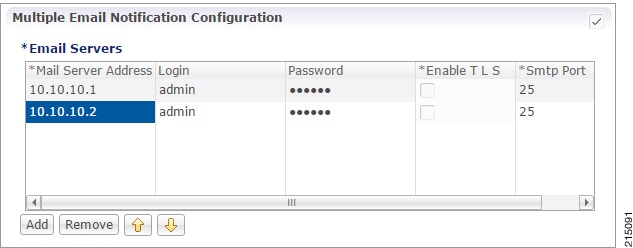
Apple Push Notifications
Notification Configuration
To configure CPS to send a message to a subscriber with an Apple iPhone or other iOS device, perform the following steps.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Log in to Policy Builder. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Go to . |
||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Click the check box next to Apple Push Notification Configuration. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
View the Notification Configuration screen. The following parameters can be configured under Apple Push Notification Configuration:
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Go to Message Configuration to configure the message to be sent for the notification configuration done above. |
Message Configuration
To create the messages for a subscriber’s Apple iPhone or the Apple iOS operating system to be sent by CPS, perform the following steps.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Select . |
||||||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
From right side, click Apple Push Notification under Create Child to open the pane.  The following parameters can be configured under Apple Push Notification:
To use Apple Push Notifications, you need to configure Service Options. For more information on the configuration, see #id_13242. |













 Feedback
Feedback