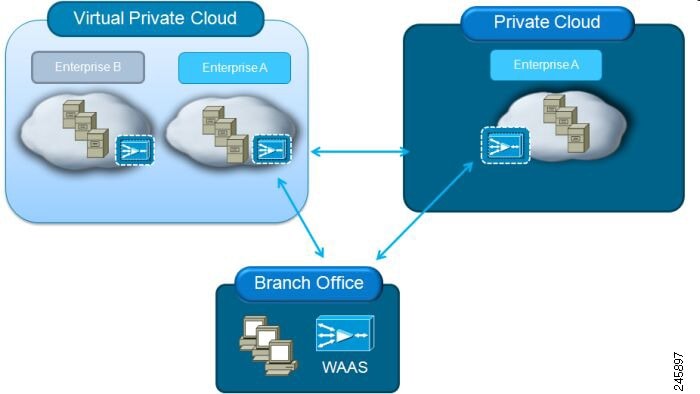
Cisco vWAAS supports on-demand provisioning and teardown, which reduces the branch office and data center footprint. Cisco vWAAS software follows the VMware ESXi standard as the preferred platform to deploy data center applications and services.
 Feedback
Feedback