Group-Based Access Control
Cisco DNA Center implements Software-Defined Access in two ways:
-
Virtual networks (VNs) provide macro-level segmentation, such as to separate IoT devices from the corporate network.
-
Group-based policies provide micro-level segmentation, such as to control what types of network traffic to permit or deny between engineering and HR groups.
Group-Based Access Control policies provide the following benefits:
-
Rich identity-based access control functionality with network automation and assurance benefits.
-
Granular access control.
-
Security groups apply to all virtual networks, which simplifies policy management.
-
Policy views help you to understand the overall policy structure, and create or update required access control policies.
-
Eliminates the need to switch between different applications to manage security groups and define protected assets.
-
Provides enhanced features for deploying enterprise-wide access control policies.
-
Restricts lateral movement of threats like ransom ware before you have identity or Network Admission Control (NAC) applications in place.
-
Provides an easy migration path to Cisco Identity Services Engine (Cisco ISE) for users who are using third-party identity applications, but want to move to Cisco ISE.
For information about creating IP pools, sites, and virtual networks in Cisco DNA Center, see the Cisco DNA Center User Guide.
For information about configuring Cisco DNA Center for Cisco ISE, see the Cisco DNA Center Installation Guide.
For information about configuring Cisco ISE for Cisco DNA Center, see the Cisco Identity Services Engine Administrator Guide.
Group-Based Access Control Policy Dashboard
The Group-Based Access Control Policy dashboard provides you with a summary of network activity, policy-related issues, and
traffic trends. Click the menu icon (![]() ) and choose to view this dashboard.
) and choose to view this dashboard.
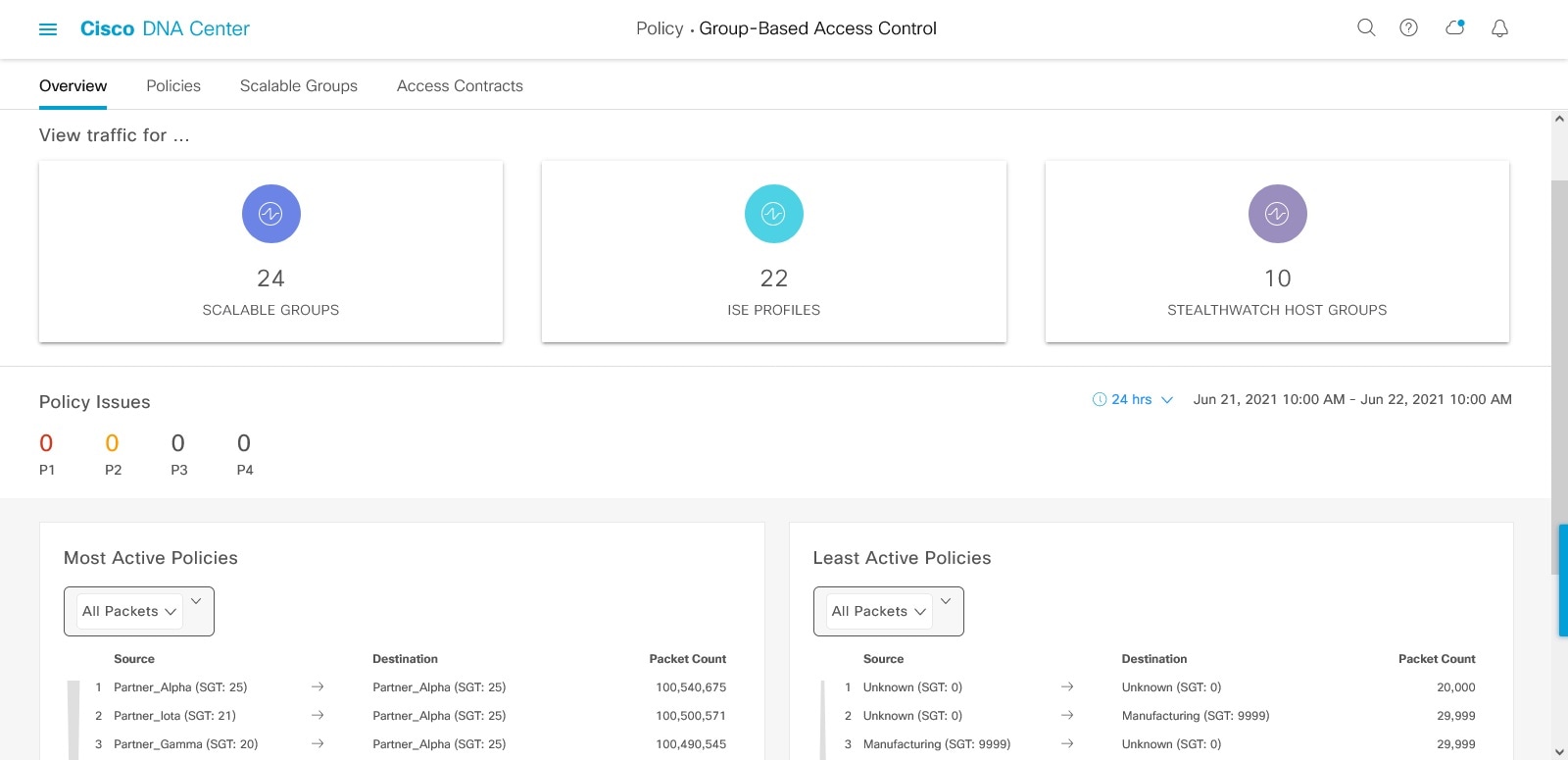
You can view the following details in this dashboard:
-
View Traffic: You can view the traffic for security groups, Cisco ISE profiles, and stealthwatch host groups. You must install the Group-Based Policy Analytics package to view this data. Group-Based Policy Analytics provides you with insights to create group-based policies by visualizing communications between assets in order to assess the impact of introducing new access controls, and understand exactly which protocols you need to allow in the policies. Cisco Group-Based Policy Analytics aggregates information on groups of assets on your network, and their communication. For more information, see Cisco Group-Based Policy Analytics.
-
View Policy-Related Issues: It displays a count of policy-related issues. Click a counter to view the details. It opens the Assurance Issues dashboard in a new browser tab, where you can view the details.
Note that this view of policy-related issues is for the currently selected time period. Use the time selector to adjust the time window, as needed.
-
View Most Active and Least Active Policies: It provides the details about the most active and least active policies. By default, this view is based on the count of total number of packets seen in the network for each policy (for each source-to-destination group pairing). You can use the drop-down list to select only the permitted packets or dropped packets. You can use the dropped packets option to see which policies are enforcing policy-based drops most actively.
Figure 2. Most and Least Active Policy Dashlets 
Note that this view of policy activity is for the currently selected time period. Use the time selector to adjust the time window, as needed.
Group-Based Access Control Policies
Access control policies define which network traffic can pass from a source security group to a destination security group.
-
Security Group: A classification category to which you can assign users, network devices, or resources. Security groups are used in access control policies. You can associate security groups with virtual networks based on your organization's network configuration, access requirements, and restrictions.
-
Contract: An access contract is a set of rules that controls the type of network traffic that is allowed to pass between the source and destination security groups. In other words, a contract is a traffic filter definition. Access contracts define the actions (permit or deny) that are performed when the traffic matches a network application, protocol, and port. The default action is to use the catch all rule when no other rules match.
-
Group-Based Access Control Policies: A group-based access control policy identifies a specific source and destination group pair and associates an access contract. The access contract specifies what types of traffic are permitted or denied between the source group and the destination group. These policies are unidirectional.
Security groups and access contracts are the basic building blocks of access control policy. While creating an access control policy, you can use the security groups and contracts that you have created earlier, or create new security groups and contracts while creating the policy. If you want to specify the network resources that can be accessed from a specific source group, you can create an access control policy with a single source and multiple destination groups. On the other hand, if you want to specify the source groups that are permitted to access a particular network resource, you can create an access control policy with a single destination and multiple source groups. For example, if you want to specify the network resources that can be accessed by the users associated with the Contractors source security group, you can create an access control policy with a single source and multiple destination groups. If you want to specify the source groups that are permitted to access the Finance Servers destination security group, you can create an access control policy with single destination and multiple source groups.
You can specify the default policy to be used when no contract is specified for a source and destination security group combination. The default policy is Permit. You can change this policy to Deny, Permit_IP_Log, or Deny_IP_Log, if necessary. You can set the default policy based on your network type—an open or closed network.

Note
We recommend that you change the default policy from Permit to Deny only if you have created explicit policies to permit necessary network traffic for all your network infrastructure devices. Failure to do so can result in loss of network connectivity.
List View
Click the List icon at the top-right corner of the Group-Based Access Control window to launch the List view.
-
Source View: Displays a list of existing policies that are organized based on the source groups. You can expand each row to view the specific source-destination policy details.
-
Destination View: Displays a list of existing policies that are organized based on the destination groups. You can expand each row to view the specific source-destination policy details.
To see which destination groups are available from a specific source group, use the Source view. To see which source groups are permitted to access a particular destination group, use the Destination view. For example, to see which destination groups are available to users who are part of the Contractors source security group, use the Source view. To see which source groups can access the Finance Servers destination security group, use the Destination view.
You can also view the policy enforcement statistics data in the policies listing table. The total number of permitted and denied policies are displayed for the selected time period.
The policy enforcement statistics are collected from the network devices that are provisioned for group-based policy and telemetry data language (TDL) subscription. These configurations are normally provisioned automatically for network devices that are part of a fabric. Manual configuration can be done for nonfabric network devices.
Note the following points while using the policy enforcement statistics data:
-
Policy enforcement statistics data is available only when the Group-Based Policy Analytics package is deployed.
-
Telemetry subscription is added as part of base provisioning for both fabric and nonfabric network devices. The TrustSec enforcement action is invoked when a new network device is added to Cisco DNA Center and assigned to a site.
-
Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) adds TrustSec enforcement for the network devices that are added to a fabric. TrustSec telemetry data is collected only when this enforcement is enabled on a network device. If it is not enabled, the telemetry subscriptions used for policy monitoring are used to collect the TDL data for TrustSec.
-
Cisco IOS XE 16.12 and later supports TDL streaming data.
-
NETCONF must be enabled on the network devices.
-
The following configuration must be added manually for the nonfabric network devices:
cts role-based enforcement vlan-list <VLAN of the endpoints> -
After upgrading, you will see the following message in the Provision > Network Devices > Inventory window:
We detected IOS-XE devices in your network where new telemetry subscription for assurance data needs to be enabled and some of the existing subscription needs to be optimized for performance. Please note that you will have to enable netconf and configure the netconf port in the Inventory credentials for these devices. Also note that these devices will receive a new subscription for group based policy monitoring telemetry. Do you want to take an action to provision these subscriptions?Click Apply Fix to push the configuration to all the network devices with site assigned.
Matrix View
Click the Grid icon at the top-right corner of the Group-Based Access Control window to launch the Matrix view. The Matrix view is a core policy view that provides an overview of all the policies for all the security groups (whether explicit or default). You can use the Matrix view to view all the source and destination policies and understand the overall policy structure. You can view, create, and update access control policies from the Matrix view.
The Matrix view contains two axes:
-
Source axis: The vertical axis lists all the source security groups.
-
Destination axis: The horizontal axis lists all the destination security groups.
Place the cursor over a cell to view the policy for a given source security group and a destination security group. The color of a cell is based on the policy that applies to that cell. The following colors indicate which policies are applied to each cell:
-
Permit: Green
-
Deny: Red
-
Custom: Gold
-
Default: Gray
Place the cursor over the Permit, Deny, Custom, or Default icon that is displayed at the top of the matrix to view the cells to which the policy is applied.
The Matrix view highlights a cell and the corresponding row (source security group) and column (destination security group) when a cell is selected. The coordinates (source and destination security groups) of the selected cell are displayed near the matrix content area.
Click a cell to open the Create Policy or Edit Policy slide-in pane for that cell. The Create Policy slide-in pane shows the source and destination security groups as read-only fields. You can only update the policy status and access contract for that cell.
You can create custom views of the policy matrix to focus only on the policies that you are interested in. To do this, from the View drop-down list, choose Create View. While creating a custom view, you can specify the subset of the security groups that you want to include in the custom view. You can save the custom views and edit them later, if required. From the View drop-down list, choose Manage Views to create, edit, duplicate, or delete custom views. The Default View shows all the source and destination security groups.
You can navigate through the matrix by dragging the cursor over the matrix content area, or by using the horizontal and vertical scroll bars. You can also use the mini-map to navigate through the matrix. The mini-map helps you to easily navigate through the matrix when the matrix size is large and extends beyond the screen size. You can move and place the mini-map anywhere on your screen. The mini-map provides the whole matrix view. The light gray portion in the mini-map represents the portion of the matrix that is currently displayed on your screen. You can drag your cursor over that area to scroll through the matrix.
 Note |
The mini-map is closed by default. Click the Expand icon to expand and view the mini-map. |
Use the Filter option to view a subset of the policy matrix for the selected set of source and destination groups. You can create a filter to focus only on the policies that you are interested in. To create the filter, select the source and destination groups that you want to include.
Policy Creation Overview
-
Define the categorizations for your organization or the portion of your organization that you plan to start with.
-
Create security groups for the categorizations that you identified.
-
Create access contracts for the types of network traffic that you wish to control. There are predefined sample access contracts to Permit or Deny all traffic, and also some example contracts showing more specific traffic filtering. You can create additional, more granular access contracts based on specific application definitions.
-
Decide which categories of network users require access to particular network resources, such as application servers and connections to other networks.
-
Create access policies, associate a source group, a destination group, and an access contract, to define how traffic is allowed to flow from the source to the destination.
Create a Security Group
Before you begin
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Create Security Group. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Create Security Group slide-in pane, enter a name and description (optional) for the security group.
Cisco DNA Center generates the tag value. You can update this value, if necessary. An error message is displayed if the value that you specified is already used by an existing security group. The valid range is from 2 to 65519. |
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Virtual Networks drop-down list, choose the virtual networks to be associated with this security group. By default, the default virtual network is selected.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Check the Propagate to ACI check box if you want the security group to be propagated to Cisco Application-Centric Infrastructure (ACI). |
||
|
Step 6 |
Choose whether you want to create the security group now or schedule it for later. If the Cisco DNA Center Automation Events for ITSM (ServiceNow) bundle is enabled, the Save Now option is disabled, and only the Schedule Later option is enabled for group-based policy changes. The scheduled task must be approved in IT Service Management (ITSM) before the scheduled time. If the task is not approved before the scheduled time, the task fails. For information on how to integrate ITSM with Cisco DNA Center, see the Cisco DNA Center ITSM Integration Guide. You can view the total number of upcoming, in-progress, and failed tasks at the top-right corner of the Security Groups window. Click the task status link to view the task details in Activities > Tasks. You can edit or cancel a task before it is executed. |
 Note |
You cannot create a security group with the name ANY or the tag value 0xFFFF/65535. Security Group ANY/65535 is a reserved internal security group that is used for the Cisco DNA Center default policy. |
Edit a Security Group
Before you begin
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
|
Step 2 |
In the Security Groups window, check the check box next to the security group that you want to edit, and then click Edit. |
|
Step 3 |
In the Edit Security Group slide-in pane, after making the necessary changes:
|
When you update the security groups, you must deploy the changes on the network devices. Click Deploy Now to deploy the changes immediately, or click Deploy Later to deploy the changes later.
Delete a Security Group
Before you begin
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the security group that you want to delete. |
|
Step 3 |
Choose one of the following options:
|
 Note |
Click the link in the Policies column of a security group to view the access control rules using that security group and the policy to which it belongs. You cannot delete a security group if it is used in any access policy. |
Synchronization of Security Groups Between Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE
While synchronizing the security groups in Cisco DNA Center with Cisco ISE:
-
If a security group is present in Cisco DNA Center and is not present in Cisco ISE, it is created in Cisco ISE.
-
If a security group is present in Cisco ISE and is not present in Cisco DNA Center, it is created in Cisco DNA Center.
-
If a security group name is the same in both Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE, but the description and ACI data are different, Cisco DNA Center is updated with the data specified in Cisco ISE.
-
If a security group name is the same in Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE, but the tag values are different, a new security group with the tag value specified in Cisco ISE is created in Cisco DNA Center. The name of the existing security group in Cisco DNA Center is updated with the suffix _DNAC.
-
If a tag value is the same but the security group name is different, the security group name in Cisco DNA Center is updated with the name specified in Cisco ISE.
An orange triangle icon is displayed next to a security group if synchronization with Cisco ISE is not completed.
Cisco ISE supports the packets coming from ACI to the TrustSec domain by synchronizing the Internal Endpoint Groups (IEPGs) and creating correlating read-only security groups in Cisco ISE. These security groups are displayed in the Security Groups window with the value ACI in the Created In column. You cannot edit or delete the security groups that are learned from ACI, but you can use them in the policies.
The Associated Contracts column shows the associated contracts for the security groups that are learned from ACI. Click the link displayed in the Associated Contracts column to view the details about the associated contracts.
When an IEPG is updated in ACI, the corresponding security group configuration is updated in Cisco ISE. A new EEPG is created in ACI when a security group is created in Cisco ISE.
Create an Access Contract
An access contract is a set of rules that controls the type of network traffic that is allowed to pass between the source and destination security groups. Access contracts define the actions (permit or deny) that are performed when the traffic matches a network application, protocol, and port.
Before you begin
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Create Access Contract. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Create Access Contract slide-in pane, enter the required details. The Modeled Access Contract check box is enabled by default. This enables Cisco DNA Center to generate the valid commands for the underlying Security Group ACLs (SGACLs). When this option is enabled, the access contract is based on a model that allows you to create and edit without the need to know the underlying command line syntax. Uncheck the Modeled Access Contract check box if you want to enter the SGACL command lines directly and store the access contract as text. Syntax checking is not done for the command line text that you enter. You must ensure that the command syntax is valid.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Create the traffic filter rules:
You can create multiple rules. To create multiple rules for a contract, click the + symbol and choose the settings for the Action and Application columns. The rules are checked in the order in which they are listed in the contract. Use the handle icon at the left end of a rule to drag and change the order of the rule. You can enable or disable logging for any traffic filter rule (including the default action) by using the Logging toggle. Logging is disabled by default. When logging is enabled, the network device sends a syslog message when the traffic filter rule is hit. This might be helpful in troubleshooting and initial testing of a policy. However, we recommend that you use this option sparingly because it might have a resource and performance impact on the network devices. |
||
|
Step 5 |
From the Default Action drop-down list, choose Deny or Permit. You can enable logging for the default action, if required. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Choose whether you want to create the access contract now or schedule it for later. If the Cisco DNA Center Automation Events for ITSM (ServiceNow) bundle is enabled, the Save Now option is disabled, and only the Schedule Later option is enabled for group-based policy changes. The scheduled task must be approved in IT Service Management (ITSM) before the scheduled time. If the task is not approved before the scheduled time, the task fails. For information on how to integrate ITSM with Cisco DNA Center, see the Cisco DNA Center ITSM Integration Guide. You can view the total number of upcoming, in-progress, and failed tasks at the top-right corner of the Access Contract window. Click the task status link to view the task details in Activities > Tasks. You can edit or cancel a task before it is executed. |
Edit an Access Contract
Before you begin
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
|
Step 2 |
In the Access Contracts window, check the check box next to the access contract that you want to edit. |
|
Step 3 |
Choose Actions > Edit. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Edit Access Contract window, after making the necessary changes, choose whether you want to update the access contract now or schedule it for later. |
You can use the Filter option to search for the contracts.
You can duplicate an existing access contract and create a new access contract by editing the required details. When you duplicate an access contract, all information in the existing access contract is copied and the copied contract has the existing contract name with the string Copy appended at the end. Click Save Now to create the duplicate contract immediately, or click Schedule Later to create the duplicate contract later.
When you update the security groups, contracts, or policies, you must deploy the changes on the network devices. If you update the policies and do not deploy the updated policies, notifications about the policy changes are not sent to the network devices, and the policies that are currently active in the network may not be consistent with the policy information displayed in Cisco DNA Center. To resolve this situation, you must deploy the updated policies on the network devices. Click Deploy Now to deploy the changes immediately, or click Deploy Later to deploy the changes later.
Cisco ISE provides the runtime policy platform for providing policy download to the network devices on behalf of Cisco DNA Center. The TrustSec Workcenter user interface screens for Security Groups, Security Group Access Control Lists (SGACLs), and Egress Policy are displayed in Read-Only mode in Cisco ISE to prevent policy synchronization issues.
Delete an Access Contract
Before you begin
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
|
Step 2 |
In the Access Contracts window, check the check box next to the access contract that you want to delete, and then choose whether you want to delete the access contract now or schedule it for later. |
You can view the sample contracts in the Access Contracts window. You can use or delete those sample contracts. However, you cannot delete the default contracts (Permit IP, Deny IP, Permit_IP_Log, and Deny_IP_Log).
Click the link in the Policies column of an access contract to view the policies that use that contract. You cannot delete a contract if it is used in a policy. You must delete the contract from that policy before you delete the contract.
Synchronization of Access Contracts Between Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE
While synchronizing the access contracts in Cisco DNA Center with Cisco ISE:
-
If a contract is present in Cisco DNA Center and is not present in Cisco ISE, it is created in Cisco ISE.
-
If a contract is present in Cisco ISE and is not present in Cisco DNA Center, it is created in Cisco DNA Center.
-
If a contract name is the same in Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE, but the description and traffic rule content are different, Cisco DNA Center is updated with the data specified in Cisco ISE.
-
If the contract name and rule are the same, but the description is different, Cisco DNA Center is updated with the description specified in Cisco ISE.
-
Text SGACL command lines in Cisco ISE are migrated as content that cannot be parsed. You can edit these contracts, but Cisco DNA Center does not parse them or check the syntax. The changes that you make in Cisco DNA Center are reflected in Cisco ISE.
-
If a policy has multiple SGACLs in Cisco ISE, those contracts are migrated as default policies in Cisco DNA Center.
An orange triangle icon is displayed next to an access contract if synchronization with Cisco ISE is incomplete.
The contracts that are learned from ACI are displayed in the Access Contracts window with the value ACI in the Created In column. You cannot edit or delete the access contracts that are learned from ACI, but you can use them in the policies while using the ACI-learned security groups. While creating or updating a policy from the Matrix view, if you select an ACI-learned security group as the destination group, the associated access contracts are displayed in the Preferred Contracts tab. You can view all the access contracts in the All Contracts tab.
Create Group-Based Access Control Policy
Security groups and access contracts are the basic building blocks of an access control policy. While creating an access control policy, you can use the security groups and contracts that you have created before, or create new security groups and contracts while creating the policy.
To specify the network resources that can be accessed from a specific source group, you can create an access control policy with a single source and multiple destination groups. On the other hand, to specify the source groups that are permitted to access a particular network resource, you can create an access control policy with a single destination and multiple source groups.
For example, if you want to specify the network resources that can be accessed by the users associated with the Contractors source security group, you can create an access control policy with a single source and multiple destination groups. If you want to specify the source groups that are permitted to access the Finance Servers destination security group, you can create an access control policy with a single destination and multiple source groups.
Group-based access control policies can also be created or updated based on the traffic flows for a given source and destination group pair.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the Policy List or Matrix view, click Create Policies. |
|
Step 2 |
To create an access control policy with a single source and multiple destination groups, click Source to Destination(s) and complete these steps: |
|
Step 3 |
To create an access control policy with a single destination and multiple source groups, click Destination to Source(s) and complete the following steps: |
Update a Group-based Access Control Policy based on Traffic Flows
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the policy matrix view, click the cell for which you want to update the group-based access control policy. |
|
Step 2 |
In the Policy Details slide-in pane, click View Traffic Flows. In the View Traffic Flows slide-in pane, you can see the rules for the selected contract or the default policy in the left pane. You can view the traffic flows that match any selected rule in the right pane. |
|
Step 3 |
Click View Traffic in the Default Action rule to see the list of flows that match that rule. While modifying an existing policy using access contracts with additional rules, use the View Traffic option for any rule to see the list of flows matching that rule. For policies that are using the Default Action rule (with no explicitly selected access contract), you can select an access contract or create a new access contract to be used by that policy. For policies with the access contract PERMIT or DENY, you can select an access contract or create a new access contract to be used by that policy. For policies with the custom access contract, you can edit the selected access contract. |
|
Step 4 |
After making the required changes, choose one of the following options:
|
Synchronization of Policies Between Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE
While synchronizing the policies in Cisco DNA Center with Cisco ISE:
-
If a policy is present in Cisco DNA Center and is not present in Cisco ISE, it is created in Cisco ISE.
-
If a policy is present in Cisco ISE and is not present in Cisco DNA Center, it is created in Cisco DNA Center.
-
If a policy contract is different in Cisco ISE, Cisco DNA Center is updated with the contract specified in Cisco ISE.
-
Policy mode information (Enabled, Disabled, or Monitor) is also imported from Cisco ISE.
Cisco ISE has an option to allow multiple SGACLs for a single policy (this option is not enabled by default in Cisco ISE). Cisco DNA Center does not support the use of multiple access contracts for a single policy. During policy synchronization, if a policy in Cisco ISE has multiple SGACLs, the Cisco DNA Center administrator is given the option to change that policy to have no contract selected (to use the default policy). The administrator can select a new or existing access contract for that policy after the policy synchronization is complete.
 icon to display the chart view or
icon to display the chart view or  to display the table view.
to display the table view.








 Feedback
Feedback