- Preface
- Product Overview
- Installing Cisco Fabric Manager
- Fabric Manager Server
- Authentication in Fabric Manager
- Fabric Manager Client
- Device Manager
- Using Cisco Fabric Services
- Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring Virtual Interfaces
- Configuring Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Configuring N-Port Virtualization
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring VSAN Trunking
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Configuring SPAN
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Configuring SAN PortChannels
- Advanced Features and Concepts
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Network Monitoring
- Performance Manager
- Nexus 5000 Management Software FAQ
- Troubleshooting Your Fabric
- Index
- Information About Fabric Authentication
- DHCHAP
- DHCHAP Compatibility with Fibre Channel Features
- About Enabling DHCHAP
- Enabling DHCHAP
- About DHCHAP Authentication Modes
- Configuring the DHCHAP Mode
- About the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
- Configuring the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
- About the DHCHAP Group Settings
- Configuring the DHCHAP Group Settings
- About the DHCHAP Password
- Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for the Local Switch
- About Password Configuration for Remote Devices
- Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for Remote Devices
- About the DHCHAP Timeout Value
- Configuring the DHCHAP Timeout Value
- Configuring DHCHAP AAA Authentication
- Enabling FC-SP on ISLs
- Default Settings
Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
Fibre Channel Security Protocol (FC-SP) capabilities provide switch-to-switch and host-to-switch authentication to overcome security challenges for enterprise-wide fabrics. Diffie-Hellman Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (DHCHAP) is an FC-SP protocol that provides authentication between Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches and other devices. DHCHAP consists of the CHAP protocol combined with the Diffie-Hellman exchange.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•![]() Information About Fabric Authentication
Information About Fabric Authentication
Information About Fabric Authentication
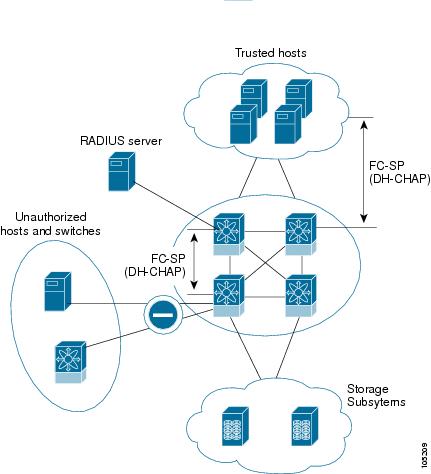
All Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches enable fabric-wide authentication from one switch to another switch, or from a switch to a host. These switch and host authentications are performed locally or remotely in each fabric. As storage islands are consolidated and migrated to enterprise-wide fabrics new security challenges arise. The approach of securing storage islands cannot always be guaranteed in enterprise-wide fabrics. For example, in a campus environment with geographically distributed switches, someone could maliciously interconnect incompatible switches or you could accidentally do so, resulting in Inter-Switch Link (ISL) isolation and link disruption.
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches support authentication features to address physical security (see Figure 23-1).
Figure 23-1 Switch and Host Authentication
DHCHAP
DHCHAP is an authentication protocol that authenticates the devices connecting to a switch. Fibre Channel authentication allows only trusted devices to be added to a fabric, which prevents unauthorized devices from accessing the switch.

Note ![]() The terms FC-SP and DHCHAP are used interchangeably in this chapter.
The terms FC-SP and DHCHAP are used interchangeably in this chapter.
DHCHAP is a mandatory password-based, key-exchange authentication protocol that supports both switch-to-switch and host-to-switch authentication. DHCHAP negotiates hash algorithms and DH groups before performing authentication. It supports MD5 and SHA-1 algorithm-based authentication.
To configure DHCHAP authentication using the local password database, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Enable DHCHAP.
Enable DHCHAP.
Step 2 ![]() Identify and configure the DHCHAP authentication modes.
Identify and configure the DHCHAP authentication modes.
Step 3 ![]() Configure the hash algorithm and DH group.
Configure the hash algorithm and DH group.
Step 4 ![]() Configure the DHCHAP password for the local switch and other switches in the fabric.
Configure the DHCHAP password for the local switch and other switches in the fabric.
Step 5 ![]() Configure the DHCHAP timeout value for reauthentication.
Configure the DHCHAP timeout value for reauthentication.
Step 6 ![]() Verify the DHCHAP configuration.
Verify the DHCHAP configuration.
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() DHCHAP Compatibility with Fibre Channel Features
DHCHAP Compatibility with Fibre Channel Features
•![]() About DHCHAP Authentication Modes
About DHCHAP Authentication Modes
•![]() About the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
About the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
•![]() Configuring the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
Configuring the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
•![]() About the DHCHAP Group Settings
About the DHCHAP Group Settings
•![]() Configuring the DHCHAP Group Settings
Configuring the DHCHAP Group Settings
•![]() Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for the Local Switch
Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for the Local Switch
•![]() About Password Configuration for Remote Devices
About Password Configuration for Remote Devices
•![]() Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for Remote Devices
Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for Remote Devices
•![]() About the DHCHAP Timeout Value
About the DHCHAP Timeout Value
•![]() Configuring the DHCHAP Timeout Value
Configuring the DHCHAP Timeout Value
•![]() Configuring DHCHAP AAA Authentication
Configuring DHCHAP AAA Authentication
DHCHAP Compatibility with Fibre Channel Features
This section identifies the impact of configuring the DHCHAP feature along with existing Cisco NX-OS features:
•![]() SAN port channel interfaces—If DHCHAP is enabled for ports belonging to a SAN port channel, DHCHAP authentication is performed at the physical interface level, not at the port channel level.
SAN port channel interfaces—If DHCHAP is enabled for ports belonging to a SAN port channel, DHCHAP authentication is performed at the physical interface level, not at the port channel level.
•![]() Port security or fabric binding—Fabric-binding policies are enforced based on identities authenticated by DHCHAP.
Port security or fabric binding—Fabric-binding policies are enforced based on identities authenticated by DHCHAP.
•![]() VSANs—DHCHAP authentication is not done on a per-VSAN basis.
VSANs—DHCHAP authentication is not done on a per-VSAN basis.
About Enabling DHCHAP
By default, the DHCHAP feature is disabled in all Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches.
You must explicitly enable the DHCHAP feature to access the configuration and verification commands for fabric authentication. When you disable this feature, all related configurations are automatically discarded.
Enabling DHCHAP
To enable DHCHAP for a Cisco MDS switch using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches, expand Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Expand Switches, expand Security, and then choose FC-SP.
You see the FC-SP (DHCHAP) configuration in the Information pane as shown in Figure 23-2.
Figure 23-2 FC-SP Configuration

The Control tab is the default. You see the FC-SP enable state for all switches in the fabric.
Step 2 ![]() In the Command drop-down list, choose enable for all switches that you want to enable FC-SP on.
In the Command drop-down list, choose enable for all switches that you want to enable FC-SP on.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Apply Changes icon to enable FC-SP and DHCHAP on the selected switches.
Click the Apply Changes icon to enable FC-SP and DHCHAP on the selected switches.
About DHCHAP Authentication Modes
The DHCHAP authentication status for each interface depends on the configured DHCHAP port mode.
When the DHCHAP feature is enabled in a switch, each Fibre Channel interface or FCIP interface may be configured to be in one of four DHCHAP port modes:
•![]() On—During switch initialization, if the connecting device supports DHCHAP authentication, the software performs the authentication sequence. If the connecting device does not support DHCHAP authentication, the link is placed in an isolated state.
On—During switch initialization, if the connecting device supports DHCHAP authentication, the software performs the authentication sequence. If the connecting device does not support DHCHAP authentication, the link is placed in an isolated state.
•![]() Auto-Active—During switch initialization, if the connecting device supports DHCHAP authentication, the software performs the authentication sequence. If the connecting device does not support DHCHAP authentication, the software continues with the rest of the initialization sequence.
Auto-Active—During switch initialization, if the connecting device supports DHCHAP authentication, the software performs the authentication sequence. If the connecting device does not support DHCHAP authentication, the software continues with the rest of the initialization sequence.
•![]() Auto-Passive (default)—The switch does not initiate DHCHAP authentication, but participates in DHCHAP authentication if the connecting device initiates DHCHAP authentication.
Auto-Passive (default)—The switch does not initiate DHCHAP authentication, but participates in DHCHAP authentication if the connecting device initiates DHCHAP authentication.
•![]() Off—The switch does not support DHCHAP authentication. Authentication messages sent to ports in this mode return error messages to the initiating switch.
Off—The switch does not support DHCHAP authentication. Authentication messages sent to ports in this mode return error messages to the initiating switch.

Note ![]() Whenever DHCHAP port mode is changed to a mode other than the Off mode, reauthentication is performed.
Whenever DHCHAP port mode is changed to a mode other than the Off mode, reauthentication is performed.
Table 23-1 identifies switch-to-switch authentication between two Cisco switches in various modes.
Configuring the DHCHAP Mode
To configure the DHCHAP mode for a particular interface using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() In the Physical Attributes pane, expand Switches > Interfaces, and then choose FC Physical.
In the Physical Attributes pane, expand Switches > Interfaces, and then choose FC Physical.
You see the interface configuration in the Information Pane.
Step 2 ![]() Click the FC-SP tab.
Click the FC-SP tab.
You see the FC-SP (DHCHAP) configuration in the Information pane as shown in Figure 23-3.
Figure 23-3 FC-SP (DHCHAP) Interface Modes

Step 3 ![]() In the Mode drop-down list, choose DHCP authentication mode for each interface that you want to support FC-SP.
In the Mode drop-down list, choose DHCP authentication mode for each interface that you want to support FC-SP.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Apply Changes icon to save these DHCHAP port mode settings.
Click the Apply Changes icon to save these DHCHAP port mode settings.
About the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
Cisco SAN switches support a default hash algorithm priority list of MD5 followed by SHA-1 for DHCHAP authentication.

Tip ![]() If you change the hash algorithm configuration, then change it globally for all switches in the fabric.
If you change the hash algorithm configuration, then change it globally for all switches in the fabric.

Configuring the DHCHAP Hash Algorithm
To configure the hash algorithm using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Choose Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Choose Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Step 2 ![]() Click the General/Password tab.
Click the General/Password tab.
You see the DHCHAP general settings mode for each switch as shown in Figure 23-4.
Figure 23-4 General/ Password Tab

Step 3 ![]() Change the DHCHAP HashList for each switch in the fabric.
Change the DHCHAP HashList for each switch in the fabric.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Apply Changes icon to save the updated hash algorithm priority list.
Click the Apply Changes icon to save the updated hash algorithm priority list.
About the DHCHAP Group Settings
All Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches support all DHCHAP groups specified in the standard: 0 (null DH group, which does not perform the Diffie-Hellman exchange), 1, 2, 3, or 4.

Tip ![]() If you change the DH group configuration, change it globally for all switches in the fabric.
If you change the DH group configuration, change it globally for all switches in the fabric.
Configuring the DHCHAP Group Settings
To change the DH group settings using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Expand Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Step 2 ![]() Click the General/Password tab.
Click the General/Password tab.
Step 3 ![]() Change the DHCHAP GroupList for each switch in the fabric.
Change the DHCHAP GroupList for each switch in the fabric.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Apply Changes icon to save the updated hash algorithm priority list.
Click the Apply Changes icon to save the updated hash algorithm priority list.
About the DHCHAP Password
DHCHAP authentication in each direction requires a shared secret password between the connected devices. To do this, you can use one of three configurations to manage passwords for all switches in the fabric that participate in DHCHAP:
•![]() Configuration 1—Use the same password for all switches in the fabric. This is the simplest configuration. When you add a new switch, you use the same password to authenticate that switch in this fabric. It is also the most vulnerable configuration if someone from the outside maliciously attempts to access any one switch in the fabric.
Configuration 1—Use the same password for all switches in the fabric. This is the simplest configuration. When you add a new switch, you use the same password to authenticate that switch in this fabric. It is also the most vulnerable configuration if someone from the outside maliciously attempts to access any one switch in the fabric.
•![]() Configuration 2—Use a different password for each switch and maintain that password list in each switch in the fabric. When you add a new switch, you create a new password list and update all switches with the new list. Accessing one switch yields the password list for all switches in that fabric.
Configuration 2—Use a different password for each switch and maintain that password list in each switch in the fabric. When you add a new switch, you create a new password list and update all switches with the new list. Accessing one switch yields the password list for all switches in that fabric.
•![]() Configuration 3—Use different passwords for different switches in the fabric. When you add a new switch, multiple new passwords corresponding to each switch in the fabric must be generated and configured in each switch. Even if one switch is compromised, the password of other switches are still protected. This configuration requires considerable password maintenance by the user.
Configuration 3—Use different passwords for different switches in the fabric. When you add a new switch, multiple new passwords corresponding to each switch in the fabric must be generated and configured in each switch. Even if one switch is compromised, the password of other switches are still protected. This configuration requires considerable password maintenance by the user.

Note ![]() All passwords are restricted to 64 alphanumeric characters and can be changed, but not deleted.
All passwords are restricted to 64 alphanumeric characters and can be changed, but not deleted.

Tip ![]() We recommend using RADIUS or TACACS+ for fabrics with more than five switches. If you need to use a local password database, you can continue to do so using Configuration 3 and using the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager to manage the password database.
We recommend using RADIUS or TACACS+ for fabrics with more than five switches. If you need to use a local password database, you can continue to do so using Configuration 3 and using the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager to manage the password database.
Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for the Local Switch
To configure the DHCHAP password for the local switch using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Expand Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
You see the FC-SP configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Local Passwords tab.
Click the Local Passwords tab.
Step 3 ![]() Click the Create Row icon to create a new local password.
Click the Create Row icon to create a new local password.
You see the Create Local Passwords dialog box.
Step 4 ![]() (Optional) Check the switches that you want to configure the same local password on.
(Optional) Check the switches that you want to configure the same local password on.
Step 5 ![]() Select the switch WNN and fill in the Password field.
Select the switch WNN and fill in the Password field.
Step 6 ![]() Click Create to save the updated password.
Click Create to save the updated password.
About Password Configuration for Remote Devices
You can configure passwords in the local authentication database for other devices in a fabric. The other devices are identified by their device name, which is also known as the switch WWN or device WWN. The password is restricted to 64 characters and can be specified in clear text (0) or in encrypted text (7).

Note ![]() The switch WWN identifies the physical switch. This WWN is used to authenticate the switch and is different from the VSAN node WWN.
The switch WWN identifies the physical switch. This WWN is used to authenticate the switch and is different from the VSAN node WWN.
Configuring DHCHAP Passwords for Remote Devices
To locally configure the remote DHCHAP password for another switch in the fabric using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Right-click an ISL and choose Enable FC-SP from the drop-down list.
Right-click an ISL and choose Enable FC-SP from the drop-down list.
You see the Enable FC-SP dialog box as shown in Figure 23-5.
Figure 23-5 Enable FC-SP Dialog Box
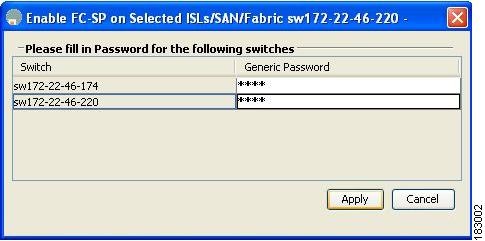
Step 2 ![]() Click Apply to save the updated password.
Click Apply to save the updated password.
About the DHCHAP Timeout Value
During the DHCHAP protocol exchange, if the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch does not receive the expected DHCHAP message within a specified time interval, authentication failure is assumed. The time ranges from 20 (no authentication is performed) to 1000 seconds. The default is 30 seconds.
When changing the timeout value, consider the following factors:
•![]() The existing RADIUS and TACACS+ timeout values.
The existing RADIUS and TACACS+ timeout values.
•![]() The same value must also be configured on all switches in the fabric.
The same value must also be configured on all switches in the fabric.
Configuring the DHCHAP Timeout Value
To configure the DHCHAP timeout value using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
Expand Switches > Security, and then choose FC-SP.
You see the FC-SP configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Click the General/Password tab.
Click the General/Password tab.
You see the DHCHAP general settings mode for each switch as shown in Figure 23-6.
Figure 23-6 General/Password Tab

Step 3 ![]() Change the DHCHAP timeout value for each switch in the fabric.
Change the DHCHAP timeout value for each switch in the fabric.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Apply Changes icon to save the updated information.
Click the Apply Changes icon to save the updated information.
Configuring DHCHAP AAA Authentication
You can configure AAA authentication to use a RADIUS or TACACS+ server group. If AAA authentication is not configured, local authentication is used by default.
To configure the AAA authentication, see the Cisco Cisco Nexus 5000 Series CLI Configuration Guide.
Enabling FC-SP on ISLs
There is an ISL pop-up menu in Fabric Manager called Enable FC-SP that enables FC-SP on switches at either end of the ISL. You are prompted for an FC-SP generic password, then asked to set FC-SP interface mode to On for affected ports. Right-click an ISL and click Enable FC-SP to access this feature.
Default Settings
Table 23-2 lists the default settings for all fabric security features in any switch.
 Feedback
Feedback