-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Fabric Manager Applications
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Configuration Files
-
Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Cisco Fabric Services
-
VSAN Configuration
-
Dynamic VSAN Configuration
-
Zone Configuration
-
Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
-
PortChannel Configuration
-
Interface Configuration
-
FCIP Configuration
-
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
-
iSCSI configuration
-
FICON Configuration
-
Configuring Intelligent Storage Services
-
Additional Configuration
-
- Part 4 - Security Configuration
- Part 5 - Network and Performance Monitoring
- Part 6 - Troubleshooting
-
GUI/CLI Usage Chart
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Table Of Contents
Performance Manager Architecture
Quick Data Collector and Flow Setup Wizards
Performance Manager
The primary purpose of Fabric Manager is to manage the network. A key management capability is network performance monitoring.
This chapter contains the following section:
•
Performance Manager Architecture
Performance Manager Architecture
Performance Manager gathers network device statistics historically and provides this information graphically using a web browser. It presents recent statistics in detail and older statistics in summary. Performance Manager also integrates with external tools such as Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
The Performance Manager has three operational stages:
•
Definition—Uses two configuration wizards. The Flow Wizard sets up flows in the switches while the Collection Wizard create a collection configuration file.
•
Collection—Reads the configuration file and collects the desired information.
•
Presentation—Generates web pages to present the collected data.
Performance Manager can collect statistics for ISLs, hosts, storage elements, and configured flows. Flows are defined based on a host-to-storage (or storage-to-host) link. Performance Manager gathers statistics from across the fabric based on collection configuration files. These files determine which SAN elements and SAN links Performance Manager gathers statistics for. Based on this configuration, Performance Manager communicates with the appropriate devices (switches, hosts, or storage elements) and collects the appropriate information at fixed five-minute intervals.
Performance Manager uses a round-robin database to hold the statistical data collected from the fabric. This data is stored based on the configured parameters in the collection configuration file. At each polling interval, Performance Manager gathers the relevant statistics and stores them in the round-robin database. This database is a fixed size and will not grow beyond its preset limits.
Performance Manager creates a series of archived data to hold summarized information present in the real-time round-robin database. This archived data is used to generate daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly consolidated reports. In this way, Performance Manager maintains significant historical data without the cost of an ever-increasing database size.
Data Interpolation
One of the unique features of Performance Manager is its ability to interpolate data when statistical polling results are missing or delayed. Other performance tools may store the missing data point as zero, but this can distort historical trending. Performance Manager interpolates the missing data point by comparing the data point that preceded the missing data and the data point stored in the polling interval after the missing data. This maintains the continuity of the performance information.
Data Collection
One year's worth of data for two variables (Rx and Tx bytes) requires a round-robin database (rrd) file size of 76K. If errors and discards are also collected, the rrd file size becomes 110K. The default internal values are:
•
600 samples of 5 minutes (2 days and 2 hours)
•
700 samples of 30 minutes (2 days and 2 hours, plus 12.5 days)
•
775 samples of 2 hours (above plus 50 days)
•
300 samples of 1 day (above plus300 days, rounded up to 365)
A 1000-port SAN requires 110 MB for a year's worth of historical data that includes errors and discards. If there were 20 switches in this SAN with equal distribution of fabric ports, about two to three SNMP packets per switch would be sent every 5 minutes for a total of about 100 request or response SNMP packets required to monitor the data.
Flows, because of their variable counter requests, are more difficult to predict storage space requirements for. But as a rule of thumb, each extra flow adds another 76 kB.
The Performance Manager collector runs as a background process on the various supported operating systems. On Microsoft Windows, it runs as a service.
Using Performance Thresholds
The Performance Manager Configuration Wizard allows you to set up two thresholds that will trigger events when the monitored traffic exceeds the percent utilization configured. These event triggers can be set as either Critical or Warning events that are reported on the Fabric Manager web client Events browser page.
Absolute value thresholds apply directly to the statistics gathered. These statistics, as a percent of the total link capacity, are compared to the percent utilization configured for the threshold type. If the statistics exceed either configured threshold, an event is shown on the Fabric Manager web client Events tab.
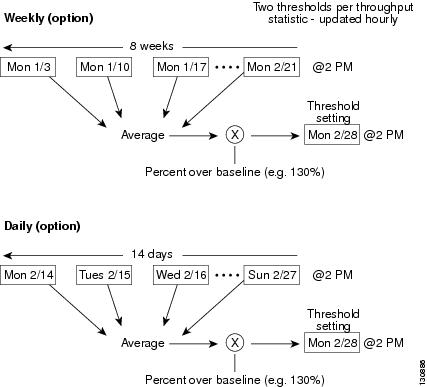
Baseline thresholds create a threshold that adapts to the typical traffic pattern for each link for the same time window each day, week, or every two weeks. Baseline thresholds are set as a percent of the average (110% to 500%), where 100% equals the calculated weighted average. Figure 6-1 shows an example of setting a baseline threshold for a weekly or daily option.
Figure 6-1 Baseline Threshold Example
The threshold is set for Monday at 2 PM. The baseline threshold is set at 130% of the average for that statistic. The average is calculated from the statistics value that occurred at 2PM on Monday, for every prior Monday (for the weekly option) or the statistics value that occurred at 2PM on each day, for every prior day (for the daily option).
Quick Data Collector and Flow Setup Wizards
The Performance Manager Flow and Performance Manager Setup wizards greatly simplify configuration. All you need to do is select the categories of statistics to capture and the wizards provide a list of flows and links to monitor. You can remove entries if desired, or just accept the provided list and start data collection. Statistics for host and storage links are not associated with a specific port on a switch, so you do not lose long term statistics if a connection is moved to a different port.

 Feedback
Feedback