- Information About Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Licensing Requirements for Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Default Settings
- Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Turning Off and Turning On Interfaces
- Monitoring Interfaces
- Configuration Examples for Interfaces in Routed Mode
- Feature History for Interfaces in Routed Mode
Routed Mode Interfaces
This chapter includes tasks to complete the interface configuration for all models in routed firewall mode. This chapter includes the following sections:
- Information About Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Licensing Requirements for Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Default Settings
- Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Turning Off and Turning On Interfaces
- Monitoring Interfaces
- Configuration Examples for Interfaces in Routed Mode
- Feature History for Interfaces in Routed Mode

Note![]() For multiple context mode, complete the tasks in this section in the context execution space. Enter the changeto context name command to change to the context you want to configure.
For multiple context mode, complete the tasks in this section in the context execution space. Enter the changeto context name command to change to the context you want to configure.
Information About Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
This section includes the following topics:
Security Levels
Each interface must have a security level from 0 (lowest) to 100 (highest). For example, you should assign your most secure network, such as the inside host network, to level 100. While the outside network connected to the Internet can be level 0. Other networks, such as DMZs can be in between. You can assign interfaces to the same security level. See Allowing Same Security Level Communication for more information.
The level controls the following behavior:
- Network access—By default, there is an implicit permit from a higher security interface to a lower security interface (outbound). Hosts on the higher security interface can access any host on a lower security interface. You can limit access by applying an ACL to the interface.
If you enable communication for same security interfaces (see Allowing Same Security Level Communication), there is an implicit permit for interfaces to access other interfaces on the same security level or lower.
- Inspection engines—Some application inspection engines are dependent on the security level. For same security interfaces, inspection engines apply to traffic in either direction.
–![]() NetBIOS inspection engine—Applied only for outbound connections.
NetBIOS inspection engine—Applied only for outbound connections.
–![]() SQL*Net inspection engine—If a control connection for the SQL*Net (formerly OraServ) port exists between a pair of hosts, then only an inbound data connection is permitted through the ASA.
SQL*Net inspection engine—If a control connection for the SQL*Net (formerly OraServ) port exists between a pair of hosts, then only an inbound data connection is permitted through the ASA.
- Filtering—HTTP(S) and FTP filtering applies only for outbound connections (from a higher level to a lower level).
If you enable communication for same security interfaces, you can filter traffic in either direction.
- established command—This command allows return connections from a lower security host to a higher security host if there is already an established connection from the higher level host to the lower level host.
If you enable communication for same security interfaces, you can configure established commands for both directions.
Dual IP Stack (IPv4 and IPv6)
The ASA supports the configuration of both IPv6 and IPv4 on an interface. You do not need to enter any special commands to do so; simply enter the IPv4 configuration commands and IPv6 configuration commands as you normally would. Make sure you configure a default route for both IPv4 and IPv6.
Licensing Requirements for Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
|
|
|
|---|---|
VLANs1: Interfaces of all types2: |
|
VLANs 1 : Interfaces of all types 2 : |
|
VLANs 1 : Interfaces of all types 2 : |
|
VLANs 1 : Interfaces of all types 2 : |
|
VLANs 1 : Interfaces of all types 2 : |
|
VLANs 1 : Base and Security Plus License: 1024 Interface Speed for SSP-10 and SSP-20: Base License—1-Gigabit Ethernet for fiber interfaces 10 GE I/O License (Security Plus)—10-Gigabit Ethernet for fiber interfaces (SSP-40 and SSP-60 support 10-Gigabit Ethernet by default.) Interfaces of all types 2 : |
|
|
|
|---|---|
Guidelines and Limitations
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature.
- For the ASA 5512-X and higher in multiple context mode, configure the physical interfaces in the system execution space according to Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)” Then, configure the logical interface parameters in the context execution space according to this chapter. For the ASASM in multiple context mode, configure switch ports and VLANs on the switch, and then assign VLANs to the ASASM according to Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
The ASA 5505 and ASAv do not support multiple context mode.
- In multiple context mode, you can only configure context interfaces that you already assigned to the context in the system configuration according to the Configuring Multiple Contexts.
- PPPoE is not supported in multiple context mode.
Supported in routed firewall mode. For transparent mode, see Chapter14, “Transparent Mode Interfaces”
Do not finish configuring failover interfaces with the procedures in this chapter. See “Failover,” to configure the failover and state links. In multiple context mode, failover interfaces are configured in the system configuration.
VLAN ID Guidelines for the ASASM
You can add any VLAN ID to the configuration, but only VLANs that are assigned to the ASA by the switch can pass traffic. To view all VLANs assigned to the ASA, use the show vlan command.
If you add an interface for a VLAN that is not yet assigned to the ASA by the switch, the interface will be in the down state. When you assign the VLAN to the ASA, the interface changes to an up state. See the show interface command for more information about interface states.
Default Settings
This section lists default settings for interfaces if you do not have a factory default configuration. For information about the factory default configurations, see Factory Default Configurations.
The default security level is 0. If you name an interface “inside” and you do not set the security level explicitly, then the ASA sets the security level to 100.

Note![]() If you change the security level of an interface, and you do not want to wait for existing connections to time out before the new security information is used, you can clear the connections using the clear local-host command.
If you change the security level of an interface, and you do not want to wait for existing connections to time out before the new security information is used, you can clear the connections using the clear local-host command.
Default State of Interfaces for the ASASM
- In single mode or in the system execution space, VLAN interfaces are enabled by default.
- In multiple context mode, all allocated interfaces are enabled by default, no matter what the state of the interface is in the system execution space. However, for traffic to pass through the interface, the interface also has to be enabled in the system execution space. If you shut down an interface in the system execution space, then that interface is down in all contexts that share it.
By default, the ASASM supports jumbo frames. Just configure the MTU for the desired packet size according to the Configuring the MAC Address, MTU, and TCP MSS.
Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
This section includes the following topics:
- Task Flow for Completing Interface Configuration
- Configuring General Interface Parameters
- Configuring the MAC Address, MTU, and TCP MSS
- Configuring IPv6 Addressing
- Allowing Same Security Level Communication
Task Flow for Completing Interface Configuration
Step 1![]() Set up your interfaces depending on your model:
Set up your interfaces depending on your model:
- ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
- ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
- ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
- ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
Step 2![]() (Multiple context mode) Allocate interfaces to the context according to Configuring Multiple Contexts.
(Multiple context mode) Allocate interfaces to the context according to Configuring Multiple Contexts.
Step 3![]() (Multiple context mode) Enter the changeto context name command to change to the context you want to configure. Configure general interface parameters, including the interface name, security level, and IPv4 address. See Configuring General Interface Parameters.
(Multiple context mode) Enter the changeto context name command to change to the context you want to configure. Configure general interface parameters, including the interface name, security level, and IPv4 address. See Configuring General Interface Parameters.
Step 4![]() (Optional) Configure the MAC address and the MTU. See Configuring the MAC Address, MTU, and TCP MSS.
(Optional) Configure the MAC address and the MTU. See Configuring the MAC Address, MTU, and TCP MSS.
Step 5![]() (Optional) Configure IPv6 addressing. See Configuring IPv6 Addressing.
(Optional) Configure IPv6 addressing. See Configuring IPv6 Addressing.
Step 6![]() (Optional) Allow same security level communication, either by allowing communication between two interfaces or by allowing traffic to enter and exit the same interface. See Allowing Same Security Level Communication.
(Optional) Allow same security level communication, either by allowing communication between two interfaces or by allowing traffic to enter and exit the same interface. See Allowing Same Security Level Communication.
Configuring General Interface Parameters
This procedure describes how to set the name, security level, IPv4 address and other options.
For the ASA 5512-X and higher and the ASAv, you must configure interface parameters for the following interface types:
For the ASA 5505 and ASASM, you must configure interface parameters for the following interface types:
Guidelines and Limitations
If you are using failover, do not use this procedure to name interfaces that you are reserving for failover and Stateful Failover communications. See “Failover,” to configure the failover and state links.
Restrictions
Prerequisites
–![]() ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
–![]() ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
–![]() ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
–![]() ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
- In multiple context mode, you can only configure context interfaces that you already assigned to the context in the system configuration according to Configuring Multiple Contexts.
- In multiple context mode, complete this procedure in the context execution space. To change from the system to a context configuration, enter the changeto context name command.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
For the ASA 5512-X and higher and ASAv: interface {{ redundant number | port-channel number | physical_interface }[. subinterface ] | mapped_name } ciscoasa(config)# interface { vlan number | mapped_name } |
If you are not already in interface configuration mode, enters interface configuration mode. The redundant number argument is the redundant interface ID, such as redundant 1. The port-channel number argument is the EtherChannel interface ID, such as port-channel 1. See Enabling the Physical Interface and Configuring Ethernet Parameters section for a description of the physical interface ID. Append the subinterface ID to the physical or redundant interface ID separated by a period (.). In multiple context mode, enter the mapped_name if one was assigned using the allocate-interface command. |
|
|
|
The name is a text string up to 48 characters, and is not case-sensitive. You can change the name by reentering this command with a new value. Do not enter the no form, because that command causes all commands that refer to that name to be deleted. |
|
ip address ip_address [ mask ] [ standby ip_address ] ciscoasa(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 standby 10.1.1.2 |
Note For use with failover, you must set the IP address and standby address manually; DHCP and PPPoE are not supported. The ip_address and mask arguments set the interface IP address and subnet mask. The standby ip_address argument is used for failover. See Configuring Active/Standby Failover or the Configuring Active/Active Failover for more information. |
|
|
|
Obtains an IP address from a DHCP server. The setroute keyword lets the ASA use the default route supplied by the DHCP server. Reenter this command to reset the DHCP lease and request a new lease. If you do not enable the interface using the no shutdown command before you enter the ip address dhcp command, some DHCP requests might not be sent. |
|
To obtain an IP address from a PPPoE server, see the VPN configuration guide. |
||
|
|
Sets the security level, where number is an integer between 0 (lowest) and 100 (highest). See Security Levels. |
|
|
|
Sets an interface to management-only mode so that it does not pass through traffic. By default, Management interfaces are configured as management-only. To disable this setting, enter the no management-only command. (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) You cannot disable management-only on the Management 0/0 interface. The management-only command is not supported for a redundant interface. |
|
Example
The following example configures parameters for VLAN 101:
The following example configures parameters in multiple context mode for the context configuration. The interface ID is a mapped name.
What to Do Next
- (Optional) Configure the MAC address and the MTU. See Configuring the MAC Address, MTU, and TCP MSS.
- (Optional) Configure IPv6 addressing. See Configuring IPv6 Addressing.
Configuring the MAC Address, MTU, and TCP MSS
This section describes how to configure MAC addresses for interfaces, how to set the MTU, and set the TCP MSS.
Information About MAC Addresses
By default, the physical interface uses the burned-in MAC address, and all subinterfaces of a physical interface use the same burned-in MAC address.
For the ASASM, all VLANs use the same MAC address provided by the backplane.
A redundant interface uses the MAC address of the first physical interface that you add. If you change the order of the member interfaces in the configuration, then the MAC address changes to match the MAC address of the interface that is now listed first. If you assign a MAC address to the redundant interface using this command, then it is used regardless of the member interface MAC addresses.
For an EtherChannel, all interfaces that are part of the channel group share the same MAC address. This feature makes the EtherChannel transparent to network applications and users, because they only see the one logical connection; they have no knowledge of the individual links. The port-channel interface uses the lowest numbered channel group interface MAC address as the port-channel MAC address. Alternatively you can manually configure a MAC address for the port-channel interface. In multiple context mode, you can automatically assign unique MAC addresses to interfaces, including an EtherChannel port interface. We recommend manually, or in multiple context mode, automatically configuring a unique MAC address in case the group channel interface membership changes. If you remove the interface that was providing the port-channel MAC address, then the port-channel MAC address changes to the next lowest numbered interface, thus causing traffic disruption.
In multiple context mode, if you share an interface between contexts, you can assign a unique MAC address to the interface in each context. This feature lets the ASA easily classify packets into the appropriate context. Using a shared interface without unique MAC addresses is possible, but has some limitations. See How the ASA Classifies Packets for more information. You can assign each MAC address manually, or you can automatically generate MAC addresses for shared interfaces in contexts. See Automatically Assigning MAC Addresses to Context Interfaces to automatically generate MAC addresses. If you automatically generate MAC addresses, you can use this procedure to override the generated address.
For single context mode, or for interfaces that are not shared in multiple context mode, you might want to assign unique MAC addresses to subinterfaces. For example, your service provider might perform access control based on the MAC address.
Information About the MTU and TCP MSS
See Controlling Fragmentation with the Maximum Transmission Unit and TCP Maximum Segment Size.
Prerequisites
–![]() ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
–![]() ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
–![]() ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
–![]() ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
- In multiple context mode, you can only configure context interfaces that you already assigned to the context in the system configuration according to Configuring Multiple Contexts.
- In multiple context mode, complete this procedure in the context execution space. To change from the system to a context configuration, enter the changeto context name command.
- To increase the MTU above 1500, enable jumbo frames according to the Enabling Jumbo Frame Support. Jumbo frames are supported by default on the ASASM; you do not need to enable them.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
For the ASA 5512-X and higher and the ASAv: interface {{ redundant number | port-channel number | physical_interface }[. subinterface ] | mapped_name } ciscoasa(config)# interface { vlan number | mapped_name } |
If you are not already in interface configuration mode, enters interface configuration mode. The redundant number argument is the redundant interface ID, such as redundant 1. The port-channel number argument is the EtherChannel interface ID, such as port-channel 1. See Enabling the Physical Interface and Configuring Ethernet Parameters section for a description of the physical interface ID. Append the subinterface ID to the physical or redundant interface ID separated by a period (.). In multiple context mode, enter the mapped_name if one was assigned using the allocate-interface command. |
|
mac-address m ac_address [ standby mac_address ] |
Assigns a private MAC address to this interface. The mac_address is in H.H.H format, where H is a 16-bit hexadecimal digit. For example, the MAC address 00-0C-F1-42-4C-DE is entered as 000C.F142.4CDE. The first two bytes of a manual MAC address cannot be A2 if you also want to use auto-generated MAC addresses. For use with failover, set the standby MAC address. If the active unit fails over and the standby unit becomes active, the new active unit starts using the active MAC addresses to minimize network disruption, while the old active unit uses the standby address. |
|
|
|
Sets the MTU between 300 and 9198 bytes (9000 for the ASAv). The default is 1500 bytes. Note When you set the MTU for a redundant or port-channel interface, the ASA applies the setting to all member interfaces. For models that support jumbo frames, if you enter a value for any interface that is greater than 1500, then you need to enable jumbo frame support. See Enabling Jumbo Frame Support. |
|
sysopt connection tcpmss [ minimum ] bytes |
Sets the maximum TCP segment size in bytes, between 48 and any maximum number. The default value is 1380 bytes. You can disable this feature by setting bytes to 0. For the minimum keyword, sets the maximum segment size to be no less than bytes, between 48 and 65535. The minimum feature is disabled by default (set to 0). |
What to Do Next
(Optional) Configure IPv6 addressing. See Configuring IPv6 Addressing.
Configuring IPv6 Addressing
Information About IPv6
This section includes information about how to configure IPv6, and includes the following topics:
IPv6 Addressing
You can configure two types of unicast addresses for IPv6:
- Global—The global address is a public address that you can use on the public network.
- Link-local—The link-local address is a private address that you can only use on the directly-connected network. Routers do not forward packets using link-local addresses; they are only for communication on a particular physical network segment. They can be used for address configuration or for the ND functions such as address resolution and neighbor discovery.
At a minimum, you need to configure a link-local address for IPv6 to operate. If you configure a global address, a link-local address is automatically configured on the interface, so you do not also need to specifically configure a link-local address. If you do not configure a global address, then you need to configure the link-local address, either automatically or manually.

Note![]() If you want to only configure the link-local addresses, see the ipv6 enable (to auto-configure) or ipv6 address link-local (to manually configure) command in the command reference.
If you want to only configure the link-local addresses, see the ipv6 enable (to auto-configure) or ipv6 address link-local (to manually configure) command in the command reference.
Modified EUI-64 Interface IDs
RFC 3513: Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing Architecture requires that the interface identifier portion of all unicast IPv6 addresses, except those that start with binary value 000, be 64 bits long and be constructed in Modified EUI-64 format. The ASA can enforce this requirement for hosts attached to the local link.
When this feature is enabled on an interface, the source addresses of IPv6 packets received on that interface are verified against the source MAC addresses to ensure that the interface identifiers use the Modified EUI-64 format. If the IPv6 packets do not use the Modified EUI-64 format for the interface identifier, the packets are dropped and the following system log message is generated:
The address format verification is only performed when a flow is created. Packets from an existing flow are not checked. Additionally, the address verification can only be performed for hosts on the local link. Packets received from hosts behind a router will fail the address format verification, and be dropped, because their source MAC address will be the router MAC address and not the host MAC address.
Configuring a Global IPv6 Address
To configure a global IPv6 address, perform the following steps.

Note![]() Configuring the global address automatically configures the link-local address, so you do not need to configure it separately.
Configuring the global address automatically configures the link-local address, so you do not need to configure it separately.
Restrictions
Prerequisites
–![]() ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
ASA 5512-X and higher—Chapter10, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5512-X and Higher)”
–![]() ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
ASA 5505—Chapter11, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)”
–![]() ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
ASASM—Chapter2, “Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module”
–![]() ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
ASAv—Chapter12, “Basic Interface Configuration (ASAv)”
- In multiple context mode, you can only configure context interfaces that you already assigned to the context in the system configuration according to Configuring Multiple Contexts.
- In multiple context mode, complete this procedure in the context execution space. To change from the system to a context configuration, enter the changeto context name command.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
For the ASA 5512-X and higher and the ASAv: interface {{ redundant number | port-channel number | physical_interface }[. subinterface ] | mapped_name } ciscoasa(config)# interface { vlan number | mapped_name } |
If you are not already in interface configuration mode, enters interface configuration mode. The redundant number argument is the redundant interface ID, such as redundant 1. The port-channel number argument is the EtherChannel interface ID, such as port-channel 1. See Enabling the Physical Interface and Configuring Ethernet Parameters for a description of the physical interface ID. Append the subinterface ID to the physical or redundant interface ID separated by a period (.). In multiple context mode, enter the mapped_name if one was assigned using the allocate-interface command. |
|
|
|
Enables stateless autoconfiguration on the interface. Enabling stateless autoconfiguration on the interface configures IPv6 addresses based on prefixes received in Router Advertisement messages. A link-local address, based on the Modified EUI-64 interface ID, is automatically generated for the interface when stateless autoconfiguration is enabled. Note Although RFC 4862 specifies that hosts configured for stateless autoconfiguration do not send Router Advertisement messages, the ASA does send Router Advertisement messages in this case. See the ipv6 nd suppress-ra command to suppress messages. |
|
ipv6 address ipv6-address/prefix-length [ standby ipv6-address ] |
Assigns a global address to the interface. When you assign a global address, the link-local address is automatically created for the interface. standby specifies the interface address used by the secondary unit or failover group in a failover pair. |
|
ipv6 address ipv6-prefix/prefix-length eui-64 ciscoasa(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:0DB8::BA98::/48 eui-64 |
Assigns a global address to the interface by combining the specified prefix with an interface ID generated from the interface MAC address using the Modified EUI-64 format. When you assign a global address, the link-local address is automatically created for the interface. Y ou do not need to specify the standby address; the interface ID will be generated automatically. |
|
|
|
Enforces the use of Modified EUI-64 format interface identifiers in IPv6 addresses on a local link. The if_name argument is the name of the interface, as specified by the nameif command, on which you are enabling the address format enforcement. See Modified EUI-64 Interface IDs for more information. |
|
Configuring IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
See “IPv6 Neighbor Discovery,” to configure IPv6 neighbor discovery.
Allowing Same Security Level Communication
By default, interfaces on the same security level cannot communicate with each other, and packets cannot enter and exit the same interface. This section describes how to enable inter-interface communication when interfaces are on the same security level, and how to enable intra-interface communication.
Information About Inter-Interface Communication
Allowing interfaces on the same security level to communicate with each other provides the following benefits:
If you use different levels for each interface and do not assign any interfaces to the same security level, you can configure only one interface per level (0 to 100).
If you enable same security interface communication, you can still configure interfaces at different security levels as usual.
Information About Intra-Interface Communication
Intra-interface communication might be useful for VPN traffic that enters an interface, but is then routed out the same interface. The VPN traffic might be unencrypted in this case, or it might be reencrypted for another VPN connection. For example, if you have a hub and spoke VPN network, where the ASA is the hub, and remote VPN networks are spokes, for one spoke to communicate with another spoke, traffic must go into the ASA and then out again to the other spoke.

Note![]() All traffic allowed by this feature is still subject to firewall rules. Be careful not to create an asymmetric routing situation that can cause return traffic not to traverse the ASA.
All traffic allowed by this feature is still subject to firewall rules. Be careful not to create an asymmetric routing situation that can cause return traffic not to traverse the ASA.
For the ASASM, before you can enable this feature, you must first correctly configure the MSFC so that packets are sent to the ASA MAC address instead of being sent directly through the switch to the destination host. Figure 13-1 shows a network where hosts on the same interface need to communicate.
Figure 13-1 Communication Between Hosts on the Same Interface
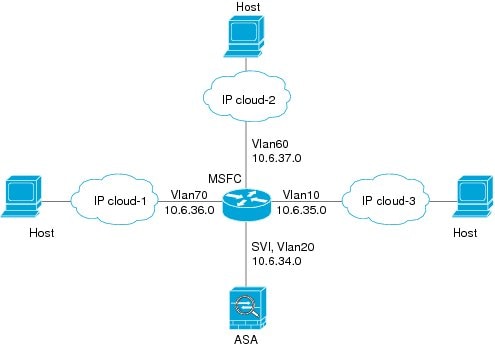
The following sample configuration shows the Cisco IOS route-map commands used to enable policy routing in the network shown in Figure 13-1:
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|---|---|
Enables interfaces on the same security level so that they can communicate with each other. |
|
Enables communication between hosts connected to the same interface. |
Turning Off and Turning On Interfaces
This section describes how to turn off and on an interface.
All interfaces are enabled by default. In multiple context mode, if you disable or reenable the interface within a context, only that context interface is affected. But if you disable or reenable the interface in the system execution space, then you affect that interface for all contexts.
Detailed Steps
Monitoring Interfaces
To monitor interfaces, enter one of the following commands:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
Configuration Examples for Interfaces in Routed Mode
This section includes the following topics:
ASA 5505 Example
The following example configures three VLAN interfaces for the Base license. The third home interface cannot forward traffic to the business interface.
Feature History for Interfaces in Routed Mode
Table 13-1 lists the release history for this feature.
 Feedback
Feedback