- Information About the Switch
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Verifying the Module Installation
- Assigning VLANs to the ASA Services Module
- Using the MSFC as a Directly Connected Router (SVIs)
- Configuring the Switch for ASA Failover
- Resetting the ASA Services Module
- Monitoring the ASA Services Module
- Feature History for the Switch for Use with the ASA Services Module
Switch Configuration for the ASA Services Module
This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series or Cisco 7600 series switch for use with the ASASM. Before completing the procedures in this chapter, configure the basic properties of your switch, including assigning VLANs to switch ports, according to the documentation that came with your switch.
This chapter includes the following sections:
- Information About the Switch
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Verifying the Module Installation
- Assigning VLANs to the ASA Services Module
- Using the MSFC as a Directly Connected Router (SVIs)
- Configuring the Switch for ASA Failover
- Resetting the ASA Services Module
- Monitoring the ASA Services Module
- Feature History for the Switch for Use with the ASA Services Module
Information About the Switch
Supported Switch Hardware and Software
You can install the ASASM in the Catalyst 6500 series and Cisco 7600 series switches. The switch includes a switch (the supervisor engine) as well as a router (the MSFC).
The switch supports Cisco IOS software on both the switch supervisor engine and the integrated MSFC router.

Note![]() The Catalyst operating system software is not supported.
The Catalyst operating system software is not supported.
The ASASM runs its own operating system.

Note![]() Because the ASASM runs its own operating system, upgrading the Cisco IOS software does not affect the operation of the ASASM.
Because the ASASM runs its own operating system, upgrading the Cisco IOS software does not affect the operation of the ASASM.
To view a matrix of hardware and software compatibility for the ASASM and Cisco IOS versions, see the Cisco ASA Series Hardware and Software Compatibility :
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/compatibility/asamatrx.html
Backplane Connection
The connection between the ASASM and the switch is a single 20-GB interface.
ASA and IOS Feature Interaction
Some ASASM features interact with Cisco IOS features. The following features involve Cisco IOS software:
- Virtual Switching System (VSS)—No ASASM configuration is required.
- Autostate—The supervisor informs the ASASM when the last interface on a given VLAN has gone down, which assists in determining whether or not a failover switch is required.
- Clearing entries in the supervisor MAC address table on a failover switch—No ASASM configuration is required.
- Version compatibility—The ASASM will be automatically powered down if the supervisor/ASASM version compatibility matrix check fails.
Information About SVIs
If you want to use the MSFC as a directly connected router (for example, as the default gateway connected to the ASASM outside interface), then add an ASASM VLAN interface to the MSFC as a switched virtual interface (SVI).
For security reasons, by default, you can configure one SVI between the MSFC and the ASASM; you can enable multiple SVIs, but be sure you do not misconfigure your network.
For example, with multiple SVIs, you could accidentally allow traffic to pass around the ASASM by assigning both the inside and outside VLANs to the MSFC. (See Figure 2-1.)
Figure 2-1 Multiple SVI Misconfiguration

You might need to bypass the ASASM in some network scenarios. Figure 2-2 shows an IPX host on the same Ethernet segment as IP hosts. Because the ASASM in routed firewall mode only handles IP traffic and drops other protocol traffic like IPX (transparent firewall mode can optionally allow non-IP traffic), you might want to bypass the ASASM for IPX traffic. Make sure that you configure the MSFC with an access list that allows only IPX traffic to pass on VLAN 201.
Figure 2-2 Multiple SVIs for IPX

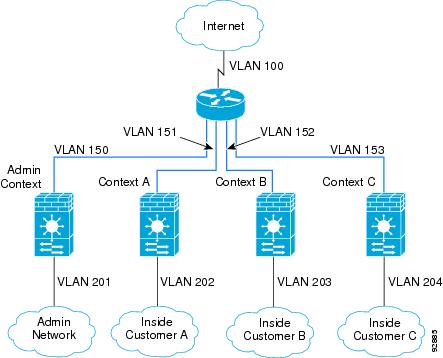
For transparent firewalls in multiple context mode, you need to use multiple SVIs because each context requires a unique VLAN on its outside interface (see Figure 2-3). You might also choose to use multiple SVIs in routed mode so that you do not have to share a single VLAN for the outside interface.
Figure 2-3 Multiple SVIs in Multiple Context Mode
Guidelines and Limitations
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature.
VLAN Guidelines and Limitations
- Use VLAN IDs 2 to 1001.
- You can use private VLANs with the ASASM. Assign the primary VLAN to the ASASM; the ASASM automatically handles secondary VLAN traffic. There is no configuration required on the ASASM for this feature; see the switch configuration guide for more information. See also the example in Assigning VLANs to the ASA Services Module, page 2-7 .
- You cannot use reserved VLANs.
- You cannot use VLAN 1.
- If you are using ASASM failover within the same switch chassis, do not assign the VLAN(s) that you are reserving for failover and stateful communications to a switch port. However, if you are using failover between chassis, you must include the VLANs in the trunk port between the chassis.
- If you do not add the VLANs to the switch before you assign them to the ASASM, the VLANs are stored in the supervisor engine database and are sent to the ASASM as soon as they are added to the switch.
- You can configure a VLAN in the ASASM configuration before it has been assigned on the switch. Note that when the switch sends the VLAN to the ASASM, the VLAN defaults to be administratively up on the ASASM, regardless of whether the you shut them down in the ASASM configuration. You need to shut them down again in this case.
In Cisco IOS software Version 12.2SXJ1 and earlier, for each ASASM in a switch, the SPAN reflector feature is enabled. This feature allows multicast traffic (and other traffic that requires a central rewrite engine) to be switched when coming from the ASASM. The SPAN reflector feature uses one SPAN session. To disable this feature, enter the following command:
Verifying the Module Installation
To verify that the switch acknowledges the ASASM and has brought it online, enter the following command.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
Displays module information. For a switch in a VSS, enter the switch keyword. |
Examples
The following is sample output from the show module command:
Assigning VLANs to the ASA Services Module
This section describes how to assign VLANs to the ASASM. The ASASM does not include any external physical interfaces. Instead, it uses VLAN interfaces. Assigning VLANs to the ASASM is similar to assigning a VLAN to a switch port; the ASASM includes an internal interface to the Switch Fabric Module (if present) or the shared bus.
Prerequisites
See the switch documentation for information about adding VLANs to the switch and assigning them to switch ports.
Guidelines
- You can assign up to 16 firewall VLAN groups to each ASASM. (You can create more than 16 VLAN groups in Cisco IOS software, but only 16 can be assigned per ASASM.) For example, you can assign all the VLANs to one group; or you can create an inside group and an outside group; or you can create a group for each customer.
- There is no limit on the number of VLANs per group, but the ASASM can only use VLANs up to the ASASM system limit (see the ASASM licensing documentation for more information).
- You cannot assign the same VLAN to multiple firewall groups.
- You can assign a single firewall group to multiple ASASMs. VLANs that you want to assign to multiple ASASMs, for example, can reside in a separate group from VLANs that are unique to each ASASM.
- See VLAN Guidelines and Limitations.
Detailed Steps
Examples
The following example shows how to create three firewall VLAN groups: one for each ASASM, and one that includes VLANs assigned to both ASASMs:
The following example shows how to configure private VLANs on the switch by assigning the primary VLAN to the ASASM:
Step 1![]() Add the primary VLAN 200 to a firewall VLAN group, and assign the group to the ASASM:
Add the primary VLAN 200 to a firewall VLAN group, and assign the group to the ASASM:
Step 2![]() Designate VLAN 200 as the primary VLAN:
Designate VLAN 200 as the primary VLAN:
Step 3![]() Designate only one secondary isolated VLAN. Designate one or more secondary community VLANs.
Designate only one secondary isolated VLAN. Designate one or more secondary community VLANs.
Step 4![]() Associate the secondary VLANs to the primary VLAN:
Associate the secondary VLANs to the primary VLAN:
Step 5![]() Classify the port mode. The mode of interface f1/0/1 is host. The mode of interface f1/0/2 is promiscuous.
Classify the port mode. The mode of interface f1/0/1 is host. The mode of interface f1/0/2 is promiscuous.
Step 6![]() Assign VLAN membership to the host port. Interface f1/0/1 is a member of primary VLAN 200 and secondary isolated VLAN 501.
Assign VLAN membership to the host port. Interface f1/0/1 is a member of primary VLAN 200 and secondary isolated VLAN 501.
Step 7![]() Assign VLAN membership to the promiscuous interface. Interface f1/0/2 is a member of primary VLAN 200. Secondary VLANs 501-503 are mapped to the primary VLAN.
Assign VLAN membership to the promiscuous interface. Interface f1/0/2 is a member of primary VLAN 200. Secondary VLANs 501-503 are mapped to the primary VLAN.
Step 8![]() If inter-VLAN routing is desired, configure a primary SVI and then map the secondary VLANs to the primary.
If inter-VLAN routing is desired, configure a primary SVI and then map the secondary VLANs to the primary.
Using the MSFC as a Directly Connected Router (SVIs)
If you want to use the MSFC as a directly connected router (for example, as the default gateway connected to the ASASM outside interface), then add an ASASM VLAN interface to the MSFC as a switched virtual interface (SVI). See Information About SVIs.
Restrictions
For security reasons, by default, you can configure one SVI between the MSFC and the ASASM; you can enable multiple SVIs, but be sure you do not misconfigure your network.
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| firewall multiple-vlan-interfaces |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
Examples
The following example shows a typical configuration with multiple SVIs:
Configuring the Switch for ASA Failover
This section includes the following topics:
- Assigning VLANs to the Secondary ASA Services Module
- Adding a Trunk Between a Primary Switch and Secondary Switch
- Ensuring Compatibility with Transparent Firewall Mode
- Enabling Autostate Messaging for Rapid Link Failure Detection
Assigning VLANs to the Secondary ASA Services Module
Because both units require the same access to the inside and outside networks, you must assign the same VLANs to both ASASMs on the switch(es). See Assigning VLANs to the Secondary ASA Services Module.
Adding a Trunk Between a Primary Switch and Secondary Switch
If you are using inter-switch failover, then you should configure an 802.1Q VLAN trunk between the two switches to carry the failover and state links. The trunk should have QoS enabled so that failover VLAN packets, which have a CoS value of 5 (higher priority), are treated with higher priority in these ports.
To configure the EtherChannel and trunk, see the documentation for your switch.
Ensuring Compatibility with Transparent Firewall Mode
To avoid loops when you use failover in transparent mode, use switch software that supports BPDU forwarding. Do not enable LoopGuard globally on the switch if the ASASM is in transparent mode. LoopGuard is automatically applied to the internal EtherChannel between the switch and the ASASM, so after a failover and a failback, LoopGuard causes the secondary unit to be disconnected because the EtherChannel goes into the err-disable state.
Enabling Autostate Messaging for Rapid Link Failure Detection
The supervisor engine can send autostate messages to the ASASM about the status of physical interfaces associated with ASASM VLANs. For example, when all physical interfaces associated with a VLAN go down, the autostate message tells the ASASM that the VLAN is down. This information lets the ASASM declare the VLAN as down, bypassing the interface monitoring tests normally required for determining which side suffered a link failure. Autostate messaging provides a dramatic improvement in the time the ASASM takes to detect a link failure (a few milliseconds as compared to up to 45 seconds without autostate support).
The switch supervisor sends an autostate message to the ASASM when:
Detailed Steps
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
Enables autostate messaging in Cisco IOS software. Autostate messaging is disabled by default. |
Resetting the ASA Services Module
This section describes how to reset the ASASM. You might need to reset the ASASM if you cannot reach it through the CLI or an external Telnet session. The reset process might take several minutes.
Detailed Steps
Examples
The following is sample output from the hw-module module reset command:
Monitoring the ASA Services Module
To monitor the ASA, enter one of the following commands:
|
|
|
|---|---|
Indicates the status of multiple VLAN interfaces (enabled or disabled). |
|
Displays the status and information about the configured VLAN interface. |
Examples
The following is sample output from the show firewall module [ mod-num ] state command:
The following is sample output from the show firewall module [ mod-num ] traffic command:
The following is sample output from the show firewall multiple-vlan-interfaces command:
The following is sample output from the show firewall module command:
The following is sample output from the show firewall module [ mod-num ] version command:
The following is sample output from the show firewall vlan-group command:
The following is sample output from the show interface vlan command:
Feature History for the Switch for Use with the ASA Services Module
Table 2-1 lists each feature change and the platform release in which it was implemented.
 Feedback
Feedback