Cisco Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance Deployment
Information About the ASAv
The ASAv brings full firewall functionality to virtualized environments to secure data center traffic and multi-tenant environments. The ASAv runs on VMware vSphere.
You can manage and monitor the ASAv using the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or CLI.
VMware System Requirements
Before deploying the ASAv, you must install the following components from VMware vSphere 5.x:
See the VMware documentation for more information about vSphere and hardware requirements:
http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs/

Note![]() You cannot install the ASAv directly on an ESXi host without using vCenter.
You cannot install the ASAv directly on an ESXi host without using vCenter.
You cannot deploy the ASAv using vCloud Director.
VMware Feature Support for the ASAv
Table 1 lists the VMware feature support for the ASAv.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Used for dynamic resource scheduling and distributed power management. |
|||
Prerequisites for the ASAv
Security Policy for a vSphere Standard Switch
For a vSphere switch, you can edit Layer 2 security policies and apply security policy exceptions for port groups used by the ASAv interfaces. See the following default settings:
You may need to modify these settings for the following ASAv configurations:
|
|
|
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guidelines and Limitations for the ASAv
Supported in single context mode only. Does not support multiple context mode.
Supported in routed and transparent firewall mode.
For failover deployments, make sure that the standby unit has the same number of vCPUs assigned to it as the primary unit (along with matching vCPU licenses).
- Supports IPv6.
- You cannot specify IPv6 addresses for the management interface when you first deploy the ASAv OVA file using the VMware vSphere Web Client; you can later add IPv6 addressing using ASDM or the CLI.
The ASAv does not support the following ASA features:
- Clustering
- Multiple context mode
- Active/Active failover
- EtherChannels
- Shared AnyConnect Premium Licenses
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
- The ASAv OVA deployment does not support localization (installing the components in non-English mode). Be sure that the VMware vCenter and the LDAP servers in your environment are installed in an ASCII-compatible mode.
- You must set your keyboard to United States English before installing the ASAv and for using the VM console.
- The memory allocated to the ASAv is sized specifically for the number of vCPUs you choose when you deploy. Do not change the memory setting in the Edit Settings dialog box unless you are requesting a license for a different number of vCPUs. Under-provisioning can affect performance, and over-provisioning causes the ASAv to warn you that it will reload; after a waiting period (24 hours for 100-125% over-provisioning; 1 hour for 125% and up), the ASAv will reload. Note: If you need to change the memory, use only the values documented in the ASAv licensing section. Do not use the VMware-recommended memory configuration minimum, default, and maximum values.
- Do not alter any vCPU hardware settings in vSphere unless you are requesting a license for a different number of vCPUs, in which case you must change the vCPU Limit value; otherwise, the correct settings are implemented when you deploy the ASAv. If you change these settings on the Edit Settings dialog box, then under-provisioning can affect performance, and over-provisioning causes the ASAv to warn you that it will reload; after a waiting period (24 hours for 100-125% over-provisioning; 1 hour for 125% and up), the ASAv will reload. Use the ASDM Home > Device Dashboard > Device Information > Virtual Resources tab or the Monitoring > Properties > System Resources Graphs > CPU pane to view the resource allocation and any resources that are over- or under-provisioned.
- During ASAv deployment, if you have a host cluster, you can either provision storage locally (on a specific host) or on a shared host. However, if you try to vMotion the ASAv to another host, using any kind of storage (SAN or local) causes an interruption in connectivity.
- If you are running ESXi 5.0:
–![]() The vSphere Web Client is not supported for ASAv OVA deployment; use the vSphere client instead.
The vSphere Web Client is not supported for ASAv OVA deployment; use the vSphere client instead.
–![]() Deployment fields might be duplicated; fill out the first instance of any given field and ignore the duplicated fields.
Deployment fields might be duplicated; fill out the first instance of any given field and ignore the duplicated fields.
Licensing Requirements for the ASAv

Note![]() You must install a Virtual CPU license on the ASAv. Until you install a license, throughput is limited to 100 Kbps so you can perform preliminary connectivity tests. A Virtual CPU license is required for regular operation.
You must install a Virtual CPU license on the ASAv. Until you install a license, throughput is limited to 100 Kbps so you can perform preliminary connectivity tests. A Virtual CPU license is required for regular operation.
Deploying the ASAv
- Accessing the vSphere Web Client and Installing the Client Integration Plug-In
- Deploying the ASAv Using the VMware vSphere Web Client
Accessing the vSphere Web Client and Installing the Client Integration Plug-In
This section describes how to access the vSphere Web Client. This section also describes how to install the Client Integration Plug-In, which is required for ASAv console access. Some Web Client features (including the plug-in) are not supported on the Macintosh. See the VMware website for complete client support information.
You can also choose to use the standalone vSphere Client, but this guide only describes the Web Client.
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Launch the VMware vSphere Web Client from your browser:
Launch the VMware vSphere Web Client from your browser:
https:// vCenter_server : port /vsphere-client/
Step 2![]() (One time only) Install the Client Integration Plug-in so you can access the ASAv console.
(One time only) Install the Client Integration Plug-in so you can access the ASAv console.
a.![]() On the sign-on screen, download the plug-in by clicking Download the Client Integration Plug-in.
On the sign-on screen, download the plug-in by clicking Download the Client Integration Plug-in.

b.![]() Close your browser and then install the plug-in using the installer.
Close your browser and then install the plug-in using the installer.
c.![]() After the plug-in installs, reconnect to the vSphere Web Client.
After the plug-in installs, reconnect to the vSphere Web Client.
Step 3![]() Enter your username and password, and click Login, or check the Use Windows session authentication check box (Windows only).
Enter your username and password, and click Login, or check the Use Windows session authentication check box (Windows only).
Deploying the ASAv Using the VMware vSphere Web Client
To deploy the ASAv, use the VMware vSphere Web Client (or the vSphere Client) and a template file in the open virtualization format (OVF); note that for the ASAv, the OVF package is provided as a single open virtual appliance (OVA) file. You use the Deploy OVF Template wizard in the vSphere Web Client to deploy the Cisco package for the ASAv. The wizard parses the ASAv OVA file, creates the virtual machine on which you will run the ASAv, and installs the package.
Most of the wizard steps are standard for VMware. For additional information about the Deploy OVF Template, see the VMware vSphere Web Client online help.
Prerequisites
You must have at least one network configured in vSphere (for management) before you deploy the ASAv.
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Download the ASAv OVA file from Cisco.com, and save it to your PC:
Download the ASAv OVA file from Cisco.com, and save it to your PC:
http://www.cisco.com/go/asa-software

Note![]() A Cisco.com login and Cisco service contract are required.
A Cisco.com login and Cisco service contract are required.
Step 2![]() In the vSphere Web Client Navigator pane, click vCenter.
In the vSphere Web Client Navigator pane, click vCenter.
Step 3![]() Click Hosts and Cluster
Click Hosts and Cluster![]() s.
s.
Step 4![]() Right-click the data center, cluster, or host where you want to deploy the ASAv, and choose Deploy OVF Template.
Right-click the data center, cluster, or host where you want to deploy the ASAv, and choose Deploy OVF Template.

The Deploy OVF Template wizard appears.
Step 5![]() In the Select Source screen, enter a URL or browse to the ASAv OVA package that you downloaded, then click Next.
In the Select Source screen, enter a URL or browse to the ASAv OVA package that you downloaded, then click Next.
Step 6![]() In the Review Details screen, review the information for the ASAv package, then click Next.
In the Review Details screen, review the information for the ASAv package, then click Next.
Step 7![]() In the Accept EULAs screen, review and accept the End User License Agreement, then click Next.
In the Accept EULAs screen, review and accept the End User License Agreement, then click Next.
Step 8![]() In the Select name and folder screen, enter a name for the ASAv virtual machine (VM) instance, select the inventory location for the VM, and then click Next.
In the Select name and folder screen, enter a name for the ASAv virtual machine (VM) instance, select the inventory location for the VM, and then click Next.
Step 9![]() In the Select Configuration screen, choose one of the following options:
In the Select Configuration screen, choose one of the following options:
Step 10![]() In the Select Storage screen:
In the Select Storage screen:
a.![]() Choose the virtual disk format. The available formats for provisioning are Thick Provision, Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed, and Thin Provision. For more information about thick and thin provisioning, see the VMware vSphere Web Client online help. To conserve disk space, choose the Thin Provision option.
Choose the virtual disk format. The available formats for provisioning are Thick Provision, Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed, and Thin Provision. For more information about thick and thin provisioning, see the VMware vSphere Web Client online help. To conserve disk space, choose the Thin Provision option.
b.![]() Select the datastore on which you want to run the ASAv.
Select the datastore on which you want to run the ASAv.
Step 11![]() In the Setup networks screen, map a network to each ASAv interface that you want to use, then click Next.
In the Setup networks screen, map a network to each ASAv interface that you want to use, then click Next.
The networks may not be in alphabetical order. If it is too difficult to find your networks, you can change the networks later from the Edit Settings dialog box. After you deploy, right-click the ASAv instance, and choose Edit Settings to access the Edit Settings dialog box. However that screen does not show the ASAv interface IDs (only Network Adapter IDs). See the following concordance of Network Adapter IDs and ASAv interface IDs:
|
|
|
|---|---|
You do not need to use all ASAv interfaces; however, the vSphere Web Client requires you to assign a network to all interfaces. For interfaces you do not intend to use, you can simply leave the interface disabled within the ASAv configuration. After you deploy the ASAv, you can optionally return to the vSphere Web Client to delete the extra interfaces from the Edit Settings dialog box. For more information, see the vSphere Web Client online help.

Note![]() For failover deployments, GigabitEthernet 0/8 is pre-configured as the failover interface.
For failover deployments, GigabitEthernet 0/8 is pre-configured as the failover interface.
Step 12![]() In the Customize template screen:
In the Customize template screen:
a.![]() Configure the management interface IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. You should also set the client IP address allowed for ASDM access, and if a different gateway is required to reach the client, enter that gateway IP address. For failover deployments, specify the IP address as a static address; you cannot use DHCP.
Configure the management interface IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. You should also set the client IP address allowed for ASDM access, and if a different gateway is required to reach the client, enter that gateway IP address. For failover deployments, specify the IP address as a static address; you cannot use DHCP.
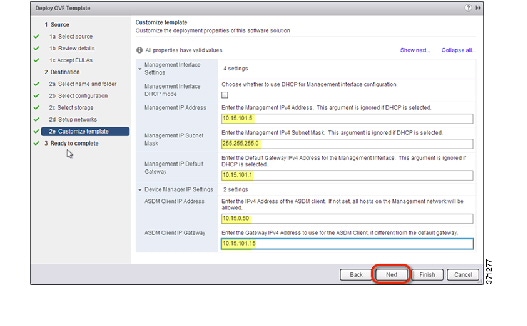
b.![]() For failover deployments, specify the management IP standby address. When you configure your interfaces, you must specify an active IP address and a standby IP address on the same network.
For failover deployments, specify the management IP standby address. When you configure your interfaces, you must specify an active IP address and a standby IP address on the same network.
–![]() When the primary unit fails over, the secondary unit assumes the IP addresses and MAC addresses of the primary unit and begins passing traffic.
When the primary unit fails over, the secondary unit assumes the IP addresses and MAC addresses of the primary unit and begins passing traffic.
–![]() The unit that is now in a standby state takes over the standby IP addresses and MAC addresses.
The unit that is now in a standby state takes over the standby IP addresses and MAC addresses.
Because network devices see no change in the MAC to IP address pairing, no ARP entries change or time out anywhere on the network.
You must also configure the failover link settings in the HA Settings area. The two units in a failover pair constantly communicate over a failover link to determine the operating status of each unit. GigabitEthernet 0/8 is pre-configured as the failover link. Enter the active and standby IP addresses for the link on the same network.
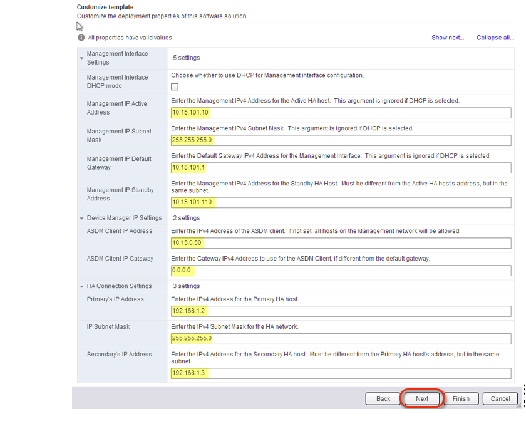
Step 13![]() In the Ready to complete screen, review the summary of the ASAv configuration, optionally check the Power on after deployment check box, and click Finish to start the deployment.
In the Ready to complete screen, review the summary of the ASAv configuration, optionally check the Power on after deployment check box, and click Finish to start the deployment.
The vSphere Web Client processes the VM; you can see the “Initialize OVF deployment” status in the Global Information area Recent Tasks pane.
When it is finished, you see the Deploy OVF Template completion status.
The ASAv VM instance then appears under the specified data center in the Inventory.

Step 14![]() If the ASAv VM is not yet running, click Power on the virtual machine.
If the ASAv VM is not yet running, click Power on the virtual machine.
Wait for the ASAv to boot up before you try to connect with ASDM or to the console. When the ASAv starts up for the first time, it reads parameters provided through the OVA file and adds them to the ASAv system configuration. It then automatically restarts the boot process until it is up and running. This double boot process only occurs when you first deploy the ASAv. To view bootup messages, access the ASAv console by clicking the Console tab.
Step 15![]() For failover deployments, repeat this procedure to add the secondary unit. See the following guidelines:
For failover deployments, repeat this procedure to add the secondary unit. See the following guidelines:
a.![]() On the Select Configuration screen, choose 1 (or 2, 3, 4) vCPU HA Secondary for the ASAv deployment configuration.
On the Select Configuration screen, choose 1 (or 2, 3, 4) vCPU HA Secondary for the ASAv deployment configuration.
b.![]() On the Customize template screen, enter the exact same IP address settings as for the primary unit (see Step 12b.) The bootstrap configurations on both units are identical except for the parameter identifying a unit as primary or secondary.
On the Customize template screen, enter the exact same IP address settings as for the primary unit (see Step 12b.) The bootstrap configurations on both units are identical except for the parameter identifying a unit as primary or secondary.
Connecting to the CLI or ASDM
After you deploy the ASAv, you can connect to it using ASDM or using the console:
- See Starting ASDM.
- See Accessing the ASAv Console.
Managing the ASAv License
Applying the ASAv License
After you deploy the ASAv, you must install a CPU license. Until you install a license, throughput is limited to 100 Kbps so you can perform preliminary connectivity tests. A CPU license is required for regular operation. You also see the following messages repeated on the console until you install a license:
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() View the serial number by clicking the License tab on the main ASDM page and then clicking More Licenses.
View the serial number by clicking the License tab on the main ASDM page and then clicking More Licenses.
Step 2![]() From the Configuration > Device Management > Licensing > Activation Key pane, write down the serial number.
From the Configuration > Device Management > Licensing > Activation Key pane, write down the serial number.

Step 3![]() Obtain a Product Authorization Key, which you can purchase from your Cisco account representative. You need to purchase a separate Product Authorization Key for each feature license. For the ASAv, the only required feature license is for vCPUs (1 to 4), but you can purchase other feature keys as well.
Obtain a Product Authorization Key, which you can purchase from your Cisco account representative. You need to purchase a separate Product Authorization Key for each feature license. For the ASAv, the only required feature license is for vCPUs (1 to 4), but you can purchase other feature keys as well.
Step 4![]() Request an activation key from Cisco.com for the serial number according to the ASA licensing guide. Be sure to request a CPU license that matches the number of CPUs you specified when you deployed the ASAv.
Request an activation key from Cisco.com for the serial number according to the ASA licensing guide. Be sure to request a CPU license that matches the number of CPUs you specified when you deployed the ASAv.
Step 5![]() After you receive the activation key from Cisco, on the Configuration > Device Management > Licensing > Activation Key pane, paste the key into the New Activation Key field.
After you receive the activation key from Cisco, on the Configuration > Device Management > Licensing > Activation Key pane, paste the key into the New Activation Key field.
Step 6![]() Click Update Activation Key.
Click Update Activation Key.
ASDM shows a status dialog box while it verifies the key.
When the key update is complete, you see the following dialog box:
Step 7![]() Click Yes to restart ASDM.
Click Yes to restart ASDM.
Upgrading the vCPU License
If you want to increase (or decrease) the number of vCPUs for your ASAv, you can request a new license, apply the new license, and change the VM properties in VMware to match the new values.

Note![]() The assigned vCPUs must match the ASAv vCPU license. The vCPU frequency limit and RAM must also be sized correctly for the vCPUs. When upgrading or downgrading, be sure to follow this procedure and reconcile the license and vCPUs immediately. The ASAv does not operate properly when there is a persistent mismatch.
The assigned vCPUs must match the ASAv vCPU license. The vCPU frequency limit and RAM must also be sized correctly for the vCPUs. When upgrading or downgrading, be sure to follow this procedure and reconcile the license and vCPUs immediately. The ASAv does not operate properly when there is a persistent mismatch.
Detailed Steps
Step 1![]() Request a new activation key for the new vCPU number.
Request a new activation key for the new vCPU number.
Step 2![]() Apply the new license key. For failover pairs, apply new licenses to both units.
Apply the new license key. For failover pairs, apply new licenses to both units.
Step 3![]() Do one of the following, depending on if you use failover or not:
Do one of the following, depending on if you use failover or not:
- Failover—In the vSphere Web Client, power off the standby ASAv. For example, click the ASAv and then click Power Off the virtual machine, or right-click the ASAv and choose Shut Down Guest OS.
- No Failover—In the vSphere Web Client, power off the ASAv. For example, click the ASAv and then click Power Off the virtual machine, or right-click the ASAv and choose Shut Down Guest OS.
Step 4![]() Click the ASAv and then click Edit Virtual machine settings (or right-click the ASAv and choose Edit Settings).
Click the ASAv and then click Edit Virtual machine settings (or right-click the ASAv and choose Edit Settings).
The Edit Settings dialog box appears.
Step 5![]() Refer to the CPU/frequency/memory requirement in the licensing section to determine the correct values for the new vCPU license.
Refer to the CPU/frequency/memory requirement in the licensing section to determine the correct values for the new vCPU license.
Step 6![]() On the Virtual Hardware tab, for the CPU, choose the new value from the drop-down list. You must also click the expand arrow to change the value for the vCPU frequency Limit.
On the Virtual Hardware tab, for the CPU, choose the new value from the drop-down list. You must also click the expand arrow to change the value for the vCPU frequency Limit.

Step 7![]() For the Memory, enter the new value for the RAM.
For the Memory, enter the new value for the RAM.
Step 9![]() Power on the ASAv. For example, click Power On the Virtual Machine.
Power on the ASAv. For example, click Power On the Virtual Machine.
a.![]() Launch ASDM on the active unit.
Launch ASDM on the active unit.
b.![]() After the standby unit finishes starting up, failover to the standby unit by choosing Monitoring > Properties > Failover > Status, and clicking Make Standby.
After the standby unit finishes starting up, failover to the standby unit by choosing Monitoring > Properties > Failover > Status, and clicking Make Standby.
c.![]() Repeat steps 3 through 9 for the active unit.
Repeat steps 3 through 9 for the active unit.
 Feedback
Feedback