About Clustering for the Secure Firewall 3100
This section describes the clustering architecture and how it works.
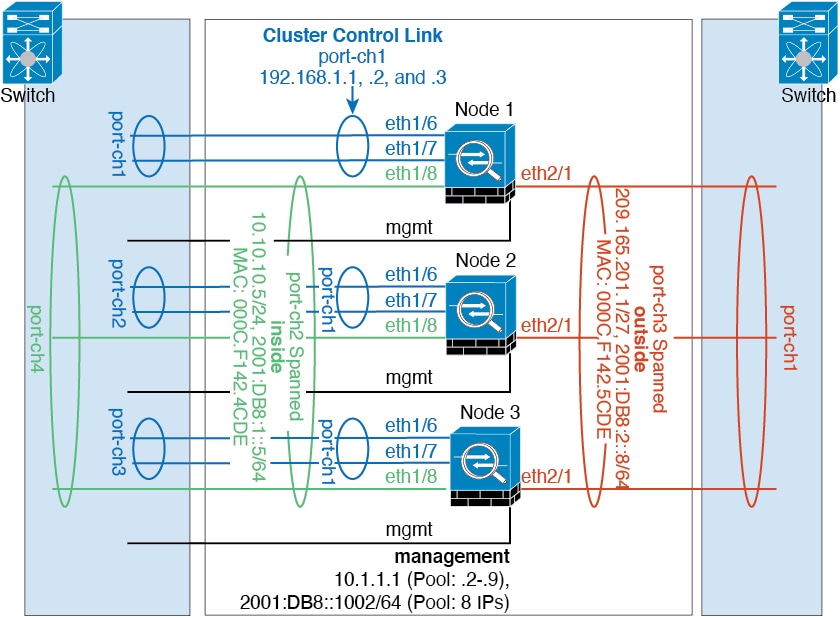
How the Cluster Fits into Your Network
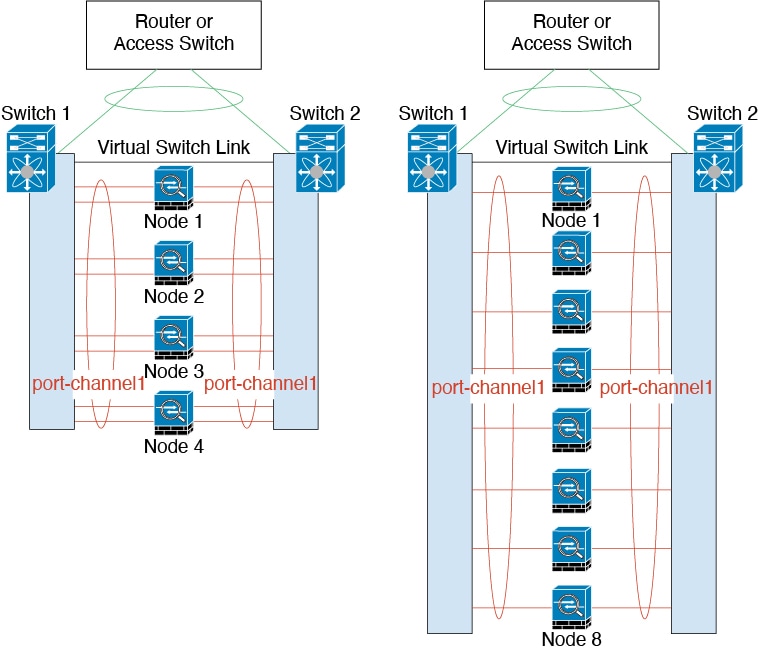
The cluster consists of multiple firewalls acting as a single unit. To act as a cluster, the firewalls need the following infrastructure:
-
Isolated, high-speed backplane network for intra-cluster communication, known as the cluster control link.
-
Management access to each firewall for configuration and monitoring.
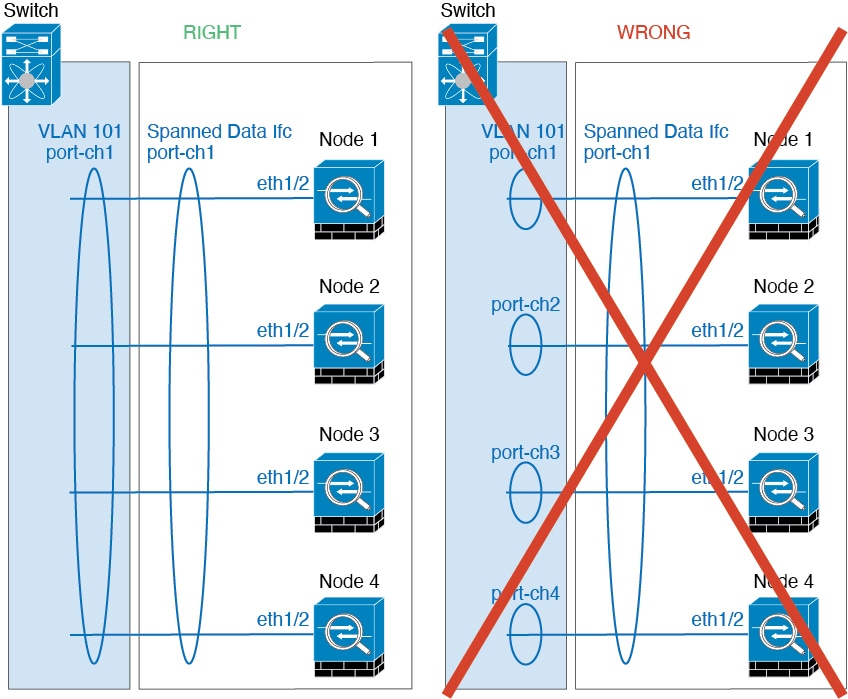
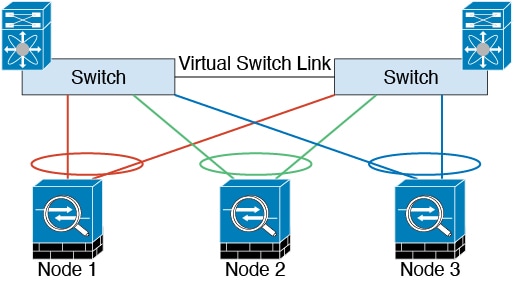
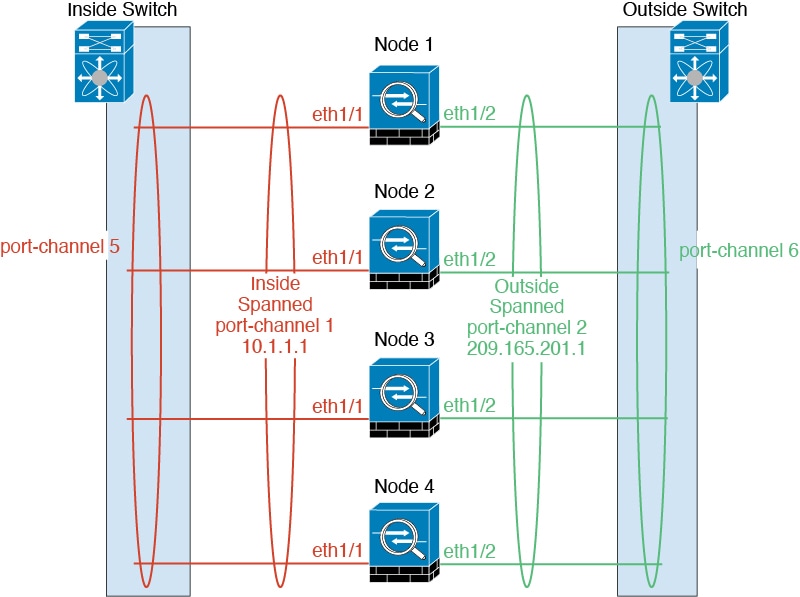
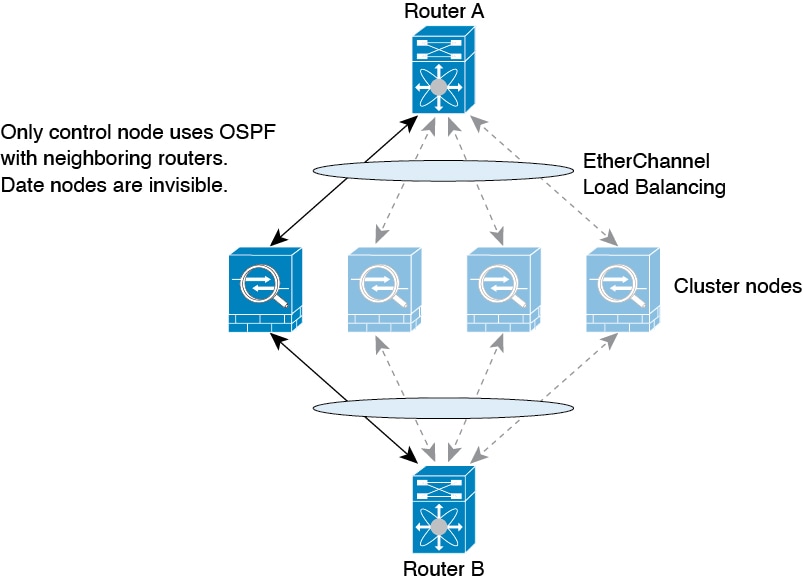
When you place the cluster in your network, the upstream and downstream routers need to be able to load-balance the data coming to and from the cluster using Spanned EtherChannels. Interfaces on multiple members of the cluster are grouped into a single EtherChannel; the EtherChannel performs load balancing between units.
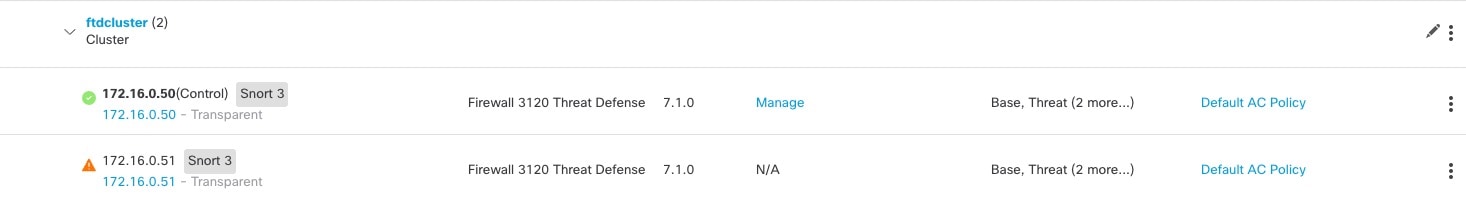
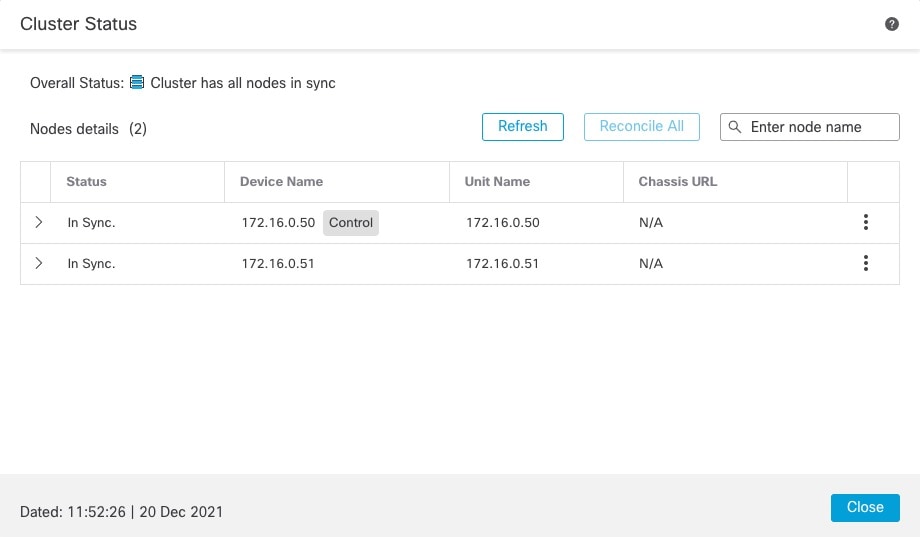
Control and Data Node Roles
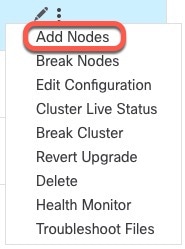
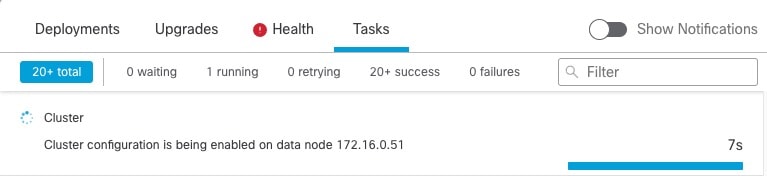
One member of the cluster is the control node. If multiple cluster nodes come online at the same time, the control node is determined by the priority setting; the priority is set between 1 and 100, where 1 is the highest priority. All other members are data nodes. When you first create the cluster, you specify which node you want to be the control node, and it will become the control node simply because it is the first node added to the cluster.
All nodes in the cluster share the same configuration. The node that you initially specify as the control node will overwrite the configuration on the data nodes when they join the cluster, so you only need to perform initial configuration on the control node before you form the cluster.
Some features do not scale in a cluster, and the control node handles all traffic for those features.
Cluster Interfaces
You can configure data interfaces as either Spanned EtherChannels. See About Cluster Interfaces for more information.
You can use regular firewall interfaces or IPS-only interfaces (inline sets or passive interfaces).
 Note |
Individual interfaces are not supported, with the exception of a management interface. |
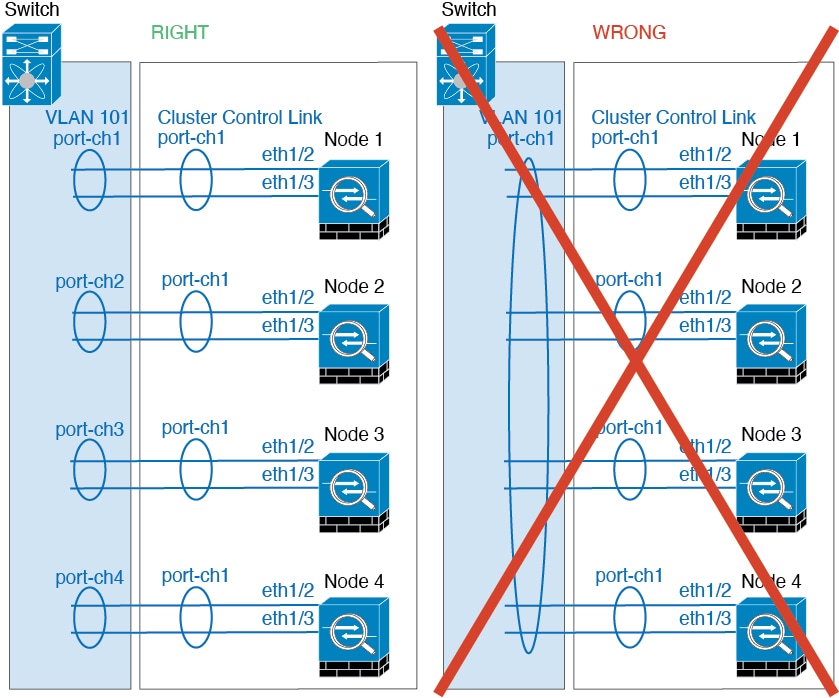
Cluster Control Link
Each unit must dedicate at least one hardware interface as the cluster control link. See Cluster Control Link for more information.
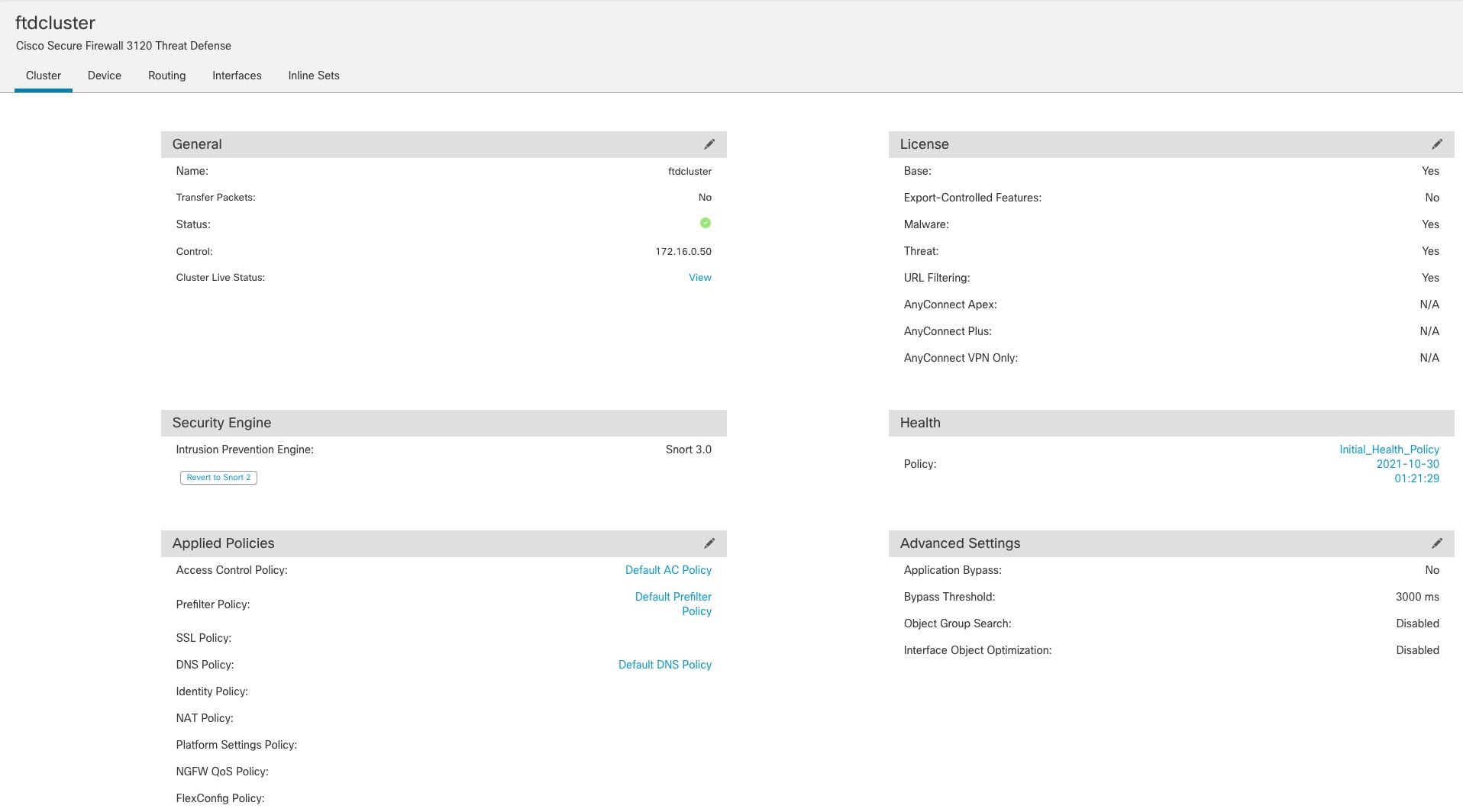
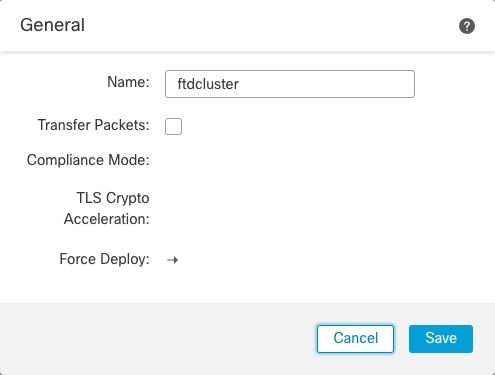
Configuration Replication
All nodes in the cluster share a single configuration. You can only make configuration changes on the control node (with the exception of the bootstrap configuration), and changes are automatically synced to all other nodes in the cluster.
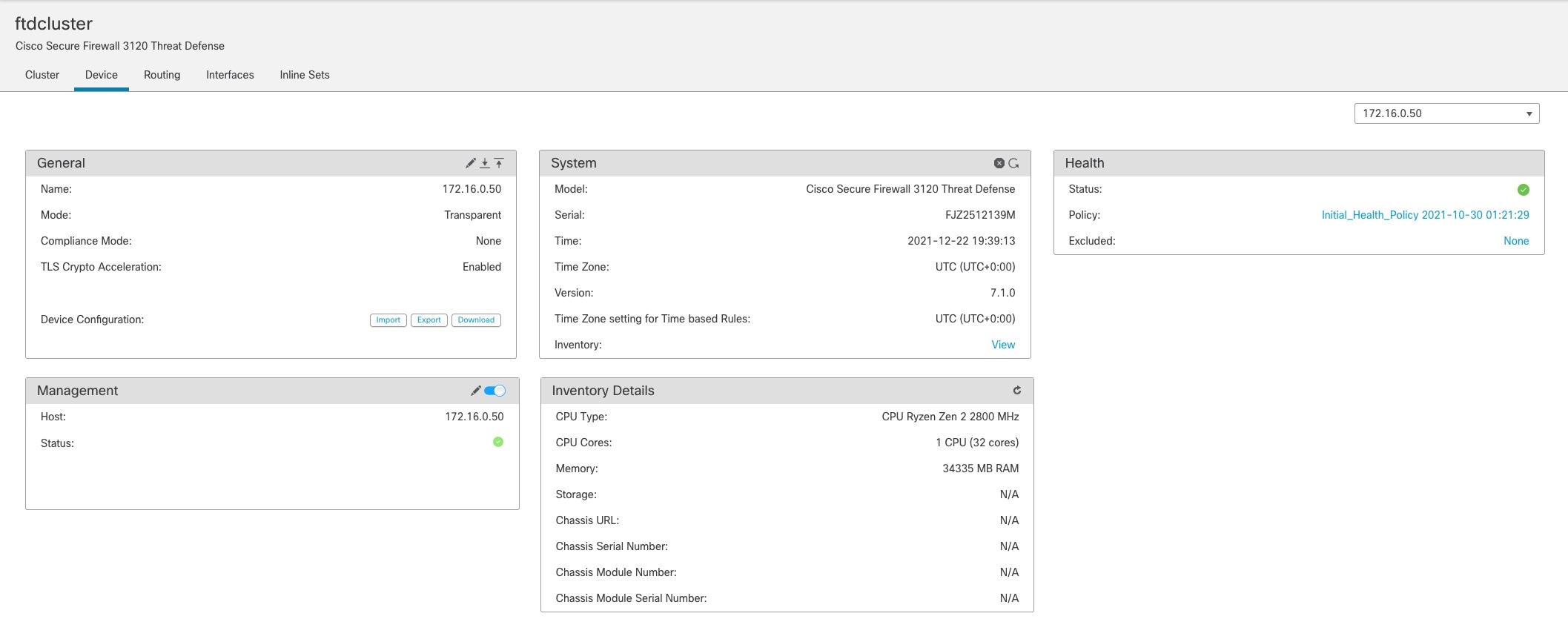
Management Network
You must manage each node using the Management interface; management from a data interface is not supported with clustering.








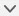

 Feedback
Feedback