-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Fabric Manager Applications
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Configuration Files
-
Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Cisco Fabric Services
-
VSAN Configuration
-
Dynamic VSAN Configuration
-
Zone Configuration
-
Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
-
PortChannel Configuration
-
Interface Configuration
-
FCIP Configuration
-
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
-
iSCSI configuration
-
FICON Configuration
-
Configuring Intelligent Storage Services
-
Additional Configuration
-
- Part 4 - Security Configuration
- Part 5 - Network and Performance Monitoring
- Part 6 - Troubleshooting
-
GUI/CLI Usage Chart
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
Using the SAN Extension Tuner Wizard
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
The SAN extension tuner is unique to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family of switches. This feature helps you optimize FCIP performance by generating SCSI I/O commands and directing such traffic to a specific virtual target. You can specify the size of the test I/O transfers and how many concurrent I/Os to generate while testing. The SAN extension tuner reports the resulting I/Os per second (IOPS) and I/O latency, which helps you determine the number of concurrent I/Os needed to maximize FCIP throughput.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
About the SAN Extension Tuner
•
Using the SAN Extension Tuner Wizard
About the SAN Extension Tuner
Applications such as remote copy and data backup use FCIP over an IP network to connect across geographically distributed SANs. To achieve maximum throughput performance across the fabric, you can tune the following configuration parameters:
•
The TCP parameters for the FCIP profile.
•
The number of concurrent SCSI I/Os generated by the application.
•
The transfer size used by the application over an FCIP link.
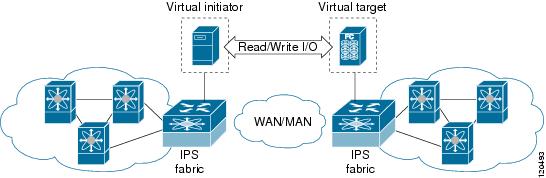
SAN extension tuner is implemented in IPS ports. This feature can generate SCSI I/O commands (read and write) to the virtual target based on your configured options (see Figure 21-1).
Figure 21-1 SCSI Command Generation to the Virtual Target
The SAN extension tuner assists with tuning by generating varying SCSI traffic workloads. It also measures throughput and response time per I/ O over an FCIP link.
SAN Extension Tuner Setup
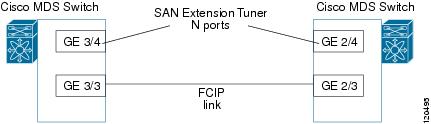
Figure 21-2 provides a sample physical setup in which the virtual N ports are created on ports that are not a part of the FCIP link for which the throughput and latency is measured.
Figure 21-2 N Port Tuning Configuration Example
Data Pattern
By default, the virtual N ports generate data using an all-zero pattern. You can optionally select a file as the data pattern to be generated one of three locations: the bootflash: directory, the volatile: directory, or the slot0: directory. This option is especially useful when testing compression over FCIP links. You can also use Canterbury corpus or artificial corpus files for benchmarking purposes.
Prerequisites
To use the SAN extension tuner, you need to obtain the SAN_EXTN_OVER_IP license (see Chapter 9, "Obtaining and Installing Licenses").
Note
Both switches on an FCIP link must have Cisco MDS SAN-OS 2.1(2) or later to use the SAN extension tuner in Fabric Manager.
Using the SAN Extension Tuner Wizard
To tune the required FCIP link using the SAN Extension Tuner Wizard in Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Right-click on the required FCIP link in the Map pane and choose SAN Extension Tuner from the popup menu, or highlight the link and choose Tools > Other > SAN Extension Tuner. You see the SAN Extension Tuner Wizard.
Step 2
Select the Ethernet port pairs that correspond to the FCIP link you want to tune and click Next.
Note
The Ethernet ports you select should be listed as down.
Step 3
Create and activate a new zone to ensure that the virtual N ports are not visible to real initiators in the SAN by clicking Yes to the zone creation dialog box.
Step 4
Optionally, change the default settings for the transfer data size, and number of concurrent SCSI read and write commands as follows:
a.
Set Transfer Size to the number of bytes that you expect your applications to use over the FCIP link.
b.
Set Read I/0 to the number of concurrent SCSI read commands you expect your applications to generate over the FCIP link.
c.
Set Write I/0 to the number of concurrent outstanding SCSI write commands you expect your applications to generate over the FCIP link.
d.
Check the Use Pattern File check box and select a file that you want to use to set the data pattern that is generated by the SAN extension tuner. See the "Data Pattern" section.
Step 5
Click Next.
Step 6
Click Start to start the tuner. The tuner sends a continuous stream of traffic until you select Stop.
Step 7
Click Show to see the latest tuning statistics. You can select this while the tuner is running or after you stop it.
Step 8
Click Stop to stop the SAN extension tuner.

 Feedback
Feedback