- Device Manager Help
- Configuring Cisco DCNM-SAN Server
- Configuring Authentication in Cisco DCNM-SAN
- Configuring Cisco DCNM-SAN Client
- Device Manager
- Configuring Performance Manager
- Configuring High Availability
- Configuring Trunking
- Configuring PortChannels
- Configuring N Port Virtualization
- Configuring Interfaces
- Configuration of Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Using the CFS Infrastructure
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Configuring FCoE
- Configuring Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Configuring SAN Device Virtualization
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Configuring FICON
- Creating Dynamic VSANs
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Advanced Fabric Features
- Configuring Users and Common Role
- Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server
- Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Cisco TrustSec Fibre Channel Link Encryption
- Configuring FIPS
- Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists
- Configuring IPsec Network Security
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring FCIP
- Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
- Configuring iSCSI
- Configuring IP Services
- Configuring IP Storage
- Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring IPv6 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring SCSI Flow Services
- Configuring SCSI Flow Statistics
- Configuring Fibre Channel Write Acceleration
- Monitoring the Network
- Monitoring Performance
- Configuring Call Home
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Scheduling Maintenance Jobs
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Server
- Monitoring Network Traffic Using SPAN
- Monitoring System Processes and Logs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Configuring FlexAttach Virtual pWWN
- Configuring Interface Buffers
- Verifying Ethernet Interfaces
- Information About Interface Buffers
- Buffer-to-Buffer Credits
- Performance Buffers
- Buffer Pools
- BB_Credit Buffers for Switching Modules
- Configuring Buffer Credits on a Generation 2, Generation 3 or Generation 4 Module
- 48-Port 8-Gbps Advanced Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 48-Port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 24-Port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 4/44-Port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 18-Port Fibre Channel/4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Multiservice Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 12-Port 4-Gbps Switching Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 4-Port 10-Gbps Switching Module BB_Credit Buffers
- BB_Credit Buffers for Fabric Switches
- Extended BB_Credits
- Buffer-to-Buffer Credit Recovery
- Buffer-to-Buffer State Change Number
- Receive Data Field Size
- Configuring Interface Buffers
- Verifying BB_Credit Configuration
Configuring Interface Buffers
This chapter describes how to configure buffer credits for the Fibre Channel interfaces.
Information About Interface Buffers
Fibre Channel interfaces use buffer credits to ensure all packets are delivered to their destination.
This section includes the following topics:
- Buffer-to-Buffer Credits
- Performance Buffers
- Buffer Pools
- BB_Credit Buffers for Switching Modules
- BB_Credit Buffers for Fabric Switches
- Extended BB_Credits
- Buffer-to-Buffer Credit Recovery
- Buffer-to-Buffer State Change Number
- Receive Data Field Size
Buffer-to-Buffer Credits
Buffer-to-buffer credits (BB_credits) are a flow-control mechanism to ensure that Fibre Channel switches do not run out of buffers, so that switches do not drop frames. BB_credits are negotiated on a per-hop basis.
The receive BB_credit (fcrxbbcredit) value may be configured for each Fibre Channel interface. In most cases, you do not need to modify the default configuration.
The receive BB_credit values depend on the module type and the port mode, as follows:
- For 16-port switching modules and full rate ports, the default value is 16 for Fx mode and 255 for E or TE modes. The maximum value is 255 in all modes. This value can be changed as required.
- For 32-port switching modules and host-optimized ports, the default value is 12 for Fx, E, and TE modes. These values cannot be changed.
- For Generation 2, Generation 3, and Generation 4 switching modules, see the “Buffer Pools” section.

Note In the Cisco MDS 9100 Series switches, the groups of ports on the left outlined in white are in dedicated rate mode. The other ports are host-optimized. Each group of 4 host-optimized ports have the same features as for the 32-port switching module.

Note Because Generation 1 modules do not support as many buffer-to-buffer credits as Generation 4 modules supports, you cannot configure an ISL on E or TE ports between a Generation 1 module such as the 16-port 1-, 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module (DS-X9016) and a Generation 4 module such as the 48 port 8-Gbps Advanced Fibre Channel module (DS-X9248-256K9) or the 32-port 8-Gbps Advanced Fibre Channel module (DS-X9232-256K9).
Performance Buffers
Regardless of the configured receive BB_credit value, additional buffers, called performance buffers, improve switch port performance. Instead of relying on the built-in switch algorithm, you can manually configure the performance buffer value for specific applications (for example, forwarding frames over FCIP interfaces).

Note Performance buffers are not supported on the Cisco MDS 9148 Fabric Switch, Cisco MDS 9124 Fabric Switch, the Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem, and the Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter.
For each physical Fibre Channel interface in any switch in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family, you can specify the amount of performance buffers allocated in addition to the configured receive BB_credit value.
The default performance buffer value is 0. If you set the performance buffer value to 0, the built-in algorithm is used. If you do not specify the performance buffer value, 0 is automatically used.
The default performance buffer value is 0. If you use the default option, the built-in algorithm is used. If you do not specify this command, the default option is automatically used.
Buffer Pools
In the architecture of Generation 2, Generation 3, and Generation 4 modules, receive buffers shared by a set of ports are called buffer groups . The receive buffer groups are organized into global and local buffer pools.
The receive buffers allocated from the global buffer pool to be shared by a port group are called a global receive buffer pool . Global receive buffer pools include the following buffer groups:
- Reserved internal buffers
- Allocated BB_credit buffers for each Fibre Channel interface (user configured or assigned by default)
- Common unallocated buffer pool for BB_credits, if any, to be used for additional BB_credits as needed
- Performance buffers (only used on 12-port 4-Gbps and 4-port 10-Gbps switching modules)

Note The 48-port and 24-port 8-Gbps modules have dual global buffer pools. Each buffer pool in the 48-port modules support 24 ports and in the 24-port modules each buffer pool supports 12 ports.
Figure 60-1 shows the allocation of BB_credit buffers on line cards (24-port and 48-port 4-Gbps line cards).
Figure 60-1 Receive Buffers for Fibre Channel Ports in a Global Buffer Pool
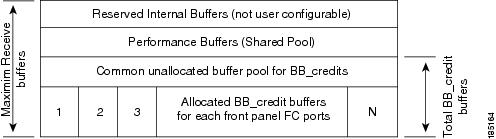
Figure 60-2 shows the default BB_credit buffer allocation model for 48-port 8-Gbps switching modules. The minimum BB_credits required to bring up a port is two buffers.
Figure 60-2 BB_Credit Buffer Allocation in 48-Port 8-Gbps Switching Modules
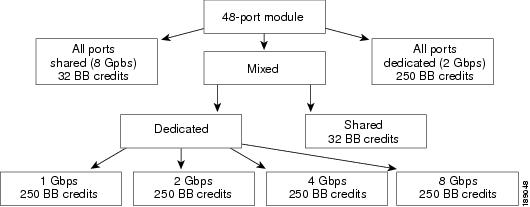
Figure 60-3 shows the default BB_credit buffer allocation model for 24-port 8-Gbps switching modules. The minimum BB_credits required to bring up a port is two buffers.
Figure 60-3 BB_Credit Buffer Allocation in 24-Port 8-Gbps Switching Modules

Figure 60-4 shows the default BB_credit buffer allocation model for 4/44-port 8-Gbps host-optimized switching modules. The minimum BB_credits required to bring up a port is two buffers.
Figure 60-4 BB_Credit Buffer Allocation in 4/44-Port 8-Gbps Switching Modules
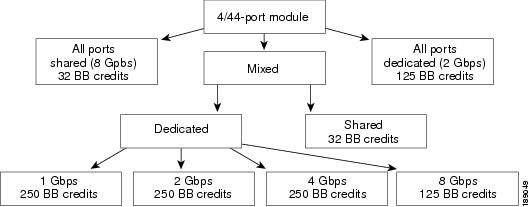
Figure 60-5 shows the default BB_credit buffer allocation model for 24-port 4-Gbps switching modules. The minimum BB_credits required to bring up a port is two buffers.
Figure 60-5 BB_Credit Buffer Allocation in 24-Port 4-Gbps Switching Modules


Note The default BB_credit buffer allocation is the same for all port speeds.
BB_Credit Buffers for Switching Modules
This section describes how buffer credits are allocated to Cisco MDS 9000 switching modules, and includes the following topics:
- Configuring Buffer Credits on a Generation 2, Generation 3 or Generation 4 Module
- 48-Port 8-Gbps Advanced Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 48-Port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 24-Port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 4/44-Port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 18-Port Fibre Channel/4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Multiservice Module BB_Credit Buffers
- 4-Port 10-Gbps Switching Module BB_Credit Buffers
Configuring Buffer Credits on a Generation 2, Generation 3 or Generation 4 Module
When you configure port mode to auto or E on a Generation 2 module, one of the ports will not come up for the following configuration:
When you configure port mode to auto or E on a Generation 3 module, one or two of the ports will not come up for the following configuration:
- Port Mode: auto or E for the first half of the ports, the second half of the ports or for all of the ports
- Rate Mode: dedicated
- Buffer Credits: default value
When you configure port mode to auto or E for all ports in the global buffer pool, you need to reconfigure buffer credits on one or more of the ports. The total number of buffer credits configured for all the ports in the global buffer pool should be reduced by 64.
48-Port 8-Gbps Advanced Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-1 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for the 48-port 8-Gbps Advanced Fibre Channel switching module.
The following guidelines apply to BB_credit buffers on 32/48-port Advanced 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 32 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
- The buffers should not be allocated automatically.
Each port group on the 32/48-port Advanced 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module consists of four/six ports. The ports in shared rate mode in a port group can have a maximum bandwidth oversubscription of 1.5:1 considering that each port group has 32-Gbps bandwidth. In case of 32 Port version, each port group of 4 ports has sufficient bandwidth (32 Gbps) to handle the line rate traffic without any oversubscription.
The following example configurations are supported by the 48-port Advanced 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- Six ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (1.5:1 oversubscription) (default).
- Two port with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus four ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (2:1 oversubscription).
- Two ports with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus four ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (2:1 oversubscription) .
- One port with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus three ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus two ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (1.33:1 oversubscription).
- Six ports with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed.
48-Port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-2 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for the 48-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module.
The following guidelines apply to BB_credit buffers on 48-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers allocated for ports 1 through 24 and 25 through 48 can be a maximum of 6000 each so that the load is distributed.
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 32 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
- The buffers should not be allocated automatically.
Each port group on the 48-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module consists of six ports. The ports in shared rate mode in a port group can have a maximum bandwidth oversubscription of 10:1 considering that each port group has 12.8-Gbps bandwidth.
The following example configurations are supported by the 48-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- Six ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (4:1 oversubscription) (default)
-
One port with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus
five ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (10:1 oversubscription) -
Two ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
four ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (4:1 oversubscription) -
One port with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
three ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed plus
two ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (4:1 oversubscription) - Six ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed
24-Port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-3 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for the 24-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module.
5001 |
|||
The following guidelines apply to BB_credit buffers on 24-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers allocated for ports 1 through 12 and 13 through 24 can be a maximum of 6000 each so that the load is distributed.
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 32 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
Each port group on the 24-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module consists of three ports. The ports in shared rate mode in a port group can have a maximum bandwidth oversubscription of 10:1 considering that each port group has 12.8-Gbps bandwidth.
The following example configurations are supported by the 24-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- Three ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (2:1 oversubscription) (default)
-
One port with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus
two ports with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (4:1 oversubscription) -
One port with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus
one port with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
one port with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (10:1 oversubscription) -
Two ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
one port with shared rate mode and 8-Gbps speed (2:1 oversubscription) - Three ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed
4/44-Port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-4 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for the 4/44-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module.
The following guidelines apply to BB_credit buffers on 4/44-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 500 buffers for dedicated rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 32 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
Each port group on the 24-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module consists of 12 ports. The ports in shared rate mode in a port group can have a maximum bandwidth oversubscription of 10:1 considering that each port group has 12.8-Gbps bandwidth.
The following example configurations are supported by the 4/44-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- Twelve ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (5:1 oversubscription) (default)
-
One port with dedicated rate mode and 8-Gbps speed plus
eleven ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (10:1 oversubscription) -
One port with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
three ports with dedicated rate mode and 3-Gbps speed plus
eight ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (2:1 oversubscription) - Twelve ports with dedicated rate mode and 1-Gbps speed
48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-5 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules.
ISL2
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
The following considerations apply to BB_credit buffers on 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 16 buffers for shared rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 16 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
Each port group on the 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module consists of 12 ports. The ports in shared rate mode have bandwidth oversubscription of 2:1 by default. However, some configurations of the shared ports in a port group can have maximum bandwidth oversubscription of 4:1 (considering that each port group has 12.8-Gbps bandwidth).
The following example configurations are supported by the 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- Twelve ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (4:1 oversubscription) (default)
-
One port with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
11 ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (5:1 oversubscription) -
One port with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
11 ports with shared rate mode and 2-Gbps speed (2.5:1 oversubscription) -
Two ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed plus
10 ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (5:1 oversubscription) -
Two ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed plus
10 ports with shared rate mode and 2-Gbps speed (2.5:1 oversubscription) - Twelve ports with dedicated rate mode and 1-Gbps speed
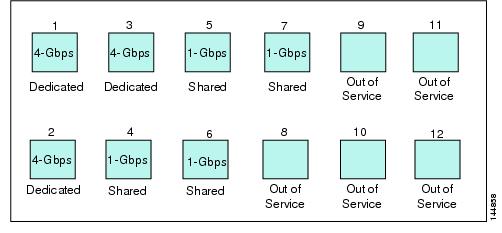
-
Three ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
four ports with shared rate mode and 1-Gbps speed plus
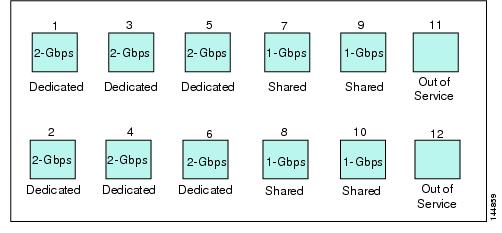
five ports put out-of-service (see Figure 60-6)
Figure 60-6 Example Speed and Rate Configuration on a 48-Port 4-Gbps Switching Module
-
Six ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed plus
four ports with shared rate mode and 1-Gbps speed plus
two ports put out-of-service (see Figure 60-7)
Figure 60-7 Example Speed and Rate Configuration on a 48-Port 4-Gbps Switching Module
24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-6 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules.
ISL3
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
The following considerations apply to BB_credit buffers on 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 16 buffers for shared rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 16 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
Each port group on the 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module consists of six ports. The ports in shared rate mode have a bandwidth oversubscription of 2:1 by default. However, some configurations of the shared ports in a port group can have a maximum bandwidth oversubscription of 4:1 (considering that each port group has 12.8-Gbps bandwidth).
The following example configurations are supported by the 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- Six ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (2:1 oversubscription) (default)
-
Two ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
four ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (with 4:1 oversubscription) -
One port with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
three ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed plus
two ports with shared rate mode and 4-Gbps speed (4:1 oversubscription) - Six ports with dedicated rate mode and 2-Gbps speed
-
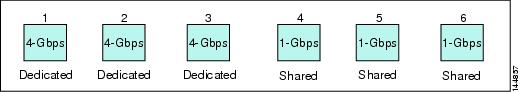
Three ports with dedicated rate mode and 4-Gbps speed plus
three ports with shared rate mode and 1-Gbps speed (see Figure 60-8)
Figure 60-8 Example Speed and Rate Configuration on a 24-Port 4-Gbps Switching Module
18-Port Fibre Channel/4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Multiservice Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-7 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 18-port 4-Gbps multiservice modules.
ISL4
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
The following considerations apply to BB_credit buffers on18-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 16 buffers for shared rate mode.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured. The minimum is 2 buffers and the maximum of 250 buffers for dedicated rate mode or 16 buffers for shared rate mode.
- Performance buffers are not supported on this module.
12-Port 4-Gbps Switching Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-8 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 12-port 4-Gbps switching modules.
ISL 5
|
||
|---|---|---|
The following considerations apply to BB_credit buffers on 12-port 4-Gbps switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 250 buffers.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 250 buffers.
- By default, 512 performance buffers are preallocated and are shared by all the ports. These buffers are configurable and the buffers are assigned to the port based on the availability of the buffers in the shared pool.
- There are 2488 extra buffers available as extended BB_credit buffers after allocating all the default BB_credit buffers for all the ports in ISL mode (5488 - (250 * 12)).

Note Extended BB_credits are allocated across all ports on the switch. That is, they are not allocated by port group.

Note By default, the ports in the 12-port 4-Gbps switching modules come up in 4-Gbps dedicated rate mode but can be configured as 1-Gbps and 2-Gbps dedicated rate mode. Shared mode is not supported.
4-Port 10-Gbps Switching Module BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-9 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 4-port 10-Gbps switching modules.
ISL6
|
F port7
|
|
|---|---|---|
Maximum BB_credit buffers on one of the ports with Enterprise license |
||

Note The ports in the 4-port 10-Gbps switching module only support 10-Gbps dedicated rate mode. FL port mode and shared rate mode are not supported.
The following considerations apply to BB_credit buffers on 4-port 10-Gbps switching modules:
- BB_credit buffers for ISL connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 750 buffers.
- BB_credit buffers for Fx port mode connections can be configured from a minimum of 2 buffers to a maximum of 750 buffers.
- By default, 512 performance buffers are preallocated and are shared by all the ports. These buffers are configurable and the buffers are assigned to the port based on the availability of the buffers in the shared pool.
- There are 2488 extra buffers available as extended BB_credits after allocating all the default BB_credit buffers for all the ports in ISL mode (5488 - (750 * 4)).

Note Extended BB_credits are allocated across all ports on the switch. That is, they are not allocated by port group.
BB_Credit Buffers for Fabric Switches
This section describes how buffer credits are allocated to Cisco MDS 9000 Fabric switches, and includes the following topics:
Cisco MDS 9148 Fabric Switch BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-10 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 48-port 8-Gbps Fibre Channel switches.
ISL8
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
The following considerations apply to BB_credit buffers on 48-port 8-Gbps Fabric Switches:
Cisco MDS 9134 Fabric Switch BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-11 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for MDS 9134 Fabric Switches.
ISL9
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
Cisco MDS 9124 Fabric Switch BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-12 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for MDS 9124 Fabric Switches.
ISL10
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
Cisco MDS 9222i Multiservice Modular Switch BB_Credit Buffers
Table 60-13 lists the BB_credit buffer allocation for 18-port 4-Gbps Multiservice Modular switches.
ISL11
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
Extended BB_Credits
To facilitate BB_credits for long-haul links, the extended BB_credits feature allows you to configure the receive buffers above the maximum value on all Generation 2, Generation 3 and Generation 4 switching modules. When necessary, you can reduce the buffers on one port and assign them to another port, exceeding the default maximum. The minimum extended BB_credits per port is 256 and the maximum is 4095.

Note Extended BB_credits are not supported on the Cisco MDS 9148 Fabric Switch, Cisco MDS 9134 Fabric Switch, Cisco MDS 9124 Fabric Switch, the Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem, and the Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter.
In general, you can configure any port in a port group to dedicated rate mode. To do this, you must first release the buffers from the other ports before configuring larger extended BB_credits for a port.

Note The ENTERPRISE_PKG license is required to use extended BB_credits on Generation 2, Generation 3 and Generation 4 switching modules. Also, extended BB_credits are not supported by ports in shared rate mode.
All ports on the Generation 2 and Generation 3 switching modules support extended BB_credits. There are no limitations for how many extended BB_credits you can assign to a port (except for the maximum and minimum limits). If necessary, you can take interfaces out of service to make more extended BB_credits available to other ports.
You can use the extended BB_credits flow control mechanism in addition to BB_credits for long-haul links.
Extended BB_credits on Generation 1 Switching Modules
The BB_credits feature allows you to configure up to 255 receive buffers on Generation 1 switching modules. To facilitate BB_credits for long haul links, you can configure up to 3,500 receive BB_credits on a Fibre Channel port on a Generation 1 switching module.
To use this feature on Generation 1 switching modules, you must meet the following requirements:
- Obtain the ENTERPRISE_PKG license. See the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Licensing Guide .
- Configure this feature in any port of the full-rate 4-port group in either the Cisco MDS 9216i Switch or in the MPS-14/2 module (see Figure 60-9).
Figure 60-9 Port Group Support for the Extended BB_Credits Feature
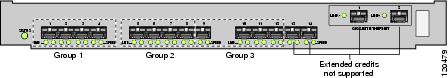
The port groups that support extended credit configurations are as follows:
– Any one port in ports 1 to 4 (identified as Group 1).
– Any one port in ports 5 to 8 (identified as Group 2).
– Any one port in ports 9 to 12 (identified as Group 3).

Note The last two Fibre Channel ports (port 13 and port 14) and the two Gigabit Ethernet ports do not support the extended BB_credits feature.
- Explicitly enable this feature in the required Cisco MDS switch.
- Disable the remaining three ports in the 4-port group if you need to assign more than 2,400 BB_credits to the first port in the port group.
– If you assign less than 2,400 extended BB_credits to any one port in a port group, the remaining three ports in that port group can retain up to 255 BB_credits based on the port mode.

Note The receive BB_credit value for the remaining three ports depends on the port mode. The default value is 16 for the Fx mode and 255 for E or TE modes. The maximum value is 255 in all modes. This value can be changed as required without exceeding the maximum value of 255 BB_credits.
– If you assign more than 2,400 (up to a maximum of 3,500) extended BB_credits to the port in a port group, you must disable the other three ports.
– Disable (explicitly) this feature if you need to nondisruptively downgrade to Cisco SAN-OS Release 1.3 or earlier. When you disable this feature, the existing extended BB_credit configuration is completely erased.

Note The extended BB_credit configuration takes precedence over the receive BB_credit and performance buffer configurations.
Extended BB_credits on Generation 2 and Generation 3 Switching Modules
To use this feature on Generation 2 or Generation 3 switching modules, you must meet the following requirements:
- Display the interface configuration in the Information pane.
- Obtain the Enterprise package (ENTERPRISE_PKG) license (see the NX-OS Family Licensing Guide ).
- Configure this feature in any port on a Generation 2 switch module. See the “Extended BB_Credits” section for more information on extended BB_credits on Generation 2 switching modules.

Note Extended BB_credits are not supported on the Cisco MDS 9124 Fabric Switch, Cisco MDS 9134 Fabric Switch, the Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem, and the Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter.
Buffer-to-Buffer Credit Recovery
Although the Fibre Channel standards require low bit error rates, bit errors do occur. Over time, the corruption of receiver-ready messages, known as R_RDY primitives, can lead to a loss of credits, which can eventually cause a link to stop transmitting in one direction. The Fibre Channel standards provide a feature for two attached ports to detect and correct this situation. This feature is called buffer-to-buffer credit recovery.
Buffer-to-buffer credit recovery functions as follows: the sender and the receiver agree to send checkpoint primitives to each other, starting from the time that the link comes up. The sender sends a checkpoint every time it has sent the specified number of frames, and the receiver sends a checkpoint every time it has sent the specified number of R_RDY primitives. If the receiver detects lost credits, it can retransmit them and restore the credit count on the sender.
The buffer-to-buffer credit recovery feature can be used on any non arbitrated loop link. This feature is most useful on unreliable links, such as MANs or WANs, but can also help on shorter, high-loss links, such as a link with a faulty fiber connection.

Note The buffer-to-buffer credit recovery feature is not compatible with the distance extension (DE) feature, also known as buffer-to-buffer credit spoofing. If you use intermediate optical equipment, such as DWDM transceivers or Fibre Channel bridges, on ISLs between switches that use DE, then buffer-to-buffer credit recovery on both sides of the ISL needs to be disabled.
Buffer-to-Buffer State Change Number
The BB_SC_N field (word 1, bits 15-12) specifies the buffer-to-buffer state change (BB_SC) number. The BB_SC_N field indicates that the sender of the port login (PLOGI), fabric login (FLOGI), or ISLs (E or TE ports) frame is requesting 2^SC_BB_N number of frames to be sent between two consecutive BB_SC send primitives, and twice the number of R_RDY primitives to be sent between two consecutive BB_SC receive primitives.
For Generation 2 and Generation 3 modules, the BB_SCN on ISLs (E or TE ports) is enabled by default. This can fail the ISLs if used with optical equipment using distance extension (DE), also known as buffer-to-buffer credit spoofing.
On a Generation-2 module, one port will not come up for the following configuration for all ports:
On a Generation-3 module, one or two ports will not come up for the following configuration for the first half of the ports, the second half of the ports, or all ports:
- Port Mode: auto or E for the first half of the ports, the second half of the ports, or for all of the ports
- Rate Mode: dedicated
- Buffer Credits: default value
When you configure port mode to auto or E and rate-mode to dedicated for all ports in the global buffer pool, you need to reconfigure buffer credits on one or more ports (other than default).

Note If you use distance extension (buffer-to-buffer credit spoofing) on ISLs between switches, the BB_SCN parameter on both sides of the ISL needs to be disabled.
Configuring Interface Buffers
This section includes the following topics:
- Configuring Buffer-to-Buffer Credits
- Configuring Performance Buffers
- Configuring Extended BB_credits
- Enabling Buffer-to-Buffer Credit Recovery
- Enabling the Buffer-to-Buffer State Change Number
- Configuring Receive Data Field Size
Configuring Buffer-to-Buffer Credits
To configure BB_credits for a Fibre Channel interface, follow these steps:
This example shows the output of the show int fc1/1 command:
16 receive B2B credit remaining
3 transmit B2B credit remaining
To configure BB_credits for a Fibre Channel interface using DCNM-SAN, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches > Interfaces , and then select FC Physical. You see the interface configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click the Bb Credit tab.
Step 3 Set any of the buffer-to-buffer credits for an interface.
Configuring Performance Buffers
To configure performance buffers for a Fibre Channel interface, follow these steps:

Note Use the show interface bbcredit command to display performance buffer values and other BB_credit information.
To configure performance buffers for a Fibre Channel interface using DCNM-SAN, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches > Interfaces , and then select FC Physical .
You see the interface configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click the BB Credit tab.
You see performance buffer information in the Perf Bufs Admin and Perf Bufs Oper columns.
Step 3 Set the performance buffers for an interface.
Configuring Extended BB_credits
To configure extended BB_credits for a MDS-14/2 interface, for a Generation 2 switching module interface (not including the Cisco MDS 9124 Fabric Switch), or for an interface in a Cisco MDS 9216i switch, follow these steps:
To configure extended BB_credits for an MDS-14/2 interface, for a Generation 2 switching module interface, or for an interface in a Cisco MDS 9216i switch using DCNM-SAN, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches > Interfaces , and then select FC Physical . You see the interface configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click the BB Credit tab.
Step 3 In the Extended column, set the extended BB_credits for the selected interface.
Enabling Buffer-to-Buffer Credit Recovery
Buffer-to-buffer credit recovery on ISLs (E or TE ports) is enabled by default.
To use buffer-to-buffer credit recovery on a port, follow these steps:
Enabling the Buffer-to-Buffer State Change Number
To use the BB_SC_N field during PLOGI or FLOGI, follow these steps:
Configuring Receive Data Field Size
To configure the receive data field size, follow these steps:
To configure the receive data field size using DCNM-SAN, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches > FC Interfaces , and then select FC Physical .
You see the interface configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click the Other tab and set the RxDataFieldSize field.
Step 3 (Optional) Set other configuration parameters using the other tabs.
Verifying BB_Credit Configuration
To display BB_credit configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
Displays the BB_credit configuration for all the interfaces. |
|
Displays the BB_credit configuration for the specified interfaces. |
For detailed information about the fields in the output from these commands, refer to the Cisco NX-OS Command Reference .
To display the BB_credit information, use the show interface bbcredit command (see Example 60-1 and Example 60-2).
Example 60-1 Displays BB_credit Information
Example 60-2 Displays BB_credit Information for a Specified Fibre Channel Interface
 Feedback
Feedback