Onboarding Overview
Review the following use cases and supported sofware versions that are compatible with cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center management.
 Note |
You must ensure that the Firewall Threat Defense device ports have external and outbound access for the cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center to onboard them. There is no requirement for an on-premises or cloud-based Security Device Controller (SDC) for this operation. For more information, see Network Requirements. To send Firewall Threat Defense Syslog events to the Cisco cloud, you can set up the Secure Event Connector (SEC). For more information, see Installing Secure Event Connectors. |
Firewall Threat Defense Devices Currently Managed by Cloud-Delivered Firewall Management Center
The following scenarios occur when you either move or migrate a device to the cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center:
-
If you delete a device from an on-premises management center or Secure Firewall Threat Defense Firewall Device Manager to onboard to the cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center, the change of managers wipes any policies configured through the on-premises management center.
-
If you migrate a device from an on-premises management center to the cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center, the device retains the majority of your previously configured policies.
 Note |
If you do not know if your device is already managed by an alternative manager, use the |
Onboarding Methods
Cloud-Delivered Firewall Management Center supports the following onboarding methods:
-
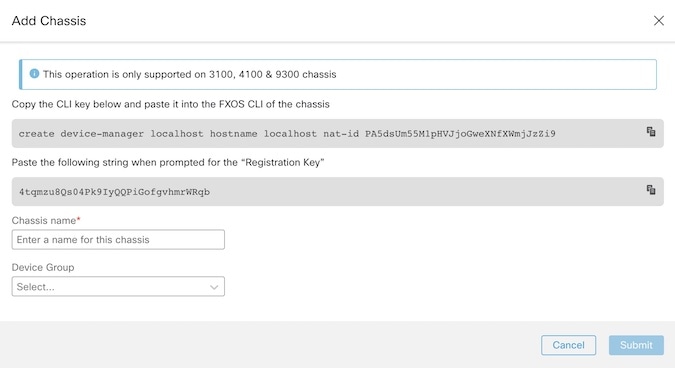
Registration Key - Onboard a device with a registration key. The initial device setup wizard is complete on the device.
-
Zero-Touch Provisioning - Onboard a new factory-shipped device with its serial number. Note that this method only supports Firepower 1000, Firepower 2100, or Secure Firewall 3100 devices.

Note
Version 7.0.3 does not support zero-touch provisioning.
-
Zero-Touch Provisioning using a device template - Onboard new factory-shipped devices using serial numbers and a device template. Note that this method only supports Firepower 1000, Firepower 2100, Secure Firewall 1200 or Secure Firewall 3100 devices.

 ).
).


 Feedback
Feedback