- Preface
- Product Overview
- Installing Cisco Fabric Manager
- Fabric Manager Server
- Authentication in Fabric Manager
- Fabric Manager Client
- Device Manager
- Using Cisco Fabric Services
- Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring Virtual Interfaces
- Configuring Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Configuring N-Port Virtualization
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring VSAN Trunking
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Configuring SPAN
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Configuring SAN PortChannels
- Advanced Features and Concepts
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Network Monitoring
- Performance Manager
- Nexus 5000 Management Software FAQ
- Troubleshooting Your Fabric
- Index
- Information About VSANs
- Configuring VSANs
- About VSAN Creation
- Creating VSANs Statically
- About Port VSAN Membership
- Assigning Static Port VSAN Membership
- About the Default VSAN
- About the Isolated VSAN
- Displaying Isolated VSAN Membership
- Operational State of a VSAN
- About Static VSAN Deletion
- Deleting Static VSANs
- About Load Balancing
- Configuring Load Balancing
- About Interop Mode
- Default Settings
Configuring and Managing VSANs
You can achieve higher security and greater stability in Fibre Channel fabrics by using virtual SANs (VSANs). VSANs provide isolation among devices that are physically connected to the same fabric. With VSANs you can create multiple logical SANs over a common physical infrastructure. Each VSAN can contain up to 239 switches and has an independent address space that allows identical Fibre Channel IDs (FC IDs) to be used simultaneously in different VSANs. This chapter includes the following sections:
Information About VSANs
A VSAN is a virtual storage area network (SAN). A SAN is a dedicated network that interconnects hosts and storage devices primarily to exchange SCSI traffic. In SANs you use the physical links to make these interconnections. A set of protocols run over the SAN to handle routing, naming, and zoning. You can design multiple SANs with different topologies.
This section describes VSANs and includes the following topics:
VSAN Topologies
With the introduction of VSANs, the network administrator can build a single topology containing switches, links, and one or more VSANs. Each VSAN in this topology has the same operation and property of a SAN. A VSAN has the following additional features:
•![]() Multiple VSANs can share the same physical topology.
Multiple VSANs can share the same physical topology.
•![]() The same Fibre Channel IDs (FC IDs) can be assigned to a host in another VSAN, which increases VSAN scalability.
The same Fibre Channel IDs (FC IDs) can be assigned to a host in another VSAN, which increases VSAN scalability.
•![]() Every instance of a VSAN runs all required protocols such as FSPF, domain manager, and zoning.
Every instance of a VSAN runs all required protocols such as FSPF, domain manager, and zoning.
•![]() Fabric-related configurations in one VSAN do not affect the associated traffic in another VSAN.
Fabric-related configurations in one VSAN do not affect the associated traffic in another VSAN.
•![]() Events causing traffic disruptions in one VSAN are contained within that VSAN and are not propagated to other VSANs.
Events causing traffic disruptions in one VSAN are contained within that VSAN and are not propagated to other VSANs.
Figure 15-1 shows a fabric with three switches, one on each floor. The geographic location of the switches and the attached devices is independent of their segmentation into logical VSANs. No communication between VSANs is possible. Within each VSAN, all members can talk to one another.
Figure 15-1 Logical VSAN Segmentation
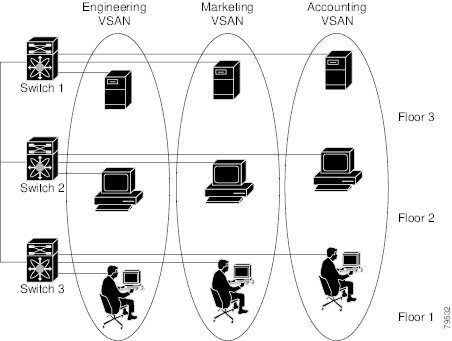
Figure 15-2 shows a physical Fibre Channel switching infrastructure with two defined VSANs: VSAN 2 (dashed) and VSAN 7 (solid). VSAN 2 includes hosts H1 and H2, application servers AS2 and AS3, and storage arrays SA1 and SA4. VSAN 7 connects H3, AS1, SA2, and SA3.
The application servers or storage arrays can be connected to the switch using Fibre Channel or virtual Fibre Channel interfaces. A VSAN can include a mixture of Fibre Channel and virtual Fibre Channel interfaces.
Figure 15-2 Example of Two VSANs

The four switches in this network are interconnected by VSAN trunk links that carry both VSAN 2 and
VSAN 7 traffic. You can configure a different inter-switch topology for each VSAN. In Figure 15-2, the inter-switch topology is identical for VSAN 2 and VSAN 7.
Without VSANs, a network administrator would need separate switches and links for separate SANs. By enabling VSANs, the same switches and links may be shared by multiple VSANs. VSANs allow SANs to be built on port granularity instead of switch granularity. Figure 15-2 illustrates that a VSAN is a group of hosts or storage devices that communicate with each other using a virtual topology defined on the physical SAN.
The criteria for creating such groups differ based on the VSAN topology:
•![]() VSANs can separate traffic based on the following requirements:
VSANs can separate traffic based on the following requirements:
–![]() Different customers in storage provider data centers
Different customers in storage provider data centers
–![]() Production or test in an enterprise network
Production or test in an enterprise network
–![]() Low and high security requirements
Low and high security requirements
–![]() Backup traffic on separate VSANs
Backup traffic on separate VSANs
–![]() Replicating data from user traffic
Replicating data from user traffic
•![]() VSANs can meet the needs of a particular department or application.
VSANs can meet the needs of a particular department or application.
VSAN Advantages
VSANs offer the following advantages:
•![]() Traffic isolation—Traffic is contained within VSAN boundaries and devices reside only in one VSAN ensuring absolute separation between user groups, if desired.
Traffic isolation—Traffic is contained within VSAN boundaries and devices reside only in one VSAN ensuring absolute separation between user groups, if desired.
•![]() Scalability—VSANs are overlaid on top of a single physical fabric. The ability to create several logical VSAN layers increases the scalability of the SAN.
Scalability—VSANs are overlaid on top of a single physical fabric. The ability to create several logical VSAN layers increases the scalability of the SAN.
•![]() Per VSAN fabric services—Replication of fabric services on a per VSAN basis provides increased scalability and availability.
Per VSAN fabric services—Replication of fabric services on a per VSAN basis provides increased scalability and availability.
•![]() Redundancy—Several VSANs created on the same physical SAN ensure redundancy. If one VSAN fails, redundant protection (to another VSAN in the same physical SAN) is configured using a backup path between the host and the device.
Redundancy—Several VSANs created on the same physical SAN ensure redundancy. If one VSAN fails, redundant protection (to another VSAN in the same physical SAN) is configured using a backup path between the host and the device.
•![]() Ease of configuration—Users can be added, moved, or changed between VSANs without changing the physical structure of a SAN. Moving a device from one VSAN to another only requires configuration at the port level, not at a physical level.
Ease of configuration—Users can be added, moved, or changed between VSANs without changing the physical structure of a SAN. Moving a device from one VSAN to another only requires configuration at the port level, not at a physical level.
Up to 256 VSANs can be configured in a switch. Of these, one is a default VSAN (VSAN 1), and another is an isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094). User-specified VSAN IDs range from 2 to 4093.
VSANs Versus Zones
Zones are always contained within a VSAN. You can define multiple zones in a VSAN.
Because two VSANs are equivalent to two unconnected SANs, zone A on VSAN 1 is different and separate from zone A in VSAN 2. Table 15-1 lists the differences between VSANs and zones.
Figure 15-3 shows the possible relationships between VSANs and zones. In VSAN 2, three zones are defined: zone A, zone B, and zone C. Zone C overlaps both zone A and zone B as permitted by Fibre Channel standards. In VSAN 7, two zones are defined: zone A and zone D. No zone crosses the VSAN boundary. Zone A defined in VSAN 2 is different and separate from zone A defined in VSAN 7.
Figure 15-3 VSANS with Zoning
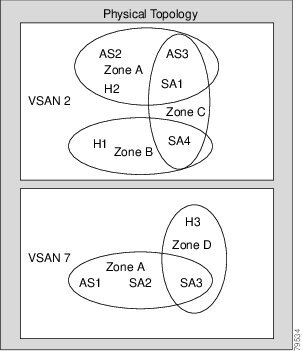
Configuring VSANs
VSANs have the following attributes:
•![]() VSAN ID—The VSAN ID identifies the VSAN as the default VSAN (VSAN 1), user-defined VSANs (VSAN 2 to 4093), and the isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094).
VSAN ID—The VSAN ID identifies the VSAN as the default VSAN (VSAN 1), user-defined VSANs (VSAN 2 to 4093), and the isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094).
•![]() State—The administrative state of a VSAN can be configured to an active (default) or suspended state. Once VSANs are created, they may exist in various conditions or states.
State—The administrative state of a VSAN can be configured to an active (default) or suspended state. Once VSANs are created, they may exist in various conditions or states.
–![]() The active state of a VSAN indicates that the VSAN is configured and enabled. By enabling a VSAN, you activate the services for that VSAN.
The active state of a VSAN indicates that the VSAN is configured and enabled. By enabling a VSAN, you activate the services for that VSAN.
–![]() The suspended state of a VSAN indicates that the VSAN is configured but not enabled. If a port is configured in this VSAN, it is disabled. Use this state to deactivate a VSAN without losing the VSAN's configuration. All ports in a suspended VSAN are disabled. By suspending a VSAN, you can preconfigure all the VSAN parameters for the whole fabric and activate the VSAN immediately.
The suspended state of a VSAN indicates that the VSAN is configured but not enabled. If a port is configured in this VSAN, it is disabled. Use this state to deactivate a VSAN without losing the VSAN's configuration. All ports in a suspended VSAN are disabled. By suspending a VSAN, you can preconfigure all the VSAN parameters for the whole fabric and activate the VSAN immediately.
•![]() VSAN name—This text string identifies the VSAN for management purposes. The name can be from 1 to 32 characters long and it must be unique across all VSANs. By default, the VSAN name is a concatenation of VSAN and a four-digit string representing the VSAN ID. For example, the default name for VSAN 3 is VSAN0003.
VSAN name—This text string identifies the VSAN for management purposes. The name can be from 1 to 32 characters long and it must be unique across all VSANs. By default, the VSAN name is a concatenation of VSAN and a four-digit string representing the VSAN ID. For example, the default name for VSAN 3 is VSAN0003.

Note ![]() A VSAN name must be unique.
A VSAN name must be unique.
•![]() Load-balancing attributes—These attributes indicate the use of the source-destination ID (src-dst-id) or the originator exchange OX ID (src-dst-ox-id, the default) for load-balancing path selection.
Load-balancing attributes—These attributes indicate the use of the source-destination ID (src-dst-id) or the originator exchange OX ID (src-dst-ox-id, the default) for load-balancing path selection.
This section describes how to create and configure VSANs and includes the following topics:
•![]() Assigning Static Port VSAN Membership
Assigning Static Port VSAN Membership
•![]() Displaying Isolated VSAN Membership
Displaying Isolated VSAN Membership
About VSAN Creation
A VSAN is in the operational state if the VSAN is active and at least one port is up. This state indicates that traffic can pass through this VSAN. This state cannot be configured.
Creating VSANs Statically
You cannot configure any application-specific parameters for a VSAN before creating the VSAN.
To create and configure VSANs using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Click the Create VSAN icon (see Figure 15-4).
Click the Create VSAN icon (see Figure 15-4).
Figure 15-4 Create VSAN Icon
You see the Create VSAN dialog box as shown in Figure 15-5.
Figure 15-5 Create VSAN Dialog Box


Note ![]() If you check the Static Domain IDs check box, Fabric Manager creates the VSAN in suspended mode and then automatically activates the VSAN.
If you check the Static Domain IDs check box, Fabric Manager creates the VSAN in suspended mode and then automatically activates the VSAN.
Step 2 ![]() Check the switches that you want in this VSAN.
Check the switches that you want in this VSAN.
Step 3 ![]() Fill in the VSAN Name and VSAN ID fields.
Fill in the VSAN Name and VSAN ID fields.
Step 4 ![]() Set the LoadBalancing value and the InterOperValue.
Set the LoadBalancing value and the InterOperValue.
Step 5 ![]() Set the Admin State to active or suspended.
Set the Admin State to active or suspended.
Step 6 ![]() Check the Static Domain Ids check box to assign an unused static domain ID to the VSAN.
Check the Static Domain Ids check box to assign an unused static domain ID to the VSAN.
Step 7 ![]() (Optional) Check the Enable Fabric Binding for Selected Switches options if you want this feature enabled.
(Optional) Check the Enable Fabric Binding for Selected Switches options if you want this feature enabled.
See Chapter 25, "Configuring Fabric Binding" for details.
Step 8 ![]() Complete the fields in this dialog box and click Create to add the VSAN or click Close.
Complete the fields in this dialog box and click Create to add the VSAN or click Close.
About Port VSAN Membership
Port VSAN membership on the switch is assigned on a port-by-port basis. By default each port belongs to the default VSAN. You can assign VSAN membership to ports using one of two methods:
•![]() Statically—Assigning VSANs to ports.
Statically—Assigning VSANs to ports.
See the "Assigning Static Port VSAN Membership" section.
•![]() Dynamically—Assigning VSANs based on the device WWN. This method is referred to as dynamic port VSAN membership (DPVM). Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches do not support DPVM.
Dynamically—Assigning VSANs based on the device WWN. This method is referred to as dynamic port VSAN membership (DPVM). Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches do not support DPVM.
VSAN trunking ports have an associated list of VSANs that are part of an allowed list (see Chapter 13, "Configuring VSAN Trunking").
Assigning Static Port VSAN Membership
To statically assign VSAN membership for an interface using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() In the Physical Attributes pane, expand Switches > Interfaces and then choose FC Physical.
In the Physical Attributes pane, expand Switches > Interfaces and then choose FC Physical.
You see the interface configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Choose the General tab.
Choose the General tab.
You see the Fibre Channel general physical information. Enter the new VSAN in the PortVSAN field.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save these changes, or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
Click Apply Changes to save these changes, or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
About the Default VSAN
The factory settings for switches in the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series have only the default VSAN 1 enabled. We recommend that you do not use VSAN 1 as your production environment VSAN. If no VSANs are configured, all devices in the fabric are considered part of the default VSAN. By default, all ports are assigned to the default VSAN.

Note ![]() VSAN 1 cannot be deleted, but it can be suspended.
VSAN 1 cannot be deleted, but it can be suspended.

Note ![]() Up to 256 VSANs can be configured in a switch. Of these, one is a default VSAN (VSAN 1), and another is an isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094). User-specified VSAN IDs range from 2 to 4093.
Up to 256 VSANs can be configured in a switch. Of these, one is a default VSAN (VSAN 1), and another is an isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094). User-specified VSAN IDs range from 2 to 4093.
About the Isolated VSAN
VSAN 4094 is an isolated VSAN. When a VSAN is deleted, all nontrunking ports are transferred to the isolated VSAN to avoid an implicit transfer of ports to the default VSAN or to another configured VSAN. This action ensures that all ports in the deleted VSAN become isolated (disabled).

Note ![]() When you configure a port in VSAN 4094 or move a port to VSAN 4094, that port is immediately isolated.
When you configure a port in VSAN 4094 or move a port to VSAN 4094, that port is immediately isolated.


Note ![]() Up to 256 VSANs can be configured in a switch. Of these, one is a default VSAN (VSAN 1), and another is an isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094). User-specified VSAN IDs range from 2 to 4093.
Up to 256 VSANs can be configured in a switch. Of these, one is a default VSAN (VSAN 1), and another is an isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094). User-specified VSAN IDs range from 2 to 4093.
Displaying Isolated VSAN Membership
To display interfaces that exist in the isolated VSAN using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Fabricxx, and then choose All VSANs in the Logical Domains pane.
Expand Fabricxx, and then choose All VSANs in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the VSAN configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Isolated Interfaces tab.
Click the Isolated Interfaces tab.
You see the interfaces that are in the isolated VSAN.
Operational State of a VSAN
A VSAN is in the operational state if the VSAN is active and at least one port is up. This state indicates that traffic can pass through this VSAN. This state cannot be configured.
About Static VSAN Deletion
When an active VSAN is deleted, all of its attributes are removed from the running configuration. VSAN-related information is maintained by the system software as follows:
•![]() VSAN attributes and port membership details are maintained by the VSAN manager. This feature is affected when you delete a VSAN from the configuration. When a VSAN is deleted, all the ports in that VSAN are made inactive and the ports are moved to the isolated VSAN. If the same VSAN is recreated, the ports do not automatically get assigned to that VSAN. You must explicitly reconfigure the port VSAN membership (see Figure 15-6).
VSAN attributes and port membership details are maintained by the VSAN manager. This feature is affected when you delete a VSAN from the configuration. When a VSAN is deleted, all the ports in that VSAN are made inactive and the ports are moved to the isolated VSAN. If the same VSAN is recreated, the ports do not automatically get assigned to that VSAN. You must explicitly reconfigure the port VSAN membership (see Figure 15-6).
Figure 15-6 VSAN Port Membership Details
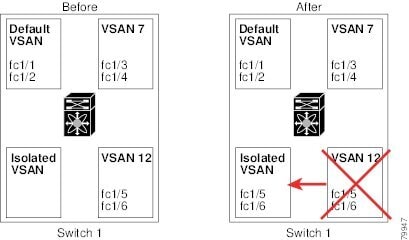
•![]() VSAN-based runtime (name server), zoning, and configuration (static routes) information is removed when the VSAN is deleted.
VSAN-based runtime (name server), zoning, and configuration (static routes) information is removed when the VSAN is deleted.
•![]() Configured VSAN interface information is removed when the VSAN is deleted.
Configured VSAN interface information is removed when the VSAN is deleted.

Note ![]() The allowed VSAN list is not affected when a VSAN is deleted (see Chapter 13, "Configuring VSAN Trunking").
The allowed VSAN list is not affected when a VSAN is deleted (see Chapter 13, "Configuring VSAN Trunking").
Any commands for a nonconfigured VSAN are rejected. For example, if VSAN 10 is not configured in the system, then a command request to move a port to VSAN 10 is rejected.
Deleting Static VSANs
To delete a VSAN and its attributes using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Click All VSANs from the Logical Domains pane.
Click All VSANs from the Logical Domains pane.
The VSANs in the fabric are listed in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Right-click the VSAN that you want to delete and click Delete Row from the drop-down menu (see Figure 15-7).
Right-click the VSAN that you want to delete and click Delete Row from the drop-down menu (see Figure 15-7).
Figure 15-7 Deleting a VSAN

You see a confirmation dialog box.
Step 3 ![]() Click Yes to confirm the deletion or No to close the dialog box without deleting the VSAN.
Click Yes to confirm the deletion or No to close the dialog box without deleting the VSAN.
About Load Balancing
Load-balancing attributes indicate the use of the source-destination ID (src-dst-id) or the originator exchange OX ID (src-dst-ox-id, the default) for load-balancing path selection.
Configuring Load Balancing
To configure load balancing on an existing VSAN using Fabric Manager, perform this task:
Step 1 ![]() Choose Fabricxx > All VSANs from the Logical Domains pane.
Choose Fabricxx > All VSANs from the Logical Domains pane.
You see the VSAN configuration in the Information pane as shown in Figure 15-8.
Figure 15-8 All VSAN Attributes

Step 2 ![]() Click a VSAN and complete the LoadBalancing field.
Click a VSAN and complete the LoadBalancing field.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save these changes, or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
Click Apply Changes to save these changes, or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
About Interop Mode
Interoperability enables the products of multiple vendors to connect with each other. Fibre Channel standards guide vendors to create common external Fibre Channel interfaces. For additional information, see the "Switch Interoperability" section on page 22-7.
Default Settings
Table 15-2 lists the default settings for all configured VSANs.
 Feedback
Feedback