- Device Manager Help
- Configuring Cisco DCNM-SAN Server
- Configuring Authentication in Cisco DCNM-SAN
- Configuring Cisco DCNM-SAN Client
- Device Manager
- Configuring Performance Manager
- Configuring High Availability
- Configuring Trunking
- Configuring PortChannels
- Configuring N Port Virtualization
- Configuring Interfaces
- Configuration of Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Using the CFS Infrastructure
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Domain Parameters
- Configuring and Managing Zones
- Configuring FCoE
- Configuring Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Configuring and Managing VSANs
- Discovering SCSI Targets
- Configuring SAN Device Virtualization
- Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
- Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
- Configuring FICON
- Creating Dynamic VSANs
- Distributing Device Alias Services
- Configuring Advanced Fabric Features
- Configuring Users and Common Role
- Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server
- Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Cisco TrustSec Fibre Channel Link Encryption
- Configuring FIPS
- Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists
- Configuring IPsec Network Security
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring FCIP
- Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
- Configuring iSCSI
- Configuring IP Services
- Configuring IP Storage
- Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring IPv6 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring SCSI Flow Services
- Configuring SCSI Flow Statistics
- Configuring Fibre Channel Write Acceleration
- Monitoring the Network
- Monitoring Performance
- Configuring Call Home
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Scheduling Maintenance Jobs
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring Fabric Configuration Server
- Monitoring Network Traffic Using SPAN
- Monitoring System Processes and Logs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Port Tracking
- Configuring FlexAttach Virtual pWWN
- Configuring Interface Buffers
- Verifying Ethernet Interfaces
- Information About SNMP Security
- SNMP Version 1 and Version 2c
- SNMP Version 3
- SNMPv3 CLI User Management and AAA Integration
- CLI and SNMP User Synchronization
- Restricting Switch Access
- Group-Based SNMP Access
- Creating and Modifying Users
- AES Encryption-Based Privacy
- Enabling SNMP Notifications
- LinkUp/LinkDown Notifications for Switches
- Configuring SNMPv2c Notifications
- Configuring SNMPv3 Notifications
- Enabling SNMP Notifications
- Configuring the Notification Target User
- Configuring LinkUp/LinkDown Notifications for Switches
- Configuring Up/Down SNMP Link-State Traps for Interfaces
- Configuring Entity (FRU) Traps
- Configuring Event Security
- Viewing the SNMP Events Log
Configuring SNMP
The CLI and SNMP use common roles in all switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family. You can use SNMP to modify a role that was created using the CLI and vice versa.
Users, passwords, and roles for all CLI and SNMP users are the same. A user configured through the CLI can access the switch using SNMP (for example, the DCNM-SAN or the Device Manager) and vice versa.
Information About SNMP Security
SNMP is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. In all Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches, three SNMP versions are available: SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 (see Figure 14-1).
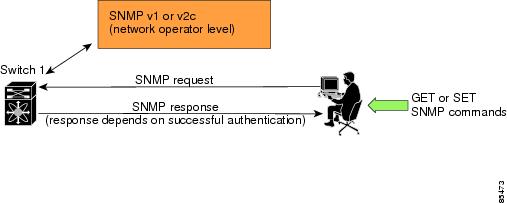
This section includes the following topics:
- SNMP Version 1 and Version 2c
- SNMP Version 3
- SNMPv3 CLI User Management and AAA Integration
- CLI and SNMP User Synchronization
- Restricting Switch Access
- Group-Based SNMP Access
- Creating and Modifying Users
- AES Encryption-Based Privacy
- Enabling SNMP Notifications
- LinkUp/LinkDown Notifications for Switches
SNMP Version 1 and Version 2c
SNMP Version 1 (SNMPv1) and SNMP Version 2c (SNMPv2c) use a community string match for user authentication. Community strings provided a weak form of access control in earlier versions of SNMP. SNMPv3 provides much improved access control using strong authentication and should be preferred over SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c wherever it is supported.
SNMP Version 3
SNMP Version 3 (SNMPv3) is an interoperable standards-based protocol for network management. SNMPv3 provides secure access to devices by a combination of authenticating and encrypting frames over the network. The security features provided in SNMPv3 are:
- Message integrity—Ensures that a packet has not been tampered with in-transit.
- Authentication—Determines the message is from a valid source.
- Encryption—Scrambles the packet contents to prevent it from being seen by unauthorized sources.
SNMPv3 provides for both security models and security levels. A security model is an authentication strategy that is set up for a user and the role in which the user resides. A security level is the permitted level of security within a security model. A combination of a security model and a security level determines which security mechanism is employed when handling an SNMP packet.
SNMPv3 CLI User Management and AAA Integration
The Cisco NX-OS software implements RFC 3414 and RFC 3415, including user-based security model (USM) and role-based access control. While SNMP and the CLI have common role management and share the same credentials and access privileges, the local user database was not synchronized in earlier releases.
SNMPv3 user management can be centralized at the AAA server level. This centralized user management allows the SNMP agent running on the Cisco MDS switch to leverage the user authentication service of the AAA server. Once user authentication is verified, the SNMP PDUs are processed further. The AAA server also is used to store user group names. SNMP uses the group names to apply the access/role policy that is locally available in the switch.
CLI and SNMP User Synchronization
Any configuration changes made to the user group, role, or password results in database synchronization for both SNMP and AAA.
To create an SNMP or CLI user, use either the username or snmp-server user commands.
-
The
authpassphrase specified in the snmp-server user command is synchronized as the password for the CLI user. - The password specified in the username command is synchronized as the auth and priv passphrases for the SNMP user.
Users are synchronized as follows:
- Deleting a user using either command results in the user being deleted for both SNMP and the CLI.
- User-role mapping changes are synchronized in SNMP and the CLI.

Note When the passphrase/password is specified in localized key/encrypted format, the password is not synchronized.

Note Starting in 3.0(1), the temporary SNMP login created for DCNM-SAN is no longer 24 hours. It is one hour.
Restricting Switch Access
You can restrict access to a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch using IP access control lists (IP-ACLs).
Group-Based SNMP Access

Note Because group is a standard SNMP term used industry-wide, we refer to role(s) as group(s) in this SNMP section.
SNMP access rights are organized by groups. Each group in SNMP is similar to a role through the CLI. Each group is defined with three accesses: read access, write access, and notification access. Each access can be enabled or disabled within each group.
You can begin communicating with the agent once your user name is created, your roles are set up by your administrator, and you are added to the roles.
Creating and Modifying Users
You can create users or modify existing users using SNMP, DCNM-SAN, or the CLI.
- SNMP—Create a user as a clone of an existing user in the usmUserTable on the switch. Once you have created the user, change the cloned secret key before activating the user. Refer to RFC 2574.
- DCNM-SAN.
- CLI—Create a user or modify an existing user using the snmp-server user command.
A network-operator and network-admin roles are available in a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch. There is also a default-role if you want to use the GUI (DCNM-SAN and Device Manager). You can also use any role that is configured in the Common Roles database.

Tip All updates to the CLI security database and the SNMP user database are synchronized. You can use the SNMP password to log into either DCNM-SAN or Device Manager. However, after you use the CLI password to log into DCNM-SAN or Device Manager, you must use the CLI password for all future logins. If a user exists in both the SNMP database and the CLI database before upgrading to Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.0(1b), then the set of roles assigned to the user becomes the union of both sets of roles after the upgrade.
AES Encryption-Based Privacy
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is the symmetric cipher algorithm. The Cisco NX-OS software uses AES as one of the privacy protocols for SNMP message encryption and conforms with RFC 3826.
The priv option offers a choice of DES or 128-bit AES encryption for SNMP security encryption. The priv option along with the aes-128 token indicates that this privacy password is for generating a 128-bit AES key. The AES priv password can have a minimum of eight characters. If the passphrases are specified in clear text, you can specify a maximum of 64 characters. If you use the localized key, you can specify a maximum of 130 characters.

Note For an SNMPv3 operation using the external AAA server, user configurations in the external AAA server require AES to be the privacy protocol to use SNMP PDU encryption.
Enabling SNMP Notifications
Notifications (traps and informs) are system alerts that the switch generates when certain events occur. You can enable or disable notifications. By default, no notification is defined or issued. If a notification name is not specified, all notifications are disabled or enabled.
With the SNMP central infra feature, you can add the traps that need to be enabled or disabled. The MIB CISCO-NOTIFICATION-CONTROL-MIB is supported to enable the use of a MIB browser to control notification generation.
LinkUp/LinkDown Notifications for Switches
You can configure which LinkUp/LinkDown notifications to enable on switches. You can enable the following types of LinkUp/LinkDown notifications:
- Cisco—Only notifications (cieLinkUp, cieLinkDown) defined in CISCO-IF-EXTENSION-MIB.my are sent for an interface, if ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable (defined in IF-MIB) is enabled for that interface.
- IETF—Only notifications (LinkUp, LinkDown) defined in IF-MIB are sent for an interface, if ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable (defined in IF-MIB) is enabled for that interface. Only the varbinds defined in the notification definition are sent with the notifications.
- IEFT extended—Only notifications (LinkUp, LinkDown) defined in IF-MIB are sent for an interface, if ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable (defined in IF-MIB) is enabled for that interface. In addition to the varbinds defined in the notification definition, varbinds defined in the IF-MIB specific to the Cisco Systems implementation are sent. This is the default setting.
- IEFT Cisco—Only notifications (LinkUp, LinkDown) defined in IF-MIB and notifications (cieLinkUp, cieLinkDown) defined in CISCO-IF-EXTENSION-MIB.my are sent for an interface, if ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable (defined in IF-MIB) is enabled for that interface. Only the varbinds defined in the notification definition are sent with the linkUp and linkDown notifications.
- IEFT extended Cisco—Only notifications (LinkUp, LinkDown) defined in IF-MIB and notifications (cieLinkUp, cieLinkDown) defined in CISCO-IF-EXTENSION-MIB.my are sent for an interface, if ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable (defined in IF-MIB) is enabled for that interface. In addition to the varbinds defined in linkUp and linkDown notification definition, varbinds defined in the IF-MIB specific to the Cisco Systems implementation are sent with the LinkUp and LinkDown notifications.

Note For more information on the varbinds defined in the IF-MIB specific to the Cisco Systems implementation, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family MIB Quick Reference.
Default Settings
Table 14-1 lists the default settings for all SNMP features in any switch.
Configuring SNMP
SNMP is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices.
This section includes the following topics:
- Assigning SNMPv3 Users to Multiple Roles
- Configuring SNMP Users from the CLI
- Enforcing SNMPv3 Message Encryption
- Assigning SNMPv3 Users to Multiple Roles
- Adding or Deleting Communities
- Deleting a Community String
Assigning SNMP Switch Contact and Location Information
You can assign the switch contact information, which is limited to 32 characters (without spaces), and the switch location.
To configure contact and location information, follow these steps:
To configure contact and location information, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches from the Physical Attributes pane.
You see the switch settings in the Information pane.
Step 2 Fill in the Location and Contact fields for each switch.
Step 3 Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
Configuring SNMP Users from the CLI
The passphrase specified in the snmp-server user command and the username command are synchronized.
Restrictions
- Avoid using the localizedkey option when configuring an SNMP user from the CLI. The localized keys are not portable across devices as they contain device engine ID information. If a configuration file is copied to the device, the passwords may not be set correctly if the configuration file was generated at a different device. Explicitly configure the desired passwords after copying the configuration into the device. Passwords specified with the localizedkey option are limited to 130 characters.
To create or modify SNMP users from the CLI, follow these steps:
To create or modify passwords for SNMP users from the CLI, follow these steps:

Note The snmp-server user command takes the engineID as an additional parameter. The engineID creates the notification target user (see the “Configuring the Notification Target User” section). If the engineID is not specified, the local user is created.
Enforcing SNMPv3 Message Encryption
By default the SNMP agent allows the securityLevel parameters of authNoPriv and authPriv for the SNMPv3 messages that use user-configured SNMPv3 message encryption with auth and priv keys.

Note Either to create a new SNMPv3 user or modify password of SNMPv3 user, the DCNM login user need to have enabled with DES/AES privacy password. Since the creating and modifying SNMP SET request need to be encrypted, the login user password needs to have the privacy password.
Detailed Steps
To enforce the message encryption for a user, follow these steps:
Alternatively, you can enforce the SNMPv3 message encryption globally on all the users using the following commands:
To enforce the message encryption for a user, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches, expand Security, and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane.
Step 2 Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see a list of users.
You see the Create Users dialog box.
Step 4 Enter the user name in the New User field.
Step 5 Select the role from the Role drop-down menu. You can enter a new role name in the field if you do not want to select one from the drop-down menu. If you do this, you must go back and configure this role appropriately.
Step 6 Enter a password for the user in Password field.
Step 8 Check the Enforce SNMP Privacy Encryption check box to encrypt management traffic.
Step 9 Click Create to create the new entry.
To enforce the SNMPv3 message encryption globally on all the users, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select a VSAN in the Logical Domains pane. This will not work if you select All VSANS.
Step 2 Expand Switches, expand Security, and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Global tab in the Information pane.
Step 3 Check the GlobalEnforcePriv check box.
Step 4 Click the Apply Changes icon to save these changes.
Assigning SNMPv3 Users to Multiple Roles
The SNMP server user configuration is enhanced to accommodate multiple roles (groups) for SNMPv3 users. After the initial SNMPv3 user creation, you can map additional roles for the user.
Restrictions
To configure multiple roles for SNMPv3 users from the CLI, follow these steps:
Creates or modifies the settings for an SNMPv3 user (NewUser) for the role1 role. |
||
Creates or modifies the settings for an SNMPv3 user (NewUser) for the role2 role. |
||
To add multiple roles to a new user, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches, expand Security, and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane.
Step 2 Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see a list of users.
You see the Create Users dialog box.
Step 4 Choose roles using the check boxes.
Step 5 Choose an option for Digest and one for Encryption.
Step 6 (Optional) Provide an expiration date for the user and the file name of an SSH key.
Step 7 Click Create to create the new roles.
Adding or Deleting Communities
You can configure read-only or read-write access for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 users. Refer to RFC 2576.
To create an SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c community, follow these steps:
To create an SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c community string, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches, expand Security, and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane.
Step 2 Click the Communities tab in the Information pane.
You see the existing communities.
You see the Create Community String dialog box.
Step 4 Check the Switch check boxes to specify one or more switches.
Step 5 Enter the community name in the Community field.
Step 6 Select the role from Role drop-down list.

Note You can enter a new role name in the field if you do not want to select one from the drop-down list. If you do this, you must go back and configure this role appropriately.
Step 7 Click Create to create the new entry.
Deleting a Community String
To delete a community string, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Switches, expand Security, and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane.
Step 2 Click the Communities tab in the Information pane.
Step 3 Click the name of the community you want to delete.
Step 4 Click Delete Row to delete this community.
Configuring SNMP Trap and Inform Notifications
You can configure the Cisco MDS switch to send notifications to SNMP managers when particular events occur.

Note You must enable the RMON traps in the SNMP configuration. For more information, refer to “Configuring RMON” section.

Note Use the SNMP-TARGET-MIB to obtain more information on the destinations to which notifications are to be sent either as traps or as informs. Refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family MIB Quick Reference.
This section includes the following topics:
- Configuring SNMPv2c Notifications
- Configuring SNMPv3 Notifications
- Enabling SNMP Notifications
- Configuring the Notification Target User
- Configuring LinkUp/LinkDown Notifications for Switches
- Configuring Up/Down SNMP Link-State Traps for Interfaces
- Configuring Entity (FRU) Traps
- Configuring Event Security
- Viewing the SNMP Events Log

Tip The SNMPv1 option is not available with the snmp-server host ip-address informs command.
Configuring SNMPv2c Notifications
To configure SNMPv2c notifications using IPv4, follow these steps:
To configure SNMPv2c notifications using IPv6, follow these steps:
To configure SNMPv2c notifications, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Events and then select SNMP Traps in the Physical Attributes pane.
You see the SNMP notification configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click the Destinations tab to add or modify a receiver for SNMP notifications.
Step 3 Click Create Row to create a new notification destination.
You see the Create Destinations dialog box.
Step 4 Check the switches for which you want to configure a new destination.
Step 5 Set the destination IP address and UDP port.
Step 6 Choose either the trap or inform radio button.
Step 7 (Optional) Set the timeout or retry count values.
Step 8 Click Create to add this destination to the selected switches.
Step 9 (Optional) Click the Other tab to enable specific notification types per switch.
Step 10 Click the Apply changes icon to create the entry.

Note Switches can forward events (SNMP traps and informs) up to 10 destinations.
Configuring SNMPv3 Notifications
To configure SNMPv3 notifications using IPv4, follow these steps:
To configure SNMPv3 notifications using IPv6, follow these steps:
To configure SNMPv3 notifications, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select v3 from the Security drop-down list in the Create Destinations dialog box.
Step 2 (Optional) Set the inform time out and retry values.
Step 3 Click Create to add this destination to the selected switches.

Note In the case of SNMPv3 notifications, the SNMP manager is expected to know the user credentials (authKey/PrivKey) based on the switch’s engineID to authenticate and decrypt the SNMP messages.
Enabling SNMP Notifications
Table 14-2 lists the CLI commands that enable the notifications for Cisco NX-OS MIBs.
Table 14-2
lists the DCNM-SAN procedures that enable the notifications for Cisco NX-OS MIBs.
Expand Events > SNMP Traps to see the check boxes listed in this table.

Note Choosing Events > SNMP Traps enables both traps and informs, depending on how you configured SNMP notifications. See the notifications displayed with the “Configuring SNMPv3 Notifications” section.
Click the FC tab and check Zone Rejects, Zone Merge Failures, Zone Merge Successes, Zone Default Policy Change, and Zone Unsuppd Mode. |
Summary Steps
You can enable or disable the supported traps at the following levels:
- Switch level—You can use snmp-server enable traps command to enable all the traps in the supported MIBs at the switch level.
- Feature level—You can use snmp-server enable traps command with the feature name to enable traps at the feature level.
- Individual traps - You can use snmp-server enable traps command with the feature name to enable traps at the individual level.

Note The snmp-server enable traps CLI command enables both traps and informs, depending on how you configured SNMP. See the notifications displayed with the snmp-server host CLI command.
To enable individual notifications, follow these steps:
Disables the specified SNMP notification. If a notification name is not specified, all notifications are disabled. |
To enable individual notifications, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Events and then select SNMP Traps in the Physical Attributes pane.
You see the SNMP notification configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 Click the FC tab to enable Fibre Channel related notifications.
Step 3 Check each notification check box that you want to enable.
Step 4 Click the Other tab to enable other notifications.
Step 5 Check each notification check box that you want to enable.
Step 6 Click the Control tab to enable notification applicable variables.
Step 7 From NX-OS Release 4.2(1), the Control tab is available for the notification control feature. This feature allows you to enable or disable all the notification-applicable variables via SNMP.
The Control tab is available for NX-OS Release 4.2(1) and later only.
Step 8 Check each notification check box that you want to enable.
Step 9 Click the Apply changes icon to create the entry.

Note In Device Manager, the no snmp-server enable traps link command disables generation of link traps in the switch, however the individual interfaces may have the link trap enabled.
To enable individual notifications using Device Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Admin > Events and then select Filters.
You see the event filters window showing a table populated by the switch
Step 2 Click the Control tab to enable notification applicable variables.
From NX-OS Release 4.2(1), the Control tab is available for the notification control feature. This feature allows you to enable or disable all the notification-applicable variables via SNMP.

Note The Control tab is available for NX-OS Release 4.2(1) and later only.
Step 3 Check each notification check box that you want to enable.
Step 4 Click the Apply changes icon to create the entry.
Configuring the Notification Target User
You must configure a notification target user on the switch for sending SNMPv3 inform notifications to the SNMP manager.
For authenticating and decrypting the received INFORM PDU, the SNMP manager should have the same user credentials in its local configuration data store of users.
To configure the notification target user, use the following command:
To configure the notification target user, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide.
The credentials of the notification target user are used for encrypting the SNMPv3 inform notification messages to the configured SNMPmanager (as in the snmp-server host command).
Configuring LinkUp/LinkDown Notifications for Switches
To configure the LinkUp/LinkDown notification for a switch using NX-OS Release 4.1(x) and earlier, follow these steps:

Note If both IETF and IETF extended are enabled, the show snmp traps command displays both as enabled. However, as a trap, you will receive only one trap with IETF extended payload.
To configure the LinkUp/LinkDown notification for a switch using NX-OS Release 4.2(1) and later, follow these steps:
Configuring Up/Down SNMP Link-State Traps for Interfaces
By default, SNMP link-state traps are enabled for all interfaces. Whenever a link toggles its state from Up to Down or vice versa, an SNMP trap is generated.
In some instances, you may find that you have numerous switches with hundreds of interfaces, many of which do not require monitoring of the link state. In such cases, you may elect to disable link-state traps.
To disable SNMP link-state traps for specific interfaces, follow these steps:
Configuring Entity (FRU) Traps
To enable individual SNMP trap control, follow these steps:
switch(config)# snmp-server enable entity_module_status_change |
||
switch(config)# snmp-server enable entity_power_status_change |
||
switch(config)# snmp-server enable entity_unrecognised_module |

Note All these traps have to do with legacy FRU traps.
Configuring Event Security
SNMP events can be secured against interception or eavesdropping in the same way that SNMP messages are secured. DCNM-SAN or Device Manager allow you to configure the message processing model, the security model, and the security level for the SNMP events that the switch generates.
Restrictions
- This is an advanced function that should only be used by administrators having experience with SNMPv3.
To configure SNMP event security, follow these steps:
Step 1 Expand Events and then select SNMP Traps.
Step 2 Click the Security tab in the Information pane.
You see the security information for SNMP notifications.
Step 3 Set the message protocol model (MPModel), security model, security name, and security level.
Step 4 Click the Apply Changes icon to save and apply your changes.
Restrictions
- Changing these values from different DCNM-SAN workstations at the same time may cause unpredictable results.
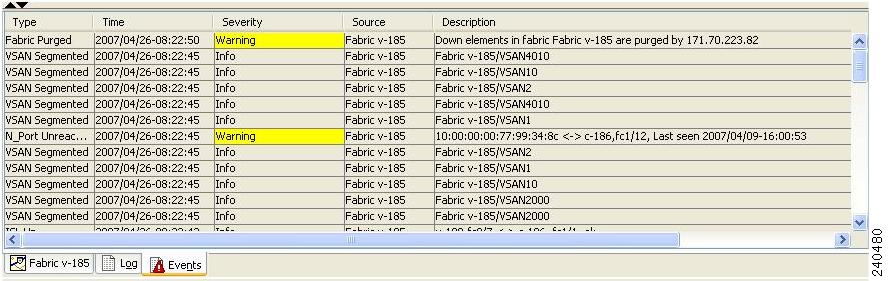
Step 1 To view the SNMP events log from DCNM-SAN, click the Events tab.
You see the Events listed with a log of events for a single switch (see Figure 14-2).
Figure 14-2 Events Information
Verifying SNMP Configuration
To display the SNMP configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
Displays the SNMP link-state trap configuration for a particular interface |
|
Displays configured SNMP informatio, counter information for SNMP contact, location, and packet settings. |
For detailed information about the fields in the output from these commands, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Command Reference .
This section covers the following topics:
- Viewing the Up/Down SNMP Link-State Traps for Interfaces
- Displaying SNMP Traps
- Displaying SNMP Security Information
Viewing the Up/Down SNMP Link-State Traps for Interfaces
Whenever you disable an SNMP link-state trap for an interface, the command is also added to the running configuration of the system.
To view the running configuration, use the show running-config command for the interface.
To view the SNMP link-state trap configuration for a particular interface, enter the show interface command.
Displaying SNMP Traps
You can use the show snmp trap command to display all the notifications and their status.
Displaying SNMP Security Information
Use the show snmp commands to display configured SNMP information (see Example 14-1 and 14-6 ).
Example 14-1 Displays SNMP User Details
Example 14-2 Displays SNMP Community Information
Example 14-3 Displays SNMP Host Information
The show snmp command displays counter information for SNMP contact, location, and packet settings. This command provides information that is used entirely by the Cisco MDS 9000 Family DCNM-SAN (refer to the System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco DCNM for SAN). See Example 14-4.
Example 14-4 Displays SNMP Information
Field Descriptions for SNMP
This section describes the field descriptions for SNMP.
IP Statistics SNMP
SNMP Security Users
SNMP Security Communities
Security Users Global

Note The privacy password and authentication password are required for an administrator to create a new user or delete an existing user in Device Manager. However, if the administrator does not provide these credentials at the time of creating a new user, Device Manager uses the authentication password of the administrator as the privacy password. If the privacy protocol defined for the user is not DES (default), the SNMP Agent in the MDS will not be able to decrypt the packet and the SNMP Agent times out. If the privacy protocol defined for the user is not DES, the user needs to provide both the privacy password and the protocol when logging in.
Additional References
For additional information related to implementing SNMP, see the following sections:
Feature History for SNMP
Table 14-3 lists the release history for this feature. Only features that were introduced or modified in Release 3.x or a later release appear in the table.
 Feedback
Feedback